栈
-栈的定义
????????栈也称堆栈,是一种先进后出,删除和插入都在栈顶操作的线性表。
-栈的特性
????????先进后出,后进先出。基本操作只有两个:出栈(push)和进栈(pop)
-基本运算
????????初始化栈、判断空、入栈、出栈、读栈顶元素。
-栈种类
????????栈分为顺序栈与链式栈两种:顺序栈类似线性表,是数组的形式;而链式栈类似链表,用指针链接每个部分。
-顺序栈
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 1024 //定义栈能容纳的大小
typedef int DataType;//存储数据类型为int
//顺序栈储存结构
typedef struct
{
DataType data[MAX];
int top;
} Stack;
//定义全局变量
Stack *s;
//初始化栈
Stack * init()
{
Stack * s;
//申请指定空间的栈
s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
//判断空
int empty(Stack *s){
//如果为空返回1,否则返回0
if (s->top == -1) return 1;
else return 0;
}
//入栈
int push(Stack *s,DataType x){
if (s->top == MAX-1){
printf("栈将溢出!");
return 0;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = x;
return 1;
}
//出栈
void pop(Stack *s){
if (empty(s)){
printf("栈已空!\n");
}else{
s->top--;
}
}
//读栈顶元素
void readtop(Stack *s){
if (!empty(s)){
printf("%d\n", s->data[s->top]);
}else{
printf("栈已空!");
return;
}
}
int main(){
s = init();
push(s, 1);//1入栈
push(s, 2);//2入栈
push(s, 3);//3入栈
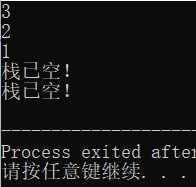
readtop(s);//读取栈顶数据->3
pop(s);//3出栈
readtop(s);//读取栈顶数据->2
pop(s);//2出栈
readtop(s);//读取栈顶数据->1
pop(s);//1出栈
readtop(s);//此时栈已空,跳出提示词
pop(s);//此时栈已空,跳出提示词
}运行结果:
?-链式栈
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int DataType;//存储数据类型为int
//定义栈结构的结点
typedef struct stack_node {
DataType element;
struct stack_node *next;
} node;
typedef struct {
node *top;
} stack;
//进栈函数
void push(stack *sp, DataType element) {
node *np;
//创建新节点
np = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
np->element = element;
//修改栈顶指针
np->next = sp->top;
sp->top = np;
}
//出栈函数
DataType pop(stack *sp) {
node *np;//将要出栈的结点指针
np = sp->top;
DataType c;//栈顶元素值
c = np->element;
sp->top = np->next;
free(np);
np = NULL;
return c;
}
//遍历输出函数
void read (stack sp) {
stack temstack = {NULL};
DataType tem;
while (sp.top != NULL) {
tem = pop(&sp);
printf("%d\n", tem);
push(&temstack, tem);
}
while (temstack.top != NULL) {
tem = pop(&temstack);
push(&sp, tem);
}
}
int main() {
stack s = {NULL};
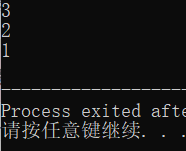
push(&s, 1);
push(&s, 2);
push(&s, 3);
read(s);
return 0;
}运行结果:
队列
????????队列基本操作与栈类似,区别是删除元素时根据先进先出原则。
-队列的特性
?????????先进先出,后进后出。允许进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(rear),允许进行删除操作的一段称为队头(front)。
-代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 50
//队列类型的定义
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MAX];
int front,rear;//front为队首指针 rear为队尾指针
}SqQueue;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef SqQueue CSqQueue;
//初始化运算
/*初始化运算得到一个空队列*/
int InitQueue(CSqQueue *Q)
{
(*Q).front=0;
(*Q).rear=0;
return 0;
}
//判空运算,队列Q为空返回1,否则返回0
int QueueEmpty(CSqQueue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear)
return 1;
return 0;
}
//判满运算
int QueueFull(CSqQueue Q)
{
if((Q.rear+1)%MAX==q.front)
return 1;
return 0;
}
//创建一个队列,创建成功返回1,创建失败返回0
int CreatQueue(CSqQueue *Q)
{
int i,n;
ElemType temp_e;
printf("请输入你想要创建的队列的长度:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n>MAX)
return -1;
for(i=1;i<=n,i++){
printf("请输入第%d个元素:\n",i);
scanf("%d",&temp_e);
EnQueue(Q,temp_e);
}
return 0;
}
//返回队列长度
int QueueLength(CSqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.rear-Q.front+MAX)%MAX;
}
//返回队首元素的值
int GetHead(CSQqueue Q,ElemType *e)
{
if(QueueEmpty(Q))
{
return-1;
}
*e=Q.data[Q.front];
return 0;
}
//入队的实现-队尾插入新元素
int EnQueue(CSqQueue *Q,ElemType *e)
{
if(QueueEmpty(*Q))
{
return-1;
}
(*Q).data[(*Q).rear]=e;
(*Q).rear=((*Q).rear+1)%MAX;
return 0;
}
//出队的实现-删除队首,并用变量e返回被删除元素
int DeQueue(CSqQueue *Q,ElemType *e)
{
if(QueueEmpty(*Q))
{
return-1;
}
e=(*Q).data[(*Q).front)];
(*Q).front=((*Q).front+1)%MAX;
return 0;
}
//打印运算的实现-输出队列Q
void ShowQueue(CSqQueue Q)
{
ElemType temp_e;
while (!=QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q,&temp_e);
printf("%d",temp_e)
}
printf("\n");
}