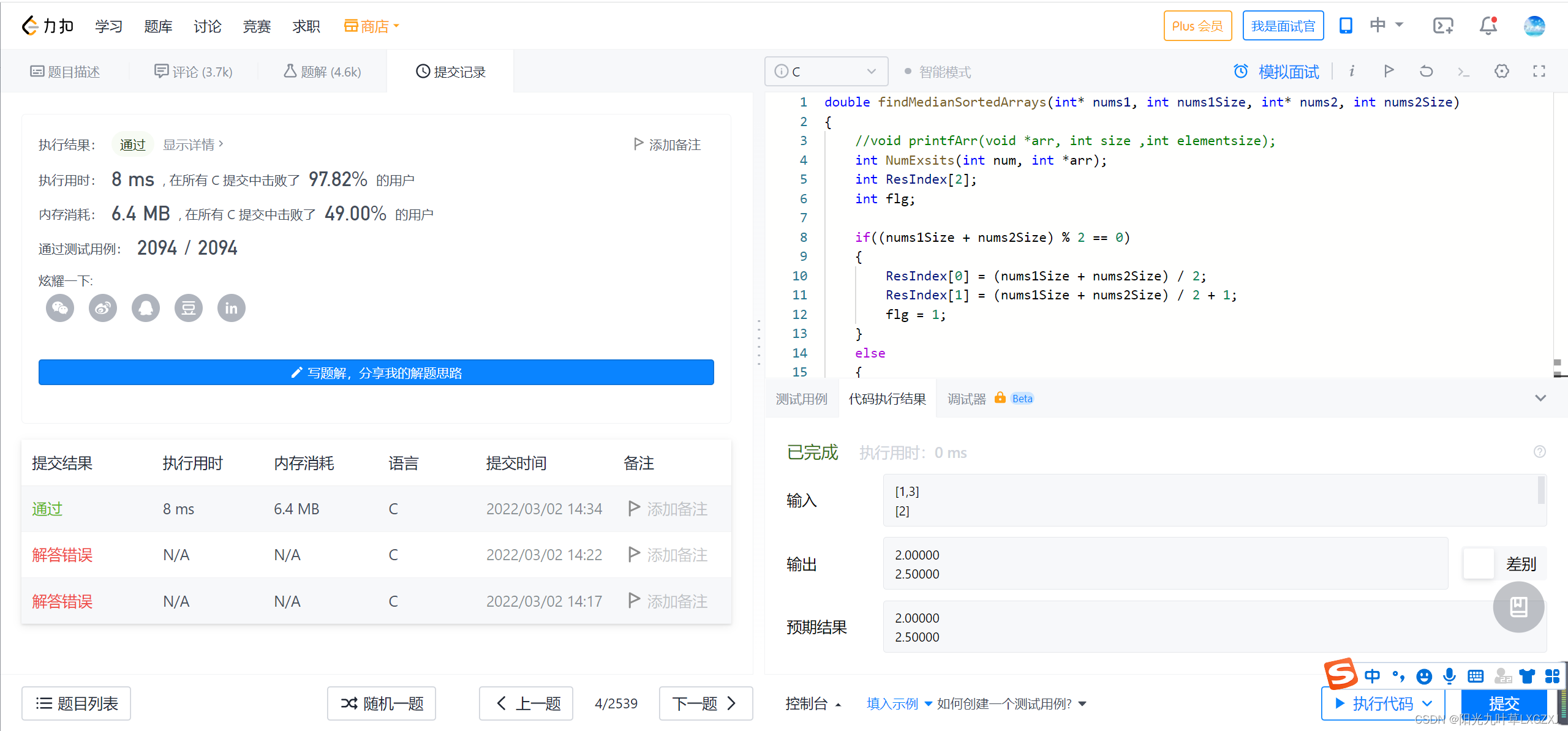
一、题目
二、解题思路
(1)思路一
由于两个数组是有序的,所以可以用插入排序或qsort方法进行数组排序合并,排完序之后,如果元素总个数n为奇数,中位数为第(n-1)/2+1个元素(不是索引位)。如果元素总个数n为偶数,中位数为第n/2+1个和第n/2个的和除以二,再根据中位数的位置在排好序的数组中遍历找出。
此思路没有用代码进行实现,由于此思路的算法复杂度为O(n^2),并且需要重新定义一个长度为m+n的数组,占用的内存会比较多。
(2)思路二
先找出中位数的位置,如果元素总个数n为奇数,中位数为第(n-1)/2+1个元素(不是索引位)。如果元素总个数n为偶数,中位数为第n/2+1个和第n/2个的和除以二。我们其实不需要用额外的数组来记录元素,只需要按照情况来划分,建议看到下面提供的代码,再对着思路二一起看,对理解有帮助。
这里需要用到一些变量来协助
int flg;
1表示元素个数为偶数
0表示元素个数为奇数
int cnt;
记录遍历了多少个元素
int ResIndex[2];
记录中位数的位置,不是记录索引号
int NumExsits(int num, int *arr)
判断num是否在数组arr中,在的话返回索引位,不在返回-1
int tmp = -1;
将NumExsits的结果赋予tmp
int twoflg = 0;
表示中位数已经取几个
情况一:两个数组同时遍历,得到了中位数:
1、数组A中的元素a大于数组B中的元素a,是否到中位数记录的位置,在的话,再判断总元素个数是奇数,直接返回中位数,如果是偶数,表示中位数是两个数的和,再判断twoflg为几,如果为1,表示之前已经取了一个,将此元素加到结果中并返回。如果为0,将此元素加到结果中继续循环。
2、数组A中的元素a小于数组B中的元素a,逻辑同上。
3、数组A中的元素a等于数组B中的元素a,是否到中位数记录的位置,在的话,再判断总元素个数是奇数,直接返回中位数,如果是偶数,表示中位数是两个数的和,再判断twoflg为几,如果为1,且结果值中为0,表示这两个元素为所求的中位数。如果res结果不为0,表示之前已经存储了一个元素,最多存储两个元素,所以直接把元素加到结果中返回。再者就是结果值为0,但中位数需要两个数才能确认的情况,把元素加到结果中继续循环。
情况二:两个数组同时遍历,没有得到中位数:
这种情况表示其中一个数组已经完全遍历完毕,只需遍历其中一个数组即可,我这里两个都写是因为其中有一个循环必然不会进入,这样不用多加判断,代码简洁一些。
1、元素个数为奇数,中位数为一个的时候,上面的情况没有过滤到元素,在数组中遍历,遍历到直接返回结果。
2、元素个数为偶数,中位数为两个的时候,上面的情况没有过滤到元素,在数组中遍历,遍历到两次,直接将结果相加再除以二返回结果即可。
3、元素个数为偶数,中位数为两个的时候,上面的情况过滤到一个元素,在数组中遍历,遍历到一次,直接将结果相加再除以二返回结果即可。
三、虚机测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main()
{
void PrintfArr(void *arr, int size ,int elementsize);
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size);
//int nums1[] = {1,2,4,5,6};
//int nums2[] = {3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13};
//int nums2[] = {3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15};
//int nums2[] = {3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16};
int nums1[] = {2,2,4,4};
int nums2[] = {2,2,4,4};
int nums1Size = sizeof(nums1) / sizeof(int);
int nums2Size = sizeof(nums2) / sizeof(int);
PrintfArr(nums1, nums1Size ,sizeof(int));
PrintfArr(nums2, nums2Size ,sizeof(int));
findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums1Size, nums2, nums2Size);
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size)
{
void PrintfArr(void *arr, int size ,int elementsize);
int NumExsits(int num, int *arr);
int ResIndex[2];
int flg;
if((nums1Size + nums2Size) % 2 == 0)
{
ResIndex[0] = (nums1Size + nums2Size) / 2;
ResIndex[1] = (nums1Size + nums2Size) / 2 + 1;
flg = 1;
}
else
{
ResIndex[0] = ((nums1Size + nums2Size) - 1) / 2 + 1;
ResIndex[1] = -1;
flg = 0;
}
PrintfArr(ResIndex,2,sizeof(int));
int x,y,cnt;
double res = 0;
int tmp = -1;
int twoflg = 0;
for(x=0,y=0,cnt=0; x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size;)
{
cnt++;
if(nums1[x] < nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
printf("nums1[x] < nums2[y]\n");
if(tmp != -1)
{
if(!flg)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
x++;
}
else if(nums1[x] > nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
printf("nums1[x] > nums2[y]\n");
if(tmp != -1)
{
if(!flg)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums2[y]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums2[y];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
y++;
}
else if(nums1[x] == nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1)
{
twoflg++;
}
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1)
{
twoflg++;
}
printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
printf("nums1[x] == nums2[y]\n");
if(twoflg > 0)
{
if(flg == 0)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(flg && twoflg == 2 && res == 0)
{
res = (res + nums1[x] + nums2[y]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(res != 0)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
}
}
x++;
y++;
if(twoflg == 2)
{
twoflg = 0;
}
}
printf("++++++++++++++++++++\n");
}
for(; x<nums1Size; x++)
{
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1 && !flg)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 0)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
for(; y<nums2Size; y++)
{
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1 && !flg)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums2[y]) / 2;
printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 0)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
}
int NumExsits(int num, int *arr)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<2; i++)
{
if(arr[i] == num)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void PrintfArr(void *arr, int size ,int elementsize)
{
if(elementsize == sizeof(int))
{
int *tmparr = (int*)arr;
int i;
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
printf("%d ",tmparr[i]);
}
}
else if(elementsize == sizeof(char))
{
char *tmparr = (char*)arr;
int i;
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
printf("%c ",tmparr[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
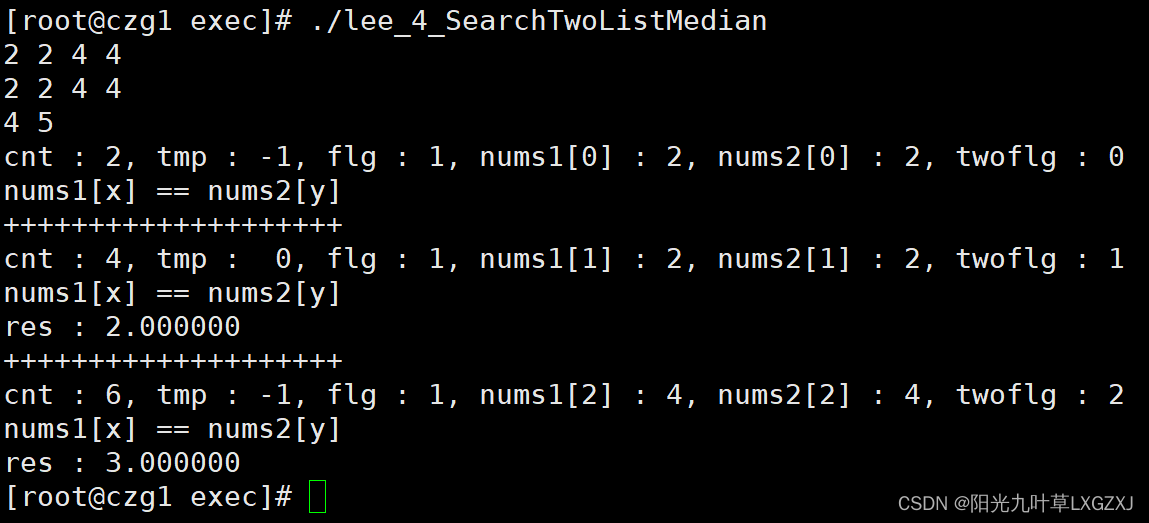
四、虚机测试截图
五、leecode提交代码
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size)
{
//void printfArr(void *arr, int size ,int elementsize);
int NumExsits(int num, int *arr);
int ResIndex[2];
int flg;
if((nums1Size + nums2Size) % 2 == 0)
{
ResIndex[0] = (nums1Size + nums2Size) / 2;
ResIndex[1] = (nums1Size + nums2Size) / 2 + 1;
flg = 1;
}
else
{
ResIndex[0] = ((nums1Size + nums2Size) - 1) / 2 + 1;
ResIndex[1] = -1;
flg = 0;
}
//printfArr(ResIndex,2,sizeof(int));
int x,y,cnt;
double res = 0;
int tmp = -1;
int twoflg = 0;
for(x=0,y=0,cnt=0; x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size;)
{
cnt++;
if(nums1[x] < nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
//printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
//printf("nums1[x] < nums2[y]\n");
if(tmp != -1)
{
if(!flg)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
x++;
}
else if(nums1[x] > nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
//printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
//printf("nums1[x] > nums2[y]\n");
if(tmp != -1)
{
if(!flg)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums2[y]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums2[y];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
y++;
}
else if(nums1[x] == nums2[y] && x<nums1Size && y<nums2Size)
{
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1)
{
twoflg++;
}
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1)
{
twoflg++;
}
//printf("cnt : %d, tmp : %2d, flg : %d, nums1[%d] : %d, nums2[%d] : %d, twoflg : %d\n",cnt,tmp,flg,x,nums1[x],y,nums2[y],twoflg);
//printf("nums1[x] == nums2[y]\n");
if(twoflg > 0)
{
if(flg == 0)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(flg && twoflg == 2 && res == 0)
{
res = (res + nums1[x] + nums2[y]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(res != 0)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
}
}
x++;
y++;
if(twoflg == 2)
{
twoflg = 0;
}
}
//printf("++++++++++++++++++++\n");
}
for(; x<nums1Size; x++)
{
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1 && !flg)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums1[x]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 0)
{
res = res + nums1[x];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
for(; y<nums2Size; y++)
{
cnt++;
tmp = NumExsits(cnt, ResIndex);
if(tmp > -1 && !flg)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 1)
{
res = (res + nums2[y]) / 2;
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
return res;
}
else if(tmp > -1 && flg && twoflg == 0)
{
res = res + nums2[y];
//printf("res : %f\n",res);
twoflg++;
}
}
return -1;
}
int NumExsits(int num, int *arr)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<2; i++)
{
if(arr[i] == num)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
六、leecode代码提交截图