前言
在写某些动态规划问题的时候,把问题描述为有限状态机的形式可以帮助我们解决这种DP问题
下面将用两道例题来解释
例题1
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.
给出了一个整数数组prices,其中prices[i]是第i天给定股票的价格。
在每一天,你可能会决定购买和/或出售股票。你在任何时候最多只能持有一股股票。然而,你可以购买它,然后立即在同一天出售。
找到并回报你能获得的最大利润。
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Total profit is 4.
Example 3:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0.
解释
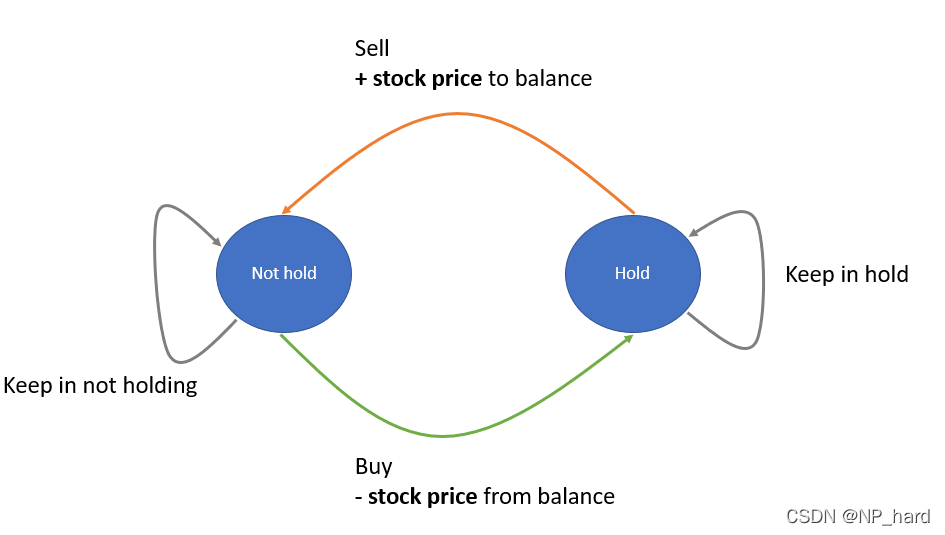
我们可以将这题的过程描述为上图所示的有限状态机,我们只有两种状态:
- 持有股票
- 不持有股票
对于持有股票,我们有两种状态转移过程:
- 继续持有股票→持有股票
- 卖掉股票→不持有股票
对于不持有股票也是同理
所以我们能写出我们的状态转移方程了
h
o
l
d
=
m
a
x
(
h
o
l
d
,
N
o
t
?
h
o
l
d
?
p
r
i
c
e
)
hold = max(hold, Not\ hold-price)
hold=max(hold,Not?hold?price)
N
o
t
?
h
o
l
d
=
m
a
x
(
N
o
t
?
h
o
l
d
,
h
o
l
d
+
p
r
i
c
e
)
Not\ hold = max(Not\ hold, hold+price)
Not?hold=max(Not?hold,hold+price)
所以问题的解决代码为
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int hold = INT_MIN;
int not_hold = 0;
for(auto price : prices){
int tmp1 = hold, tmp2 = not_hold;
hold = max(tmp1, tmp2-price);
not_hold = max(tmp2, tmp1+price);
}
return not_hold;
}
};
这里的
hold初始化为无穷小,是为了hold = max(tmp1, tmp2-price)这条语句能正常初始化
例题2
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
Find the maximum profit you can achieve. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times) with the following restrictions:
After you sell your stock, you cannot buy stock on the next day (i.e., cooldown one day).
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions simultaneously (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
你会得到一个数组prices,其中prices[i]是第i天给定股票的价格。
找到你能获得的最大利润。您可以按照以下限制完成任意数量的交易(即多次购买和出售一股股票):
卖出股票后,你不能在第二天(即冷却一天)购买股票。
注意:您不能同时进行多笔交易(即,您必须在再次购买之前出售股票)。
Example 1:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,0,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: transactions = [buy, sell, cooldown, buy, sell]
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1]
Output: 0
解释
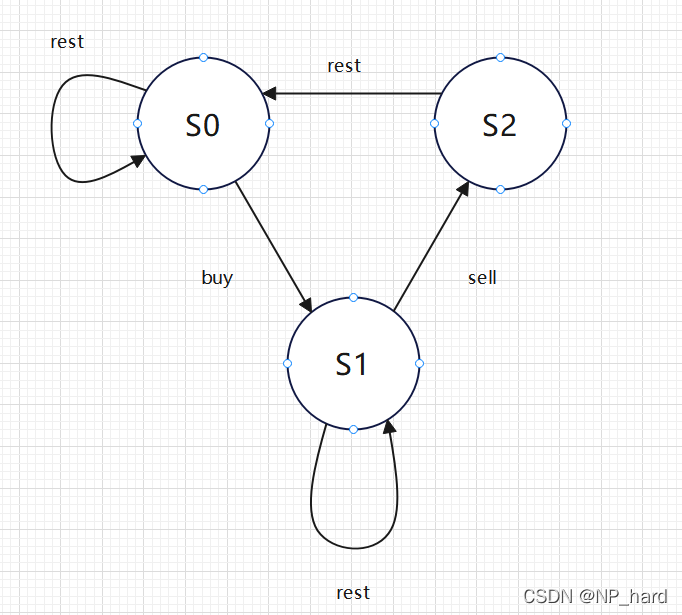
这题就不解释了,很上面那题差不多
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
if(prices.size()==1)return 0;
int s0 = 0, s1 = -prices[0], s2 = INT_MIN;
for(int i=1; i<prices.size(); i++){
int tmp = s0;
s0 = max(s0, s2);
s2 = s1 + prices[i];
s1 = max(s1, tmp-prices[i]);
}
return max(s0, s2);
}
};