SG函数
S G SG SG 函数是对游戏图中每一个节点的评估函数。
若 S G ( x ) = 0 SG(x)=0 SG(x)=0 则为必败状态,若 S G ( x ) ≠ 0 S G ( x ) ≠ 0 SG(x)?=0,则为必胜状态
S G 定 理 : SG定理: SG定理:所有一般胜利下的公平组合游戏都能转化成尼姆数表达的尼姆堆博弈,一个博弈的尼姆值 定义为这个博弈的等价尼姆数,即:对于当前游戏 X X X,它可以被拆分为多个子游戏 x 1 , x 2 , . . . x n x_1,x_2,...x_n x1?,x2?,...xn?,那么 S G ( X ) = S G ( x 1 ) ? S G ( x 2 ) ? S G ( x 3 ) . . . ? S G ( x n ) SG(X)=SG(x_1)\bigoplus SG(x_2) \bigoplus SG(x_3)...\bigoplus SG(x_n) SG(X)=SG(x1?)?SG(x2?)?SG(x3?)...?SG(xn?)
对于由 n n n 个有向图游戏组成的组合游戏 设它们的起点分别为 s 1 , s 2 , s 3 , . . . s n s_1,s_2,s_3,...s_n s1?,s2?,s3?,...sn?,先手胜利时当且仅当 S G ( s 1 ) ? S G ( s 2 ) ? S G ( s 3 ) . . . ? S G ( s n ) ≠ 0 SG(s_1) \bigoplus SG(s_2) \bigoplus SG(s_3)...\bigoplus SG(s_n) \neq 0 SG(s1?)?SG(s2?)?SG(s3?)...?SG(sn?)?=0
求
S
G
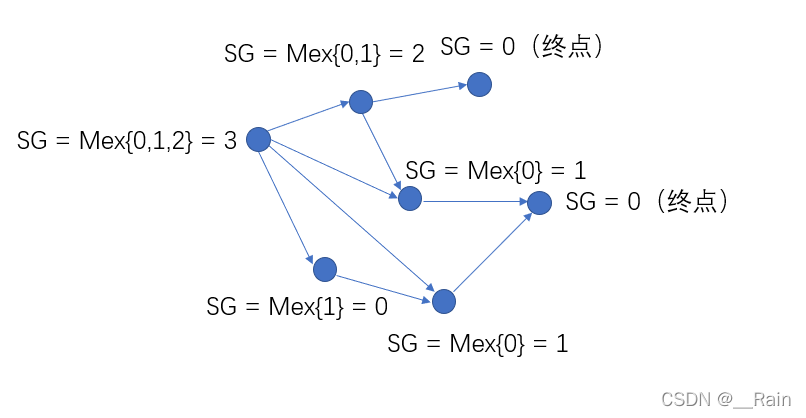
SG
SG 函数
设
x
x
x 的后继状态
y
1
,
y
2
,
.
.
.
y
n
y_1,y_2,...y_n
y1?,y2?,...yn?
S
G
(
x
)
=
m
e
x
(
S
G
(
y
1
)
,
S
G
(
y
2
)
,
.
.
.
S
G
(
y
n
)
)
SG(x)=mex(SG(y_1),SG(y_2),...SG(y_n))
SG(x)=mex(SG(y1?),SG(y2?),...SG(yn?))
S-Nim
题意:
给定一个大小为
n
n
n 的集合
S
S
S,
q
q
q 组查询,每次查询给定
m
m
m 堆石头,每堆石头的个数
x
i
x_i
xi?,两人轮流从中取石头,每次取石头的个数来自集合
S
S
S,问先拿者是否有必胜策略
n
<
=
100
,
S
i
<
=
10000
,
q
<
=
100
,
m
<
=
100
,
x
i
<
=
10000
n<=100,S_i<=10000,q<=100,m<=100,x_i<=10000
n<=100,Si?<=10000,q<=100,m<=100,xi?<=10000
思路:
S
G
SG
SG 函数,多个游戏
s
g
sg
sg 函数经典例题
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e4 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m;
int a[maxn], sg[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void work()
{
mem(sg, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= maxn - 9; ++i){// 预处理石子数为i的sg函数
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) if(i >= a[j]) vis[sg[i-a[j]]] = 1;// 标记后继状态sg函数值
while(vis[sg[i]]) ++sg[i];// 求mex
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) if(i >= a[j]) vis[sg[i-a[j]]] = 0;// 消除标记
}
int q;cin >> q;
while(q--){
cin >> m;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1, x; i <= m; ++i){
cin >> x;
ans ^= sg[x];// 子游戏sg函数值异或一遍
}
cout << (ans ? "W" : "L");
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
// int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
while(cin >> n && n)
work();
return 0;
}
黑黑白白
思路:
S
G
SG
SG 函数,单个游戏
设
s
g
[
x
]
sg[x]
sg[x] 表示先手轮到
x
x
x 点时的取胜情况,
s
g
[
x
]
=
1
sg[x]=1
sg[x]=1 表示必胜状态
- 当子状态有必败状态时,该状态为必胜状态。
- 当子状态全部为必胜状态,该状态为必败状态。
遍历这棵树,把所有孩子结点的答案向上合并
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m;
vector <int> e[maxn];
int sg[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int fa){
bool f = 1;//因为判断必胜状态的条件是存在某个子状态,根据定义的sg函数含义,初始设为1
for(auto to : e[x]) if(to != fa)
{
dfs(to, x);
f &= sg[to];// 企图&出来0
}
sg[x] = !f;
}
void work()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) e[i].clear(), sg[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
int x, y;cin >> x >> y;
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(m, m);
cout << (sg[m] ? "Gen" : "Dui") << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}
春联
思路:
S
G
SG
SG 函数,单个游戏
题解
看了下题解,就是用最后一个字符往前推必胜和必败点
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m, k;
int sg[maxn], mp[30], vis[30];
string s;
int ans = 0;
int get(){
mem(vis, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= 26; ++i){
if(mp[i] != n + 1) vis[sg[mp[i]]] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0; ; ++i) if(!vis[i]) return i;
}
void work()
{
cin >> s;n = s.size();s = "@" + s;
for(int i = 1; i <= 26; ++i) mp[i] = n + 1;
for(int i = n; i >= 1; --i){
s[i] -= 'a' - 1;
sg[i] = get();
mp[s[i]] = i;
}
cout << (get() ? "kou" : "yukari");
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}
寒冬信使2
思路:
S
G
SG
SG 函数,单个游戏
把
w
w
w 看成
1
1
1,
b
b
b 看成
0
0
0, 可以得到一个
01
01
01 串, 把状态压缩成
X
=
∑
i
=
0
n
?
1
2
i
?
(
s
i
=
=
′
w
′
)
X=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}2^i*(s_{i}=='w')
X=∑i=0n?1?2i?(si?==′w′)
可以发现操作只会让
X
X
X 的值减少或者不变,于是可以记录每个状态的
S
G
SG
SG 函数,
X
X
X 的
S
G
SG
SG 函数为
0
0
0 输出
N
o
No
No,否则输出
Y
e
s
Yes
Yes
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m;
string s;
bitset <109> vis;
int sg[maxn];
void init(){
for(int i = 1; i < 1 << 10; ++i)// 二进制枚举预处理所有01串状态
{
vis.reset();
for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
{
if(i & (1 << j))// 第j位为1
{
if(j == 0) vis[sg[i ^ (1 << j)]] = 1;//操作二
else
{
for(int k = 0; k < j; ++k) vis[sg[i ^ (1 << j) ^ (1 << k)]] = 1;// 操作一
}
}
while(vis[sg[i]]) ++sg[i];//状态i的sg函数
}
}
}
void work()
{
cin >> n >> s;
int st = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if(s[i] == 'w') st |= 1 << (i);
cout << (sg[st] ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
init();
int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}
D 与 S
思路:
k
k
k 个关键点是必胜点,如果一个节点直接连着连着两个必胜点,那么这个点就会变成必胜点,把初始的
k
k
k 个点放入队列不断更新即可
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m, k;
vector <int> e[maxn];
int sg[maxn], deg[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) e[i].clear(), sg[i] = deg[i] = 0;
queue <int> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++i){
int x;cin >> x;
sg[x] = 1;
q.push(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int x, y;cin >> x >> y;
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front();q.pop();
for(auto to : e[x]){
if(sg[to]) continue;
++deg[to];
if(deg[to] >= 2){
sg[to] = 1;
q.push(to);
}
}
}
cout << (sg[1] ? "yes" : "no") << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}
Anti-SG游戏
S J 定 理 : SJ定理: SJ定理: 对于任意一个 A n t i ? S G Anti - SG Anti?SG 游戏,如果我们规定:当局面中所有的单一游戏的 S G SG SG 值为 0 0 0 时,游戏结束,则先手必胜当且仅当:
- 游戏的 S G SG SG 函数值不为 0 0 0 且游戏中某个单一游戏的 S G SG SG 函数值大于 1 1 1。
- 游戏的 S G SG SG 函数值为 0 0 0 且游戏中没有任意一个单一游戏的 S G SG SG 函数值大于 1 1 1 。
P4279 [SHOI2008]小约翰的游戏
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m, k;
int a[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> n;
int sg = 0;bool f = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cin >> a[i];
sg ^= a[i];
if(a[i] > 1) f = 1;
}
if(!f && !sg || f && sg) cout << "John\n";
else cout << "Brother\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}
Multi - SG游戏
条纹 黑暗爆炸 - 2940
题意:
思路:
具体递推公式好像需要打表找规律
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ld long double
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mem(x, d) memset(x, d, sizeof(x))
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e3 + 9;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
ll n, m;
int a, b, c;
bool vis[maxn];
int sg[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(a > b) swap(a, b); if(b > c) swap(b, c); if(a > b) swap(a, b);
for(int i = a; i <= maxn - 9; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j + a <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-a]] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j + b <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-b]] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j + c <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-c]] = 1;
while(vis[sg[i]]) ++sg[i];
for(int j = 0; j + a <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-a]] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j + b <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-b]] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j + c <= i; ++j) vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j-c]] = 0;
}
cin >> m;
while(m--){
cin >> n;
cout << (sg[n] ? 1 : 2) << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// int TT;cin>>TT;while(TT--)
work();
return 0;
}