二叉搜索树
文章目录
二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一颗空树,或者具有以下性质:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
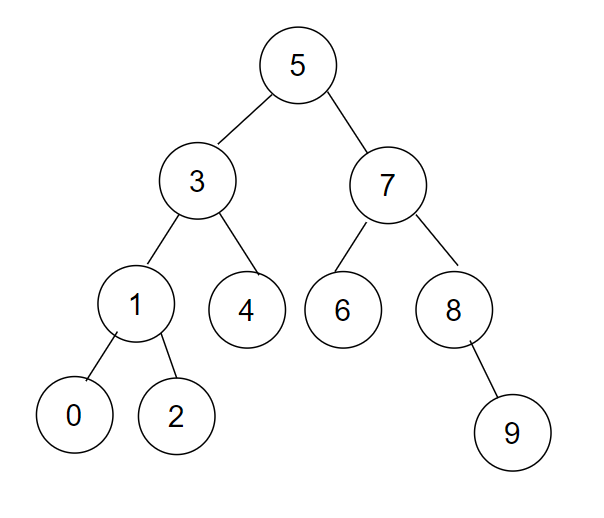
最坏查找高度次就可以确认一个值在不在树中,查找时间复杂度:O(N)(最坏情况:全部是左子树或者全部是右子树):

注意不是O(logN),只有在当树的形状接近完全二叉树或者满二叉树,才能达到logN,在实际中搜索二叉树在极端情况下没办法保证效率,所以我们要对搜索二叉树进一步学习它的特性扩展延伸:AVLTree和红黑树,他们对搜索二叉树,左右高度提出要求,非常接近完全二叉树,他们效率可以达到O(logN),AVLTree 红黑树以及B树系列都是在搜索树基础上演变出来,各有特点,适用于不同的场景
二叉搜索树的操作
二叉搜索树的节点结构
struct BSTreeNode//二叉搜索树节点
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
二叉搜索树的结构
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
private:
Node* _root;
};
二叉搜索树的查找
若根节点不为空:如果根节点key等于查找key,则返回该节点,如果根节点key大于查找key,则在其左子树查找,如果根节点key小于查找key,则在其右子树查找,否则返回NULL
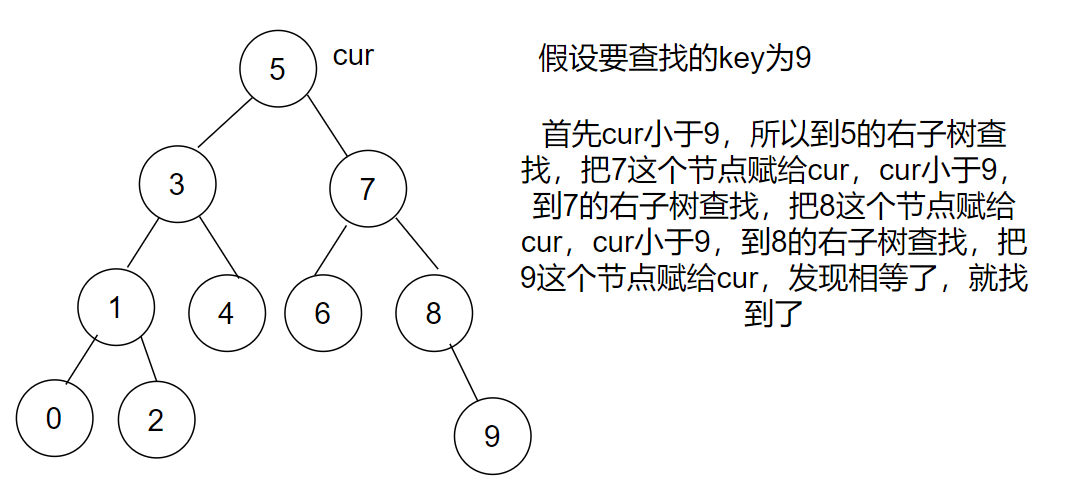
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->__left;
}
else if(cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return NULL;
}
二叉搜索树的插入
插入的具体过程如下:
a. 树为空,则直接插入
b. 树不为空,按照二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当根节点为空时,新创建一个节点即为根节点
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;//记录父亲节点,以便找到位置后进行与父亲链接
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明要插入的值有
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
//链接
if(parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
二叉搜索树的遍历
中序访问二叉搜索树,打印有序数组
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->_left);
cout<<root->_key<<" ";
InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去,外面就不用传_droot
}
int main()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = {5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9};
for(auto e:a)
{
t.insert(e);
}
t.Inorder();
}
二叉搜索树的删除

删除的原则:保持搜索树的结构
删除一个值等于key的节点,分情况分析:
- 要删除的是叶子节点非常好处理,删除自己,父亲指向自己的位置的指针置空
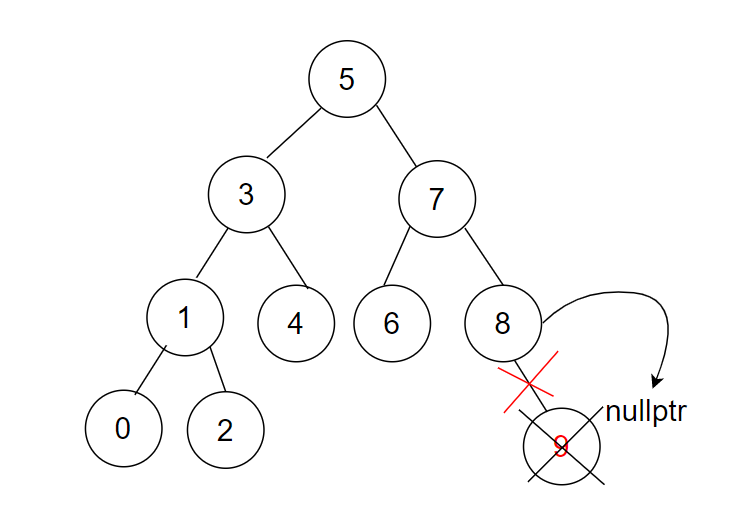
- 要删除的节点是只有一个孩子的节点,删除当前节点,把孩子交给父亲顶替自己位置
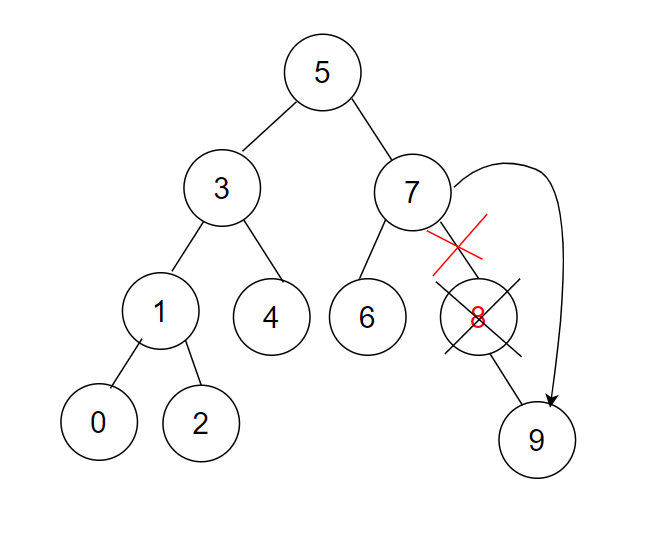
- 要删除的是有两个孩子的节点不好处理,解决方案是替换法删除:
去孩子里面找一个值(左子树的最大节点,左子树最右节点就是最大的,或者右子树的最小节点,右子树最左节点就是最小的)能替换自己位置的节点,这两个节点去替换后,都符合特征1或者2,可以直接删除

注意:情况1可以当成特征2的情况去处理
删除之找右子树的最左节点:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur= cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)//删除节点是父亲的啥就把孩子赋给父亲的啥
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
else
{
//左右都不为空,替换法删除
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
//Node* parent = nullptr;//这里不能设置成nullptr,当rightMin走到这里就是要删除节点的右子树中最左节点时,下面的循环进不去,此时parent就是nullptr,后面访问parent会报错
Node* parent = cur;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
parent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//走到了最左
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if(rightMin == parent->left)//不一定肯定rightMin就是parent的左孩子,当Node* parent = nullptr这个代码的注释说明的情况发生时,rightMin就是parent的右孩子
{
parent->_left = rightMin->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = rightMin->_right;
}
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
删除之找左子树的最右节点:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(cur->_key<key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//cur->_key == key
{
//找到了,准备开始删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//情况1:_right = nullptr
//情况2:_right != nullptr
//情况1和情况2合并
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//情况1:_left = nullptr
//情况2:_left != nullptr
//情况1和情况2合并
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//左右都不为nullptr,替换法删除
{
//情况3
//先找到左子树的最大节点(最右边的节点)
Node* leftMax = cur->_left;
Node* maxParent = cur;//这里不能给nullptr,需要给cur,因为下面的循环可能进不去(当此时的leftMax就是最大节点时),此时如果给了nullptr,maxParent就为空,下面就会访问空指针出错
while(leftMax->right)
{
maxParent = leftMax;
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//交换值
cur->_key = leftMax->_key;
//删除
if(maxParent->_left == leftMax)
{
maxParent->_left = leftMax->_left;
}
else
{
maxParent->_right = leftMax->_left;
}
delete leftMax;
//递归
/*Node* leftMax = cur->_left;
while(leftMax->right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//用临时变量来保存这个替换的值
K max = leftMax->_key;
//递归调用
this->Erase(max);//值为max的这个值一定没有右孩子,即递归终止条件
cur->_key = min;*/
}
return true;
}
}
return flase;
}
二叉搜索树插入的递归写法

如果root的key小于要插入节点的key,则递归到右子树去插入,如果root的key大于要插入节点的key,则递归到左子树去插入,如果相等说明已经存在这个key,插入失败,这里参数列表的root设置为引用,就可以解决链接的问题:
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)//引用很巧,相当于root是传过来的别名,注意这里的引用是关键,我们插入时的位置找到时,并不知道链接关系该怎么处理,这里传引用,就解决了这个问题
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else
{
if(root->_key<key)
{
return _Insert(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Insert(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root,key)
}
二叉搜索树查找的递归写法
如果root的key小于要插入节点的key,则递归到右子树去查找,如果root的key大于要插入节点的key,则递归到左子树去查找,如果相等说明找到了:
Node* _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return root;
}
if(root->_key < key)
{
_FindR(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
_FindR(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
//找到了
return root;
}
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root,key);//套一层,因为递归需要将根节点传过去
}
二叉搜索树删除的递归写法
如果root的key小于要删除节点的key,则递归到右子树去删除,如果root的key大于要删除节点的key,则递归到左子树去删除,如果相等说明找到了要删除的节点,进行删除,删除又回到了上面非递归写法讲解的那三种情况:
-
要删除的是叶子节点非常好处理,删除自己,父亲指向自己的位置的指针置空
-
要删除的节点是只有一个孩子的节点,删除当前节点,把孩子交给父亲顶替自己位置
-
要删除的是有两个孩子的节点不好处理,解决方案是替换法删除:
去孩子里面找一个值(左子树的最大节点,左子树最右节点就是最大的,或者右子树的最小节点,右子树最左节点就是最小的)能替换自己位置的节点,这两个节点去替换后,都符合特征1或者2,可以直接删除
注意:情况1可以当成特征2的情况去处理
删除右子树最小节点转换成删除右子树中的rightMin这个节点,这个节点肯定没有左孩子,所以属于上面情况,这里可以递归处理:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if(root->_key < key)
{
return _Erase(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Erase(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
}
else if(root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
}
else
{
//左右节点都存在,替代法删除
Node* rightMin = root->_right;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
root->_key = rightMin->_key;
return _EraseR(root->_right,rightMin->_key);//删除右子树最小节点转换成删除右子树中的rightMin这个节点,这个节点肯定没有左孩子,所以属于上面情况
//如果右子树越大,付出代价就越大,相当于重新查找了一遍
}
return true;
}
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
_EraseR(_root,const K& key);
}
二叉搜索树增删查改操作代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode//二叉搜索树节点
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
//拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
//现代赋值重载
//t1 = t2;
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
std::swap(_root,t._root);
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~BSTree()
{
_Destory(_root);
}
//涉及深浅拷贝,需要实现拷贝构造 operator=等
//二叉树的查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->__left;
}
else if(cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//搜索树的插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当根节点为空时,新创建一个节点即为根节点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//找到要插入的位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;//记录父亲节点,以便找到位置后进行与父亲链接
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明要插入的值有
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
//二叉树的删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur= cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)//删除节点是父亲的啥就把孩子赋给父亲的啥
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
else
{
//左右都不为空,替换法删除
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
//Node* parent = nullptr;//这里不能设置成nullptr,当rightMin走到这里就是要删除节点的右子树中最左节点时,下面的循环进不去,此时parent就是nullptr,后面访问parent会报错
Node* parent = cur;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
parent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//走到了最左
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if(rightMin == parent->left)//不一定肯定rightMin就是parent的左孩子,当Node* parent = nullptr这个代码的注释说明的情况发生时,rightMin就是parent的右孩子
{
parent->_left = rightMin->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = rightMin->_right;
}
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
//中序遍历
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
//销毁二叉搜索树
void _Destory(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destory(root->left);
_Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
二叉搜索树的应用
- K模型
K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树
在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
- KV模型
每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。该种方式在现实生
活中非常常见:比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是<word, count>就构成一种键值对。
比如:实现一个简单的英汉词典dict,可以通过英文找到与其对应的中文,具体实现方式如下:
<单词,中文含义>为键值对构造二叉搜索树,注意:二叉搜索树需要比较,键值对比较时只比较Key查询英文单词时,只需给出英文单词,就可快速找到与其对应的key。
Key搜索场景
1、宿舍楼门禁
宿舍楼里面同学的学号都存储到BSTree stuNumSet;
2、小区车库,扫描台干系统
将小区业主的车牌号录入系统,放到BSTree carNumSet;
Key的搜索场景就是查找一个东西在不在的问题
KV搜索场景(key-value)
1、高铁站,网上买票,刷身份证进站。
12306实名制购票,每张票都关联一个人的身份证号,刷身份证进站,机器读取到的是你的身份证号码,系统要通过身份证号,找到身份证号关联的车票,看有没有当天这趟车次的车票信息,有的话,直接开门禁
2、你在淘宝买了衣服,用电话号码可以查到包裹运输信息
3、简单中英互翻的字典
KV模型我们只需要在Key模型上稍加修改即可,KV模型需要注意的是查找还是按照key去查找:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
namespace KV
{
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
private:
//增删查改的递归写法
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)//注意这里的引用是关键,我们插入时的位置找到时,并不知道链接关系该怎么处理,这里传引用,就解决了这个问题
{
if (root == nullptr)//插入
{
root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;//找不到
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);//右树中去找
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);//左树中去找
}
else
{
return root;//找到了,返回
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
//找到了要删除的节点
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;//先把root保存起来
root = root->_right;
delete del;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;//先把root保存起来
root = root->_left;//将左孩子链接给父亲,这里的root是父亲的_left的别名
delete del;
}
else
{
//递归
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//用临时变量来保存这个替换的值
root->_key = leftMax->_key;
return _Erase(root->_left, leftMax->_key);
}
return true;
}
}
//涉及深浅拷贝,需要实现拷贝构造 operator=等
void _Destory(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destory(root->_left);
_Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key, root->value);
copyNode->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
copyNode->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return copyNode;
}
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree<K, V>& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
//t1 = t2
BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
_Destory(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去
cout << endl;
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);//套一层,因为递归需要将根节点传过去
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
}
简单中英文互翻字典:
//简单中英文互翻字典
void TestBSTree3()
{
KV::BSTree<string,string> dict;
dict.InsertR("tree", "树");
dict.InsertR("left", "左边、剩余");
dict.InsertR("right", "右边");
dict.InsertR("sort", "排序");
//...插入词库中的所有中英文
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
cout << "单词拼写错误,词库中无此单词" << str << endl;
}
else
{
cout << str << "中文翻译:" << ret->_value << endl;
}
}
}

统计一个文本中每个单词出现的次数:
//统计一个文本中每个单词出现的次数
void TestBSTree4()
{
//统计水果出现的次数
string arr[] = { "苹果","西瓜","香蕉","苹果","香蕉","苹果","西瓜" };
KV::BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto& str: arr)
{
//先查找水果在不在搜索树中
//1、不在则插入<水果名,1>
//KV::BSTreeNode<string,int>* ret = countTree.FindR(str);
auto ret = countTree.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)//没有该水果,将该水果插入
{
countTree.InsertR(str, 1);
}
else//找到了,次数+1
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}
 # 二叉搜索树
# 二叉搜索树
文章目录
二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一颗空树,或者具有以下性质:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树

最坏查找高度次就可以确认一个值在不在树中,查找时间复杂度:O(N)(最坏情况:全部是左子树或者全部是右子树):

注意不是O(logN),只有在当树的形状接近完全二叉树或者满二叉树,才能达到logN,在实际中搜索二叉树在极端情况下没办法保证效率,所以我们要对搜索二叉树进一步学习它的特性扩展延伸:AVLTree和红黑树,他们对搜索二叉树,左右高度提出要求,非常接近完全二叉树,他们效率可以达到O(logN),AVLTree 红黑树以及B树系列都是在搜索树基础上演变出来,各有特点,适用于不同的场景
二叉搜索树的操作
二叉搜索树的节点结构
struct BSTreeNode//二叉搜索树节点
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
二叉搜索树的结构
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
private:
Node* _root;
};
二叉搜索树的查找
若根节点不为空:如果根节点key等于查找key,则返回该节点,如果根节点key大于查找key,则在其左子树查找,如果根节点key小于查找key,则在其右子树查找,否则返回NULL

Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->__left;
}
else if(cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return NULL;
}
二叉搜索树的插入

插入的具体过程如下:
a. 树为空,则直接插入
b. 树不为空,按照二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当根节点为空时,新创建一个节点即为根节点
if(_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;//记录父亲节点,以便找到位置后进行与父亲链接
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明要插入的值有
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
//链接
if(parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
二叉搜索树的遍历
中序访问二叉搜索树,打印有序数组
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if(_root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->_left);
cout<<root->_key<<" ";
InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去,外面就不用传_droot
}
int main()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = {5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9};
for(auto e:a)
{
t.insert(e);
}
t.Inorder();
}
二叉搜索树的删除

删除的原则:保持搜索树的结构
删除一个值等于key的节点,分情况分析:
- 要删除的是叶子节点非常好处理,删除自己,父亲指向自己的位置的指针置空

- 要删除的节点是只有一个孩子的节点,删除当前节点,把孩子交给父亲顶替自己位置

- 要删除的是有两个孩子的节点不好处理,解决方案是替换法删除:
去孩子里面找一个值(左子树的最大节点,左子树最右节点就是最大的,或者右子树的最小节点,右子树最左节点就是最小的)能替换自己位置的节点,这两个节点去替换后,都符合特征1或者2,可以直接删除

注意:情况1可以当成特征2的情况去处理
删除之找右子树的最左节点:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur= cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)//删除节点是父亲的啥就把孩子赋给父亲的啥
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
else
{
//左右都不为空,替换法删除
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
//Node* parent = nullptr;//这里不能设置成nullptr,当rightMin走到这里就是要删除节点的右子树中最左节点时,下面的循环进不去,此时parent就是nullptr,后面访问parent会报错
Node* parent = cur;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
parent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//走到了最左
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if(rightMin == parent->left)//不一定肯定rightMin就是parent的左孩子,当Node* parent = nullptr这个代码的注释说明的情况发生时,rightMin就是parent的右孩子
{
parent->_left = rightMin->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = rightMin->_right;
}
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
删除之找左子树的最右节点:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(cur->_key<key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//cur->_key == key
{
//找到了,准备开始删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//情况1:_right = nullptr
//情况2:_right != nullptr
//情况1和情况2合并
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//情况1:_left = nullptr
//情况2:_left != nullptr
//情况1和情况2合并
if(parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//左右都不为nullptr,替换法删除
{
//情况3
//先找到左子树的最大节点(最右边的节点)
Node* leftMax = cur->_left;
Node* maxParent = cur;//这里不能给nullptr,需要给cur,因为下面的循环可能进不去(当此时的leftMax就是最大节点时),此时如果给了nullptr,maxParent就为空,下面就会访问空指针出错
while(leftMax->right)
{
maxParent = leftMax;
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//交换值
cur->_key = leftMax->_key;
//删除
if(maxParent->_left == leftMax)
{
maxParent->_left = leftMax->_left;
}
else
{
maxParent->_right = leftMax->_left;
}
delete leftMax;
//递归
/*Node* leftMax = cur->_left;
while(leftMax->right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//用临时变量来保存这个替换的值
K max = leftMax->_key;
//递归调用
this->Erase(max);//值为max的这个值一定没有右孩子,即递归终止条件
cur->_key = min;*/
}
return true;
}
}
return flase;
}
二叉搜索树插入的递归写法

如果root的key小于要插入节点的key,则递归到右子树去插入,如果root的key大于要插入节点的key,则递归到左子树去插入,如果相等说明已经存在这个key,插入失败,这里参数列表的root设置为引用,就可以解决链接的问题:
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)//引用很巧,相当于root是传过来的别名,注意这里的引用是关键,我们插入时的位置找到时,并不知道链接关系该怎么处理,这里传引用,就解决了这个问题
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else
{
if(root->_key<key)
{
return _Insert(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Insert(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root,key)
}
二叉搜索树查找的递归写法
如果root的key小于要插入节点的key,则递归到右子树去查找,如果root的key大于要插入节点的key,则递归到左子树去查找,如果相等说明找到了:
Node* _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return root;
}
if(root->_key < key)
{
_FindR(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
_FindR(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
//找到了
return root;
}
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root,key);//套一层,因为递归需要将根节点传过去
}
二叉搜索树删除的递归写法
如果root的key小于要删除节点的key,则递归到右子树去删除,如果root的key大于要删除节点的key,则递归到左子树去删除,如果相等说明找到了要删除的节点,进行删除,删除又回到了上面非递归写法讲解的那三种情况:
-
要删除的是叶子节点非常好处理,删除自己,父亲指向自己的位置的指针置空
-
要删除的节点是只有一个孩子的节点,删除当前节点,把孩子交给父亲顶替自己位置
-
要删除的是有两个孩子的节点不好处理,解决方案是替换法删除:
去孩子里面找一个值(左子树的最大节点,左子树最右节点就是最大的,或者右子树的最小节点,右子树最左节点就是最小的)能替换自己位置的节点,这两个节点去替换后,都符合特征1或者2,可以直接删除
注意:情况1可以当成特征2的情况去处理
删除右子树最小节点转换成删除右子树中的rightMin这个节点,这个节点肯定没有左孩子,所以属于上面情况,这里可以递归处理:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if(root->_key < key)
{
return _Erase(root->_right,key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Erase(root->_left,key);
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
}
else if(root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
}
else
{
//左右节点都存在,替代法删除
Node* rightMin = root->_right;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
root->_key = rightMin->_key;
return _EraseR(root->_right,rightMin->_key);//删除右子树最小节点转换成删除右子树中的rightMin这个节点,这个节点肯定没有左孩子,所以属于上面情况
//如果右子树越大,付出代价就越大,相当于重新查找了一遍
}
return true;
}
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
_EraseR(_root,const K& key);
}
二叉搜索树增删查改操作代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode//二叉搜索树节点
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
//拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
//现代赋值重载
//t1 = t2;
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
std::swap(_root,t._root);
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~BSTree()
{
_Destory(_root);
}
//涉及深浅拷贝,需要实现拷贝构造 operator=等
//二叉树的查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->__left;
}
else if(cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//搜索树的插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当根节点为空时,新创建一个节点即为根节点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//找到要插入的位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;//记录父亲节点,以便找到位置后进行与父亲链接
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明要插入的值有
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
//二叉树的删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur= cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,删除
if(cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)//当要删除的节点是根节点时
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)//删除节点是父亲的啥就把孩子赋给父亲的啥
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else if(cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if(cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
else
{
//左右都不为空,替换法删除
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
//Node* parent = nullptr;//这里不能设置成nullptr,当rightMin走到这里就是要删除节点的右子树中最左节点时,下面的循环进不去,此时parent就是nullptr,后面访问parent会报错
Node* parent = cur;
while(rightMin->_left)
{
parent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//走到了最左
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if(rightMin == parent->left)//不一定肯定rightMin就是parent的左孩子,当Node* parent = nullptr这个代码的注释说明的情况发生时,rightMin就是parent的右孩子
{
parent->_left = rightMin->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = rightMin->_right;
}
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
//中序遍历
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
//销毁二叉搜索树
void _Destory(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destory(root->left);
_Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
二叉搜索树的应用
- K模型
K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树
在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
- KV模型
每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。该种方式在现实生
活中非常常见:比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是<word, count>就构成一种键值对。
比如:实现一个简单的英汉词典dict,可以通过英文找到与其对应的中文,具体实现方式如下:
<单词,中文含义>为键值对构造二叉搜索树,注意:二叉搜索树需要比较,键值对比较时只比较Key查询英文单词时,只需给出英文单词,就可快速找到与其对应的key。
Key搜索场景
1、宿舍楼门禁
宿舍楼里面同学的学号都存储到BSTree stuNumSet;
2、小区车库,扫描台干系统
将小区业主的车牌号录入系统,放到BSTree carNumSet;
Key的搜索场景就是查找一个东西在不在的问题
KV搜索场景(key-value)
1、高铁站,网上买票,刷身份证进站。
12306实名制购票,每张票都关联一个人的身份证号,刷身份证进站,机器读取到的是你的身份证号码,系统要通过身份证号,找到身份证号关联的车票,看有没有当天这趟车次的车票信息,有的话,直接开门禁
2、你在淘宝买了衣服,用电话号码可以查到包裹运输信息
3、简单中英互翻的字典
KV模型我们只需要在Key模型上稍加修改即可,KV模型需要注意的是查找还是按照key去查找:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
namespace KV
{
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
private:
//增删查改的递归写法
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)//注意这里的引用是关键,我们插入时的位置找到时,并不知道链接关系该怎么处理,这里传引用,就解决了这个问题
{
if (root == nullptr)//插入
{
root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;//找不到
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);//右树中去找
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);//左树中去找
}
else
{
return root;//找到了,返回
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
//找到了要删除的节点
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;//先把root保存起来
root = root->_right;
delete del;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;//先把root保存起来
root = root->_left;//将左孩子链接给父亲,这里的root是父亲的_left的别名
delete del;
}
else
{
//递归
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}//找到了
//用临时变量来保存这个替换的值
root->_key = leftMax->_key;
return _Erase(root->_left, leftMax->_key);
}
return true;
}
}
//涉及深浅拷贝,需要实现拷贝构造 operator=等
void _Destory(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destory(root->_left);
_Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key, root->value);
copyNode->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
copyNode->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return copyNode;
}
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree<K, V>& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
//t1 = t2
BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
_Destory(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);//套一层的目的是可以将_root私有成员传过去
cout << endl;
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);//套一层,因为递归需要将根节点传过去
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
}
简单中英文互翻字典:
//简单中英文互翻字典
void TestBSTree3()
{
KV::BSTree<string,string> dict;
dict.InsertR("tree", "树");
dict.InsertR("left", "左边、剩余");
dict.InsertR("right", "右边");
dict.InsertR("sort", "排序");
//...插入词库中的所有中英文
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
cout << "单词拼写错误,词库中无此单词" << str << endl;
}
else
{
cout << str << "中文翻译:" << ret->_value << endl;
}
}
}

统计一个文本中每个单词出现的次数:
//统计一个文本中每个单词出现的次数
void TestBSTree4()
{
//统计水果出现的次数
string arr[] = { "苹果","西瓜","香蕉","苹果","香蕉","苹果","西瓜" };
KV::BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto& str: arr)
{
//先查找水果在不在搜索树中
//1、不在则插入<水果名,1>
//KV::BSTreeNode<string,int>* ret = countTree.FindR(str);
auto ret = countTree.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)//没有该水果,将该水果插入
{
countTree.InsertR(str, 1);
}
else//找到了,次数+1
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}
