1 数据结构简介
1.1 什么是数据结构
简单地说,数据结构是以某种特定的布局方式存储数据的容器。这种“布局方式”决定了 数据结构对于某些操作是高效的,而对于其他操作则是低效的。所以我们需要理解各种数据 结构,才能在处理实际问题时选取最合适的数据结构。
数据结构=逻辑结构+物理结构(顺序、链式、索引、散列) 。
逻辑结构:数据元素间抽象化的相互关系 。
物理结构:(存储结构),在计算机存储器中的存储形式。
2 数据结构逻辑分类
数据结构从逻辑上划分为三种基本类型:
2.1 线性结构
数据结构中的元素存在一对一的相互关系;
常见的线性结构:
线性表,栈,队列,串(一维数组)等。
2.2树形结构
数据结构中的元素存在一对多的相互关系;
常见树形结构:
二叉树,红黑树,B 树,哈夫曼树等。
2.3图形结构
数据结构中的元素存在多对多的相互关系;
常见图形结构:
有向图,无向图,简单图等。
3 线性结构
3.1 栈的定义
栈是一种只能从一端存取数据且遵循 “后进先出(LIFO)” 原则的线性存储结构。
3.2 实现栈容器
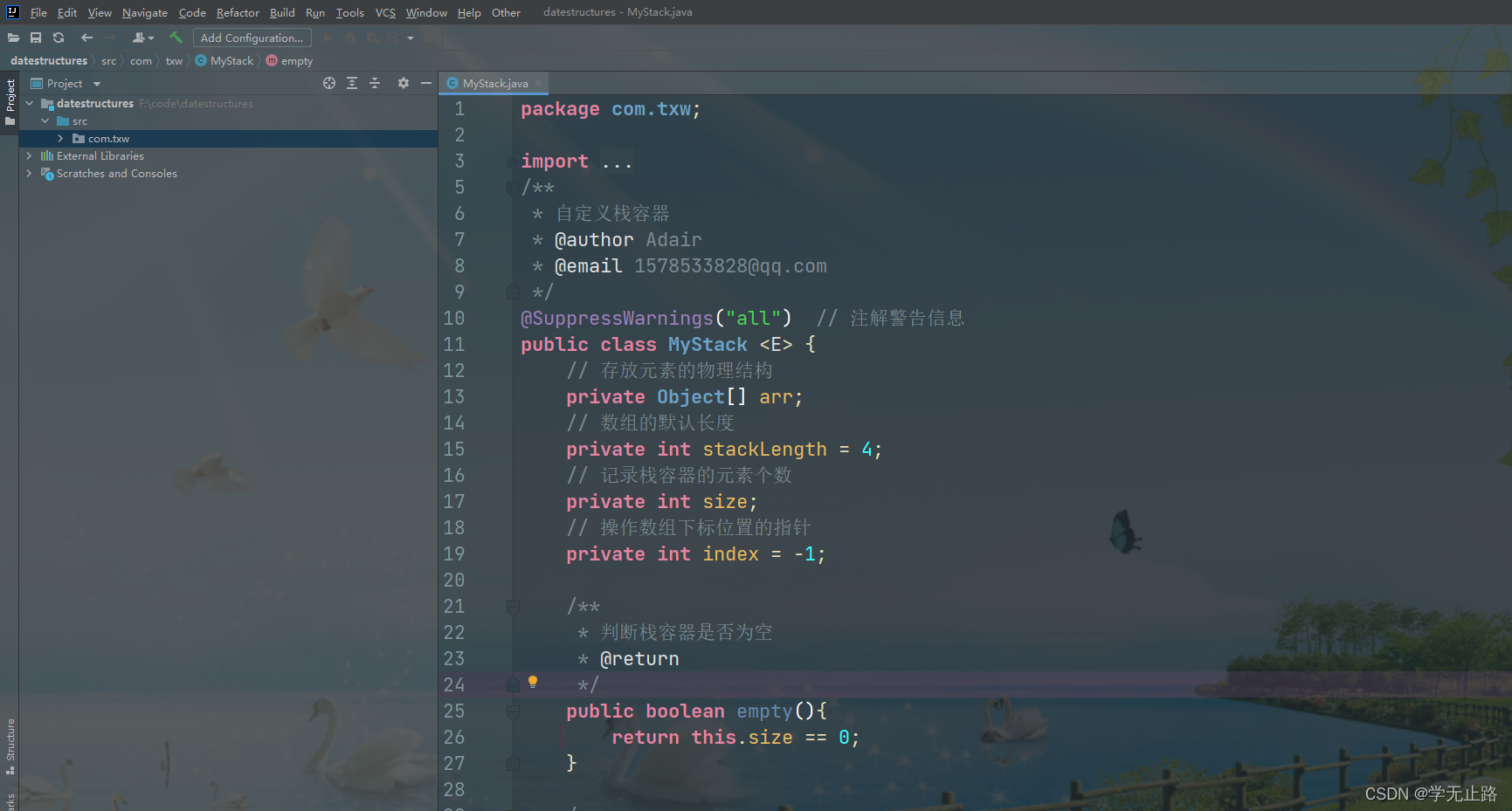
3.2.1 创建栈容器类
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 自定义栈容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyStack <E> {
// 存放元素的物理结构
private Object[] arr;
// 数组的默认长度
private int stackLength = 4;
// 记录栈容器的元素个数
private int size;
// 操作数组下标位置的指针
private int index = -1;
/**
* 判断栈容器是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean empty(){
return false;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public E pop(){
return null;
}
/**
* 向栈容器中添加元素
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E push(E item){
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
如图所示:
3.2.2 实现添加元素
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 向栈容器中添加元素
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E push(E item){
// 初始化数组
this.capacity();
// 向数组中添加元素
this.arr[++ index] = item;
// 记录元素个数
this.size ++;
return item;
}
/**
* 数组初始化或者以1.5倍容量对数组扩容
*/
public void capacity(){
// 数据初始化
if (this.arr == null){
this.arr = new Object [stackLength];
}
// 以1.5倍对数组扩容
if (this.size - (this.stackLength - 1) > 0){
this.stackLength = this.stackLength + (this.stackLength >> 1);
this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr,this.stackLength);
}
}
如图所示:
3.2.2 实现获取元素
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public E pop(){
// 如果栈容器中没有元素则抛出异常
if (this.index == -1){
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
// 记录元素个数
size --;
// 返回栈顶元素
return (E) this.arr[index --];
}
如图所示:
3.2.3 判断栈容器是否为空
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
/**
* 自定义栈容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyStack <E> {
// 存放元素的物理结构
private Object[] arr;
// 数组的默认长度
private int stackLength = 4;
// 记录栈容器的元素个数
private int size;
// 操作数组下标位置的指针
private int index = -1;
/**
* 判断栈容器是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean empty(){
return this.size == 0;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public E pop(){
// 如果栈容器中没有元素则抛出异常
if (this.index == -1){
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
// 记录元素个数
size --;
// 返回栈顶元素
return (E) this.arr[index --];
}
/**
* 向栈容器中添加元素
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E push(E item){
// 初始化数组
this.capacity();
// 向数组中添加元素
this.arr[size ++] = item;
// 记录元素个数
this.size ++;
return item;
}
/**
* 数组初始化或者以1.5倍容量对数组扩容
*/
public void capacity(){
// 数据初始化
if (this.arr == null){
this.arr = new Object [stackLength];
}
// 以1.5倍对数组扩容
if (this.size - (this.stackLength - 1) > 0){
this.stackLength = this.stackLength + (this.stackLength >> 1);
this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr,this.stackLength);
}
}
}
如图所示:
测试的代码如下:
package com.txw;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
/**
* 自定义栈容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyStack <E> {
// 存放元素的物理结构
private Object[] arr;
// 数组的默认长度
private int stackLength = 4;
// 记录栈容器的元素个数
private int size;
// 操作数组下标位置的指针
private int index = -1;
/**
* 判断栈容器是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean empty(){
return this.size == 0;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public E pop(){
// 如果栈容器中没有元素则抛出异常
if(this.index == -1){
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
// 记录元素个数
this.size--;
// 返回栈顶元素
return (E) this.arr[index --];
}
/**
* 向栈容器中添加元素
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E push(E item){
// 初始化数组
this.capacity();
// 向数组中添加元素
this.arr[size ++] = item;
// 记录元素个数
this.size ++;
return item;
}
/**
* 数组初始化或者以1.5倍容量对数组扩容
*/
private void capacity(){
// 数据初始化
if(this.arr == null){
this.arr = new Object[this.stackLength];
}
// 以1.5倍对数组扩容
if(this.size - (this.stackLength-1) >= 0){
this.stackLength = this.stackLength + (this.stackLength >> 1);
this.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr,this.stackLength);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack<String> myStack= new MyStack<>();
myStack.push("a");
myStack.push("b");
myStack.push("c");
myStack.push("d");
myStack.push("e");
myStack.push("f");
System.out.println(myStack.size);
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
}
}
4 链表结构
4.1链表结构的定义
4.1.1 什么是链表
链表结构是由许多节点构成的,每个节点都包含两部分:
1.数据部分:保存该节点的实际数据。
2.地址部分:保存的是上一个或下一个节点的地址。
4.1.2 链表分类
1.单向链表
2.双向链表
3.双向循环链表
4.1.3 链表的特点
1…结点在存储器中的位置是任意的,即逻辑上相邻的数据元素在物理上不一定相邻。
2.访问时只能通过头或者尾指针进入链表,并通过每个结点的指针域向后或向前扫描 其余结点,所以寻找第一个结点和最后一个结点所花费的时间不等。
链表的优缺点:
1.优点:数据元素的个数可以自由扩充 、插入、删除等操作不必移动数据,只需修 改链接指针,修改效率较高。
2.缺点:必须采用顺序存取,即存取数据元素时,只能按链表的顺序进行访问,访问 节点效率较低。
4.2 单向链表结构
4.2.1 单向链表定义
单向链表(单链表)是链表的一种,其特点是链表的链接方向是单向的,对链表的访问 要通过从头部开始顺序读取。
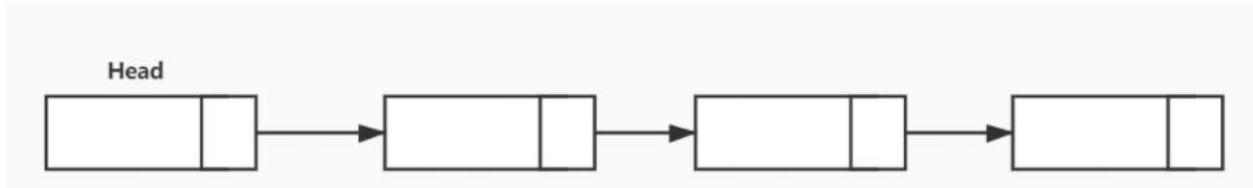
4.2.2 实现单向链表
4.2.2.1 创建链表接口
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于链表结构存取元素的方法API定义
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public interface MyList<E> {
void add(E element);
E get(int index);
int size();
E remove(int index);
}
如图所示: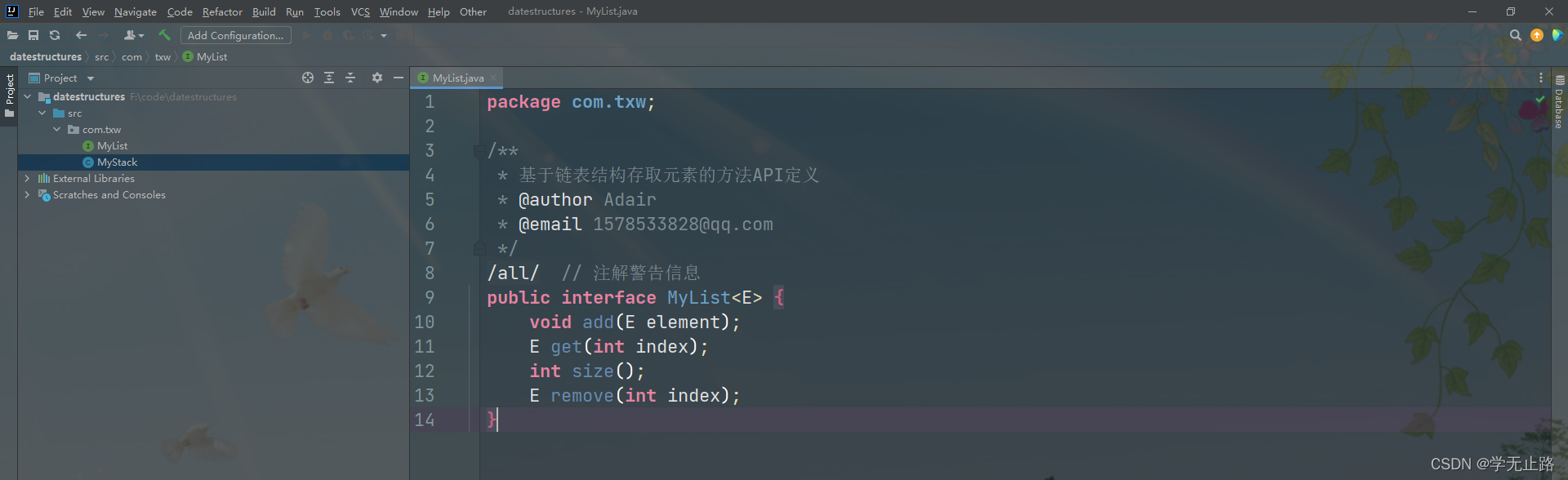
4.2.2.2 创建单向链表类
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于单向链表实现元素存取的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MySinglyLinkedList<E> implements MyList {
/**
* 向链表中添加元素
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(Object element) {
}
/**
* 据元素的位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return null;
}
/**
* 获取元素个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return 0;
}
/**
* 根据元素的位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
return null;
}
}
4.2.2.3 创建节点类
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 定义单向链表中的节点对象
*/
class Node<E>{
// 存储元素
private E item;
// 存储下一个节点对象的地址
private Node next;
Node(E item,Node next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
如图所示: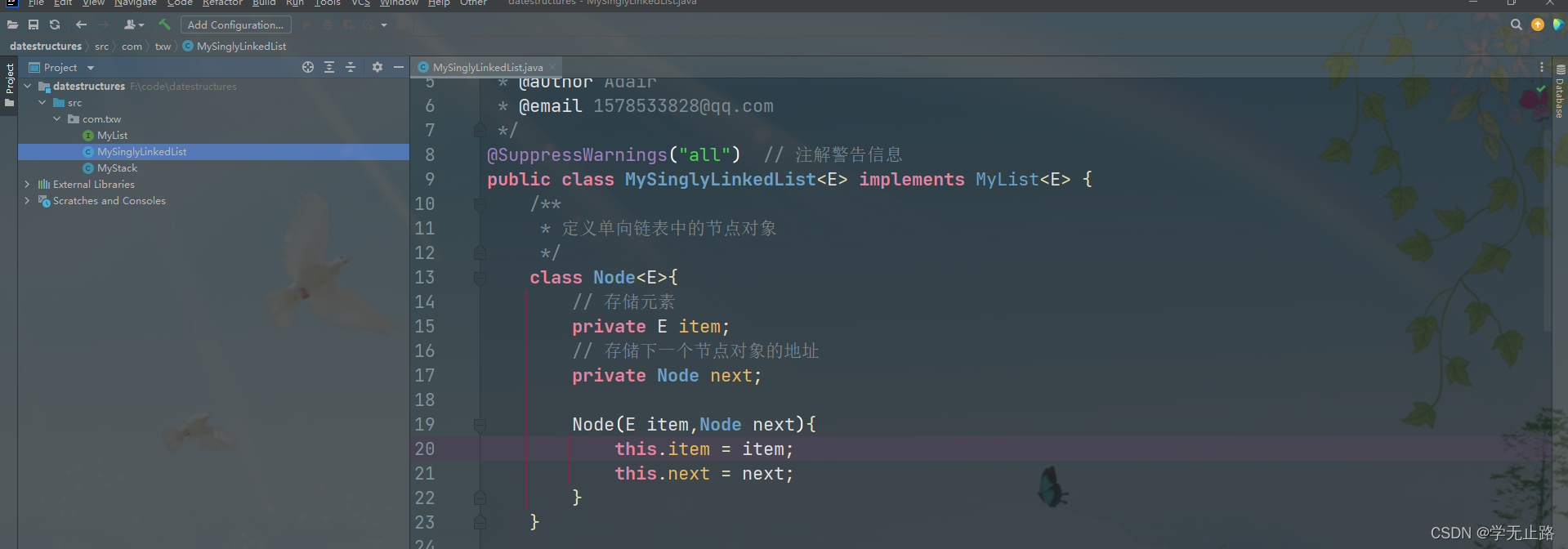
4.2.2.4 实现添加元素方法
演示的代码如下:
// 存放链表中的头节点。
private Node head;
// 记录元素个数。
private int size;
/**
* 向链表中添加元素
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(E element) {
// 创建节点
Node<E> node = new Node<>(element,null);
// 找到尾节点
Node tail = getTail();
// 节点的挂接
if(tail == null)
this.head = node;
else
tail.next = node;
// 记录元素个数
this.size++;
}
/**
* 找尾节点
* @return
*/
private Node getTail() {
// 头节点是否存在
if(this.head == null){
return null;
}
// 查找尾节点
Node node = this.head;
while (true){
if(node.next == null) {
break;
}
// 移动指针,指向下一个节点
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
如图所示: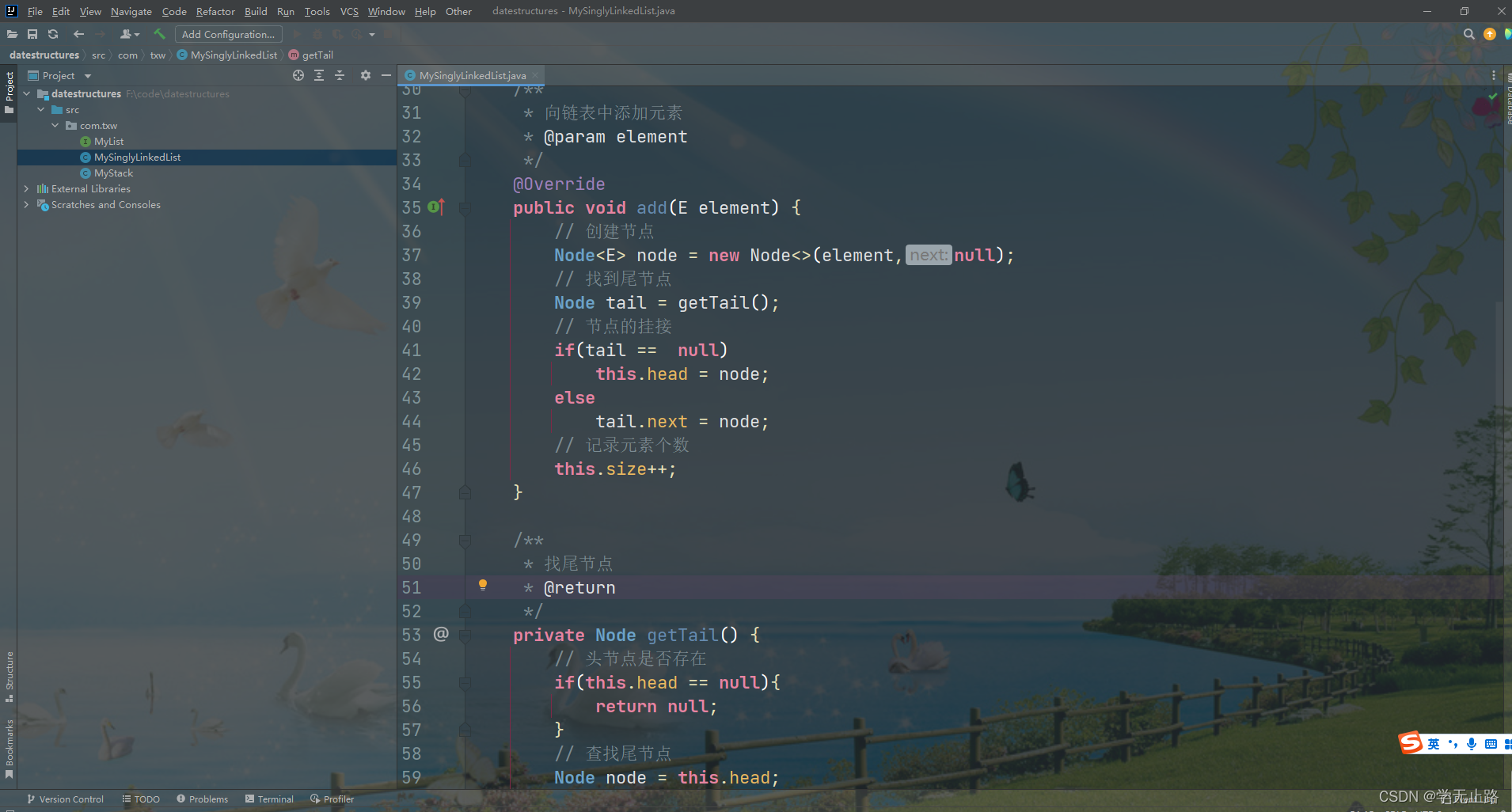
4.2.2.5 实现获取元素方法
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 据元素的位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
// 校验Index的合法性
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置获取指定节点
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 将该节点中的元素返回
return node.item;
}
/**
* 对Index进行校验
* @param index
*/
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(!(index >= 0 && index < this.size)){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + " Size: " + this.size);
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取节点
* @param index
* @return
*/
private Node getNode(int index){
Node<E> node = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
如图所示: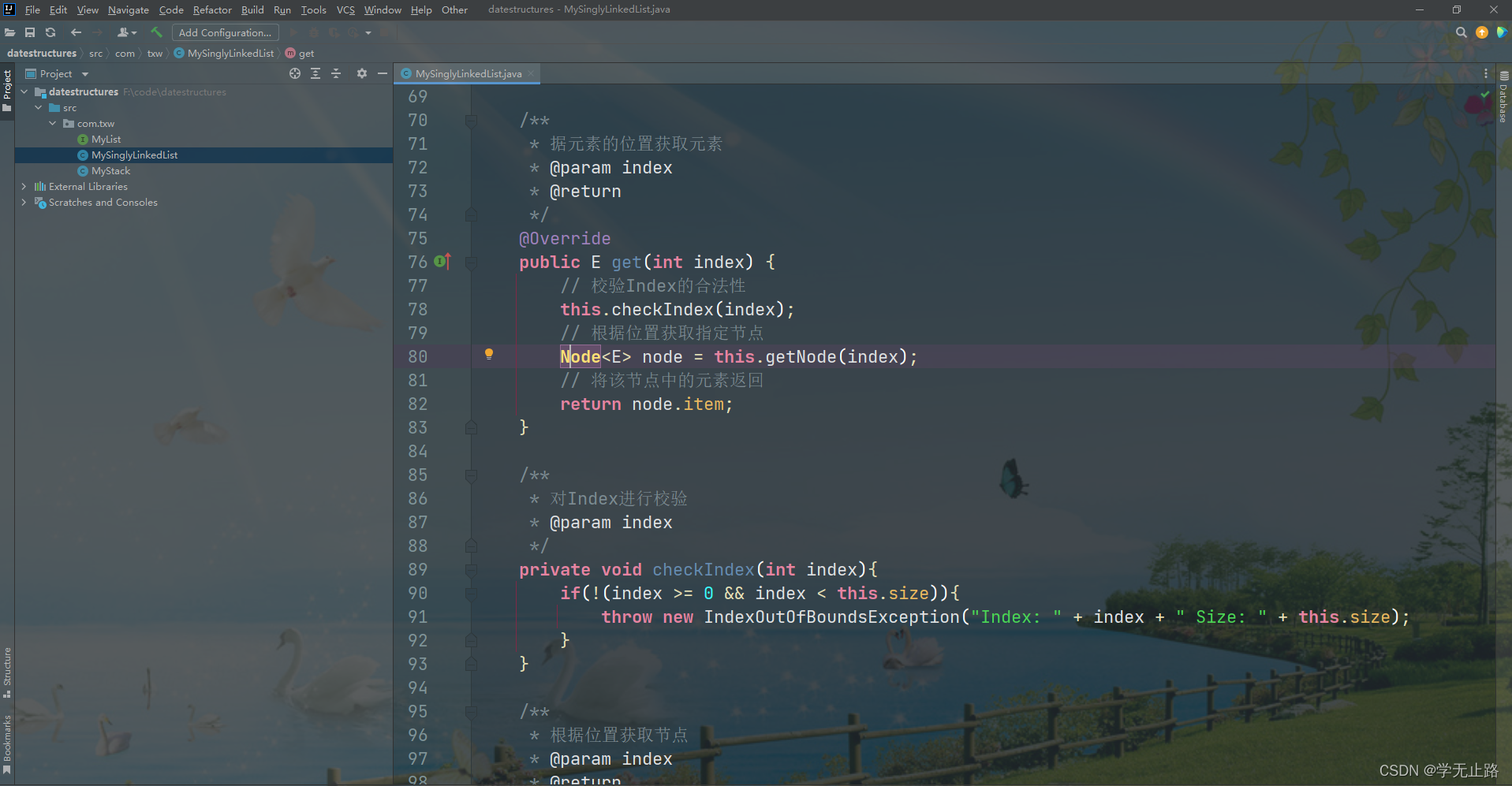
4.2.2.6 实现删除元素方法
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 根据元素的位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
// 校验Index的合法性
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置找到该节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 获取该节点对象中的元素
E item = node.item;
// 将该节点对象从单向链表中移除
// 判断当前删除的节点是否为头结点
if(this.head == node){
this.head = node.next;
}else{
Node<E> temp = this.head;
for(int i=0;i< index - 1;i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node.next;
}
node.next = null;
// 记录元素个数
this.size--;
// 将该元素返回
return item;
}
如图所示: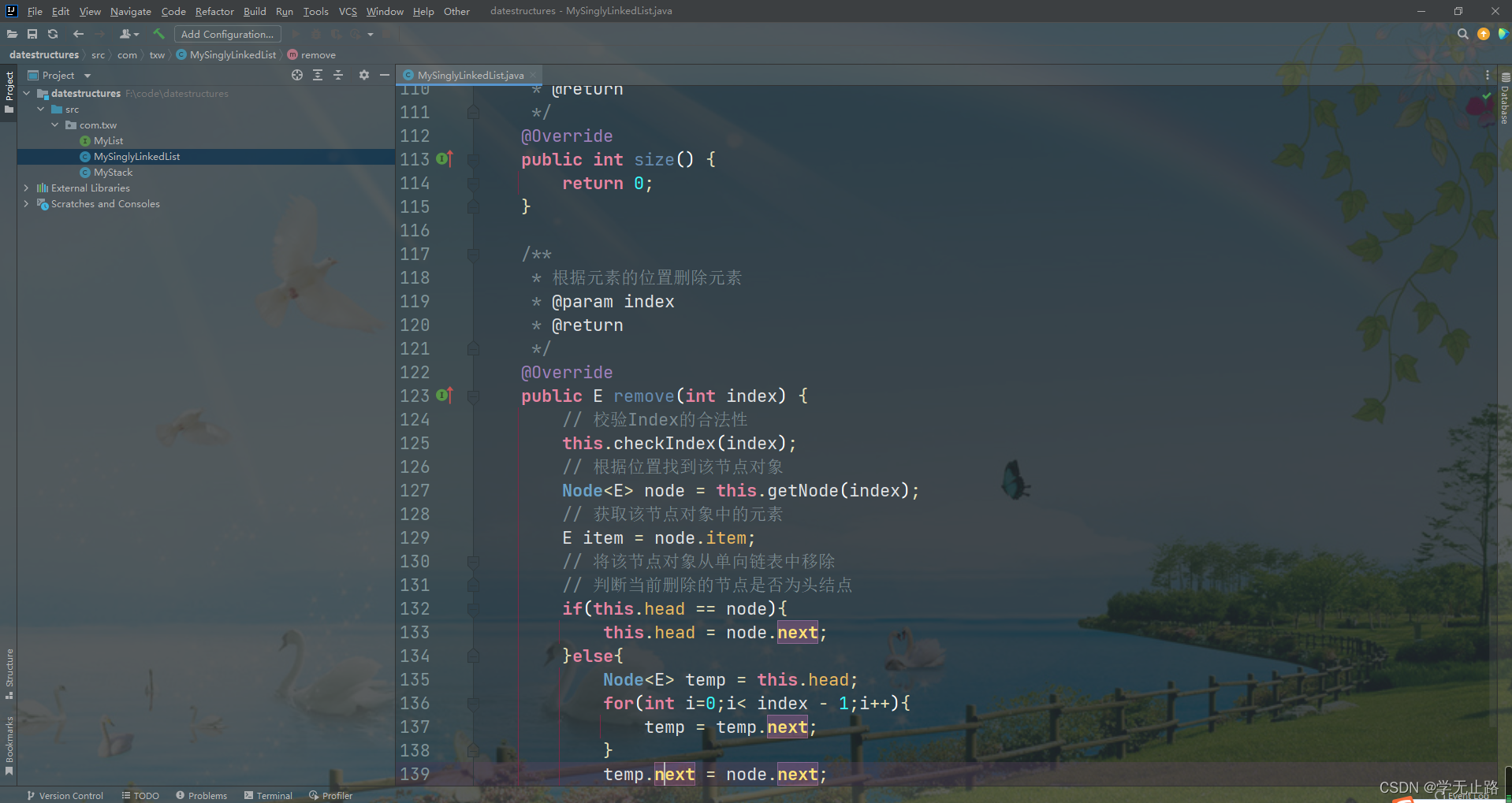
4.2.2.7 实现获取元素个数
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取元素个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
如图所示: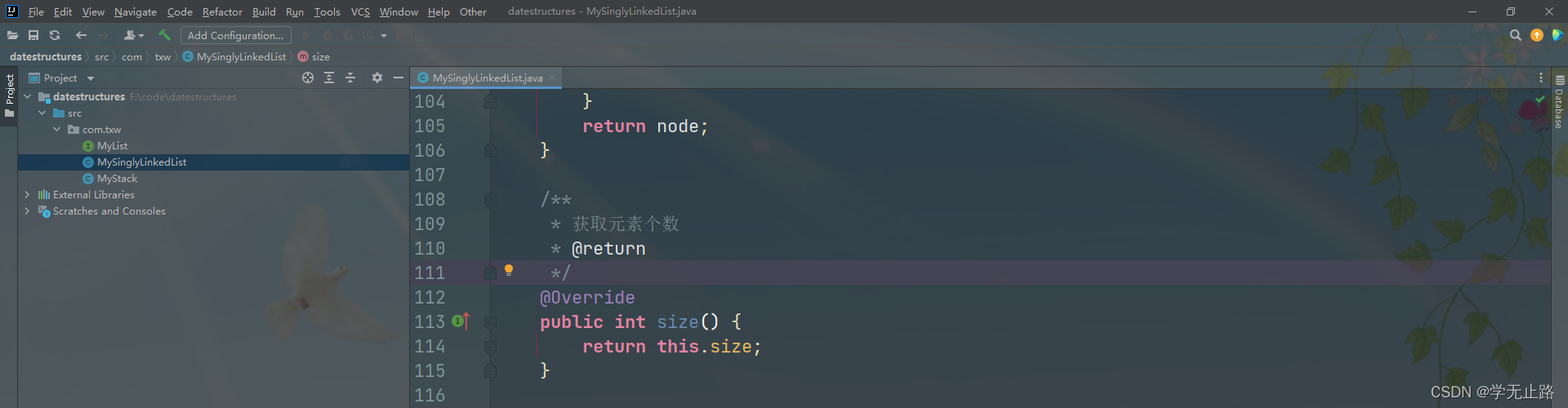
演示测试的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于单向链表实现元素存取的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MySinglyLinkedList<E> implements MyList<E> {
/**
* 定义单向链表中的节点对象
*/
class Node<E>{
// 存储元素
private E item;
// 存储下一个节点对象的地址
private Node next;
Node(E item,Node next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
// 存放链表中的头节点。
private Node head;
// 记录元素个数。
private int size;
/**
* 向链表中添加元素
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(E element) {
// 创建节点
Node<E> node = new Node<>(element,null);
// 找到尾节点
Node tail = getTail();
// 节点的挂接
if(tail == null)
this.head = node;
else
tail.next = node;
// 记录元素个数
this.size++;
}
/**
* 找尾节点
* @return
*/
private Node getTail() {
// 头节点是否存在
if(this.head == null){
return null;
}
// 查找尾节点
Node node = this.head;
while (true){
if(node.next == null) {
break;
}
// 移动指针,指向下一个节点
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 据元素的位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
// 校验Index的合法性
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置获取指定节点
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 将该节点中的元素返回
return node.item;
}
/**
* 对Index进行校验
* @param index
*/
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(!(index >= 0 && index < this.size)){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + " Size: " + this.size);
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取节点
* @param index
* @return
*/
private Node getNode(int index){
Node<E> node = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 获取元素个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
/**
* 根据元素的位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
// 校验Index的合法性
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置找到该节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 获取该节点对象中的元素
E item = node.item;
// 将该节点对象从单向链表中移除
// 判断当前删除的节点是否为头结点
if(this.head == node){
this.head = node.next;
}else{
Node<E> temp = this.head;
for(int i=0;i< index - 1;i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node.next;
}
node.next = null;
// 记录元素个数
this.size--;
// 将该元素返回
return item;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySinglyLinkedList<String> mySinglyLinkedList = new MySinglyLinkedList<>();
mySinglyLinkedList.add("a");
mySinglyLinkedList.add("b");
mySinglyLinkedList.add("c");
mySinglyLinkedList.add("d");
System.out.println(mySinglyLinkedList.size());
System.out.println(mySinglyLinkedList.remove(0));
for(int i=0;i<mySinglyLinkedList.size();i++){
System.out.println(mySinglyLinkedList.get(i));
}
}
}
如图所示: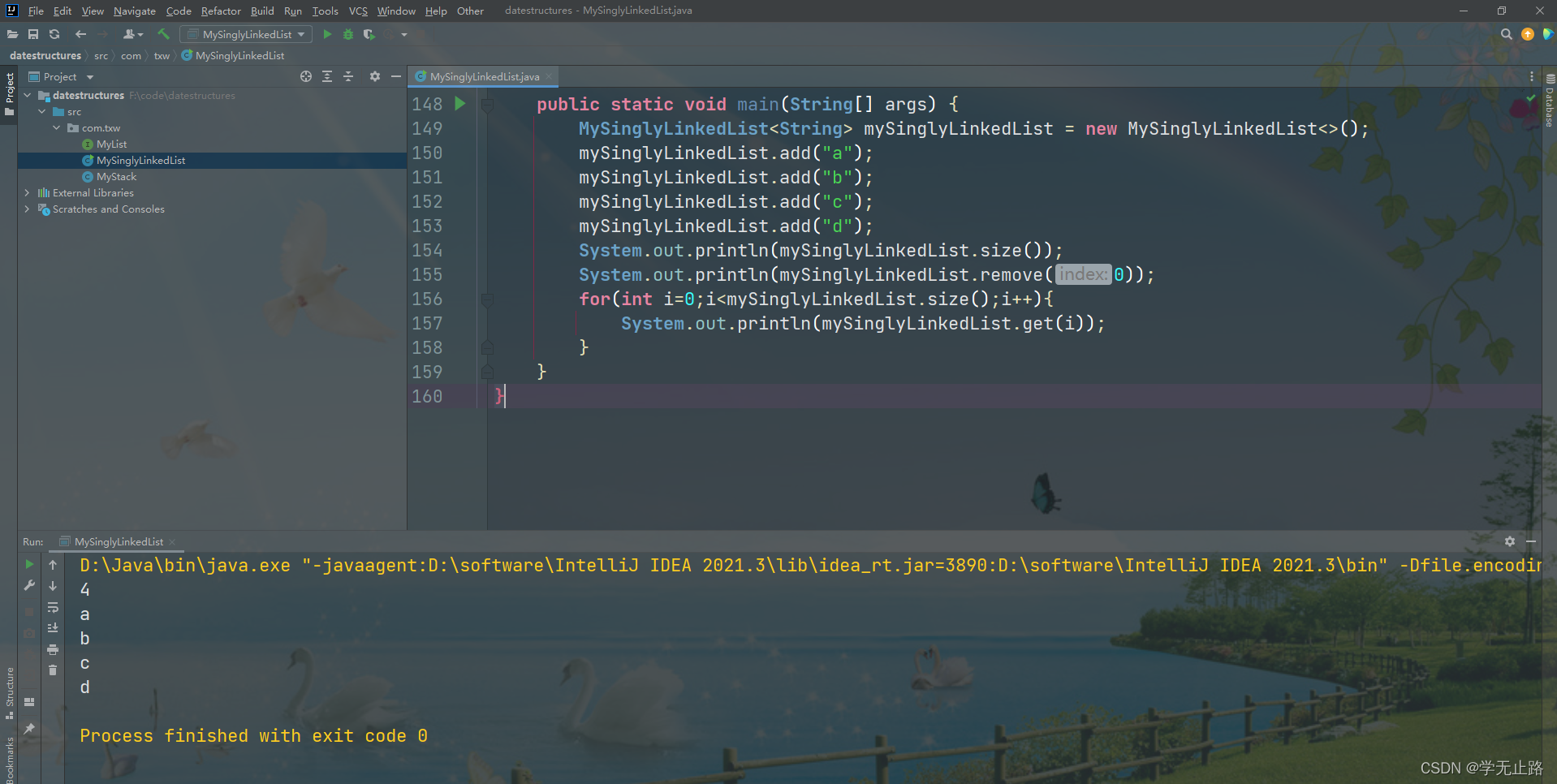
4.3 双向链表结构
4.3.1 双向链表定义
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直 接前驱和直接后继。如图所示: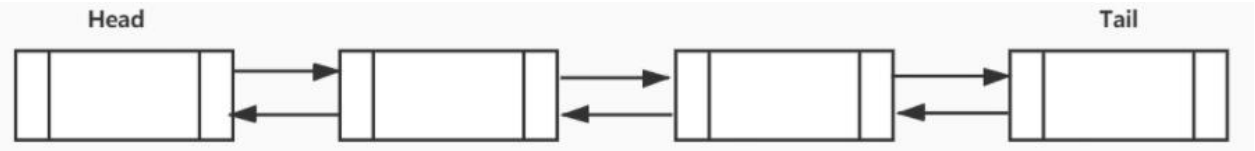
4.3.2 实现双向链表
4.3.2.1 创建双向链表类
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于双向链表实现元素存取的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyDoublyLinkedList<E> implements MyList<E> {
/**
* 向双向链表中添加元素的方法
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(E element) {
}
/**
* 根据指定位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return null;
}
/**
* 返回元素的个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return 0;
}
/**
* 根据指定位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
如图所示: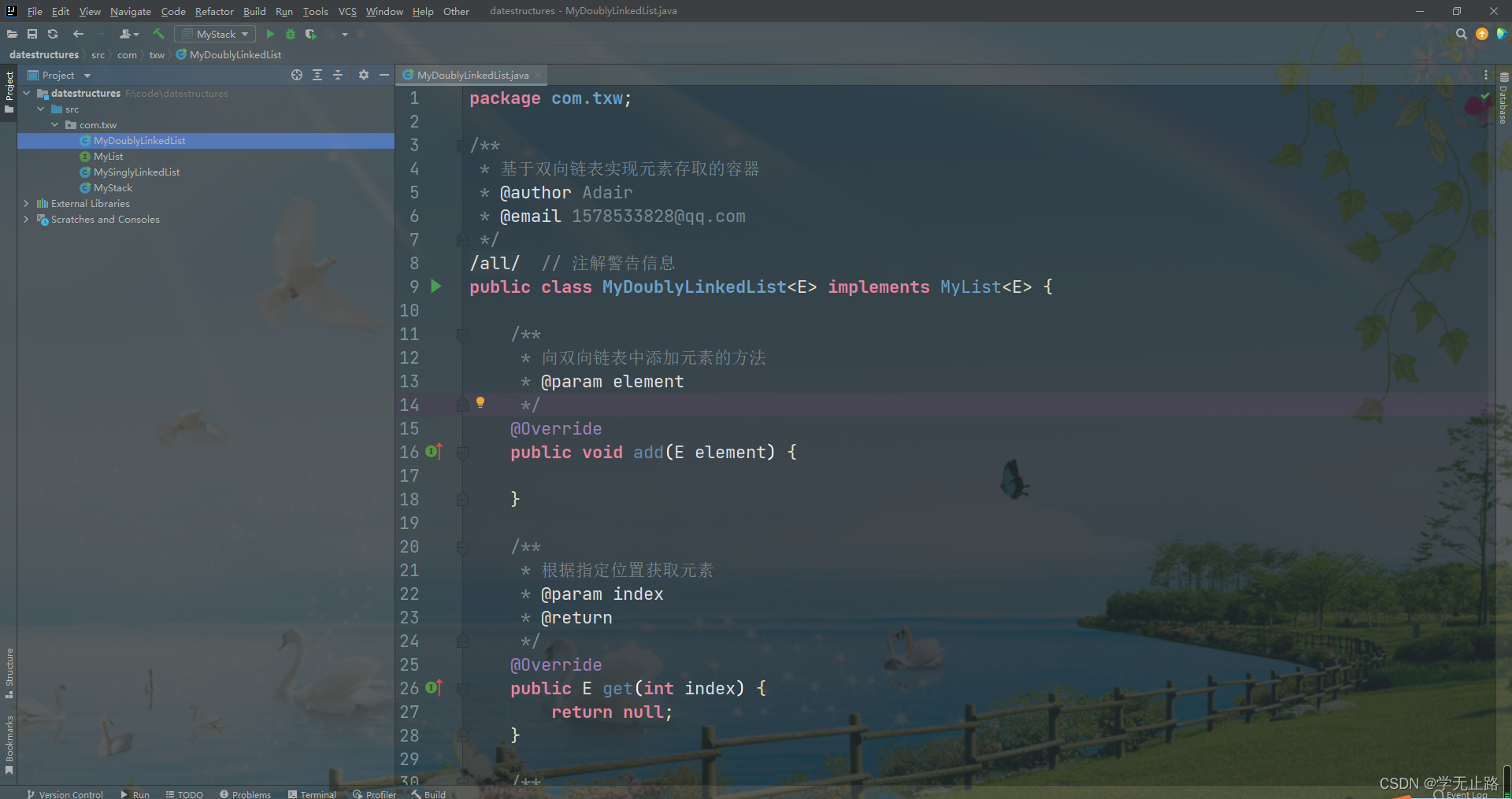
4.3.2.2 创建节点类
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 定义双向链表的节点对象
*/
class Node<E>{
// 记录元素
E item;
// 记录前一个节点对象
Node<E> prev;
// 记录下一个节点对象
Node<E> next;
Node(Node<E> prev,E item,Node<E> next){
this.prev = prev;
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
如图所示: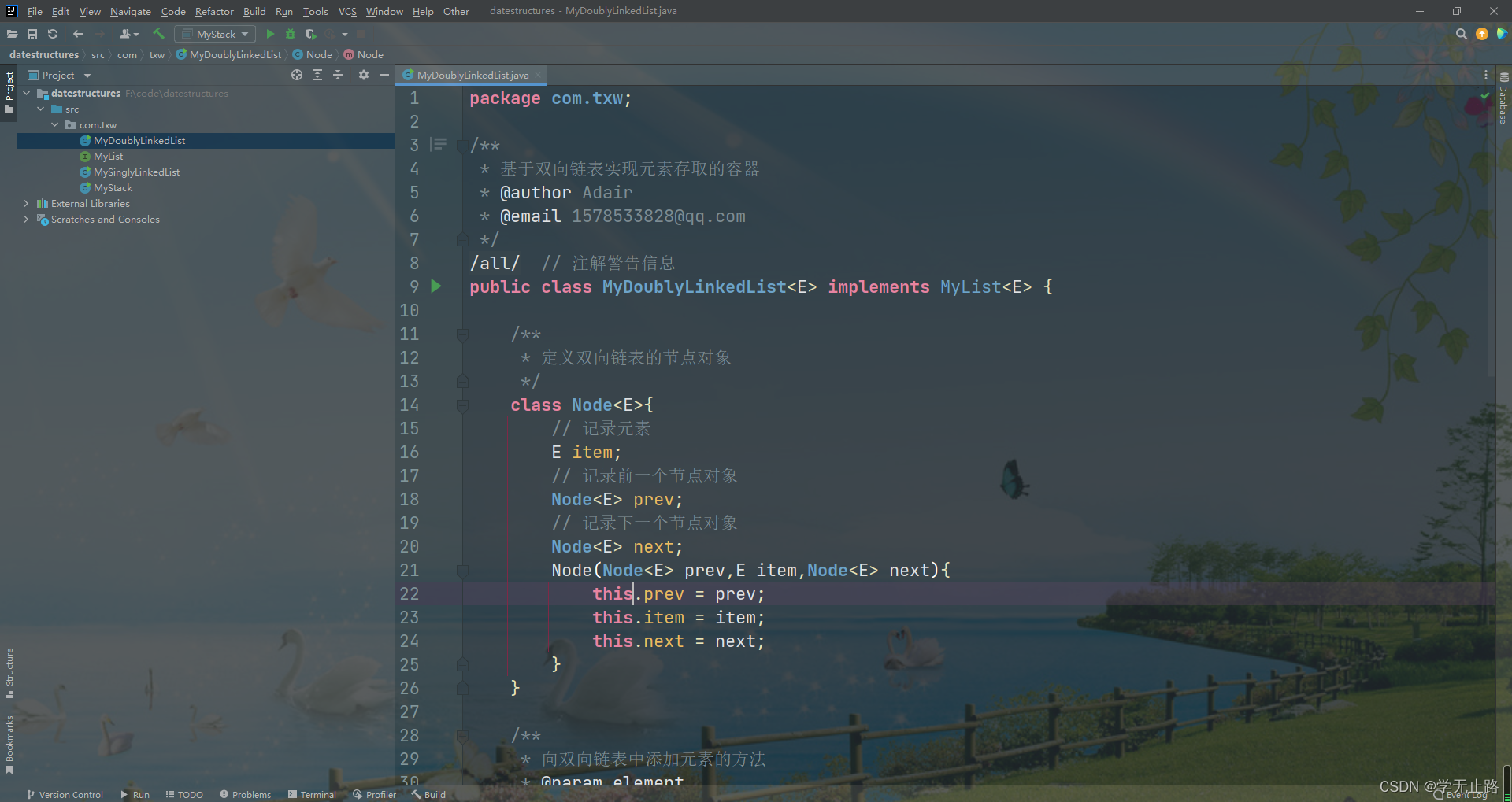
4.3.2.3 实现添加元素方法
演示的代码如下:
// 记录头节点
private Node head;
// 记录尾节点
private Node tail;
// 记录元素个数。
private int size;
/**
* 向双向链表中添加元素的方法
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(E element) {
this.linkLast(element);
}
/**
* 将节点对象添加到双向链表的尾部
*/
private void linkLast(E element){
// 获取尾节点
Node t = this.tail;
// 创建节点对象
Node<E> node = new Node<>(t,element,null);
// 将新节点定义为尾节点
this.tail = node;
if(t == null){
this.head = node;
}else{
t.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}
如图所示:
4.3.2.4 实现获取元素方法
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 根据指定位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
// 对Index做合法性校验
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置查找节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
return node.item;
}
/**
* 校验Index的合法性
*/
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(!(index >= 0 && index < this.size)){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + " Size: " + size);
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取指定节点对象
*/
private Node getNode(int index){
// 判断当前位置距离头或者尾哪个节点更近
if(index < (this.size >> 1)){
Node node = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}else{
Node node = this.tail;
for(int i = this.size - 1;i > index;i --){
node = node.prev;
}
return node;
}
}
如图所示:
4.3.2.5 实现删除元素方法
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 根据指定位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
// 对Index进行合法性校验
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据指定位置获取节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 获取节点对象中的元素
E item = node.item;
// 判断当前节点是否为头节点
if(node.prev ==null){
this.head = node.next;
}else{
// 完成当前节点的直接前驱节点与当前节点的直接后继节点的挂接
node.prev.next = node.next;
}
// 判断当前节点是否为尾节点
if(node.next == null){
this.tail = node.prev;
}else{
// 完成当前节点的直接后继节点与当前节点的直接前驱节点的挂接
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
// 当前节点断掉与它直接前驱节点的连接
node.prev = null;
// 当前节点断掉与它直接后继节点的连接
node.next = null;
node.item = null;
// 记录元素个数
this.size--;
return item;
}
如图所示:
4.3.2.6 获取元素的个数
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 返回元素的个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
如图所示:
4.3.2.7 实现在双向链表的头添加元素
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 在双向链表的头添加元素
* @param element
*/
public void addFirst(E element){
this.linkFirst(element);
}
/**
* 在链表的头添加元素
* @param element
*/
private void linkFirst(E element){
// 获取头节点对象
Node head = this.head;
Node node = new Node(null,element,head);
// 将新节点定义为头节点
this.head = node;
// 判断当前链表中是否有节点如果没有,那么该节点既是头节点也是尾节点
if(head == null){
this.tail = node;
}else{
head.prev = node;
}
// 记录元素个数
this.size++;
}
如图所示:
4.3.2.8 实现在双向链表的尾添加元素
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 在链表的尾添加元素
* @param element
*/
public void addLast(E element){
this.linkLast(element);
}
如图所示:
演示测试的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于双向链表实现元素存取的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyDoublyLinkedList<E> implements MyList<E> {
/**
* 定义双向链表的节点对象
*/
class Node<E>{
// 记录元素
E item;
// 记录前一个节点对象
Node<E> prev;
// 记录下一个节点对象
Node<E> next;
Node(Node<E> prev,E item,Node<E> next){
this.prev = prev;
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
// 记录头节点
private Node head;
// 记录尾节点
private Node tail;
// 记录元素个数。
private int size;
/**
* 向双向链表中添加元素的方法
* @param element
*/
@Override
public void add(E element) {
this.linkLast(element);
}
/**
* 将节点对象添加到双向链表的尾部
*/
private void linkLast(E element){
// 获取尾节点
Node t = this.tail;
// 创建节点对象
Node<E> node = new Node<>(t,element,null);
// 将新节点定义为尾节点
this.tail = node;
if(t == null){
this.head = node;
}else{
t.next = node;
}
this.size ++;
}
/**
* 根据指定位置获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E get(int index) {
// 对Index做合法性校验
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置查找节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
return node.item;
}
/**
* 校验Index的合法性
*/
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(!(index >= 0 && index < this.size)){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + " Size: " + size);
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取指定节点对象
*/
private Node getNode(int index){
// 判断当前位置距离头或者尾哪个节点更近
if(index < (this.size >> 1)){
Node node = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}else{
Node node = this.tail;
for(int i = this.size - 1;i > index;i --){
node = node.prev;
}
return node;
}
}
/**
* 返回元素的个数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
/**
* 根据指定位置删除元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
// 对Index进行合法性校验
this.checkIndex(index);
// 根据指定位置获取节点对象
Node<E> node = this.getNode(index);
// 获取节点对象中的元素
E item = node.item;
// 判断当前节点是否为头节点
if(node.prev ==null){
this.head = node.next;
}else{
// 完成当前节点的直接前驱节点与当前节点的直接后继节点的挂接
node.prev.next = node.next;
}
// 判断当前节点是否为尾节点
if(node.next == null){
this.tail = node.prev;
}else{
// 完成当前节点的直接后继节点与当前节点的直接前驱节点的挂接
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
// 当前节点断掉与它直接前驱节点的连接
node.prev = null;
// 当前节点断掉与它直接后继节点的连接
node.next = null;
node.item = null;
// 记录元素个数
this.size --;
return item;
}
/**
* 在双向链表的头添加元素
* @param element
*/
public void addFirst(E element){
this.linkFirst(element);
}
/**
* 在链表的头添加元素
* @param element
*/
private void linkFirst(E element){
// 获取头节点对象
Node head = this.head;
Node node = new Node(null,element,head);
// 将新节点定义为头节点
this.head = node;
// 判断当前链表中是否有节点如果没有,那么该节点既是头节点也是尾节点
if(head == null){
this.tail = node;
}else{
head.prev = node;
}
// 记录元素个数
this.size ++;
}
/**
* 在链表的尾添加元素
* @param element
*/
public void addLast(E element){
this.linkLast(element);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*MyList<String> myList = new MyDoublyLinkedList<>();
myList.add("a");
myList.add("b");
myList.add("c");
myList.add("d");
System.out.println(myList.remove(2));
System.out.println(myList.size());
for(int i=0;i<myList.size();i++){
System.out.println(myList.get(i));
}*/
MyDoublyLinkedList<String> list = new MyDoublyLinkedList<>();
list.add("a");
list.addFirst("A");
list.addLast("B");
list.addFirst("C");
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
如图所示:
5 树形结构
5.1 树形结构简介
树结构是一种非线性存储结构,存储的是具有“一对多”关系的数据元素的集合。如图所示: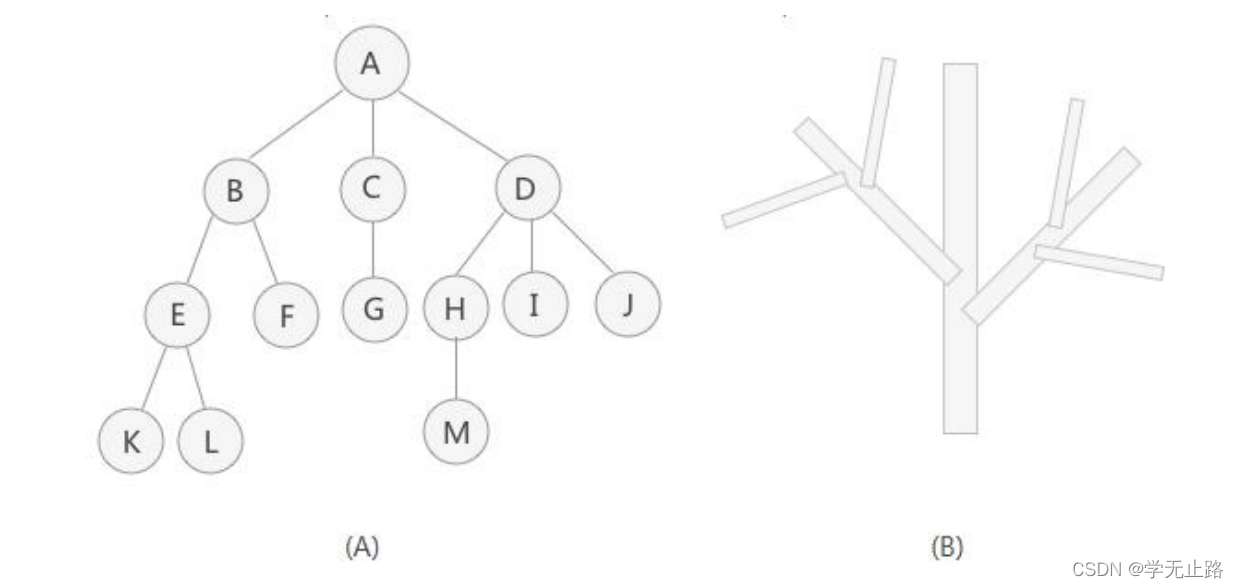
5.2 树的相关术语
5.2.1 结点(Node)
使用树结构存储的每一个数据元素都被称为“结点”。
5.2.2 结点的度(Degree of Node)
某个结点所拥有的子树的个数。
5.2.3 树的深度(Degree of Tree)
树中结点的最大层次数。
5.2.4 4叶子结点(Leaf Node)
度为 0 的结点,也叫终端结点。
5.2.5 5分支结点(Branch Node)
度不为 0 的结点,也叫非终端结点或内部结点。
5.2.6 孩子(Child)
也可称之为子树或者子结点,表示当前结点下层的直接结点。
5.2.7 双亲(Parent)
也可称之为父结点,表示当前结点的直接上层结点。
5.2.8 根节点(Root Node)
没有双亲结点的结点。在一个树形结构中只有一个根节点。
5.2.9 祖先(Ancestor)
从当前结点上层的所有结点。
5.2.10 子孙(Descendant)
当前结点下层的所有结点。
2.11 兄弟(Brother)
同一双亲的孩子。
5.3 二叉树简介
二叉树(Binary Tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构 往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其 算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。二叉树特点是每个结点最多只能有两棵子树, 且有左右之分。
5.3.1 二叉树分类
5.3.1.1 满二叉树
满二叉树指除最后一层外,每一层上的所有节点都有两个子节点。如图所示: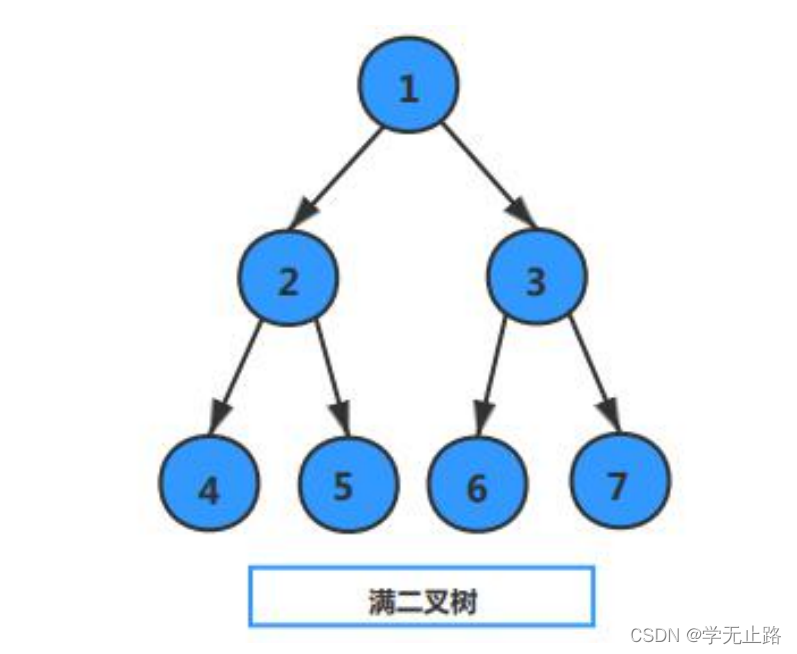
5.3.1.2 完全二叉树
完全二叉树,除最后一层可能不满以外,其他各层都达到该层节点的最大数,最后一层 如果不满,该层所有节点都全部靠左排。如图所示: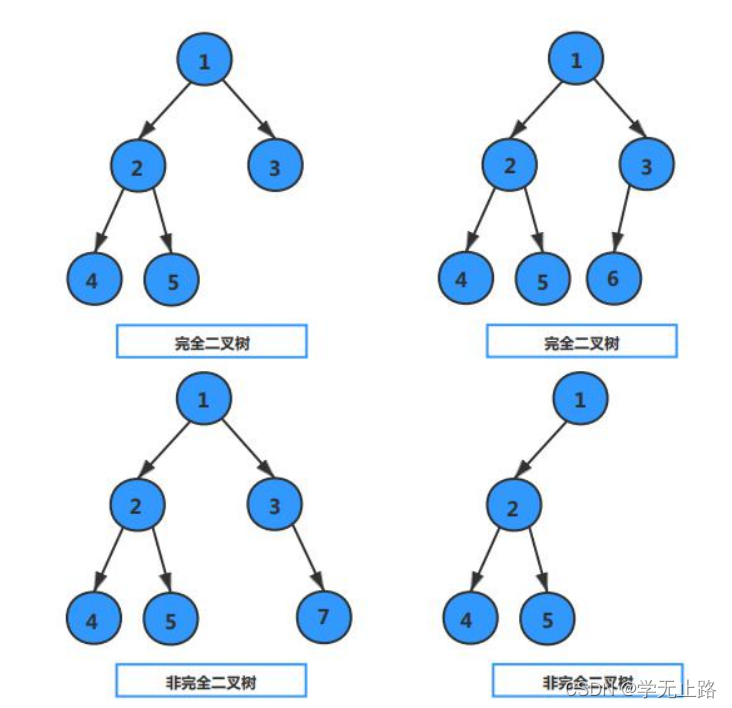
5.3.2 二叉树遍历
二叉树遍历的方式:
1.前序遍历:根-左-右
2.中序遍历:左-根-右
3.后序遍历:左-右-根
4.层序遍历:从上至下逐层遍历
5.3.2.1 前序遍历
前序遍历顺序:根-左-右,如图所示: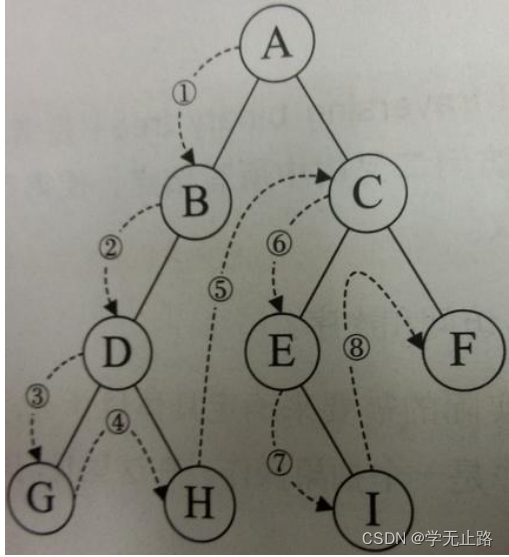
5.3.2.2 中序遍历
中序遍历顺序:左-根-右,如图所示: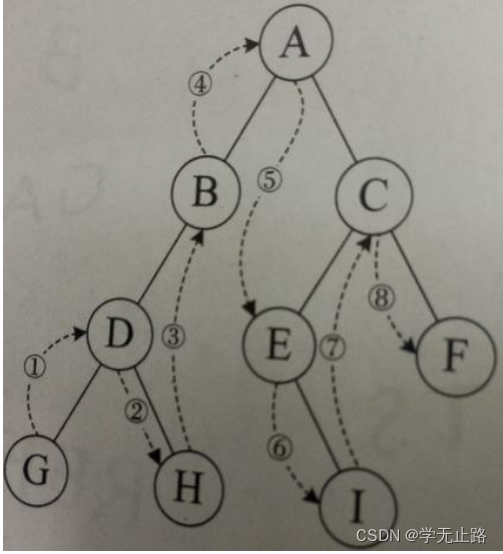
5.3.2.3 后序遍历
后序遍历顺序:左-右-根,如图所示: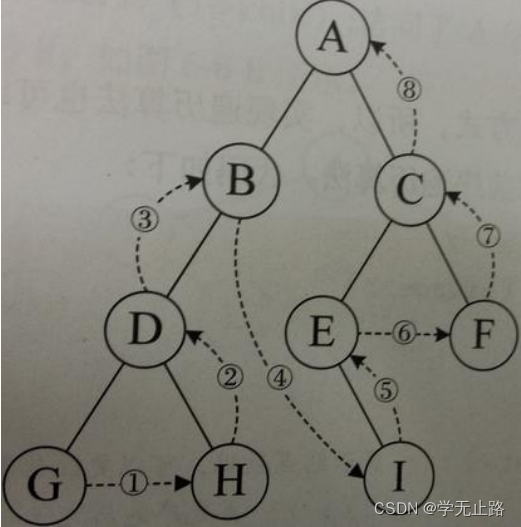
5.3.2.4 层序遍历
层序遍历顺序:
从根节点出发,依次访问左右孩子结点,再从左右孩子出发,依次它们的孩子结点,直 到节点访问完毕。如图所示: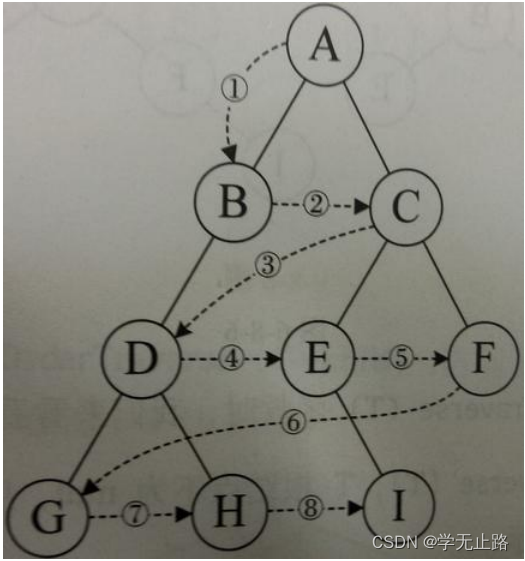
5.3.3 二叉树排序
5.3.3.1 二叉树排序分析
利用二叉树结构以及遍历方式可以实现基于二叉树的元素排序处理。如图所示: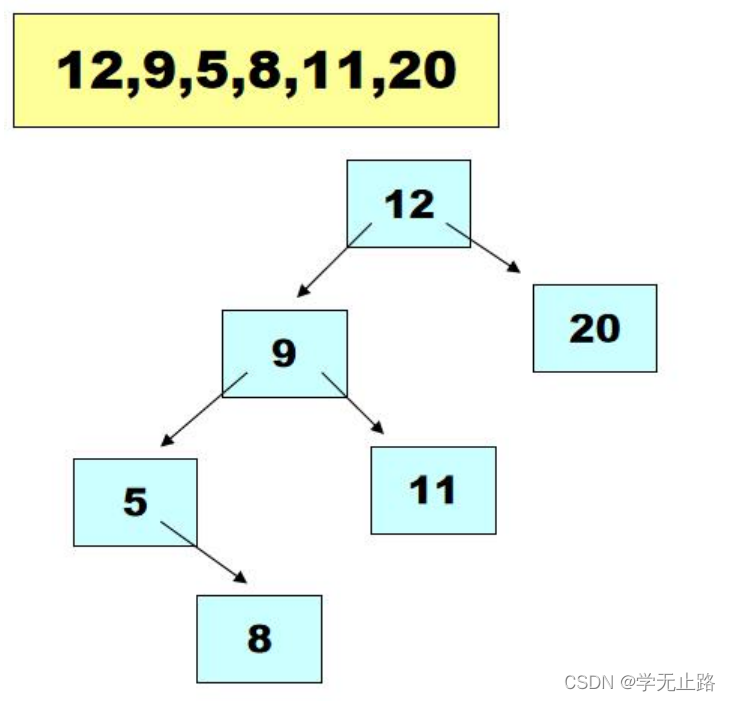
5.3.3.2 二叉树排序实现
5.3.3.2.1 创建二叉树排序器类
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于二叉树结构实现元素排序处理的排序器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class BinaryTreeSort<E extends Integer>{
/**
* 将元素添加到排序器中
* @param element
*/
public void add(E element){
}
/**
* 对元素进行排序
*/
public void sort(){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
如图所示:
5.3.3.2.2 创建结点类
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 定义结点类
*/
class Node<E extends Integer>{
// 存放元素
private E item;
// 存放左子树地址
private Node left;
// 存放右子树地址
private Node right;
Node(E item){
this.item = item;
}
/**
* 添加结点
*/
public void addNode(Node node){
// 完成新结点中的元素与当前结点中的元素的判断.
// 如果新结点中的元素小于当前结点中的元素,那么新结点则放到当前结点的左子树中。
if(node.item.intValue() < this.item.intValue()){
if(this.left == null)
this.left = node;
else
this.left.addNode(node);
}else{
// 如果新结点中的元素大于当前结点中的元素,那么新结点则放到当前结点的右子树中。
if(this.right == null)
this.right = node;
else
this.right.addNode(node);
}
}
/**
* 使用中序遍历二叉树
*/
public void inorderTraversal(){
// 找到最左侧的那个结点
if(this.left != null)this.left.inorderTraversal();
System.out.println(this.item);
if(this.right != null)this.right.inorderTraversal();
}
}
如图所示:
5.3.3.2.3 实现向排序器中添加元素方法
演示的代码如下:
// 存放树的根节点的地址
private Node root;
/**
* 将元素添加到排序器中
* @param element
*/
public void add(E element){
// 实例化结点对象
Node<E> node = new Node<>(element);
// 判断当前二叉树中是否有根结点。如果没有那么新结点则为根结点
if(this.root == null)
this.root = node;
else
this.root.addNode(node);
}
如图所示:
5.3.3.2.4 实现排序器中排序方法
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 对元素进行排序
*/
public void sort(){
// 判断根结点是否为空
if(this.root == null)return ;
this.root.inorderTraversal();
}
如图所示:
演示测试的代码如下:
package com.txw;
/**
* 基于二叉树结构实现元素排序处理的排序器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class BinaryTreeSort<E extends Integer>{
/**
* 定义结点类
*/
class Node<E extends Integer>{
// 存放元素
private E item;
// 存放左子树地址
private Node left;
// 存放右子树地址
private Node right;
Node(E item){
this.item = item;
}
/**
* 添加结点
*/
public void addNode(Node node){
// 完成新结点中的元素与当前结点中的元素的判断.
// 如果新结点中的元素小于当前结点中的元素,那么新结点则放到当前结点的左子树中。
if(node.item.intValue() < this.item.intValue()){
if(this.left == null)
this.left = node;
else
this.left.addNode(node);
}else{
// 如果新结点中的元素大于当前结点中的元素,那么新结点则放到当前结点的右子树中。
if(this.right == null)
this.right = node;
else
this.right.addNode(node);
}
}
/**
* 使用中序遍历二叉树
*/
public void inorderTraversal(){
// 找到最左侧的那个结点
if(this.left != null)this.left.inorderTraversal();
System.out.println(this.item);
if(this.right != null)this.right.inorderTraversal();
}
}
// 存放树的根节点的地址
private Node root;
/**
* 将元素添加到排序器中
* @param element
*/
public void add(E element){
// 实例化结点对象
Node<E> node = new Node<>(element);
// 判断当前二叉树中是否有根结点。如果没有那么新结点则为根结点
if(this.root == null)
this.root = node;
else
this.root.addNode(node);
}
/**
* 对元素进行排序
*/
public void sort(){
// 判断根结点是否为空
if(this.root == null)return ;
this.root.inorderTraversal();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreeSort<Integer> sort = new BinaryTreeSort<>();
// 1,8,6,3,5,2
sort.add(1);
sort.add(8);
sort.add(6);
sort.add(3);
sort.add(5);
sort.add(2);
sort.sort();
}
}
如图所示: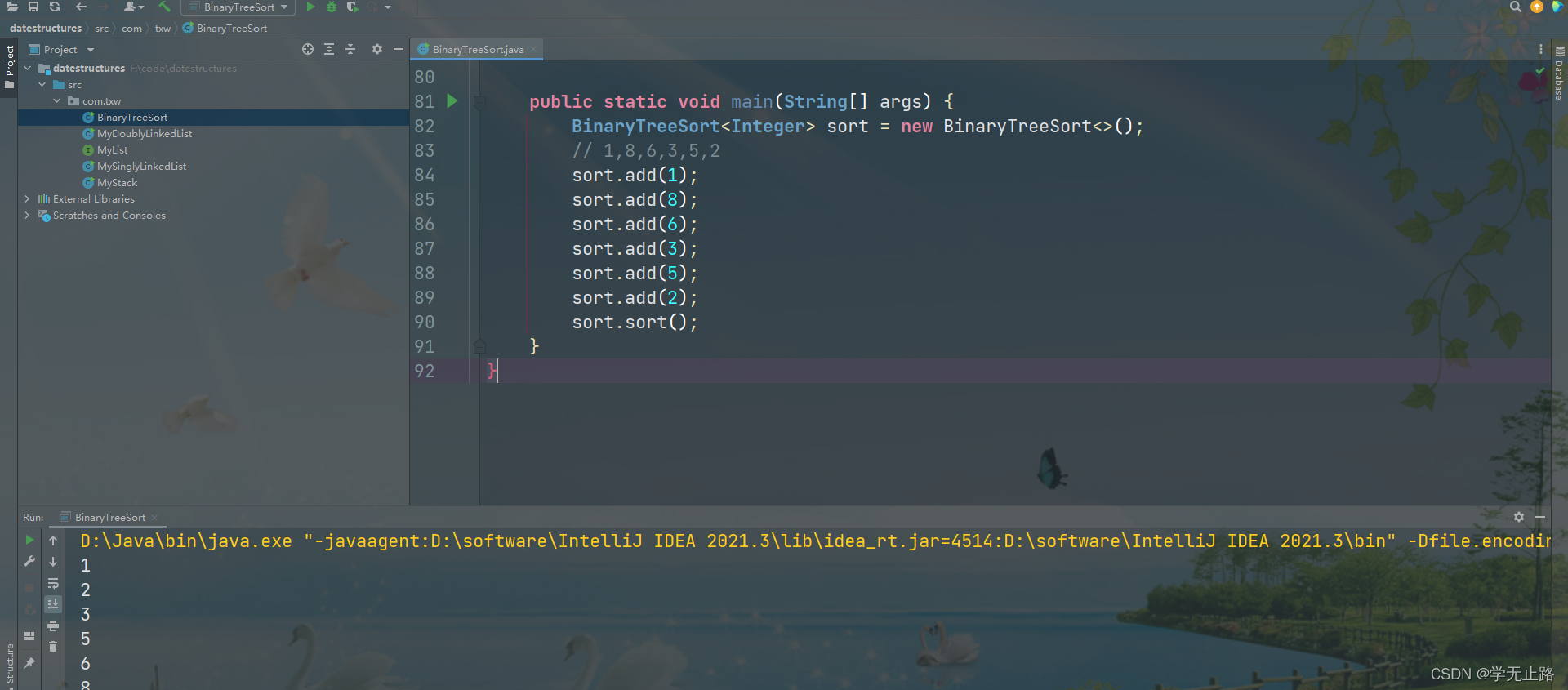
6 自定义树形结构容器
6.1 树形结构定义
能够找到当前结点的父结点
能够找到当前结点的子结点
能够找到当前结点的兄弟结点
能够找到当前结点的祖先结点
能够找到当前结点的子孙节点
6.2 自定义树形结构分析
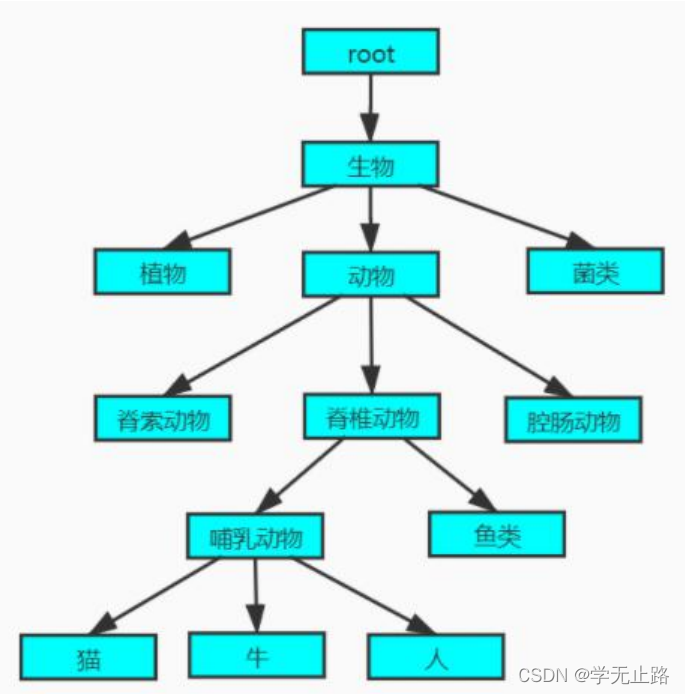
6.3 实现自定义树形结构容器
6.3.1 创建树形结构容器类
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 基于树形结构实现元素存储的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyTree<E>{
/**
* 向容器中添加元素
* @param parent
* @param item
*/
public void add(E parent,E item){
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的父结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E getParent(E item){
return null;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的子结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getChild(E item){
return null;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的兄弟结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getBrother(E item){
return null;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的祖先结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getForefathers(E item){
return null;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的子孙结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getGrandChildren(E item){
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
如图所示:
6.3.2 实现添加元素方法
演示的代码如下:
// String--->String
private Map<E,E> map = new HashMap<>();
// String ---->List
private Map<E,List<E>> map2 = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 向容器中添加元素
* @param parent
* @param item
*/
public void add(E parent,E item){
// 完成在单结点之间映射
this.map.put(item,parent);
// 完成多结点之间映射
List<E> list = this.map2.get(parent);
// 判断当前结点下是否含有子结点,如果没有则创建一个新的List
if(list == null){
list = new ArrayList<>();
this.map2.put(parent,list);
}
list.add(item);
}
如图所示:
6.3.3 获取当前结点的父结点与子结点
6.3.3.1 获取父结点
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取当前结点的父结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E getParent(E item){
return this.map.get(item);
}
如图所示:
6.3.3.2 获取子结点
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取当前结点的子结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getChild(E item){
return this.map2.get(item);
}
如图所示:
6.3.4 获取当前结点的兄弟结点
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取当前结点的兄弟结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getBrother(E item){
// 获取当前结点的父结点
E parent = this.getParent(item);
// 获取当前父结点的所有的子结点
List<E> list = this.getChild(parent);
List<E> brother = new ArrayList<>();
if(list != null){
brother.addAll(list);
brother.remove(item);
}
return brother;
}
如图所示:
6.3.5 获取当前结点的祖先结点
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取当前结点的祖先结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getForefathers(E item){
// 获取当前结点的父结点
E parent = this.getParent(item);
// 结束递归的边界条件
if(parent == null){
return new ArrayList<>();
}
// 递归调用,再次获取当前结点父结点的父结点
List<E> list = this.getForefathers(parent);
// 将递归到的所有结点元素添加到返回的List中
list.add(parent);
return list;
}
如图所示:
6.3.6 获取当前结点的子孙节点
演示的代码如下:
/**
* 获取当前结点的子孙结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getGrandChildren(E item){
// 存放所有子孙结点中的元素
List<E> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取当前结点的子结点
List<E> child = this.getChild(item);
// 结束递归的边界条件
if (child == null){
return list;
}
// 遍历子结点
for(int i=0;i<child.size();i++){
// 获取节点中的元素
E ele = child.get(i);
List<E> temp = this.getGrandChildren(ele);
list.add(ele);
list.addAll(temp);
}
return list;
}
如图所示:
6.3.7 测试自定义容器
演示的代码如下:
package com.txw;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 基于树形结构实现元素存储的容器
* @author Adair
* @email 1578533828@qq.com
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all") // 注解警告信息
public class MyTree<E>{
// String--->String
private Map<E,E> map = new HashMap<>();
// String ---->List
private Map<E,List<E>> map2 = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 向容器中添加元素
* @param parent
* @param item
*/
public void add(E parent,E item){
// 完成在单结点之间映射
this.map.put(item,parent);
// 完成多结点之间映射
List<E> list = this.map2.get(parent);
// 判断当前结点下是否含有子结点,如果没有则创建一个新的List
if(list == null){
list = new ArrayList<>();
this.map2.put(parent,list);
}
list.add(item);
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的父结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public E getParent(E item){
return this.map.get(item);
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的子结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getChild(E item){
return this.map2.get(item);
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的兄弟结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getBrother(E item){
// 获取当前结点的父结点
E parent = this.getParent(item);
// 获取当前父结点的所有的子结点
List<E> list = this.getChild(parent);
List<E> brother = new ArrayList<>();
if(list != null){
brother.addAll(list);
brother.remove(item);
}
return brother;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的祖先结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getForefathers(E item){
// 获取当前结点的父结点
E parent = this.getParent(item);
// 结束递归的边界条件
if(parent == null){
return new ArrayList<>();
}
// 递归调用,再次获取当前结点父结点的父结点
List<E> list = this.getForefathers(parent);
// 将递归到的所有结点元素添加到返回的List中
list.add(parent);
return list;
}
/**
* 获取当前结点的子孙结点
* @param item
* @return
*/
public List<E> getGrandChildren(E item){
// 存放所有子孙结点中的元素
List<E> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取当前结点的子结点
List<E> child = this.getChild(item);
// 结束递归的边界条件
if (child == null){
return list;
}
// 遍历子结点
for(int i=0;i<child.size();i++){
// 获取节点中的元素
E ele = child.get(i);
List<E> temp = this.getGrandChildren(ele);
list.add(ele);
list.addAll(temp);
}
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化容器
MyTree<String> myTree = new MyTree<>();
// 添加元素
myTree.add("root","生物");
myTree.add("生物","植物");
myTree.add("生物","动物");
myTree.add("生物","菌类");
myTree.add("动物","脊椎动物");
myTree.add("动物","脊索动物");
myTree.add("动物","腔肠动物");
myTree.add("脊椎动物","哺乳动物");
myTree.add("脊椎动物","鱼类");
myTree.add("哺乳动物","猫");
myTree.add("哺乳动物","牛");
myTree.add("哺乳动物","人");
System.out.println("---------获取父结点---------");
String parent = myTree.getParent("鱼类");
System.out.println(parent);
System.out.println("---------获取子结点---------");
List<String> child= myTree.getChild("动物");
for(int i=0;i<child.size();i++){
System.out.println(child.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---------获取兄弟结点---------");
List<String> brother = myTree.getBrother("脊椎动物");
for(int i=0;i<brother.size();i++){
System.out.println(brother.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---------获取祖先结点---------");
List<String> foreFathers = myTree.getForefathers("人");
for(int i=0;i<foreFathers.size();i++){
System.out.println(foreFathers.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---------获取子孙结点---------");
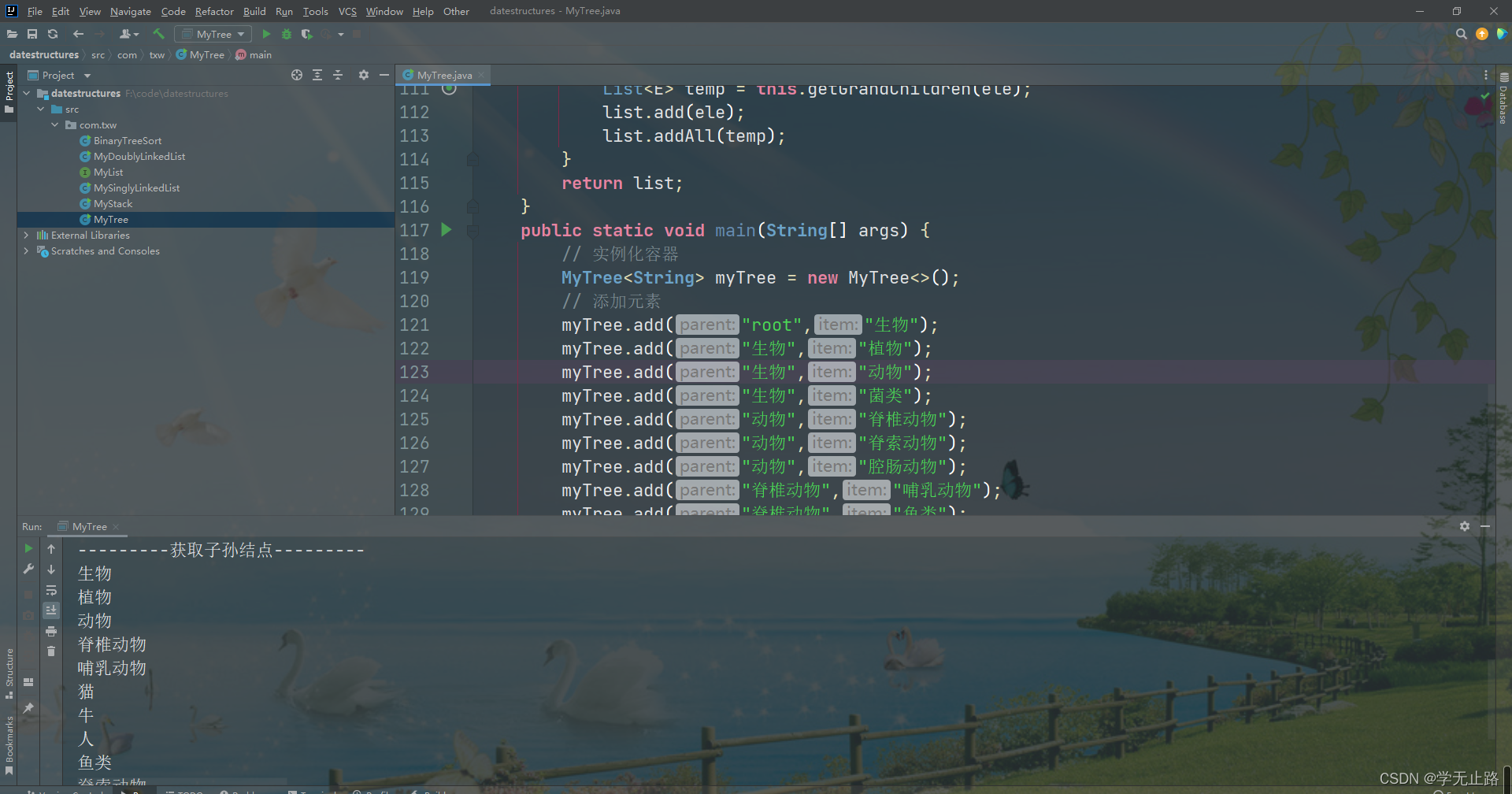
List<String> grandChildren = myTree.getGrandChildren("root");
for(int i =0;i<grandChildren.size();i++){
System.out.println(grandChildren.get(i));
}
}
}
如图所示: