📋 个人简介
-
💖 作者简介:大家好,我是菀枯😜
-
🎉 支持我:点赞👍+收藏??+留言📝
-
💬格言:不要在低谷沉沦自己,不要在高峰上放弃努力!??
一.为什么使用链表
在学习链表以前,我们存储数据用的方式就是数组。使用数组的好处就是便于查找数据,但缺点也很明显。
- 使用前需声明数组的长度,一旦声明长度就不能更改
- 插入和删除操作需要移动大量的数组元素,效率慢
- 只能存储一种类型的数据.
为了解决上述的问题,我们就可以使用链表来存储数据。
二.链表的概念
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
三.链表的实现
3.1 创建链表前须知
结点:链表中每一个元素称为“结点”,每个结点都应包括两个部分:一为用户需要用的实际数据;二为下一个结点的地址,
头结点:在单链表的第一个结点之前附设一个结点,这个节点不存储数据,称之为头结点
3.2 定义结构体
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDateType; //链表中存储的数据类型,可换成其他
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLDateType date;
struct SListNode* next; //指向下一个节点的指针
}SListNode;
3.3 申请一个节点
SListNode* BuyListNode(SLDateType x)
{
SListNode* newNode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (NULL == newNode)
{
printf("malloc error\n"); //内存开辟失败
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newNode->date = x; // 给新节点赋值
newNode->next = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
3.4 链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pphead/*要改动头指针,所以要传递二级指针*/, SLDateType x)
{
SListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x); //申请节点
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
}

3.5 链表的尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pphead, SLDateType x)
{
SListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL) //若头指针为空,则链表为空链表,直接将新节点接到头指针后
{
*pphead = newNode;
}
else
{
SListNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL) //找链表的尾部
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;//将新节点接到尾部
}
}
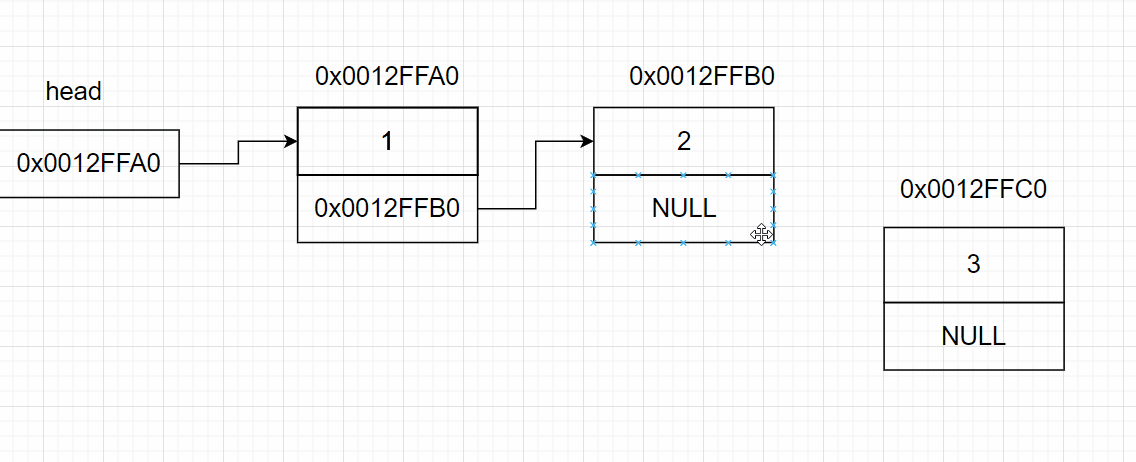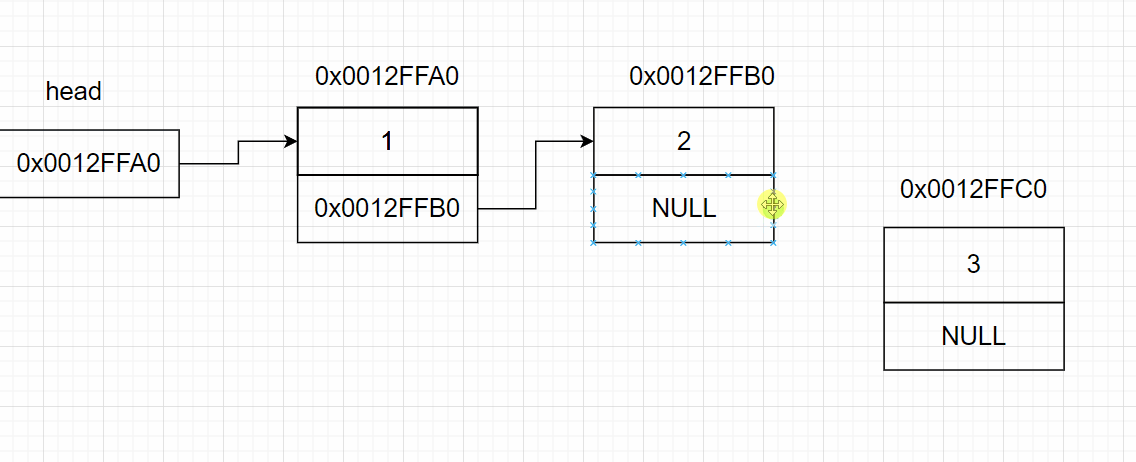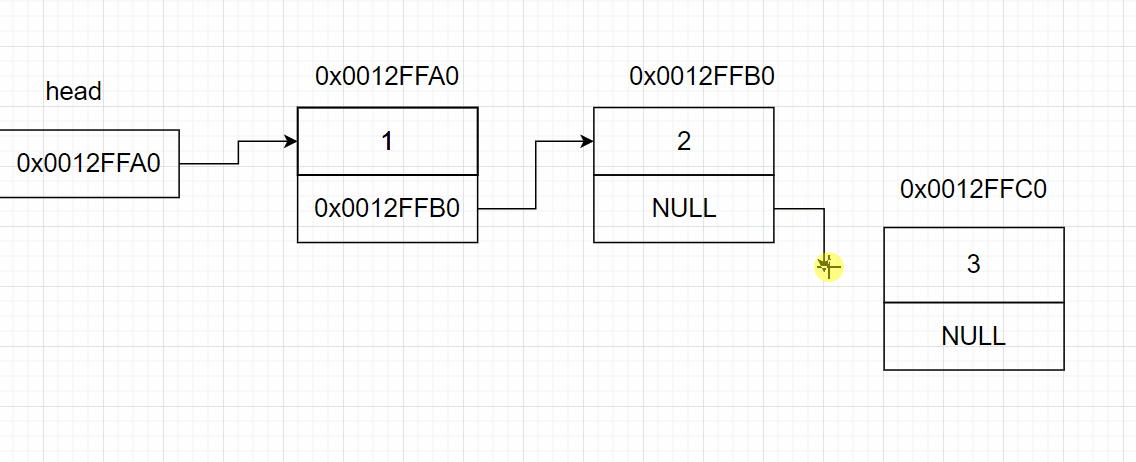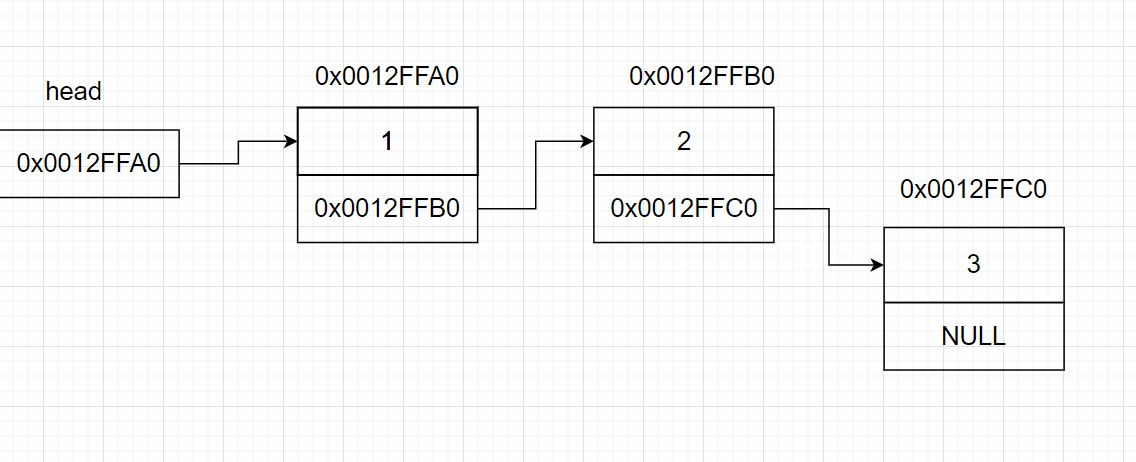
3.6 链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)//链表为空,则不进行任何操作
{
return;
}
else if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) //链表只有一个节点
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else//其余情况
{
SListNode* tail = *pphead; //链表的尾部节点
SListNode* pre = NULL;//链表尾的前一个节点
while (tail->next != NULL)//找尾
{
pre = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
pre->next = tail->next; //将尾节点的指针域赋值给前一个节点的指针域
free(tail);
}
}
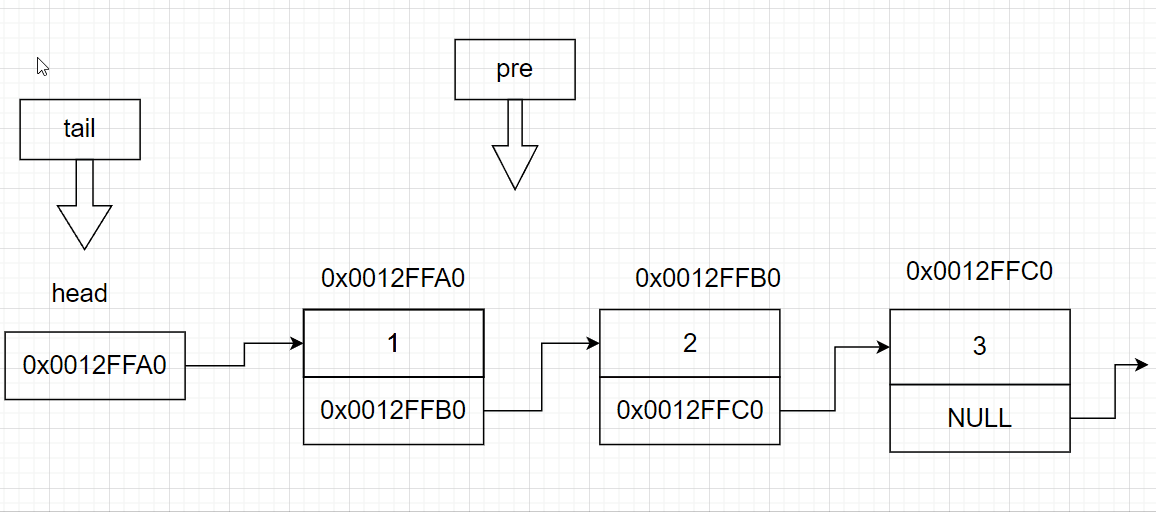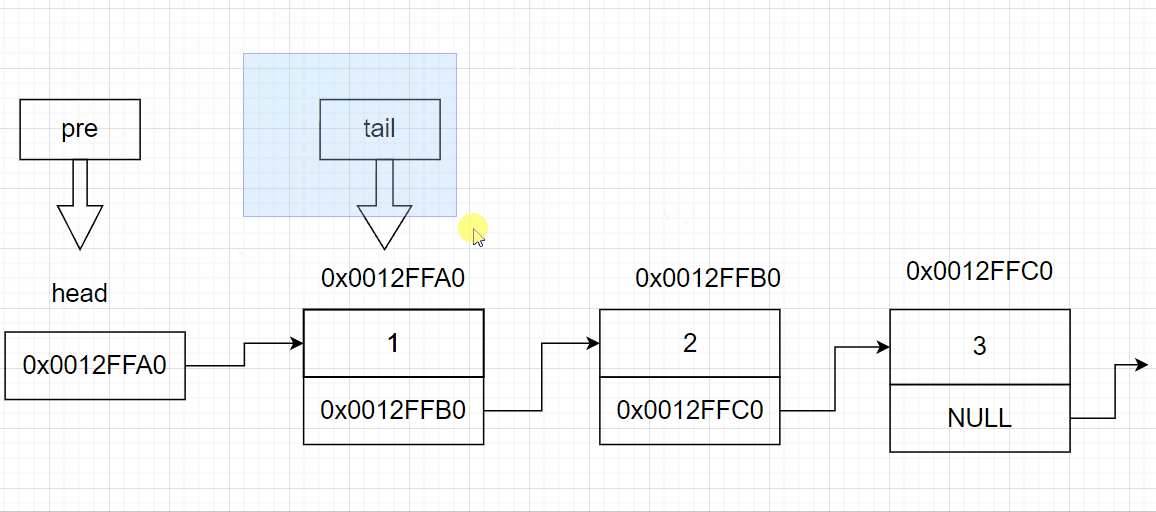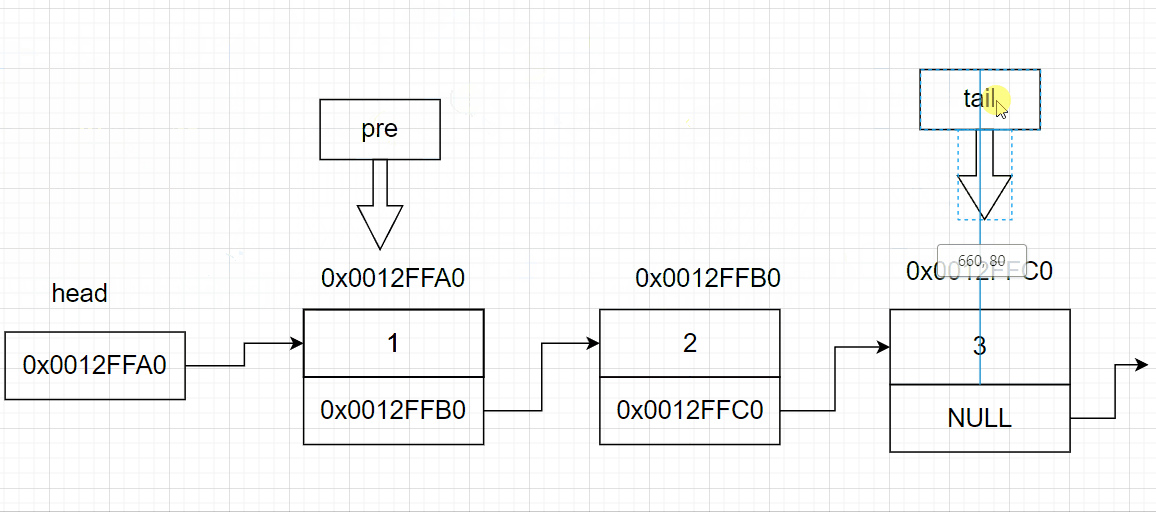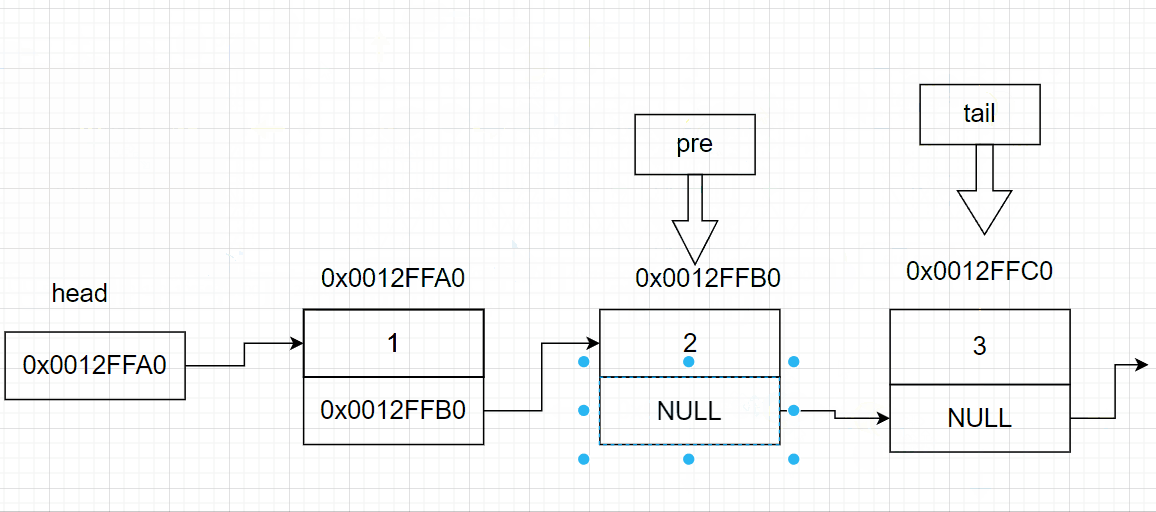
3.7 链表的头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL) //链表为空什么也不做
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* head = *pphead;//记录原本的第一个节点
*pphead = head->next; //让头指针指向第二个节点
free(head);//释放第一个节点
}
}
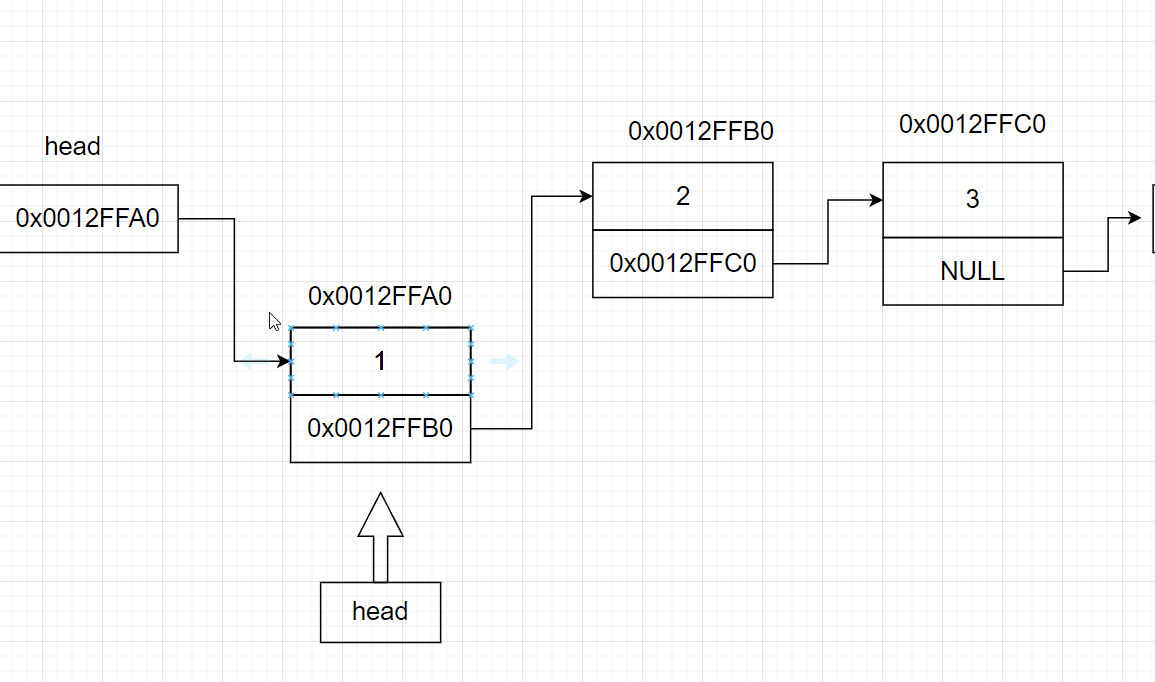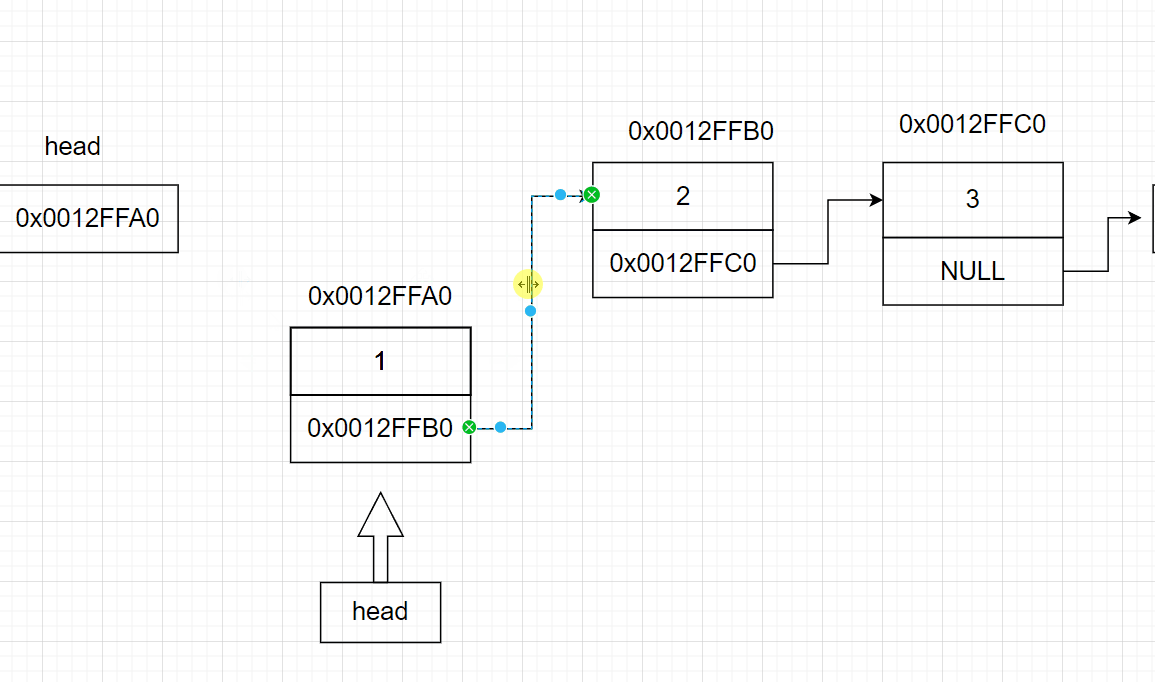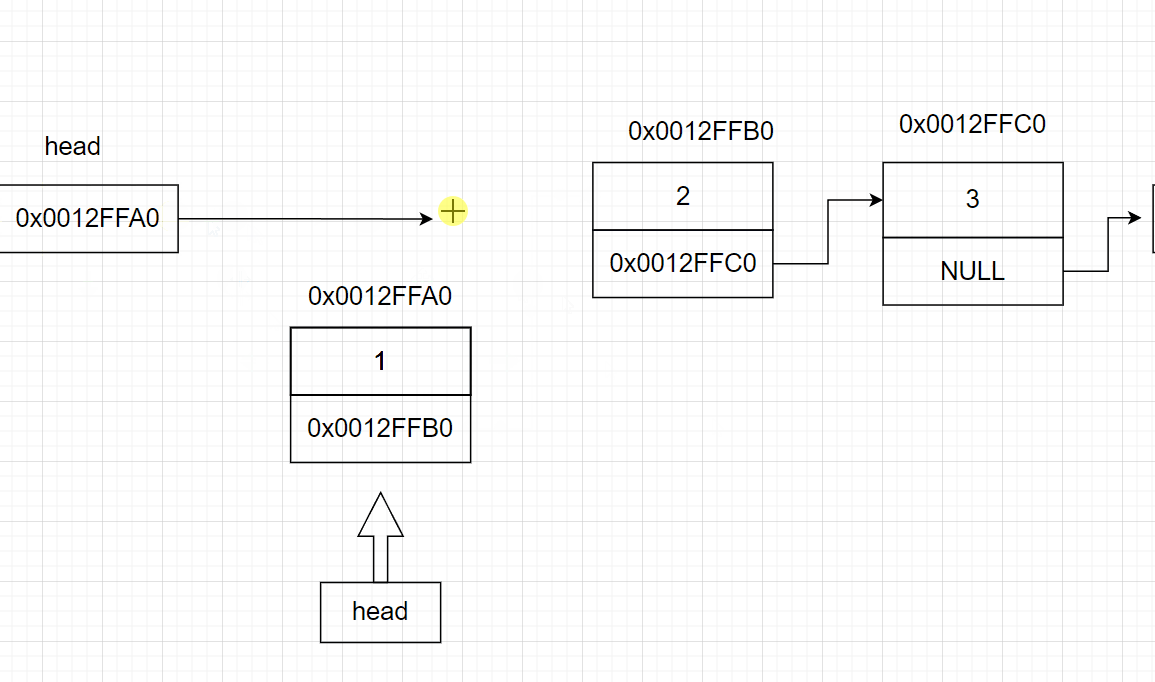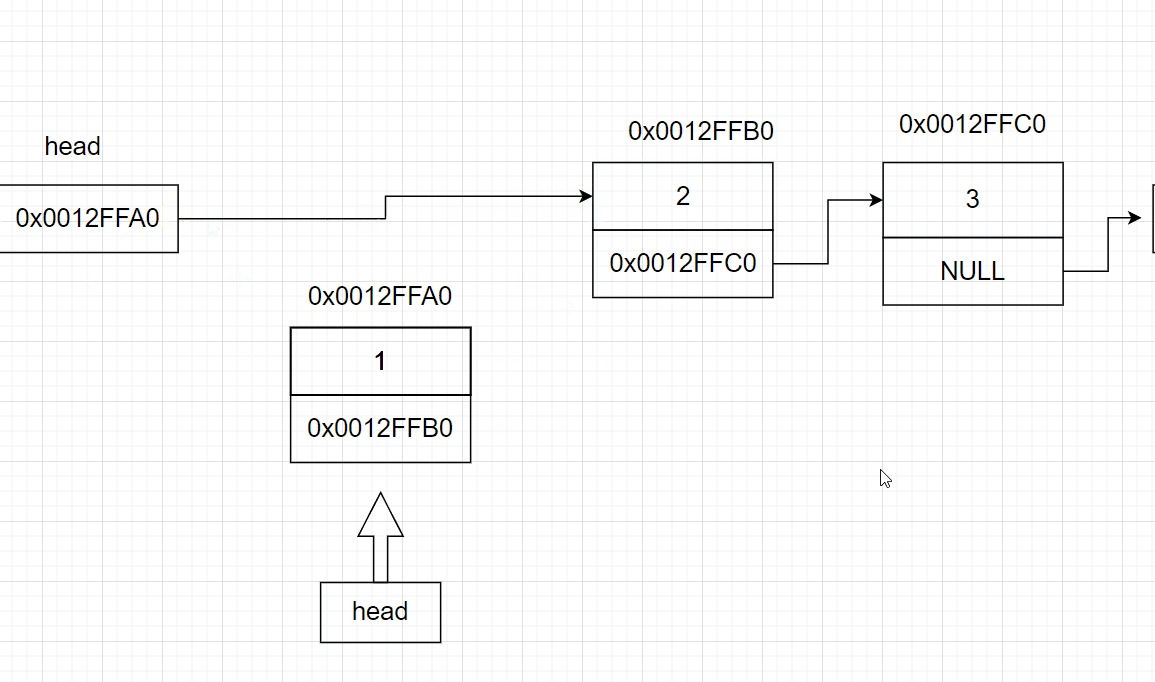
3.8 寻找某节点
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, SLDateType x)
{
SListNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->date == x) //找到则返回该节点
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL; //未找到则返回空
}
3.9 在指定节点前插入节点
void SListInsert(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos/*要插入的位置*/, SLDateType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *pphead; //当前所指向的位置
SListNode* pre = NULL; //前一个节点
while (cur != pos)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
SListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
pre->next = newNode;
newNode->next = cur;
}
}
3.10 删除指定节点前的节点
void SListErase(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos/*要插入的位置*/)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *pphead;
SListNode* pre = *pphead;
while (cur != pos)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
pre->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
}
}
3.11 链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode** pphead)
{
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
while (*pphead != NULL)
{
SListNode* cur = *pphead;
*pphead = cur->next;
free(cur);
}
}
}
结语
欢迎各位参考与指导!!!