str1.cpp?
// str1.cpp -- introducing the string class
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// using string constructors
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string one("Lottery Winner!"); // ctor #1
cout << one << endl; // overloaded <<
string two(20, '$'); // ctor #2
cout << two << endl;
string three(one); // ctor #3
cout << three << endl;
one += " Oops!"; // overloaded +=
cout << one << endl;
two = "Sorry! That was ";
three[0] = 'P';
string four; // ctor #4
four = two + three; // overloaded +, =
cout << four << endl;
char alls[] = "All's well that ends well";
string five(alls, 20); // ctor #5
cout << five << "!\n";
string six(alls + 6, alls + 10); // ctor #6
cout << six << ", ";
string seven(&five[6], &five[10]); // ctor #6 again
cout << seven << "...\n";
string eight(four, 7, 16); // ctor #7
//将four的第八个字符(位置7)开始,将16个字符复制到eight中
cout << eight << " in motion!" << endl;
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Lottery Winner!
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$
Lottery Winner!
Lottery Winner! Oops!
Sorry! That was Pottery Winner!
All's well that ends!
well, well...
That was Pottery in motion!?strfile.cpp
// strfile.cpp -- read strings from a file
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
ifstream fin;
fin.open("tobuy.txt");
if (fin.is_open() == false)
{
cerr << "Can't open file. Bye.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
string item;
int count = 0;
getline(fin, item, ':');
while (fin) // while input is good
{
++count;
cout << count << ": " << item << endl;
getline(fin, item, ':');
}
cout << "Done\n";
fin.close();
// std::cin.get();
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
?tobuy.txt
sardines:chocolate ice cream:pop corn:leeks:
cottage cheese;olive oil:butter:tofu:
hangman.cpp?
// hangman.cpp -- some string methods
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
using std::string;
const int NUM = 26;
const string wordlist[NUM] = { "apiary", "beetle", "cereal",
"danger", "ensign", "florid", "garage", "health", "insult",
"jackal", "keeper", "loaner", "manage", "nonce", "onset",
"plaid", "quilt", "remote", "stolid", "train", "useful",
"valid", "whence", "xenon", "yearn", "zippy" };
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::tolower;
using std::endl;
std::srand(std::time(0));
char play;
cout << "Will you play a word game? <y/n> ";
cin >> play;
play = tolower(play);
while (play == 'y')
{
string target = wordlist[std::rand() % NUM];
int length = target.length();
string attempt(length, '-');
string badchars;
int guesses = 6;
cout << "Guess my secret word. It has " << length
<< " letters, and you guess\n"
<< "one letter at a time. You get " << guesses
<< " wrong guesses.\n";
cout << "Your word: " << attempt << endl;
while (guesses > 0 && attempt != target)
{
char letter;
cout << "Guess a letter: ";
cin >> letter;
if (badchars.find(letter) != string::npos
|| attempt.find(letter) != string::npos)
{
cout << "You already guessed that. Try again.\n";
continue;
}
int loc = target.find(letter);
if (loc == string::npos)
{
cout << "Oh, bad guess!\n";
--guesses;
badchars += letter; // add to string
}
else
{
cout << "Good guess!\n";
attempt[loc] = letter;
// check if letter appears again
loc = target.find(letter, loc + 1);
while (loc != string::npos)
{
attempt[loc] = letter;
loc = target.find(letter, loc + 1);
}
}
cout << "Your word: " << attempt << endl;
if (attempt != target)
{
if (badchars.length() > 0)
cout << "Bad choices: " << badchars << endl;
cout << guesses << " bad guesses left\n";
}
}
if (guesses > 0)
cout << "That's right!\n";
else
cout << "Sorry, the word is " << target << ".\n";
cout << "Will you play another? <y/n> ";
cin >> play;
play = tolower(play);
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
?执行结果:
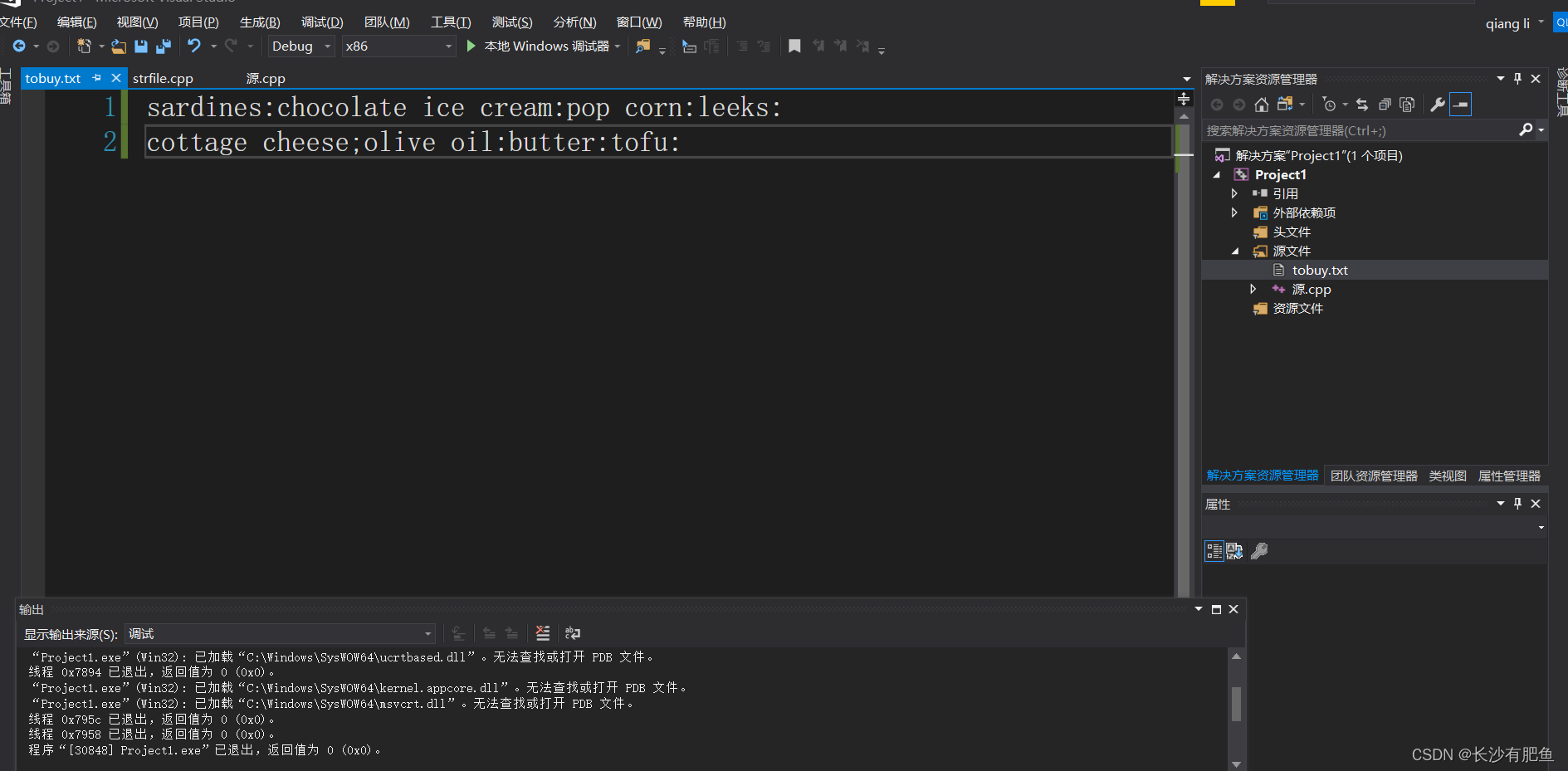
1: sardines
2: chocolate ice cream
3: pop corn
4: leeks
5:
cottage cheese;olive oil
6: butter
7: tofu
Donehangman.cpp?
// hangman.cpp -- some string methods
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
using std::string;
const int NUM = 26;
const string wordlist[NUM] = { "apiary", "beetle", "cereal",
"danger", "ensign", "florid", "garage", "health", "insult",
"jackal", "keeper", "loaner", "manage", "nonce", "onset",
"plaid", "quilt", "remote", "stolid", "train", "useful",
"valid", "whence", "xenon", "yearn", "zippy" };
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::tolower;
using std::endl;
std::srand(std::time(0));
char play;
cout << "Will you play a word game? <y/n> ";
cin >> play;
play = tolower(play);
while (play == 'y')
{
string target = wordlist[std::rand() % NUM];
int length = target.length();
string attempt(length, '-');
string badchars;
int guesses = 6;
cout << "Guess my secret word. It has " << length
<< " letters, and you guess\n"
<< "one letter at a time. You get " << guesses
<< " wrong guesses.\n";
cout << "Your word: " << attempt << endl;
while (guesses > 0 && attempt != target)
{
char letter;
cout << "Guess a letter: ";
cin >> letter;
if (badchars.find(letter) != string::npos
|| attempt.find(letter) != string::npos)
{
cout << "You already guessed that. Try again.\n";
continue;
}
int loc = target.find(letter);
if (loc == string::npos)
{
cout << "Oh, bad guess!\n";
--guesses;
badchars += letter; // add to string
}
else
{
cout << "Good guess!\n";
attempt[loc] = letter;
// check if letter appears again
loc = target.find(letter, loc + 1);
while (loc != string::npos)
{
attempt[loc] = letter;
loc = target.find(letter, loc + 1);
}
}
cout << "Your word: " << attempt << endl;
if (attempt != target)
{
if (badchars.length() > 0)
cout << "Bad choices: " << badchars << endl;
cout << guesses << " bad guesses left\n";
}
}
if (guesses > 0)
cout << "That's right!\n";
else
cout << "Sorry, the word is " << target << ".\n";
cout << "Will you play another? <y/n> ";
cin >> play;
play = tolower(play);
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Will you play a word game? <y/n> y
Guess my secret word. It has 6 letters, and you guess
one letter at a time. You get 6 wrong guesses.
Your word: ------
Guess a letter: e
Good guess!
Your word: -ee-e-
6 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: l
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: -ee-e-
Bad choices: l
5 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: g
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: -ee-e-
Bad choices: lg
4 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: a
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: -ee-e-
Bad choices: lga
3 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: v
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: -ee-e-
Bad choices: lgav
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: l
You already guessed that. Try again.
Guess a letter: p
Good guess!
Your word: -eepe-
Bad choices: lgav
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: p
You already guessed that. Try again.
Guess a letter: k
Good guess!
Your word: keepe-
Bad choices: lgav
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: c
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: keepe-
Bad choices: lgavc
1 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: r
Good guess!
Your word: keeper
That's right!
Will you play another? <y/n> n
ByeGuess a letter: o
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: ------
Bad choices: gno
3 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: e
Oh, bad guess!
Your word: ------
Bad choices: gnoe
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: p
Good guess!
Your word: -p----
Bad choices: gnoe
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: a
Good guess!
Your word: ap-a--
Bad choices: gnoe
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: i
Good guess!
Your word: apia--
Bad choices: gnoe
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: r
Good guess!
Your word: apiar-
Bad choices: gnoe
2 bad guesses left
Guess a letter: y
Good guess!
Your word: apiary
That's right!
Will you play another? <y/n> n
Byestr2.cpp?
// str2.cpp -- capacity() and reserve()
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string empty;
string small = "bit";
string larger = "Elephants are a girl's best friend";
cout << "Sizes:\n";
cout << "\tempty: " << empty.size() << endl;
cout << "\tsmall: " << small.size() << endl;
cout << "\tlarger: " << larger.size() << endl;
cout << "Capacities:\n";
cout << "\tempty: " << empty.capacity() << endl;
cout << "\tsmall: " << small.capacity() << endl;
cout << "\tlarger: " << larger.capacity() << endl;
empty.reserve(50);
cout << "Capacity after empty.reserve(50): "
<< empty.capacity() << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Sizes:
empty: 0
small: 3
larger: 34
Capacities:
empty: 15
small: 15
larger: 47
Capacity after empty.reserve(50): 63smrtptrs.cpp?
// smrtptrs.cpp -- using three kinds of smart pointers
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
class Report
{
private:
std::string str;
public:
Report(const std::string s) : str(s) { std::cout << "Object created!\n"; }
~Report() { std::cout << "Object deleted!\n"; }
void comment() const { std::cout << str << "\n"; }
};
int main()
{
{
std::auto_ptr<Report> ps(new Report("using auto_ptr"));
ps->comment(); // use -> to invoke a member function
}
{
std::shared_ptr<Report> ps(new Report("using shared_ptr"));
ps->comment();
}
{
std::unique_ptr<Report> ps(new Report("using unique_ptr"));
ps->comment();
}
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Object created!
using auto_ptr
Object deleted!
Object created!
using shared_ptr
Object deleted!
Object created!
using unique_ptr
Object deleted!
fowl.cpp?
// fowl.cpp -- auto_ptr a poor choice
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
auto_ptr<string> films[5] =
{
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Fowl Balls")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Duck Walks")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Chicken Runs")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Turkey Errors")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Goose Eggs"))
};
auto_ptr<string> pwin;
pwin = films[2]; // films[2] loses ownership
cout << "The nominees for best avian baseball film are\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << *films[i] << endl;
cout << "The winner is " << *pwin << "!\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:?
The nominees for best avian baseball film are
Fowl Balls
Duck Walksfow2.cpp??
将auto_ptr修改为shared_ptr得到的结果如下所示:
// fow2.cpp -- auto_ptr a poor choice
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
shared_ptr<string> films[5] =
{
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Fowl Balls")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Duck Walks")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Chicken Runs")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Turkey Errors")),
auto_ptr<string>(new string("Goose Eggs"))
};
shared_ptr<string> pwin;
pwin = films[2]; // films[2] loses ownership
cout << "The nominees for best avian baseball film are\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << *films[i] << endl;
cout << "The winner is " << *pwin << "!\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
The nominees for best avian baseball film are
Fowl Balls
Duck Walks
Chicken Runs
Turkey Errors
Goose Eggs
The winner is Chicken Runs!vect1.cpp?
// vect1.cpp -- introducing the vector template
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
const int NUM = 5;
int main()
{
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
vector<int> ratings(NUM);
vector<string> titles(NUM);
cout << "You will do exactly as told. You will enter\n"
<< NUM << " book titles and your ratings (0-10).\n";
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
cout << "Enter title #" << i + 1 << ": ";
getline(cin, titles[i]);
cout << "Enter your rating (0-10): ";
cin >> ratings[i];
cin.get();
}
cout << "Thank you. You entered the following:\n"
<< "Rating\tBook\n";
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
cout << ratings[i] << "\t" << titles[i] << endl;
}
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:?
You will do exactly as told. You will enter
5 book titles and your ratings (0-10).
Enter title #1: The Cat Who Knew C++
Enter your rating (0-10): 6
Enter title #2: Felonious Felines
Enter your rating (0-10): 4
Enter title #3: Warlords of Wonk
Enter your rating (0-10): 3
Enter title #4: Don't Touch That Metaphor
Enter your rating (0-10): 5
Enter title #5: Panic Oriented Programming
Enter your rating (0-10): 8
Thank you. You entered the following:
Rating Book
6 The Cat Who Knew C++
4 Felonious Felines
3 Warlords of Wonk
5 Don't Touch That Metaphor
8 Panic Oriented Programming?vect2.cpp
// vect2.cpp -- methods and iterators
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
struct Review {
std::string title;
int rating;
};
bool FillReview(Review & rr);
void ShowReview(const Review & rr);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::vector;
vector<Review> books;
Review temp;
while (FillReview(temp))
books.push_back(temp);
int num = books.size();
if (num > 0)
{
cout << "Thank you. You entered the following:\n"
<< "Rating\tBook\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
ShowReview(books[i]);
cout << "Reprising:\n"
<< "Rating\tBook\n";
vector<Review>::iterator pr;
for (pr = books.begin(); pr != books.end(); pr++)
ShowReview(*pr);
vector <Review> oldlist(books); // copy constructor used
if (num > 3)
{
// remove 2 items
books.erase(books.begin() + 1, books.begin() + 3);//移除第二项和第四项
cout << "After erasure:\n";
for (pr = books.begin(); pr != books.end(); pr++)
ShowReview(*pr);
// insert 1 item
books.insert(books.begin(), oldlist.begin() + 1,
oldlist.begin() + 2);//[1,2)在开始的位置处插入第二项内容
cout << "After insertion:\n";
for (pr = books.begin(); pr != books.end(); pr++)
ShowReview(*pr);
}
books.swap(oldlist);
cout << "Swapping oldlist with books:\n";
for (pr = books.begin(); pr != books.end(); pr++)
ShowReview(*pr);
}
else
cout << "Nothing entered, nothing gained.\n";
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
bool FillReview(Review & rr)
{
std::cout << "Enter book title (quit to quit): ";
std::getline(std::cin, rr.title);
if (rr.title == "quit")
return false;
std::cout << "Enter book rating: ";
std::cin >> rr.rating;
if (!std::cin)
return false;
// get rid of rest of input line
while (std::cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
return true;
}
void ShowReview(const Review & rr)
{
std::cout << rr.rating << "\t" << rr.title << std::endl;
}
执行结果:
Enter book title (quit to quit): The Cat Who Knew C++
Enter book rating: 5
Enter book title (quit to quit): Candid Canines
Enter book rating: 7
Enter book title (quit to quit): Warriors of Wonk
Enter book rating: 4
Enter book title (quit to quit): Quantum Manners
Enter book rating: 8
Enter book title (quit to quit): quit
Thank you. You entered the following:
Rating Book
5 The Cat Who Knew C++
7 Candid Canines
4 Warriors of Wonk
8 Quantum Manners
Reprising:
Rating Book
5 The Cat Who Knew C++
7 Candid Canines
4 Warriors of Wonk
8 Quantum Manners
After erasure:
5 The Cat Who Knew C++
8 Quantum Manners
After insertion:
7 Candid Canines
5 The Cat Who Knew C++
8 Quantum Manners
Swapping oldlist with books:
5 The Cat Who Knew C++
7 Candid Canines
4 Warriors of Wonk
8 Quantum Mannersvect3.cpp?
// vect3.cpp -- using STL functions
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
struct Review {
std::string title;
int rating;
};
bool operator<(const Review & r1, const Review & r2);
bool worseThan(const Review & r1, const Review & r2);
bool FillReview(Review & rr);
void ShowReview(const Review & rr);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
vector<Review> books;
Review temp;
while (FillReview(temp))
books.push_back(temp);
if (books.size() > 0)
{
cout << "Thank you. You entered the following "
<< books.size() << " ratings:\n"
<< "Rating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), ShowReview);
sort(books.begin(), books.end());
cout << "Sorted by title:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), ShowReview);
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), worseThan);
cout << "Sorted by rating:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), ShowReview);
random_shuffle(books.begin(), books.end());
cout << "After shuffling:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), ShowReview);
}
else
cout << "No entries. ";
cout << "Bye.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
bool operator<(const Review & r1, const Review & r2)
{
if (r1.title < r2.title)
return true;
else if (r1.title == r2.title && r1.rating < r2.rating)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool worseThan(const Review & r1, const Review & r2)
{
if (r1.rating < r2.rating)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool FillReview(Review & rr)
{
std::cout << "Enter book title (quit to quit): ";
std::getline(std::cin, rr.title);
if (rr.title == "quit")
return false;
std::cout << "Enter book rating: ";
std::cin >> rr.rating;
if (!std::cin)
return false;
// get rid of rest of input line
while (std::cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
return true;
}
void ShowReview(const Review & rr)
{
std::cout << rr.rating << "\t" << rr.title << std::endl;
}
执行结果:
Enter book title (quit to quit): The Cat Who Can Teach You Weight Loss
Enter book rating: 8
Enter book title (quit to quit): The Dogs of Dharma
Enter book rating: 6
Enter book title (quit to quit): The Wimps of Wonk
Enter book rating: 3
Enter book title (quit to quit): Farewell and Delete
Enter book rating: 7
Enter book title (quit to quit): quit
Thank you. You entered the following 4 ratings:
Rating Book
8 The Cat Who Can Teach You Weight Loss
6 The Dogs of Dharma
3 The Wimps of Wonk
7 Farewell and Delete
Sorted by title:
Rating Book
7 Farewell and Delete
8 The Cat Who Can Teach You Weight Loss
6 The Dogs of Dharma
3 The Wimps of Wonk
Sorted by rating:
Rating Book
3 The Wimps of Wonk
6 The Dogs of Dharma
7 Farewell and Delete
8 The Cat Who Can Teach You Weight Loss
After shuffling:
Rating Book
3 The Wimps of Wonk
6 The Dogs of Dharma
8 The Cat Who Can Teach You Weight Loss
7 Farewell and Delete
Bye.copyit.cpp?
// copyit.cpp -- copy() and iterators
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int casts[10] = { 6, 7, 2, 9 ,4 , 11, 8, 7, 10, 5 };
vector<int> dice(10);
// copy from array to vector
copy(casts, casts + 10, dice.begin());
cout << "Let the dice be cast!\n";
// create an ostream iterator
ostream_iterator<int, char> out_iter(cout, " ");
// copy from vector to output
copy(dice.begin(), dice.end(), out_iter);
cout << endl;
cout << "Implicit use of reverse iterator.\n";
copy(dice.rbegin(), dice.rend(), out_iter);
cout << endl;
cout << "Explicit use of reverse iterator.\n";
// vector<int>::reverse_iterator ri; // use if auto doesn't work
for (auto ri = dice.rbegin(); ri != dice.rend(); ++ri)
cout << *ri << ' ';
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
6 7 2 9 4 11 8 7 10 5
Implicit use of reverse iterator.
5 10 7 8 11 4 9 2 7 6
Explicit use of reverse iterator.
5 10 7 8 11 4 9 2 7 6inserts.cpp?
// inserts.cpp -- copy() and insert iterators
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
void output(const std::string & s) { std::cout << s << " "; }
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string s1[4] = { "fine", "fish", "fashion", "fate" };
string s2[2] = { "busy", "bats" };
string s3[2] = { "silly", "singers" };
vector<string> words(4);
copy(s1, s1 + 4, words.begin());
for_each(words.begin(), words.end(), output);
cout << endl;
// construct anonymous back_insert_iterator object
copy(s2, s2 + 2, back_insert_iterator<vector<string> >(words));
//back_insert_iterator只能用于允许在尾部快速插入的容器
//front_insert_iterator只能用于允许在起始位置做时间固定插入的容器类型
for_each(words.begin(), words.end(), output);
cout << endl;
// construct anonymous insert_iterator object
copy(s3, s3 + 2, insert_iterator<vector<string> >(words, words.begin()));
//在其实位置插入s3的内容
for_each(words.begin(), words.end(), output);
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:?
fine fish fashion fate
fine fish fashion fate busy bats
silly singers fine fish fashion fate busy batslist.cpp?
// list.cpp -- using a list
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
void outint(int n) { std::cout << n << " "; }
int main()
{
using namespace std;
list<int> one(5, 2); // list of 5 2s
int stuff[5] = { 1,2,4,8, 6 };
list<int> two;
two.insert(two.begin(), stuff, stuff + 5);
int more[6] = { 6, 4, 2, 4, 6, 5 };
list<int> three(two);
three.insert(three.end(), more, more + 6);
cout << "List one: ";
for_each(one.begin(), one.end(), outint);
cout << endl << "List two: ";
for_each(two.begin(), two.end(), outint);
cout << endl << "List three: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
three.remove(2);
cout << endl << "List three minus 2s: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
three.splice(three.begin(), one);
cout << endl << "List three after splice: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
cout << endl << "List one: ";
for_each(one.begin(), one.end(), outint);
three.unique();
cout << endl << "List three after unique: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
three.sort();
three.unique();
cout << endl << "List three after sort & unique: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
two.sort();
three.merge(two);
cout << endl << "Sorted two merged into three: ";
for_each(three.begin(), three.end(), outint);
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
List one: 2 2 2 2 2
List two: 1 2 4 8 6
List three: 1 2 4 8 6 6 4 2 4 6 5
List three minus 2s: 1 4 8 6 6 4 4 6 5
List three after splice: 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 8 6 6 4 4 6 5
List one:
List three after unique: 2 1 4 8 6 4 6 5
List three after sort & unique: 1 2 4 5 6 8
Sorted two merged into three: 1 1 2 2 4 4 5 6 6 8 8setops.cpp??
// setops.cpp -- some set operations
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int N = 6;
string s1[N] = { "buffoon", "thinkers", "for", "heavy", "can", "for" };
string s2[N] = { "metal", "any", "food", "elegant", "deliver","for" };
set<string> A(s1, s1 + N);
set<string> B(s2, s2 + N);
ostream_iterator<string, char> out(cout, " ");
cout << "Set A: ";
copy(A.begin(), A.end(), out);
cout << endl;
cout << "Set B: ";
copy(B.begin(), B.end(), out);
cout << endl;
cout << "Union of A and B:\n";
set_union(A.begin(), A.end(), B.begin(), B.end(), out);
cout << endl;
cout << "Intersection of A and B:\n";
set_intersection(A.begin(), A.end(), B.begin(), B.end(), out);
//set_intersection查找两个集合的交集
cout << endl;
cout << "Difference of A and B:\n";
set_difference(A.begin(), A.end(), B.begin(), B.end(), out);
//set_difference查找两个集合的差
cout << endl;
set<string> C;
cout << "Set C:\n";
set_union(A.begin(), A.end(), B.begin(), B.end(),
insert_iterator<set<string> >(C, C.begin()));
copy(C.begin(), C.end(), out);
cout << endl;
string s3("grungy");
C.insert(s3);
cout << "Set C after insertion:\n";
copy(C.begin(), C.end(), out);
cout << endl;
cout << "Showing a range:\n";
copy(C.lower_bound("ghost"), C.upper_bound("spook"), out);
//lower_bound将键作为参数并返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向集合中第一个不小于键参数的成员
//upper_bound将键作为参数并返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向集合中第一个大于键参数的成员
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行效果:
Set A: buffoon can for heavy thinkers
Set B: any deliver elegant food for metal
Union of A and B:
any buffoon can deliver elegant food for heavy metal thinkers
Intersection of A and B:
for
Difference of A and B:
buffoon can heavy thinkers
Set C:
any buffoon can deliver elegant food for heavy metal thinkers
Set C after insertion:
any buffoon can deliver elegant food for grungy heavy metal thinkers
Showing a range:
grungy heavy metalERROR:
“std::pair<std::_Tree_iterator<std::_Tree_val<std::_Tree_simple_types<_Ty>>>,std::_Tree_iterator<std::_Tree_val<std::_Tree_simple_types<_Ty>>>>”后面接“auto”是非法的(是否忘记了“;”?)?? ?
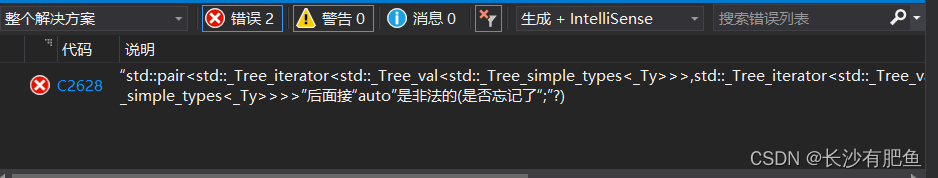
?去掉auto: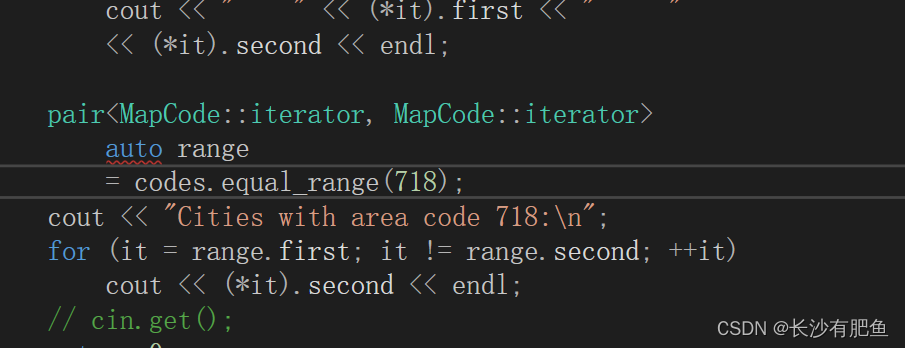
multmap.cpp?
// multmap.cpp -- use a multimap
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
typedef int KeyType;
typedef std::pair<const KeyType, std::string> Pair;
typedef std::multimap<KeyType, std::string> MapCode;
int main()
{
using namespace std;
MapCode codes;
codes.insert(Pair(415, "San Francisco"));
codes.insert(Pair(510, "Oakland"));
codes.insert(Pair(718, "Brooklyn"));
codes.insert(Pair(718, "Staten Island"));
codes.insert(Pair(415, "San Rafael"));
codes.insert(Pair(510, "Berkeley"));
cout << "Number of cities with area code 415: "
<< codes.count(415) << endl;
cout << "Number of cities with area code 718: "
<< codes.count(718) << endl;
cout << "Number of cities with area code 510: "
<< codes.count(510) << endl;
cout << "Area Code City\n";
MapCode::iterator it;
for (it = codes.begin(); it != codes.end(); ++it)
cout << " " << (*it).first << " "
<< (*it).second << endl;
pair<MapCode::iterator, MapCode::iterator> range
= codes.equal_range(718);
cout << "Cities with area code 718:\n";
for (it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it)
cout << (*it).second << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
?执行结果:
Number of cities with area code 415: 2
Number of cities with area code 718: 2
Number of cities with area code 510: 2
Area Code City
415 San Francisco
415 San Rafael
510 Oakland
510 Berkeley
718 Brooklyn
718 Staten Island
Cities with area code 718:
Brooklyn
Staten Islandfunctor.cpp?
// functor.cpp -- using a functor
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
template<class T> // functor class defines operator()()
class TooBig
{
private:
T cutoff;
public:
TooBig(const T & t) : cutoff(t) {}
bool operator()(const T & v) { return v > cutoff; }
};
void outint(int n) { std::cout << n << " "; }
int main()
{
using std::list;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::for_each;
using std::remove_if;
TooBig<int> f100(100); // limit = 100
int vals[10] = { 50, 100, 90, 180, 60, 210, 415, 88, 188, 201 };
list<int> yadayada(vals, vals + 10); // range constructor
list<int> etcetera(vals, vals + 10);
// C++0x can use the following instead
// list<int> yadayada = {50, 100, 90, 180, 60, 210, 415, 88, 188, 201};
// list<int> etcetera {50, 100, 90, 180, 60, 210, 415, 88, 188, 201};
cout << "Original lists:\n";
for_each(yadayada.begin(), yadayada.end(), outint);
cout << endl;
for_each(etcetera.begin(), etcetera.end(), outint);
cout << endl;
yadayada.remove_if(f100); // use a named function object
etcetera.remove_if(TooBig<int>(200)); // construct a function object
cout << "Trimmed lists:\n";
for_each(yadayada.begin(), yadayada.end(), outint);
cout << endl;
for_each(etcetera.begin(), etcetera.end(), outint);
cout << endl;
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Original lists:
50 100 90 180 60 210 415 88 188 201
50 100 90 180 60 210 415 88 188 201
Trimmed lists:
50 100 90 60 88
50 100 90 180 60 88 188
funadap.cpp
// funadap.cpp -- using function adapters
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
void Show(double);
const int LIM = 6;
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double arr1[LIM] = { 28, 29, 30, 35, 38, 59 };
double arr2[LIM] = { 63, 65, 69, 75, 80, 99 };
vector<double> gr8(arr1, arr1 + LIM);
vector<double> m8(arr2, arr2 + LIM);
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed);
cout.precision(1);
cout << "gr8:\t";
for_each(gr8.begin(), gr8.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
cout << "m8: \t";
for_each(m8.begin(), m8.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
vector<double> sum(LIM);
transform(gr8.begin(), gr8.end(), m8.begin(), sum.begin(),
plus<double>());
cout << "sum:\t";
for_each(sum.begin(), sum.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
vector<double> prod(LIM);
transform(gr8.begin(), gr8.end(), prod.begin(),
bind1st(multiplies<double>(), 2.5));
cout << "prod:\t";
for_each(prod.begin(), prod.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
void Show(double v)
{
std::cout.width(6);
std::cout << v << ' ';
}
执行效果:?
gr8: 28.0 29.0 30.0 35.0 38.0 59.0
m8: 63.0 65.0 69.0 75.0 80.0 99.0
sum: 91.0 94.0 99.0 110.0 118.0 158.0
prod: 70.0 72.5 75.0 87.5 95.0 147.5strgstl.cpp?
// strgstl.cpp -- applying the STL to a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string letters;
cout << "Enter the letter grouping (quit to quit): ";
while (cin >> letters && letters != "quit")
{
cout << "Permutations of " << letters << endl;
sort(letters.begin(), letters.end());
cout << letters << endl;
while (next_permutation(letters.begin(), letters.end()))
cout << letters << endl;
cout << "Enter next sequence (quit to quit): ";
}
cout << "Done.\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行效果:
Enter the letter grouping (quit to quit): aw1
Permutations of aw1
1aw
1wa
a1w
aw1
w1a
wa1
Enter next sequence (quit to quit): all
Permutations of all
all
lal
lla
Enter next sequence (quit to quit): quit
Done.listrmv.cpp?
// listrmv.cpp -- applying the STL to a string
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
void Show(int);
const int LIM = 10;
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int ar[LIM] = { 4, 5, 4, 2, 2, 3, 4, 8, 1, 4 };
list<int> la(ar, ar + LIM);
list<int> lb(la);
cout << "Original list contents:\n\t";
for_each(la.begin(), la.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
la.remove(4);
cout << "After using the remove() method:\n";
cout << "la:\t";
for_each(la.begin(), la.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator last;
last = remove(lb.begin(), lb.end(), 4);
cout << "After using the remove() function:\n";
cout << "lb:\t";
for_each(lb.begin(), lb.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
lb.erase(last, lb.end());
cout << "After using the erase() method:\n";
cout << "lb:\t";
for_each(lb.begin(), lb.end(), Show);
cout << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
void Show(int v)
{
std::cout << v << ' ';
}
执行结果:
Original list contents:
4 5 4 2 2 3 4 8 1 4
After using the remove() method:
la: 5 2 2 3 8 1
After using the remove() function:
lb: 5 2 2 3 8 1 4 8 1 4
After using the erase() method:
lb: 5 2 2 3 8 1usealgo.cpp?
//usealgo.cpp -- using several STL elements
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
char toLower(char ch) { return tolower(ch); }
string & ToLower(string & st);
void display(const string & s);
int main()
{
vector<string> words;
cout << "Enter words (enter quit to quit):\n";
string input;
while (cin >> input && input != "quit")
words.push_back(input);
cout << "You entered the following words:\n";
for_each(words.begin(), words.end(), display);
cout << endl;
// place words in set, converting to lowercase
set<string> wordset;
transform(words.begin(), words.end(),
insert_iterator<set<string> >(wordset, wordset.begin()),
ToLower);
cout << "\nAlphabetic list of words:\n";
for_each(wordset.begin(), wordset.end(), display);
cout << endl;
// place word and frequency in map
map<string, int> wordmap;
set<string>::iterator si;
for (si = wordset.begin(); si != wordset.end(); si++)
wordmap[*si] = count(words.begin(), words.end(), *si);
// display map contents
cout << "\nWord frequency:\n";
for (si = wordset.begin(); si != wordset.end(); si++)
cout << *si << ": " << wordmap[*si] << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
string & ToLower(string & st)
{
transform(st.begin(), st.end(), st.begin(), toLower);
return st;
}
void display(const string & s)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
执行结果:
Enter words (enter quit to quit):
The dog saw the cat and thought the cat fat
The cat thought the cat perfect
quit
You entered the following words:
The dog saw the cat and thought the cat fat The cat thought the cat perfect
Alphabetic list of words:
and cat dog fat perfect saw the thought
Word frequency:
and: 1
cat: 4
dog: 1
fat: 1
perfect: 1
saw: 1
the: 5
thought: 2valvect.cpp?
// valvect.cpp -- comparing vector and valarray
#include <iostream>
#include <valarray>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
vector<double> data;
double temp;
cout << "Enter numbers (<=0 to quit):\n";
while (cin >> temp && temp > 0)
data.push_back(temp);
sort(data.begin(), data.end());
int size = data.size();
valarray<double> numbers(size);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
numbers[i] = data[i];
valarray<double> sq_rts(size);
sq_rts = sqrt(numbers);
valarray<double> results(size);
results = numbers + 2.0 * sq_rts;
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed);
cout.precision(4);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout.width(8);
cout << numbers[i] << ": ";
cout.width(8);
cout << results[i] << endl;
}
cout << "done\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter numbers (<=0 to quit):
3.3 1.8 5.2 10 14.4 21.6 26.9 0
1.8000: 4.4833
3.3000: 6.9332
5.2000: 9.7607
10.0000: 16.3246
14.4000: 21.9895
21.6000: 30.8952
26.9000: 37.2730
donevslice.cpp?
// vslice.cpp -- using valarray slices
#include <iostream>
#include <valarray>
#include <cstdlib>
const int SIZE = 12;
typedef std::valarray<int> vint; // simplify declarations
void show(const vint & v, int cols);
int main()
{
using std::slice; // from <valarray>
using std::cout;
vint valint(SIZE); // think of as 4 rows of 3
int i;
for (i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i)
valint[i] = std::rand() % 10;
cout << "Original array:\n";
show(valint, 3); // show in 3 columns
vint vcol(valint[slice(1, 4, 3)]); // extract 2nd column
cout << "Second column:\n";
show(vcol, 1); // show in 1 column
vint vrow(valint[slice(3, 3, 1)]); // extract 2nd row
cout << "Second row:\n";
show(vrow, 3);
valint[slice(2, 4, 3)] = 10; // assign to 2nd column
cout << "Set last column to 10:\n";
show(valint, 3);
cout << "Set first column to sum of next two:\n";
// + not defined for slices, so convert to valarray<int>
valint[slice(0, 4, 3)] = vint(valint[slice(1, 4, 3)])
+ vint(valint[slice(2, 4, 3)]);
show(valint, 3);
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
void show(const vint & v, int cols)
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int lim = v.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lim; ++i)
{
cout.width(3);
cout << v[i];
if (i % cols == cols - 1)
cout << endl;
else
cout << ' ';
}
if (lim % cols != 0)
cout << endl;
}
执行结果:
Original array:
1 7 4
0 9 4
8 8 2
4 5 5
Second column:
7
9
8
5
Second row:
0 9 4
Set last column to 10:
1 7 10
0 9 10
8 8 10
4 5 10
Set first column to sum of next two:
17 7 10
19 9 10
18 8 10
15 5 10
ilist.cpp?
// ilist.cpp -- use initializer_list
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
double sum(std::initializer_list<double> il);
double average(const std::initializer_list<double> & ril);
int main()
{
using std::cout;
cout << "List 1: sum = " << sum({ 2,3,4 })
<< ", ave = " << average({ 2,3,4 }) << '\n';
std::initializer_list<double> dl = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5 };
cout << "List 2: sum = " << sum(dl)
<< ", ave = " << average(dl) << '\n';
dl = { 16.0, 25.0, 36.0, 40.0, 64.0 };
cout << "List 3: sum = " << sum(dl)
<< ", ave = " << average(dl) << '\n';
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
double sum(std::initializer_list<double> il)
{
double tot = 0;
for (auto p = il.begin(); p != il.end(); p++)
tot += *p;
return tot;
}
double average(const std::initializer_list<double> & ril)
{
double tot = 0;
int n = ril.size();
double ave = 0.0;
if (n > 0)
{
for (auto p = ril.begin(); p != ril.end(); p++)
tot += *p;
ave = tot / n;
}
return ave;
}执行结果:
List 1: sum = 9, ave = 3
List 2: sum = 16.5, ave = 3.3
List 3: sum = 181, ave = 36.2