0.前言🐑
🌵🌵
大家好啊,2天不见,甚是想念,呜呜网课要结束了,今天就要开始线下上课了,ε=(′ο`*)))唉,美好生活不复返了。话不多说,今天开始回顾链表中的无头单向非循环链表。

🌵🌵

本节重点:
- 链表&顺序表对比
- 单链表各个接口的实现
1.链表 🐱
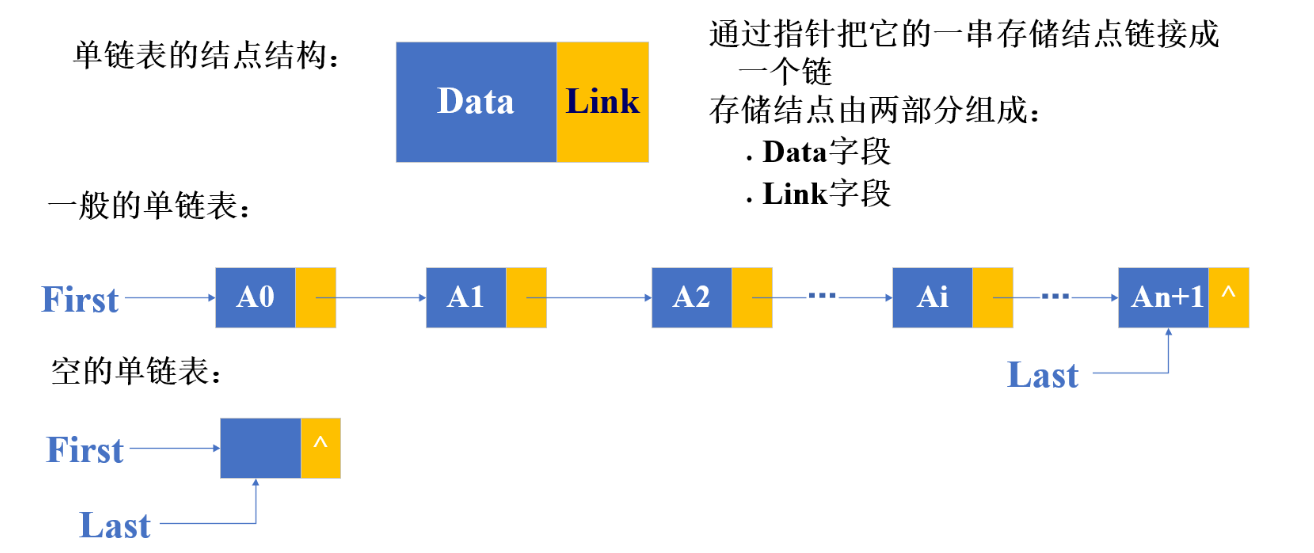
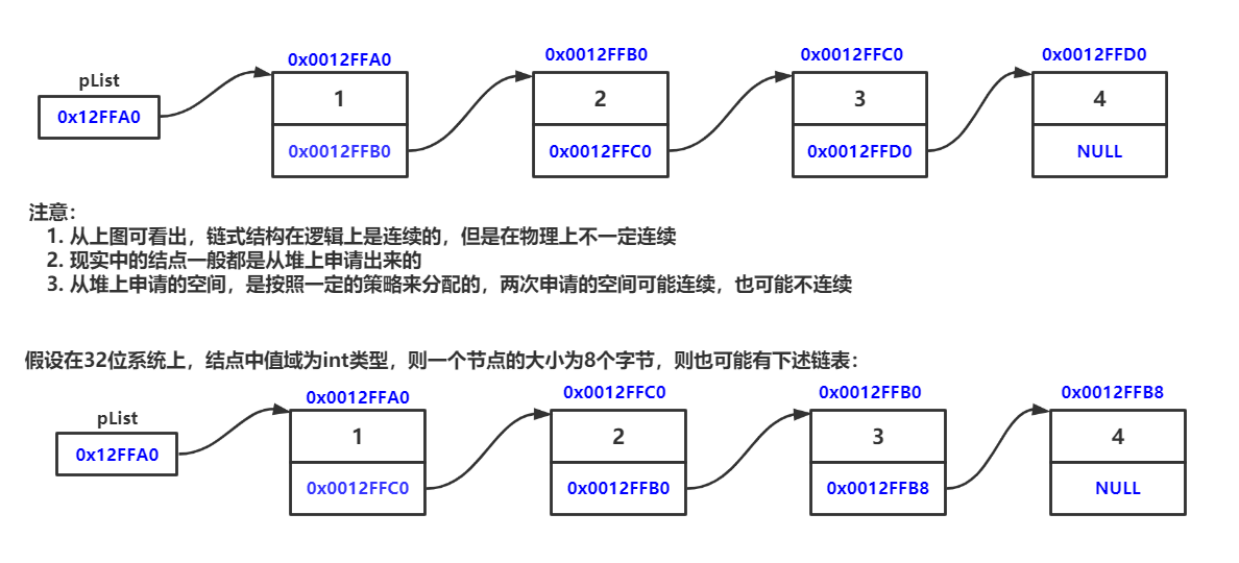
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
关于顺序表的不足:
- 扩容有性能消耗且有可能存在空间浪费。
扩容时,如果扩小了,大量插入数据时,频繁扩容,性能消耗较大;如果扩大了,又会存在空间浪费。
例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。- 头部或中间插入数据时,需要挪动数据,降低效率
链表优点
- 按需申请内存,不存在空间浪费
- 任意位置O(1)时间插入删除数据
链表缺点
- 不支持下标的随机访问
总结:顺序表和链表相辅相成,使用要看具体应用场景
2.单链表🐶
struct SListNode
{
int data;
struct SListNode* next;
};
void Test()
{
struct SListNode* node1 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
struct SListNode* node2 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
struct SListNode* node3 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
struct SListNode* node4 = (struct SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SListNode));
printf("%p\n", node1);
printf("%p\n", node2);
printf("%p\n", node3);
printf("%p\n", node4);
}
//node1 等其实只是结点地址
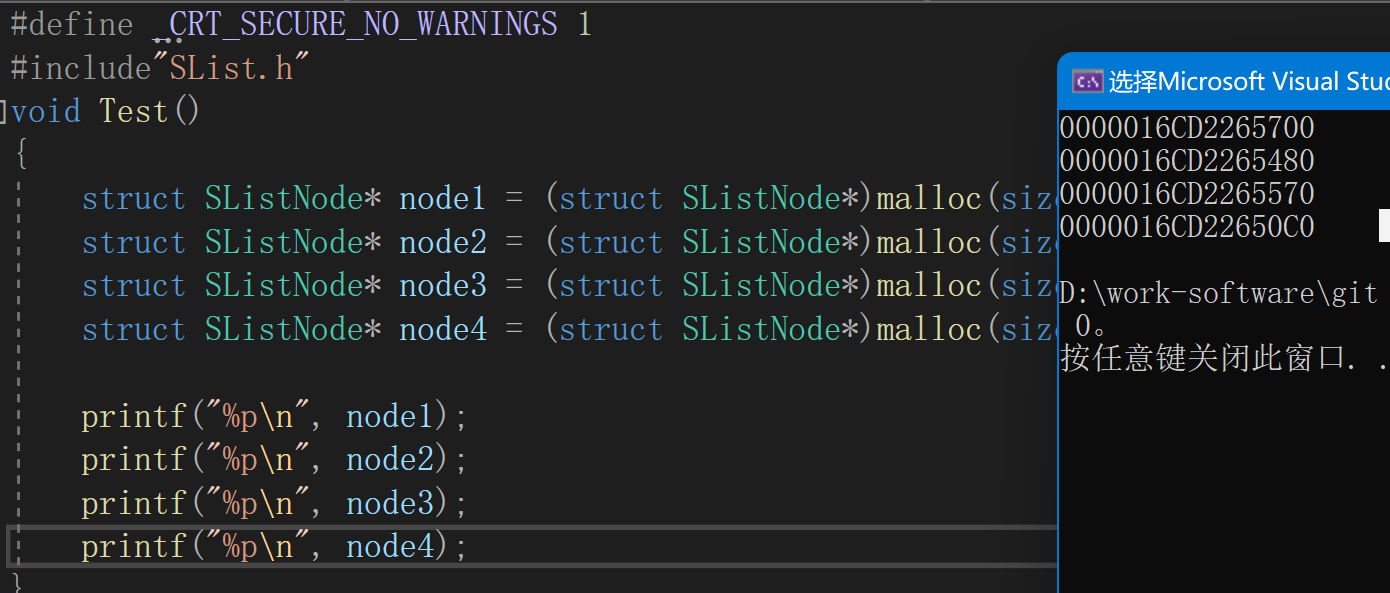
地址均不连续,堆上使用的空间地址由高到低
逻辑结构&物理结构
链表逻辑结构线性,但物理结构是非线性的。
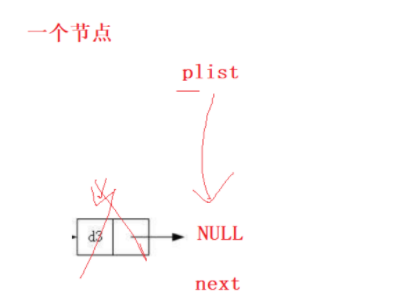
pList(头结点)是指针变量,存的是第一个节点的地址
当我们看到链表的实现都有箭头指向下一个节点,但实际上是没有箭头的,只不过是把下一个节点的地址存到了当前节点的next的值
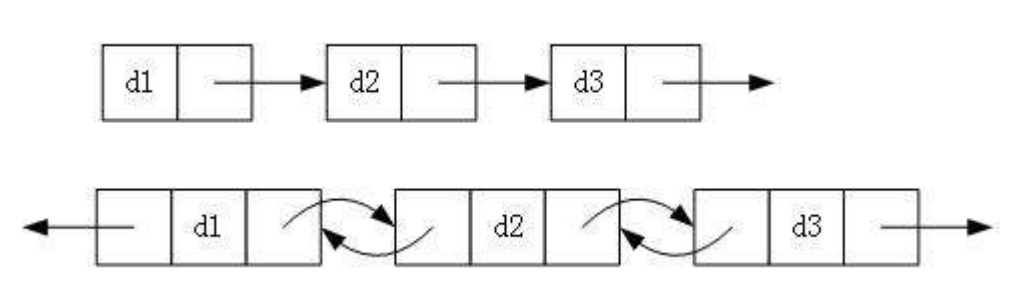
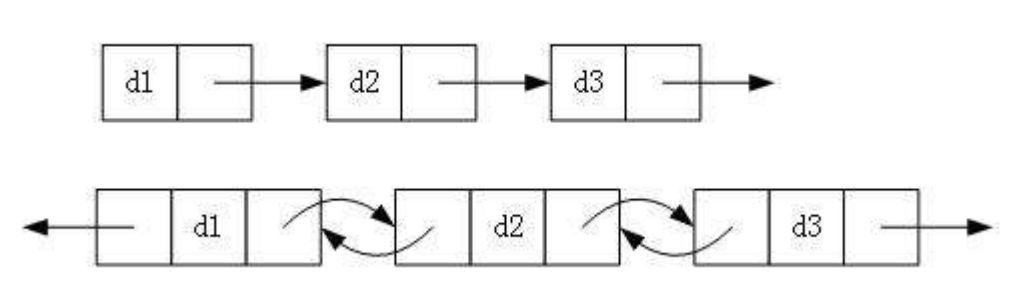
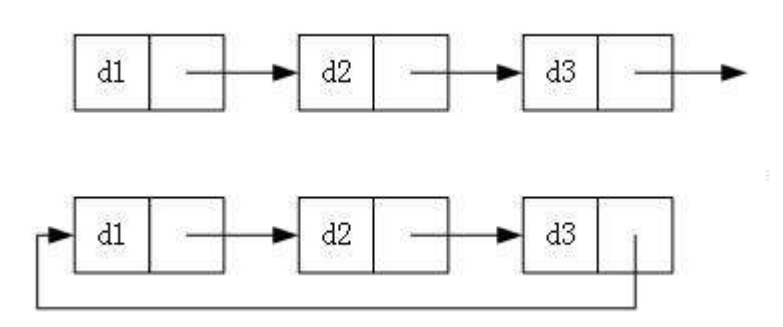
链表组合
单向双向
带头不带头
循环非循环
最多有8种组合
虽然有这么的组合,但实际中最常用的只有2种:

无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了。
3.单链表实现🐦
定义
typedef int SListDataType;
typedef struct SListNode // Single Link List
{
SListDataType data;
struct SListNode *next; //存储下一个节点的地址
} SListNode;
创建节点
SListNode *CreateNewNode(SListDataType x)
{
SListNode *newNode = (SListNode *)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc newNode fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* pList)
{
//不需要assert(plist)
SListNode* cur = pList;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;//cur->next里面存的就是下一个结点的地址
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
提问:这里需要用断言吗?为什么不需要?
记住:一定不能为空的才需要用断言,此处既是链表为空,那我们就什么也不打印就好了啊,断言太暴力了。
提问:这里需要传二级指针吗?为什么?
可以传,但没必要,Print只是打印数据,不会修改数据,因此不需要传二级指针。
查找
查找不需要修改,也就不用传址调用,也就不需要传二级指针。
但如果传了也没问题。
//单链表查找
SListNode *SListFind(SListNode *plist, SListDataType x)
{
SListNode *cur = plist;
// while(cur != NULL)
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
//查找兼具修改的作用
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
效果展示:
尾删
没有节点,无法删除,直接return
一个节点,直接free掉并置空即可,但注意需要对实参进行操作,所以需要传实参地址,也就是传二级指针
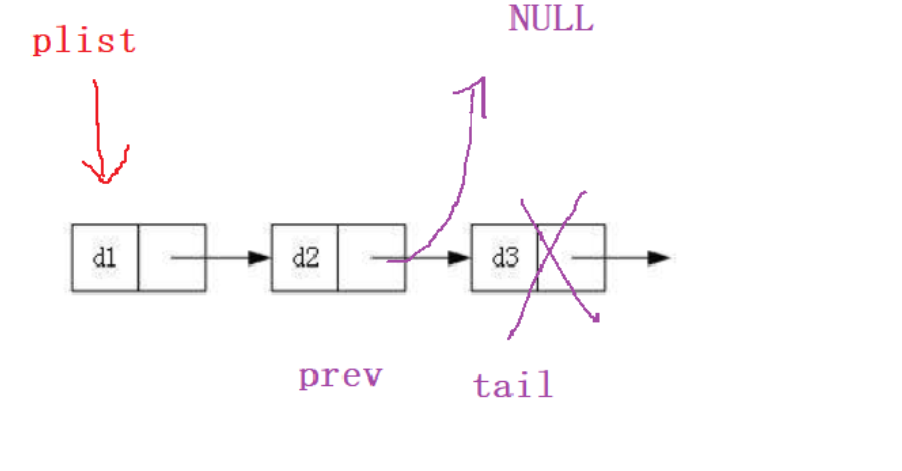
注意:free 之后要置空,因为free掉的是指针指向的内容,但指针还是指向那块空间的,因此要把指针置空多个节点
多个节点时,删除尾节点需要把prev->next置为NULL 再把tail free掉。
如果用多个节点的代码去针对单个节点的情况,会产生解引用空指针的情况。
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppList)
{
//1.没有节点,无法删除,直接return
if(*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
//2.单个节点
else if((*ppList)->next == NULL)
{
free(*ppList);
*ppList = NULL;
}
//3.多个节点
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* tail = *ppList;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;//尾删时要将最后一个结点的上一个结点的next置为NULL才行
}
}
效果展示:
传引用:
void SListPopBack(SListNode*& pList)
{
//1.没有节点,无法删除,直接return
if(pList == NULL)
{
return;
}
//2.单个节点
else if((pList)->next == NULL)
{
free(pList);
pList = NULL;
}
//3.多个节点
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* tail = pList;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;//尾删时要将最后一个结点的上一个结点的next置为NULL才行
}
}
效果展示:
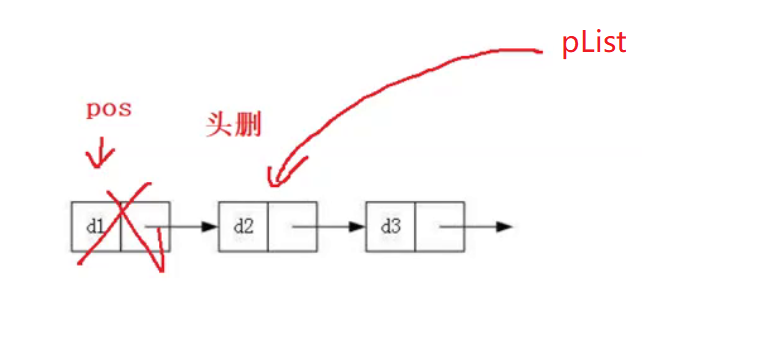
头删
没有节点:
直接return单个节点:
多个节点:
void SListPopFront(SListNode **ppList)
{
// 1.没有节点
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 2.单个节点
// 3.多个节点
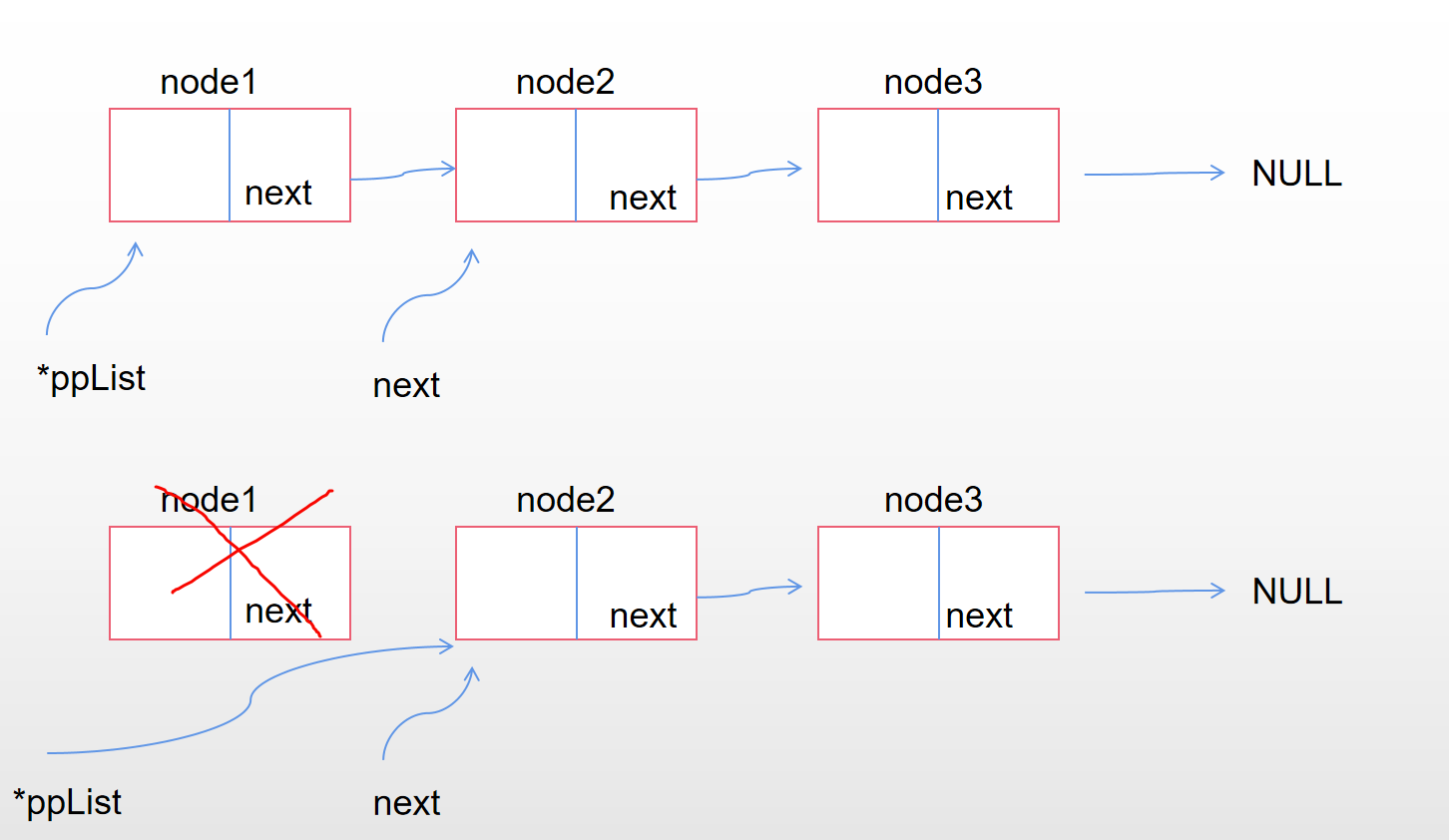
//先写多个节点的情况,再去比较单个节点能否适用,发现恰好可以匹配。
//保存plist->next,如果直接free plist就找不到后面的空间了
SListNode *next = (*ppList)->next;
free(*ppList);//这里只是释放了*ppList指向的那块空间内容,但*ppList还是指向那块空间的。
*ppList = next;
}
效果展示:
传引用:
void SListPopFront(SListNode *&pList)
{
// 1.没有节点
if (pList == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 2.单个节点
// 3.多个节点
//先写多个节点的情况,再去比较单个节点能否适用,发现恰好可以匹配。
//保存plist->next,如果直接free plist就找不到后面的空间了
SListNode *next = pList->next;
free(pList); //这里只是释放了*ppList指向的那块空间内容,但*ppList还是指向那块空间的。
pList = next;
}
效果展示:
头插
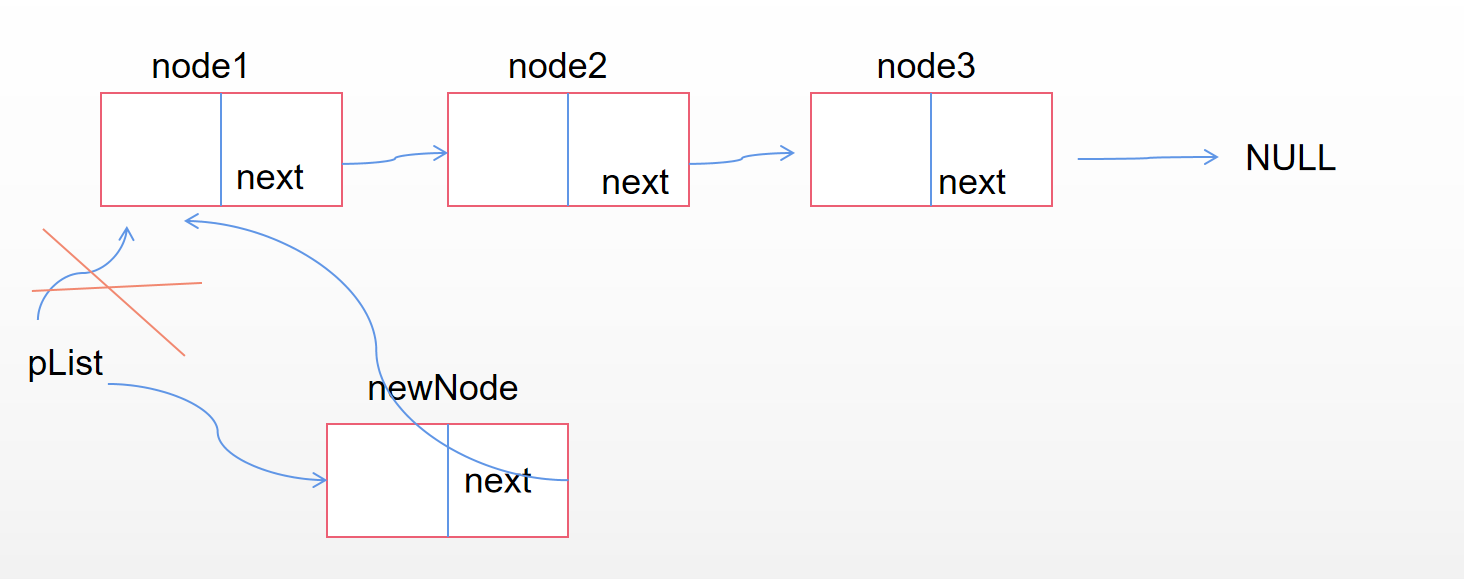
void SListPushFront(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x)
{
//即使传进来的是NULL也能解决
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
newNode->next = pList; //pList指向的就是第一个节点,其实存的也就是第一个节点的地址
pList = newNode;
}
如果头插时链表为空,也是可以的。
pList == NULL,newNode->next 指向NULL,然后再让pList指向newNode,完美解决。
传引用的写法:
void SListPushFront(SListNode *&plist, SListDataType x)
{
//即使传进来的是NULL也能解决
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
newNode->next = plist; //*pplist 其实就是 plist
plist = newNode;
}
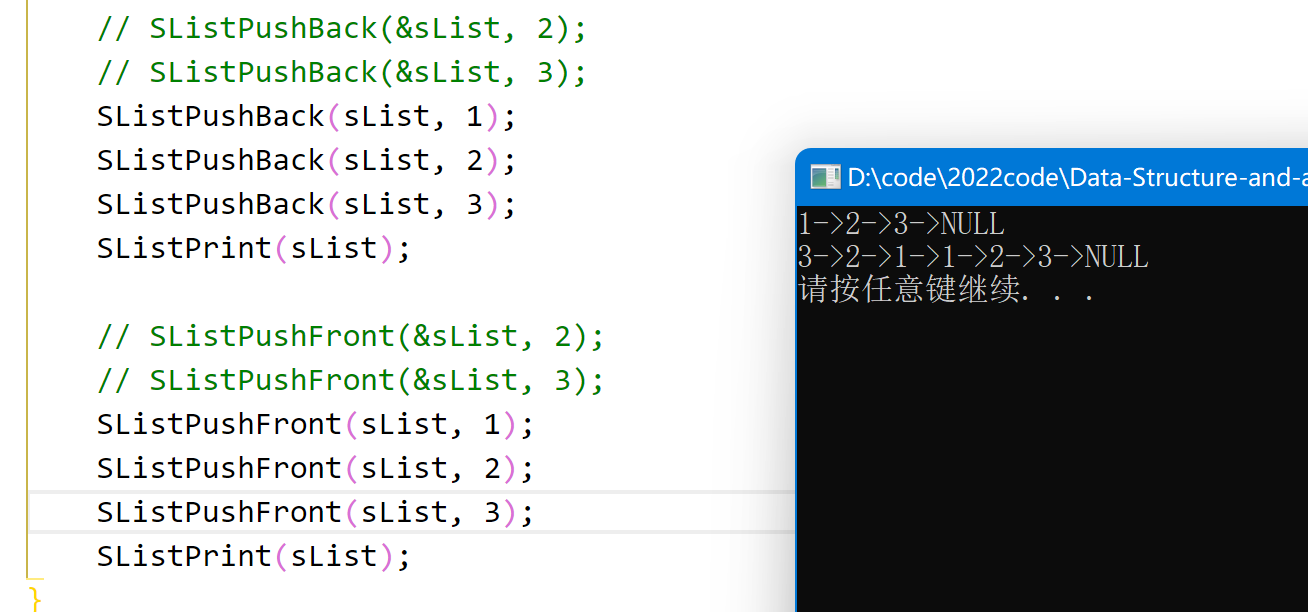
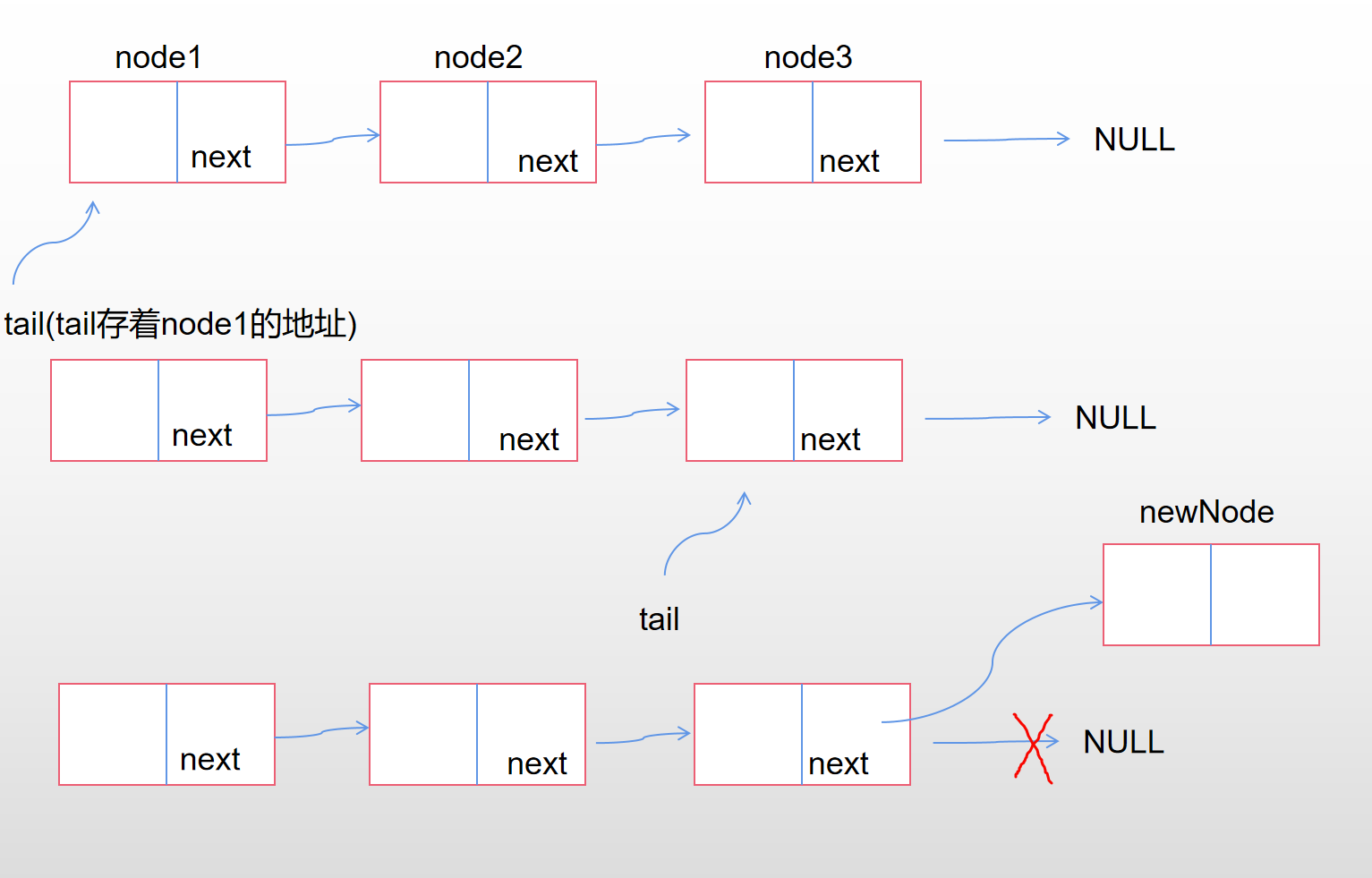
尾插
- 链表本身为空,直接插入就好。
- 链表不为空,遍历找到尾。
- 注意需要用二级指针,因为在判断空链表的情况时,需要对实参sList进行操作,才需要传址调用。
*ppList 其实就是 pList
void SListPushBack(SListNode **ppList, SListDataType x)
{
//同样不需要断言空,因为本来就有可能传空链表
SListNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
//1.空链表
if(*ppList == NULL)
{
*ppList = newNode;//也就是把newNode的地址覆盖掉sList原来的NULL地址
//要修改sList必须传址调用
}
//2.正常链表,去找尾
else
{
SListNode* tail = *ppList;//不能直接修改plist,plist一改就找不到链表了
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//出来时tail->next 指向的是NULL
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
带上头节点可以不用传址调用,因为不需要修改plist
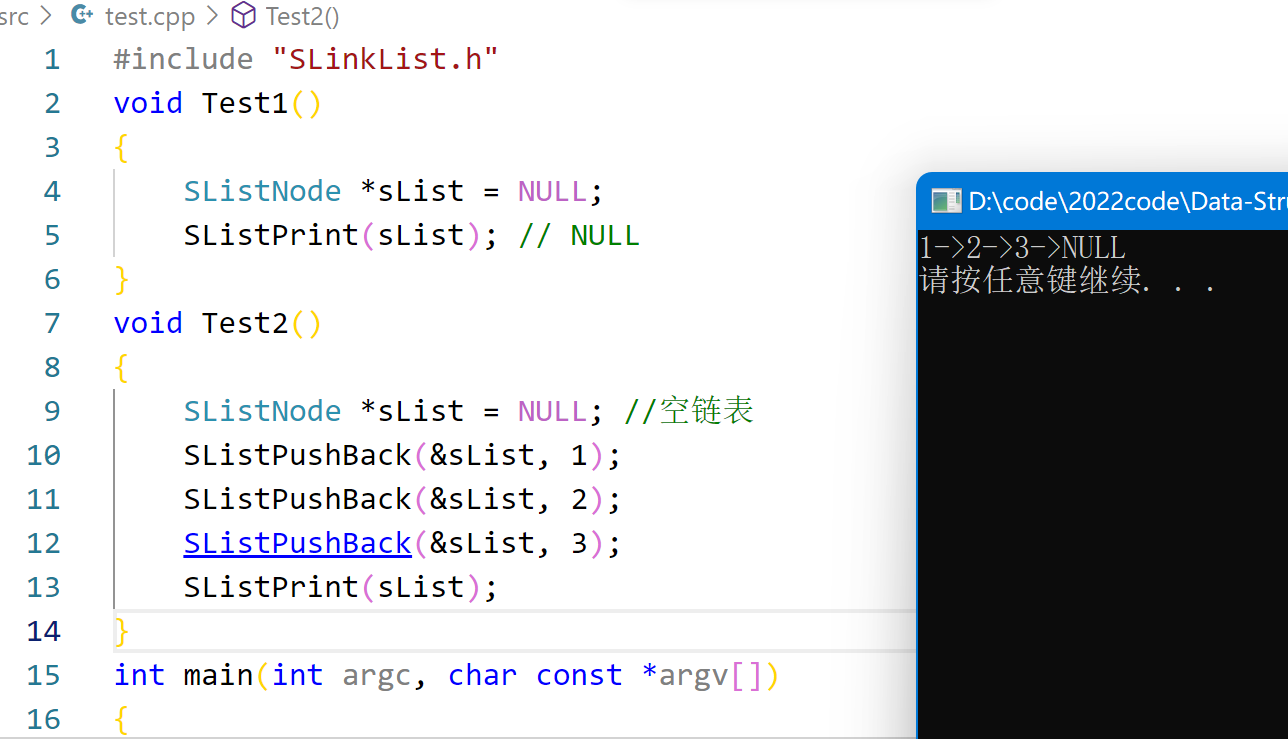
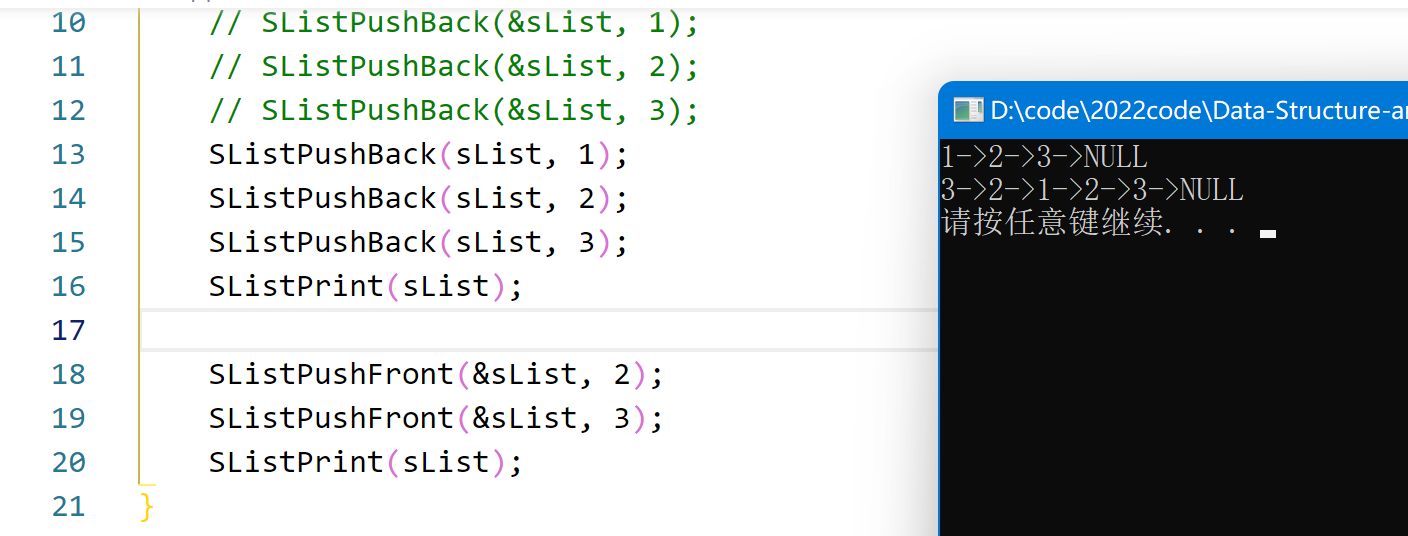
演示效果:
如果不想用二级指针,也可以传引用。
void SListPushBack(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x)
{
//同样不需要断言空,因为本来就有可能传空链表
SListNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
//1.空链表
if(pList == NULL)
{
pList = newNode;//也就是把newNode的地址覆盖掉pList原来的NULL地址
//传进来空链表,要修改plist必须传址调用
}
//2.正常链表,去找尾
else
{
SListNode* tail = pList;//不能直接修改plist,plist一改就找不到链表了
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//出来时tail->next 指向的是NULL
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
效果展示:
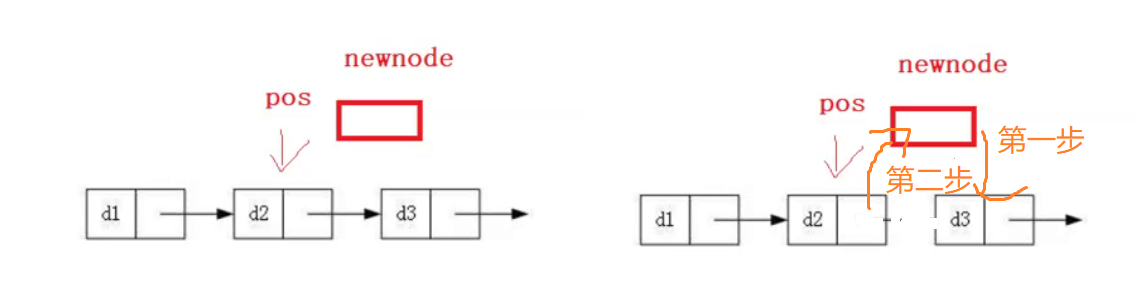
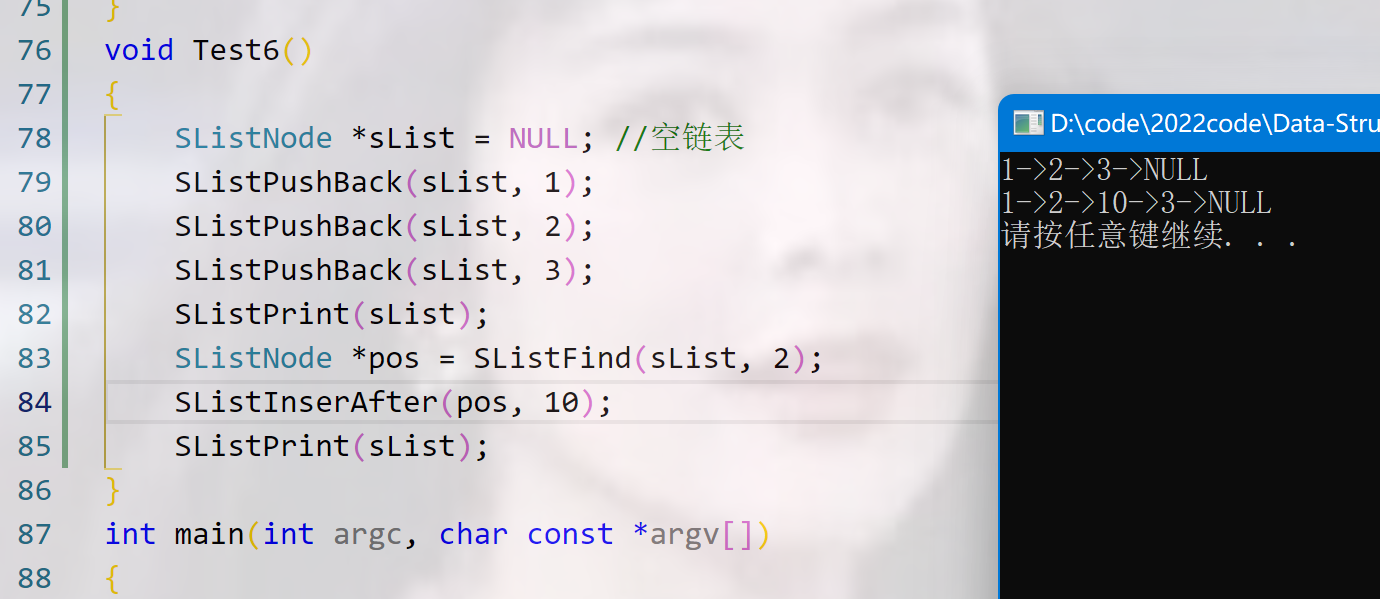
pos后插入
2种插入方式:
注意要操作顺序,如果先让pos-> next 指向了newNode 之后就找不到pos的下一个了。
第二种:
将pos的下一个临时保存起来就行,这样顺序就没关了。
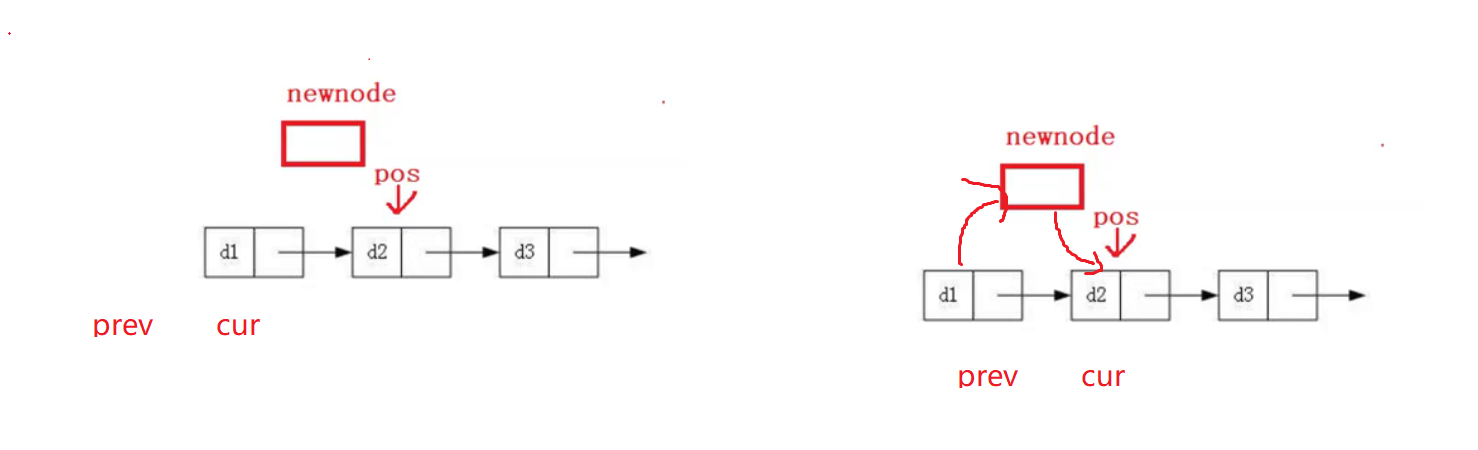
//在pos后面插入
void SListInserAfter(SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
//注意顺序不要反了
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}
//或者临时保存 pos->next
//在pos后面插入
void SListInserAfter(SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
SListNode* next = pos->next;//这样就无需关心顺序问题了
pos->next = newNode;
newNode->next = next;
}
效果展示:
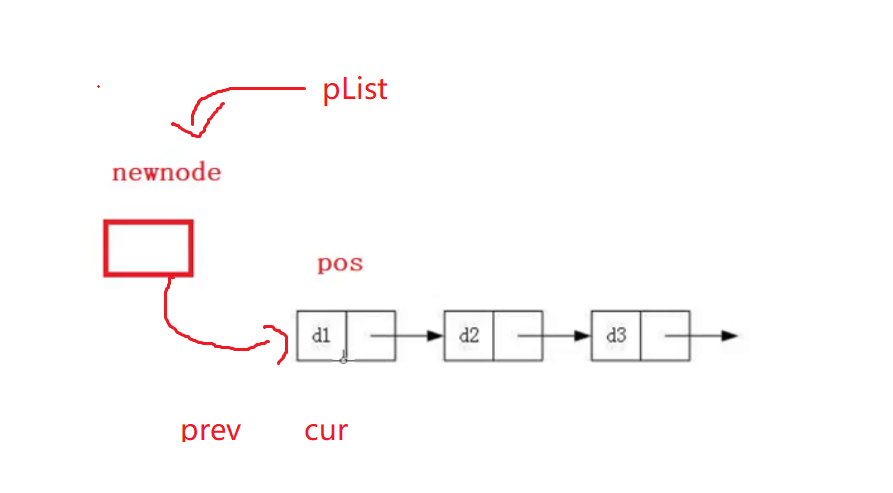
pos前插入
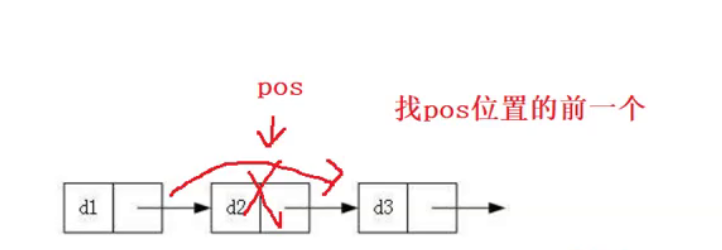
除了要让 newNode 指向pos,还需pos之前的节点指向 newNode ,因此需要找到pos的前一个位置,只能从头开始遍历,非常麻烦且不实用。
- 多个节点的情况:
- 如果pos是第一个节点呢?
如果还让prev指向newNode,那就发生了空指针解引用的问题。可以直接用 if 过滤掉这种情况。
pos是第一个节点的,其实就相当于是头插,但是头插的话,需要改变实参的sList,要让传进来的pList指向newNode,因此还需要传二级指针或者传引用。
void SListInserBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
if(*ppList == pos)//相当于头插
{
newNode->next = pos;
*ppList = newNode;
}
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = cur;
}
}
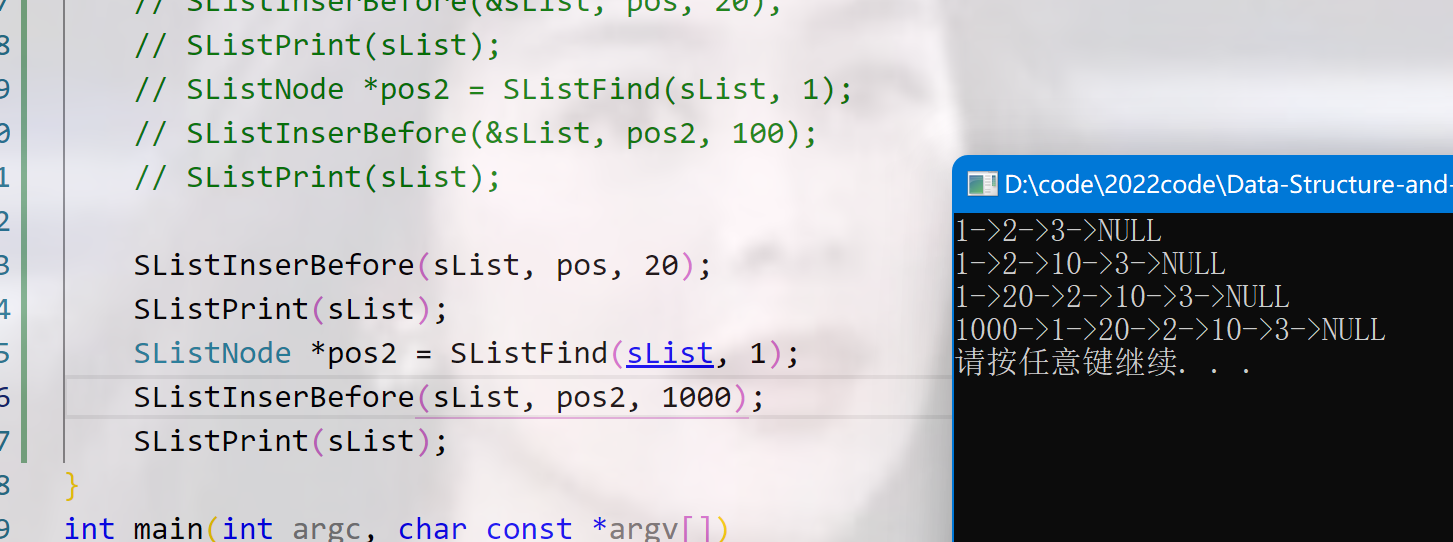
效果展示:
传引用的写法:
void SListInserBefore(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
if (pList == pos) //相当于头插
{
newNode->next = pos;
pList = newNode;
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = NULL;
SListNode *cur = pList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = cur;
}
}
效果展示:
提问:
在一个无头(不告诉头指针)单链表的某一个节点前面插入一个值x,怎么插?
这里没告诉头,就不能从头开始遍历去找pos的前一个了。
其实我们可以先后插,然后交换data

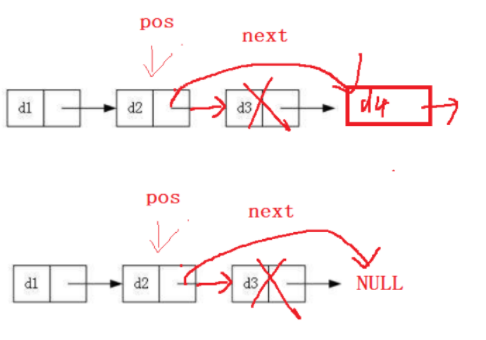
pos后擦除
只有一个节点:
没有可删除的,直接return多个节点
先记录pos的下一个节点,如何让pos指向它的下一个节点的下一个节点,再free 之前记录的pos的下一个节点并置空。
后一个为空时,同样适用。
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode *pos)
{
assert(pos);
//只有一个节点的情况
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode *next = pos->next;
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}
}
pos擦除
多个节点,需要找pos位置的前一个节点prev,然后free pos,让prev指向pos后面的那个
pos指向的是第一个节点,其实就相当于头删,需要改变实参,因此传二级指针或传引用。需要先保存pList的下一个节点,然后free pos,再让pList指向next
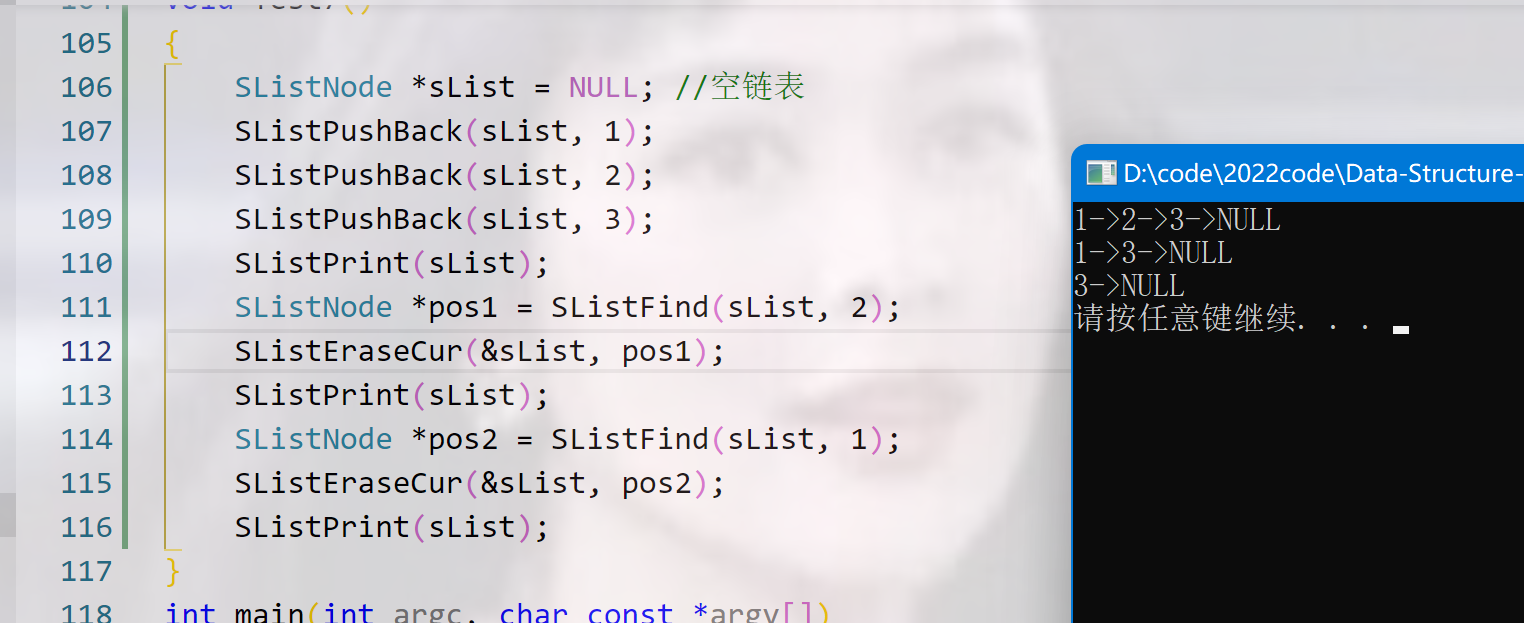
void SListEraseCur(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos)
{
//pos指向第一个节点,相当于头删
if(pos == *ppList)
{
SListNode* next = (*ppList)->next;
free(*ppList);
*ppList = next;
}
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//出来时cur指向的pos,prev指向pos前一个
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
}
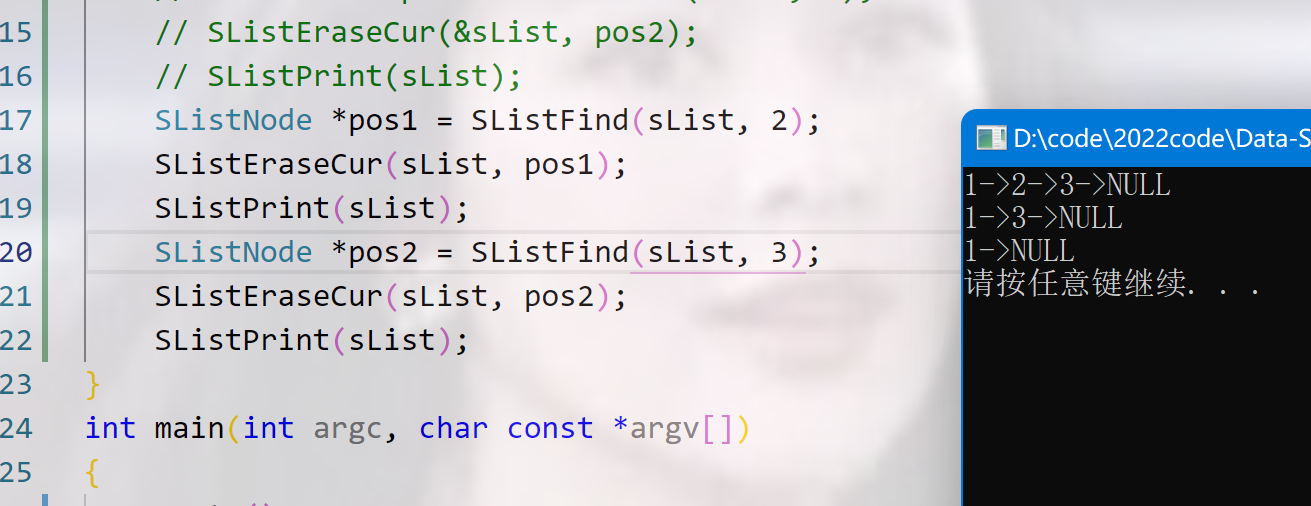
效果展示:
void SListEraseCur(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos)
{
// pos指向第一个节点,相当于头删
if (pos == pList)
{
SListNode *next = pList->next;
free(pList);
pList = next;
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = NULL;
SListNode *cur = pList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//出来时cur指向的pos,prev指向pos前一个
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
}
效果展示:
4.源代码:🐘
SLinkList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int SListDataType;
typedef struct SListNode // Single Link List
{
SListDataType data;
struct SListNode *next; //存储下一个节点的地址
} SListNode;
void SListPrint(SListNode *pList);
SListNode *CreateNewNode(SListDataType x);
// void SListPushBack(SListNode **ppList, SListDataType x);
void SListPushBack(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x);
void SListPushFront(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x);
// void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SListDataType x);
// void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppList);
void SListPopBack(SListNode *&pList);
// void SListPopFront(SListNode **ppList);
void SListPopFront(SListNode *&pList);
SListNode *SListFind(SListNode *plist, SListDataType x);
void SListInserAfter(SListNode *pos, SListDataType x);
// void SListInserBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos, SListDataType x);
void SListInserBefore(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos, SListDataType x);
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode *pos);
void SListEraseCur(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos);
// void SListEraseCur(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos);
SLinkList.cpp
#include "SLinkList.h"
void SListPrint(SListNode *pList)
{
//不需要assert(plist)
SListNode *cur = pList;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next; // cur->next里面存的就是下一个结点的地址
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
SListNode *CreateNewNode(SListDataType x)
{
SListNode *newNode = (SListNode *)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc newNode fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// void SListPushBack(SListNode **ppList, SListDataType x)
// {
// //同样不需要断言空,因为本来就有可能传空链表
// SListNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
// //1.空链表
// if(*ppList == NULL)
// {
// *ppList = newNode;//也就是把newNode的地址覆盖掉pList原来的NULL地址
// //传进来空链表,要修改plist必须传址调用
// }
// //2.正常链表,去找尾
// else
// {
// SListNode* tail = *ppList;//不能直接修改plist,plist一改就找不到链表了
// while (tail->next != NULL)
// {
// tail = tail->next;
// }
// //出来时tail->next 指向的是NULL
// tail->next = newNode;
// }
// }
void SListPushBack(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x)
{
//同样不需要断言空,因为本来就有可能传空链表
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
// 1.空链表
if (pList == NULL)
{
pList = newNode; //也就是把newNode的地址覆盖掉pList原来的NULL地址
//传进来空链表,要修改plist必须传址调用
}
// 2.正常链表,去找尾
else
{
SListNode *tail = pList; //不能直接修改plist,plist一改就找不到链表了
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
//出来时tail->next 指向的是NULL
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode *&pList, SListDataType x)
{
//即使传进来的是NULL也能解决
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
newNode->next = pList; // pList指向的就是第一个节点,其实存的也就是第一个节点的地址
pList = newNode;
}
// void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppList)
// {
// //1.没有节点,无法删除,直接return
// if(*ppList == NULL)
// {
// return;
// }
// //2.单个节点
// else if((*ppList)->next == NULL)
// {
// free(*ppList);
// *ppList = NULL;
// }
// //3.多个节点
// else
// {
// SListNode* prev = NULL;
// SListNode* tail = *ppList;
// while (tail->next != NULL)
// {
// prev = tail;
// tail = tail->next;
// }
// free(tail);
// tail = NULL;
// prev->next = NULL;//尾删时要将最后一个结点的上一个结点的next置为NULL才行
// }
// }
void SListPopBack(SListNode *&pList)
{
// 1.没有节点,无法删除,直接return
if (pList == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 2.单个节点
else if ((pList)->next == NULL)
{
free(pList);
pList = NULL;
}
// 3.多个节点
else
{
SListNode *prev = NULL;
SListNode *tail = pList;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL; //尾删时要将最后一个结点的上一个结点的next置为NULL才行
}
}
// void SListPopFront(SListNode **ppList)
// {
// // 1.没有节点
// if (*ppList == NULL)
// {
// return;
// }
// // 2.单个节点
// // 3.多个节点
// //先写多个节点的情况,再去比较单个节点能否适用,发现恰好可以匹配。
// //保存plist->next,如果直接free plist就找不到后面的空间了
// SListNode *next = (*ppList)->next;
// free(*ppList);//这里只是释放了*ppList指向的那块空间内容,但*ppList还是指向那块空间的。
// *ppList = next;
// }
void SListPopFront(SListNode *&pList)
{
// 1.没有节点
if (pList == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 2.单个节点
// 3.多个节点
//先写多个节点的情况,再去比较单个节点能否适用,发现恰好可以匹配。
//保存plist->next,如果直接free plist就找不到后面的空间了
SListNode *next = pList->next;
free(pList); //这里只是释放了*ppList指向的那块空间内容,但*ppList还是指向那块空间的。
pList = next;
}
//单链表查找
SListNode *SListFind(SListNode *plist, SListDataType x)
{
SListNode *cur = plist;
// while(cur != NULL)
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
//查找兼具修改的作用
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// //在pos后面插入
// void SListInserAfter(SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
// {
// assert(pos);
// SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
// //注意顺序不要反了
// newNode->next = pos->next;
// pos->next = newNode;
// }
//或者临时保存 pos->next
//在pos后面插入
void SListInserAfter(SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
SListNode *next = pos->next; //这样就无需关心顺序问题了
pos->next = newNode;
newNode->next = next;
}
// void SListInserBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos, SListDataType x)
// {
// assert(pos);
// SListNode* newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
// if(*ppList == pos)//相当于头插
// {
// newNode->next = pos;
// *ppList = newNode;
// }
// else
// {
// SListNode* prev = NULL;
// SListNode* cur = *ppList;
// while (cur != pos)
// {
// prev = cur;
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// prev->next = newNode;
// newNode->next = cur;
// }
// }
void SListInserBefore(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos, SListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode *newNode = CreateNewNode(x);
if (pList == pos) //相当于头插
{
newNode->next = pos;
pList = newNode;
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = NULL;
SListNode *cur = pList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = newNode;
newNode->next = cur;
}
}
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode *pos)
{
assert(pos);
//只有一个节点的情况
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode *next = pos->next;
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}
}
// void SListEraseCur(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos)
// {
// //pos指向第一个节点,相当于头删
// if(pos == *ppList)
// {
// SListNode* next = (*ppList)->next;
// free(*ppList);
// *ppList = next;
// }
// else
// {
// SListNode* prev = NULL;
// SListNode* cur = *ppList;
// while (cur != pos)
// {
// prev = cur;
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// //出来时cur指向的pos,prev指向pos前一个
// prev->next = cur->next;
// free(cur);
// cur = NULL;
// }
// }
void SListEraseCur(SListNode *&pList, SListNode *pos)
{
// pos指向第一个节点,相当于头删
if (pos == pList)
{
SListNode *next = pList->next;
free(pList);
pList = next;
}
else
{
SListNode *prev = NULL;
SListNode *cur = pList;
while (cur != pos)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//出来时cur指向的pos,prev指向pos前一个
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
}
Test.cpp
#include "SLinkList.h"
void Test1()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL;
SListPrint(sList); // NULL
}
void Test2()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
// SListPushBack(&sList, 1);
// SListPushBack(&sList, 2);
// SListPushBack(&sList, 3);
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
// SListPushFront(&sList, 2);
// SListPushFront(&sList, 3);
SListPushFront(sList, 1);
SListPushFront(sList, 2);
SListPushFront(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
}
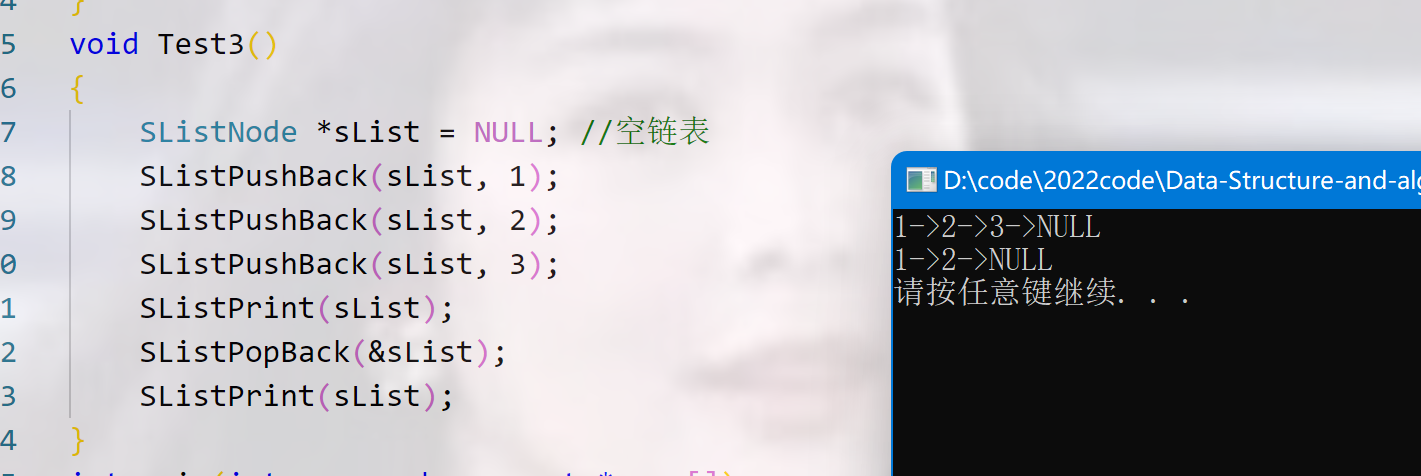
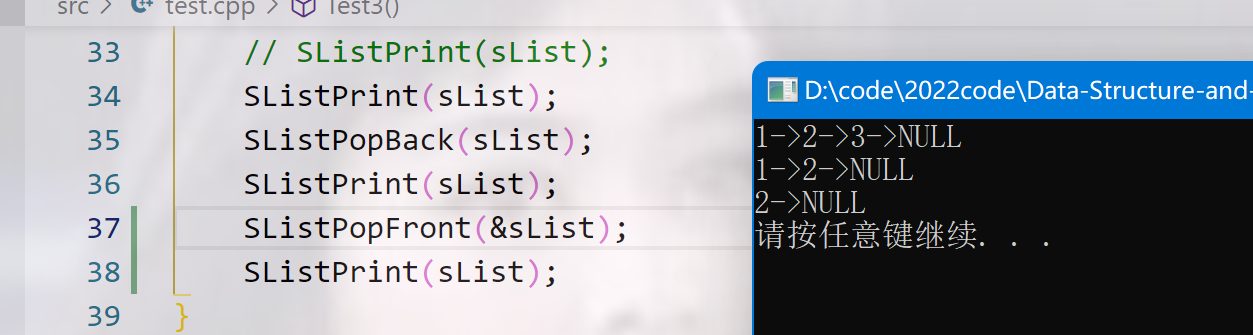
void Test3()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
// SListPrint(sList);
// SListPopBack(&sList);
// SListPrint(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
SListPopBack(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
// SListPopFront(&sList);
SListPopFront(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
}
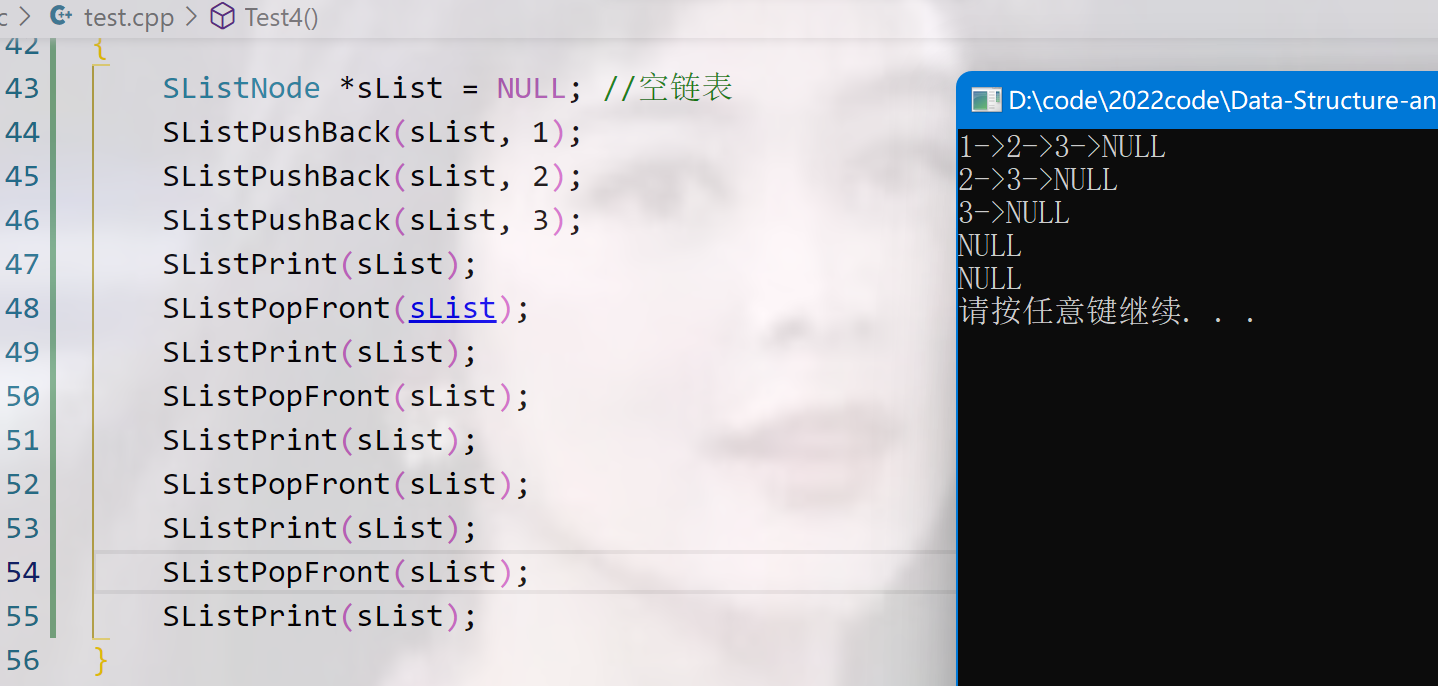
void Test4()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
SListPopFront(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
SListPopFront(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
SListPopFront(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
SListPopFront(sList);
SListPrint(sList);
}
void Test5()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
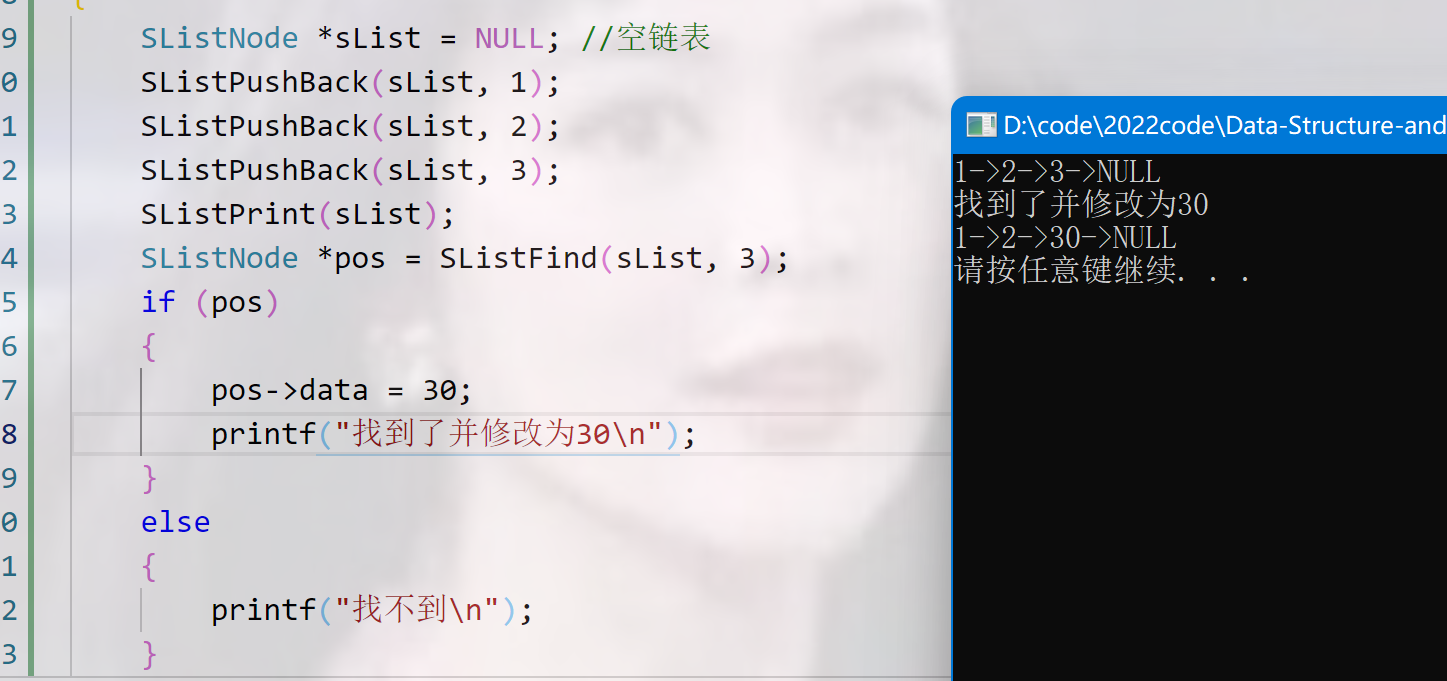
SListNode *pos = SListFind(sList, 3);
if (pos)
{
pos->data = 30;
printf("找到了并修改为30\n");
}
else
{
printf("找不到\n");
}
SListPrint(sList);
}
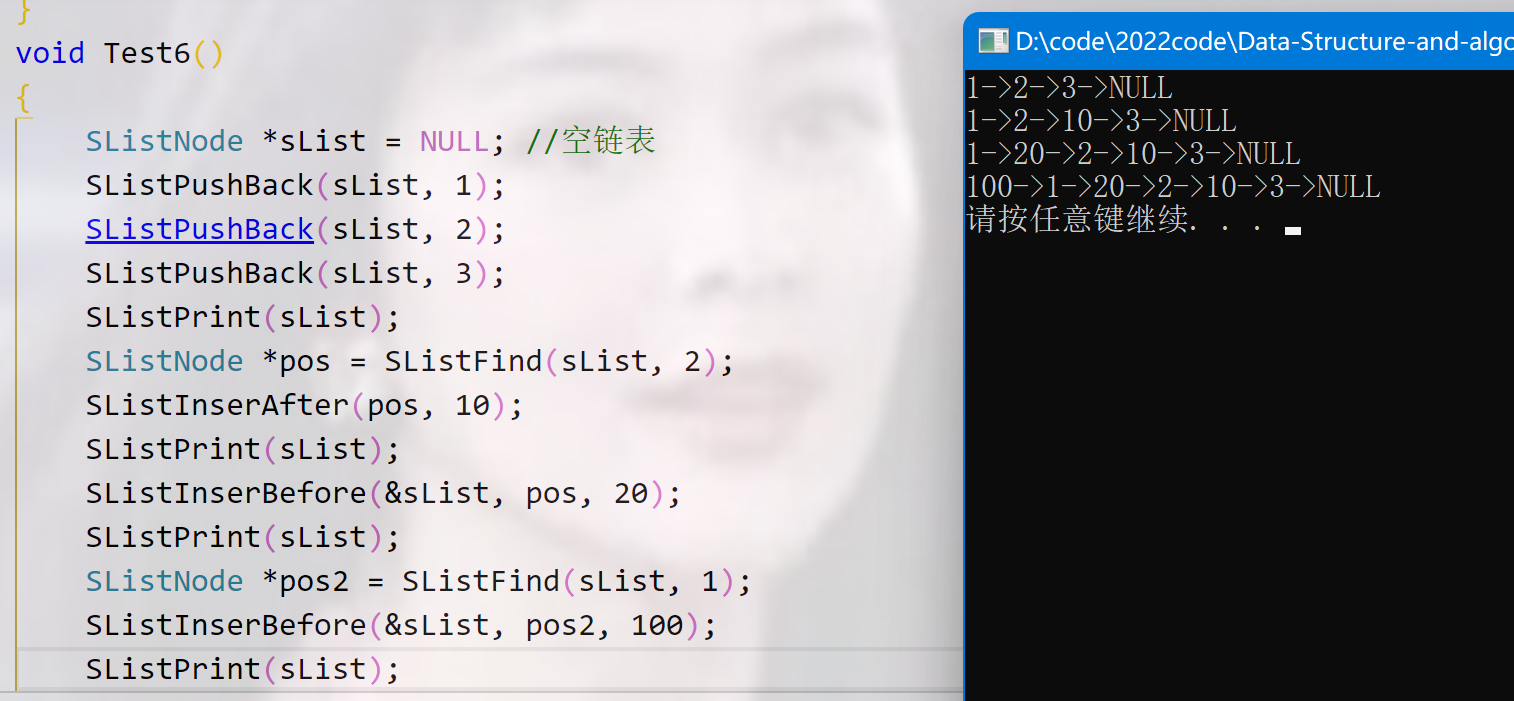
void Test6()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
SListNode *pos = SListFind(sList, 2);
SListInserAfter(pos, 10);
SListPrint(sList);
// SListInserBefore(&sList, pos, 20);
// SListPrint(sList);
// SListNode *pos2 = SListFind(sList, 1);
// SListInserBefore(&sList, pos2, 100);
// SListPrint(sList);
SListInserBefore(sList, pos, 20);
SListPrint(sList);
SListNode *pos2 = SListFind(sList, 1);
SListInserBefore(sList, pos2, 1000);
SListPrint(sList);
SListNode *pos3 = SListFind(sList, 1000);
SListEraseAfter(pos3);
SListPrint(sList);
}
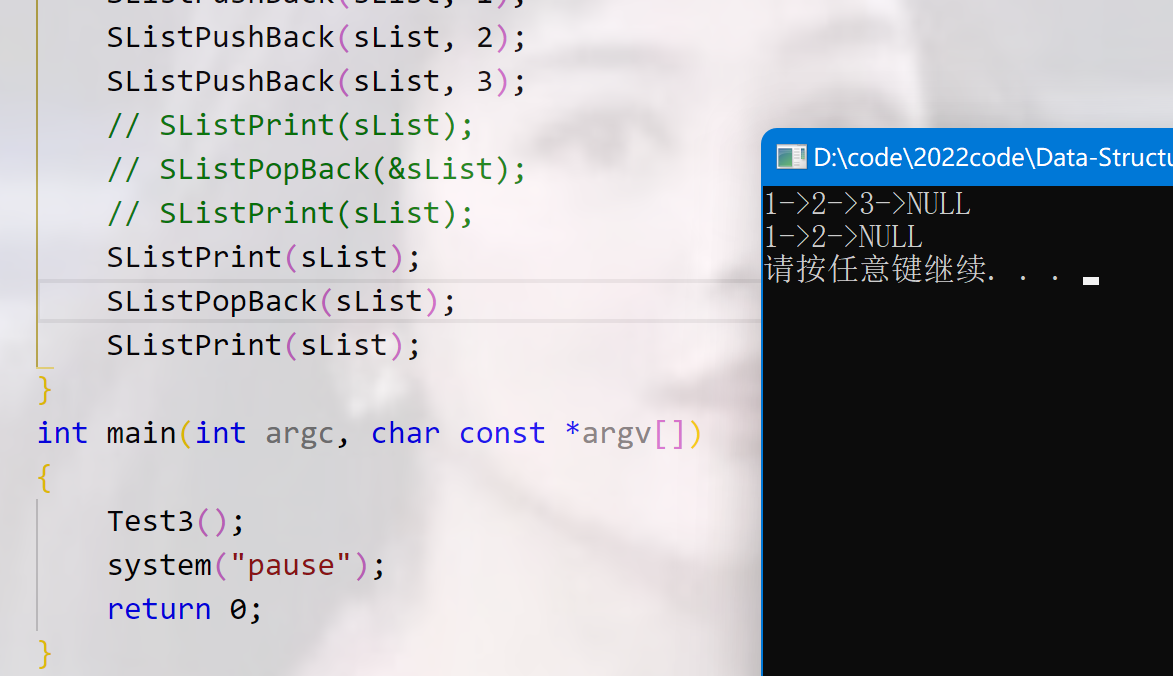
void Test7()
{
SListNode *sList = NULL; //空链表
SListPushBack(sList, 1);
SListPushBack(sList, 2);
SListPushBack(sList, 3);
SListPrint(sList);
// SListNode *pos1 = SListFind(sList, 2);
// SListEraseCur(&sList, pos1);
// SListPrint(sList);
// SListNode *pos2 = SListFind(sList, 1);
// SListEraseCur(&sList, pos2);
// SListPrint(sList);
SListNode *pos1 = SListFind(sList, 2);
SListEraseCur(sList, pos1);
SListPrint(sList);
SListNode *pos2 = SListFind(sList, 3);
SListEraseCur(sList, pos2);
SListPrint(sList);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
Test7();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.尾声🐜
🌵🌵
今天的单链表就回顾到这里啦。
写文不易,如果有帮助烦请点个赞~ 👍👍👍
🌹🌹Thanks?(・ω・)ノ🌹🌹
👀👀由于笔者水平有限,在今后的博文中难免会出现错误之处,本人非常希望您如果发现错误,恳请留言批评斧正,希望和大家一起学习,一起进步ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ,期待您的留言评论。
附GitHub仓库链接