我是菜鸡,大佬勿喷,AC的只有1,3两题,水平有限,仅供参考。
7-1 Simple Lie Detection (20 分)

Lie detection usually uses a set of prepared questions to ask the testee, and the result is obtained by analyzing the testee’s reactions. The more advanced technology uses a polygraph (测谎仪) to monitor the physical activities of the testee. Our simple polygraph here is to make a judgment by analyzing the characteristics of the answers to the questions.
First, we ask the testee to complete N multiple choice questions, each with a single answer. Each question has 8 options, which are represented by the lowercase English letters a-h. Then we can obtain a string of length N, consisting of only the lowercase English letters a-h. Score each string, and those whose score exceeds a certain threshold (阈值) T are judged as “suspected liars”. The scoring rules are as follows:
- the string starts with an f has its score ?2;
- the string ends with an a has its score ?1;
- for every longest segment of answeres where the same letter is chosen
for consecutive questions, if the segment length is larger than 5,
the score is to +3; - if an a is immediately followed by e or h, the score is to ?4;
- for every longest segment of answeres where consecutively increasing
letters are chosen to answer consecutive questions (such as abcd or
defgh), if the segment length is larger than 3, the score is to +5.
Your job is to score the answers and make a judgement.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives 3 positive integers N (6≤N≤100), the number of questions; T (≤100), the threshold for judging a liar; and K (≤100), the number of testees.
Then K lines follow, each gives the string of answers of a testee.
Output Specification:
For each testee, print in a line the total score of his/her answers. If the score exceeds the threshold, print !!! after the score.
Sample Input:
12 1 6
fghaebcdeddd
ahhhhhhgbaaa
cdefffffffff
fffffghecaaa
feeeeeeeegcb
aaaaaabbbbbb
Sample Output:
-1
-2
8!!!
-3
1
6!!!
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int n,t,k;
int judge(string s){
int ans=0;
if(s[0]=='f')
ans-=2;
if(s[n-1]=='a')
ans-=1;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
if( (s[i]=='a' && s[i+1]=='e') || (s[i]=='a' && s[i+1]=='h') )
ans-=4;
}
for(int i=0;i<n-5;i++){//判断连续相等元素
bool same6=true;
int j;
for(j=i+1;j<i+6;j++)
if(s[j]!=s[i]){//若出现不同元素
same6=false;
break;
}
if(same6==true){//如果相同的有5个以上
ans+=3;
for(int k=--j;k<n;k++){//把后续相同的略过
if(s[k]==s[j])
i=k;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n-3;i++){//判断连续上升元素
int coconsecutive_num=0;
bool isconse=true;
int j;
for(j=i;j<i+4;j++)
if( (int) (s[j]-s[i]) != j-i){//若出现非连续上升元素
isconse=false;
break;
}
if(isconse==true){
ans+=5;
for(int k=--j;k<n;k++){//把后续连续上升的略过
if((int) (s[k]-s[j]) == k-j)
i=k;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>t>>k;
string tstr;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
cin>>tstr;
int score=judge(tstr);
if(score>t) //若大于阈值
cout<<score<<"!!!";
else
cout<<score;
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
7-2 The First K Largest Numbers (25 分)
The task is simple: find the first K largest numbers from a given sequence of N integers, and output them in descending order.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 2 positive integers N (≤106) and K (≤5). Then N integer keys (in the range [?230,230]) are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in descending order the Kth largest numbers.
All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input 1:
10 4
40 25 60 -15 30 -21 80 -1 -5 27
Sample Output 1:
80 60 40 30
Sample Input 2:
4 5
23 -17 99 1
Sample Output 2:
99 23 1 -17
7-3 Is It A Binary Search Tree - Again (25 分)
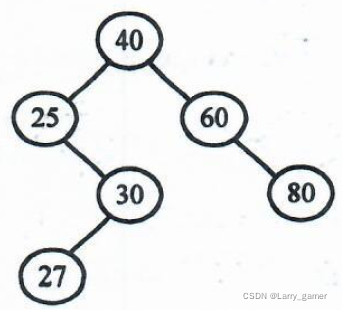
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than
the node’s key. - The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater
than or equal to the node’s key. - Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
A binary tree with positive keys can be represented by an array, which stores the keys in level-order as in a complete tree, with all the NULL nodes represented by ?1. For example, the following tree is stored in an array as { 40, 25, 60, -1, 30, -1, 80, -1, -1, 27 }.
Now given a sequence of integers in an array, you are supposed to tell if it corresponds to a BST, and output its inorder traversal sequence.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤1000). Then N integer keys (in the range (0, 100000)) are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, first print in a line YES if the sequence does correspond to a BST, or NO if not. Then print in the next line the inorder traversal sequence of that tree. It is guaranteed that the tree is non-empty.
All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input 1:
10
40 25 60 -1 30 -1 80 -1 -1 27
Sample Output 1:
YES
25 27 30 40 60 80
Sample Input 2:
11
40 50 60 -1 30 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 35
Sample Output 2:
NO
50 30 35 40 60
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
int A[maxn];
int n;
vector<int> ans;
void inorder(int root){
if(root*2 <=n)
judge_inorder(root*2);
if(A[root] != -1 && root<=n){
ans.push_back(A[root]);
}
if(root*2+1 <= n)
judge_inorder(root*2 + 1);
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>A[i];
bool isbst=true;
inorder(1);
for(int i=0;i<ans.size()-1;i++)
if(ans[i]>ans[i+1]){
isbst=false;
break;
}
if(isbst)
cout<<"YES\n";
else
cout<<"NO\n";
for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++){
cout<<ans[i];
if(i!=ans.size()-1)
cout<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
7-4 The Rescue (30 分)

When a group of hikers get lost in a forest and call the rescue team, the team leader would send the hikers a sequence of instructions. By following these instructions, the hikers can always move to a spot that the rescue team can reach, no matter where their original location was. Your job is to generate such a sequence for each given map.
A map is a rectangular(矩形) area consists of n×m unit square areas. There is alway one square X that is marked to be the rescue spot. Some of the areas are blocked and marked to be #, meaning that the hikers cannot enter this block. We assume that the boundaries of the map are all blocked.
An instruction is an integer that represents a direction: 0 for North, 1 for East, 2 for South, and 3 for West. For example, the sequence of instructions 3001 tells the hikers to move toward West and enter the neighboring area first, then head toward North and cross two units, and finally move toward East into the neighboring area. If the destination area is blocked, the hikers must stay in the current area and wait for the next instruction. The sequence you generate must be able to direct the hikers to move into X no matter where they were in that map. Once they arrive at X, they will ignore the rest of the instructions.
There are many different ways of generating the sequence. Here we design a greedy algorithm, hoping to generate a not-too-long sequence. The algorithm works as the following:
- Step 1: find the shortest paths from X to every other areas which the
hikers might be in, and pick the furthest area A. - Step 2: generate sequence s for directing from A to X along the
shortest path. - Step 3: update the map according to s – that is, mark all the
possible areas that the hikers might be in after following s. - Step 4: if X is the only possible area that contains the hikers,
stop; else goto Step 1.
The final sequence can be obtained by concatenating all the s’ generated in order.
Notice that while the shortest path might not be unique, you are supposed to output the smallest sequence. Sequence a1,a2,?,an is smaller than sequence b1,b2,?,bn if ther exists 1≤k≤n so that ai=bi for all i<k, and ak<bk.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 2 positive numbers 3≤n,m≤100. Then n lines follow, each contains m characters to represent the map. The rescue spot is X, a block is #, and O represents an open area.
Output Specification:
Output in a line the sequence of instructions. There must be no space between the numbers, nor at the beginning or the end of the line.
It is guaranteed that the solution exists.
Sample Input:
4 5
O#OOO
OOXOO
OO##O
OOO#O
Sample Output:
0011300121133
Hint:
During the 1st round, there are 3 candidates for A, as shown below:
O#OOO
OOXOO
OO##O
AOA#A
To direct them to X with the smallest sequence, we must choose the one at the lower-left corner, with the sequence 0011. Since at the very beginning, the hikers might be in any of the open areas, we apply 0011 to every open area, and obtain a map as shown below:
?#OO?
OOXO?
OO##O
OO?#O
where ? means that currently it is a possible position of the hikers. Now clearly we must pick the ? in the last row to be the next A, and direct it to X with 3001. After applying this sequence to other areas marked by ?, we update the map as the following:
?#OO?
OOXOO
OO##O
OOO#O
Now both ?'s have the same path length to X. We pick the upper-left corner to be A since it has the smaller sequence 211. The map is updated as the following:
O#OOO
OOXO?
OO##O
OOO#O
Finally apply 33, we can direct the last ? to X.
Hence the output sequence is 0011 3001 211 33.