DFS,BFS市面上都有很多的代码和视频,很多写的不明就里。其实一个是(基于栈的)递归,一个是队列的遍历。可以参照以下流程。顺一遍下来,就可以解决各种问题了。
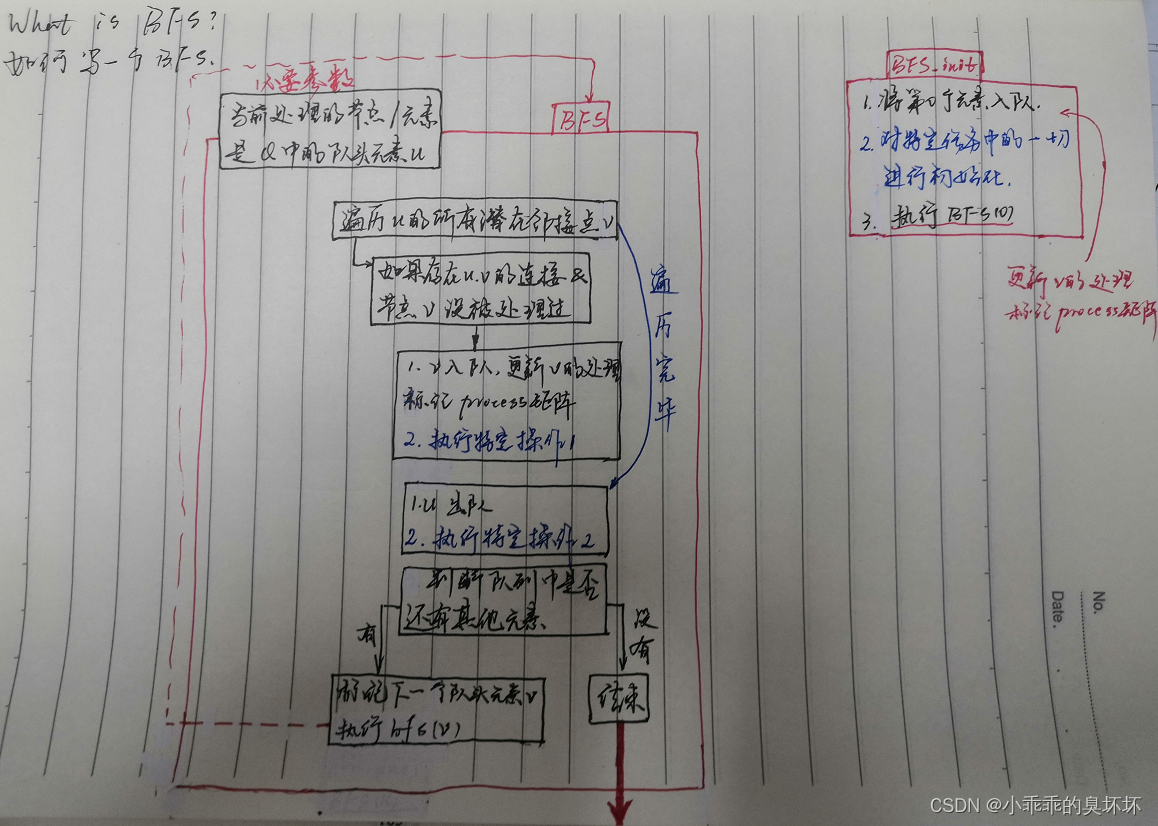
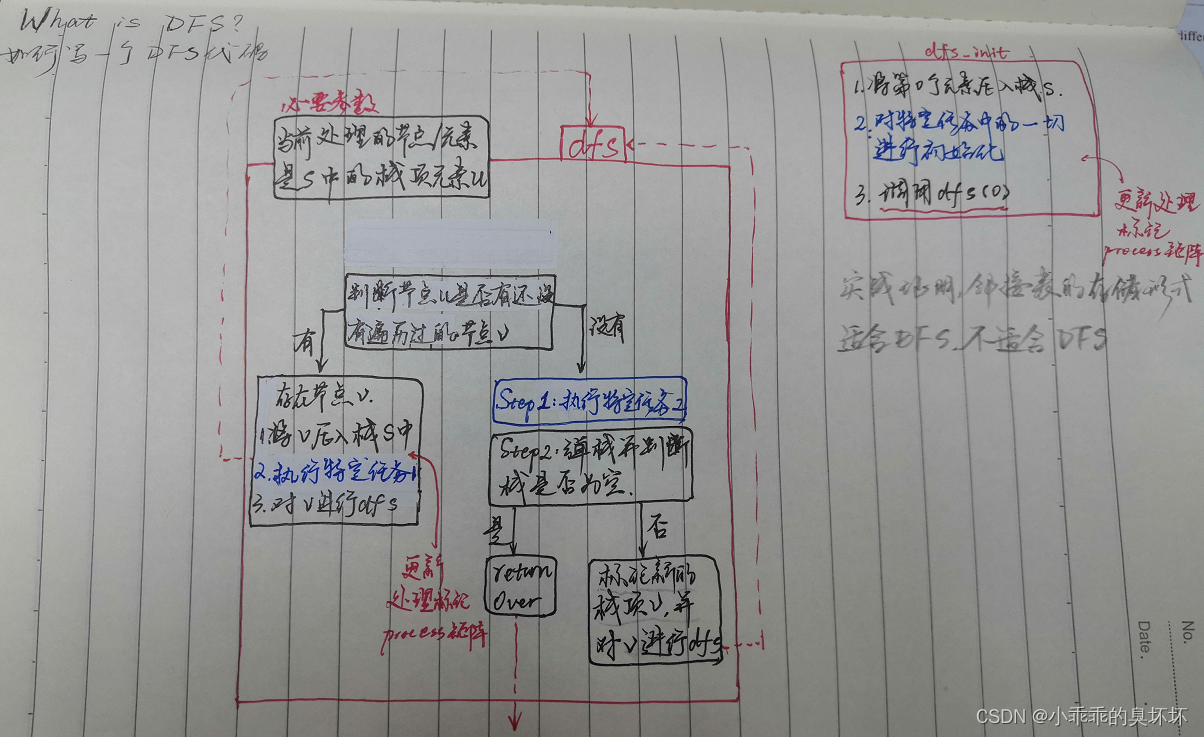
例题1:DFS遍历
代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class reWriteDFS {
public static int time = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();//n个节点
int[][] M = new int[n][n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int id = cin.nextInt();
int degree = cin.nextInt();
for (int j=0;j<degree;j++){
int neighbour = cin.nextInt();
M[id-1][neighbour-1] = 1;
}
}
Stack<Integer> S = new Stack<>();
int[] d = new int[n];
int[] f = new int[n];
int[] process = new int[n];
dfs_init(d, f, S, M, n, process);
for (int i:d){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
for (int i:f){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public static void dfs_init(int[] d, int[] f, Stack<Integer> S, int[][] M, int n, int[] process){
S.push(0);
time++;
process[0] = 1;
d[0] = time;
dfs(0, d, f, S, M, n, process);
}
public static void dfs(int u, int[] d, int[] f, Stack<Integer> S, int[][] M, int n, int[] process){
int tag = hasNext(u, M, process);
if(tag ==-1){
time++;
f[u] = time;
S.pop();
if(S.size()==0){
return;
}
else {
int v = S.peek();
dfs(v, d, f, S, M, n, process);
}
}
else {
S.push(tag);
time++;
d[tag] = time;
process[tag] = 1;
dfs(tag, d, f, S, M, n, process);
}
}
public static int hasNext(int u, int[][] M, int[] process){
for (int i=0;i<process.length;i++){
if(M[u][i]==1 && process[i]==0){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
例题2:用DFS求连通块
代码:
import java.util.Stack;
public class uva572 {
public static int id = 0;
static class Position {
int x;
int y;
Position(){}
public Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String map[] = new String[5];
map[0] = "****@";
map[1] = "*@@*@";
map[2] = "*@**@";
map[3] = "@@@*@";
map[4] = "@@**@";
int[][] group = new int[5][5];
int[][] process = new int[5][5];
Stack<Position> S = new Stack<>();
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
for (int j=0;j<5;j++){
//对每一个元素进行判断,如果是*,process[i][j]就设置为-1,如果是@就设置为1
if(map[i].charAt(j)=='*'){
process[i][j] = -1;
}
else if(map[i].charAt(j)=='@' && process[i][j] == 0){
Position u = new Position(i,j);
S.push(u);
process[i][j] = 1;
id++;
group[i][j] = id;
dfs(u, process, group, S, map);
}
else if(map[i].charAt(j)=='@' && process[i][j] == 1){
continue;
}
}
}
System.out.println(id);
}
public static void dfs(Position u, int[][] process, int[][] group, Stack<Position> S, String map[]){
Position v = hasNext(u, map, process);
if(v.x==-1 && v.y==-1){
S.pop();
if (S.size()==0){
return;
}
else {
Position tag = S.peek();
dfs(tag, process, group, S, map);
}
}
else {
S.push(v);
process[v.x][v.y] = 1;
group[v.x][v.y] = id;
dfs(v, process, group, S, map);
}
}
public static Position hasNext(Position u, String map[], int[][] process){
for (int i=-1;i<=1;i++){
for (int j=-1;j<=1;j++){
int x_new = u.x+i;
int y_new = u.y+j;
if(x_new<5 && x_new>=0 && y_new<5 && y_new>=0){//下标符合,不符合都不用看
if(map[x_new].charAt(y_new)=='*'){
process[x_new][y_new] = -1;
}
else if(process[x_new][y_new] == 0){//只要找到了还没有被处理过的@,那就返回他的位置
return new Position(x_new, y_new);
}
}
}
}
return new Position(-1, -1);
}
}
例题3:BFS遍历
代码:
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class rewriteBFS {
public static int time = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();
int[] process = new int[n];
ArrayDeque<Integer> Q = new ArrayDeque<>();
int[] d = new int[n];
int[] f = new int[n];
//分别使用两种存储方式进行bfs
/* //1.连接矩阵
int[][] M = new int[n][n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int id = cin.nextInt();
int degree = cin.nextInt();
for (int j=0;j<degree;j++){
int neighbour = cin.nextInt();
M[id-1][neighbour-1] = 1;
}
}
bfs_init1(M, process, Q, d, f);*/
ArrayList<Integer> al[] = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
al[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int id = cin.nextInt();
int degree = cin.nextInt();
for (int j=0;j<degree;j++){
int neighbour = cin.nextInt();
al[id-1].add(neighbour-1);
}
}
bfs_init2(al, process, Q, d, f);
for (int i:d){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int i:f){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public static void bfs_init1(int[][] M, int[] process, ArrayDeque<Integer> Q, int[] d, int[] f){
Q.addLast(0);
process[0] = 1;
bfs1(0, M, process, Q, d, f);
}
public static void bfs1(int u, int[][] M, int[] process, ArrayDeque<Integer> Q, int[] d, int[] f){
for (int i=0;i<process.length;i++){
if(M[u][i]==1 && process[i]==0){
Q.addLast(i);
process[i] = 1;
time++;
d[i] = time;
f[i] = f[u]+1;
}
}
Q.removeFirst();
if(Q.size()==0){
return;
}
else {
int v = Q.getFirst();
bfs1(v, M, process, Q, d, f);
}
}
public static void bfs_init2(ArrayList<Integer> al[], int[] process, ArrayDeque<Integer> Q, int[] d, int[] f){
Q.addLast(0);
process[0] = 1;
bfs2(0, al, process, Q, d, f);
}
public static void bfs2(int u, ArrayList<Integer> al[], int[] process, ArrayDeque<Integer> Q, int[] d, int[] f){
for (int i=0;i<al[u].size();i++){
int v = al[u].get(i);
if(process[v]==0){
Q.addLast(v);
process[v] = 1;
time++;
d[v] = time;
f[v] = f[u]+1;
}
}
Q.removeFirst();
if(Q.size()==0){
return;
}
else {
int v = Q.getFirst();
bfs2(v, al, process, Q, d, f);
}
}
}
例题4:用BFS求最短路
代码:
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ShortestRoad {
public static int distance = 0;
static class Position{
int x;
int y;
public Position(){}
public Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] map = new int[6][5];
for (int i=0;i<6;i++){
for (int j=0;j<5;j++){
map[i][j] = cin.nextInt();
}
}
int[][] process = new int[6][5];
int[][] d = new int[6][5];
ArrayDeque<Position> aq = new ArrayDeque<>();
dfs_init(d, process, map, aq);
for (int i=0;i<6;i++){
for (int j=0;j<5;j++){
System.out.print(d[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void dfs_init(int[][] d, int[][] process, int[][] map, ArrayDeque<Position> aq){
Position u = new Position(0,0);
aq.addLast(u);
process[0][0] = 1;
bfs(u, d, process, map, aq);
}
public static void bfs(Position u, int[][] d, int[][] process, int[][] map, ArrayDeque<Position> aq){
int[] s = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] t = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
int x_new = u.x+s[i];
int y_new = u.y+t[i];
if(x_new<6 && x_new>=0 && y_new<5 && y_new>=0){//保证下标不越界
if(map[x_new][y_new] == 1){//如果是墙
process[x_new][y_new] = -1;
}
else {//如果是通道
if(process[x_new][y_new]==0){//如果没有被处理过
Position v = new Position(x_new, y_new);
aq.addLast(v);
d[v.x][v.y] = d[u.x][u.y] + 1;
process[v.x][v.y] = 1;
}
else {
continue;
}
}
}
}
//此时遍历完其所有潜在相邻节点
aq.removeFirst();
if(aq.size()==0){
return;
}
else {
Position tag = aq.getFirst();
bfs(tag, d, process, map, aq);
}
}
}
输入:
0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 1
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
输出:
0 1 0 11 12
1 0 9 10 11
2 0 8 0 0
3 0 7 8 9
4 5 6 0 10
5 6 7 8 9