目录
- 栈:先进后出
- 队列:先进先出
1. 实现栈(数组)
MyStack.java
public class MyStack {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public MyStack() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//判断是否栈满
public boolean isFull() {
if (this.usedSize == this.elem.length) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//push
public void push(int item) {
if(isFull()) {
//扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = item;
this.usedSize++;
}
//pop
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空了!");
}
int val = this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
this.usedSize--;
return val;
}
//peek
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空了!");
}
return this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
}
//判断为空
public boolean empty() {
if(this.usedSize == 0) return true;
return false;
}
}2. 实现队列(链式)
MyQueueLinked.java
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class MyQueueLinked {
private Node front;
private Node rear;
private int usedSize = 0;
//入队列
public void offer(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if (this.front == null) {
this.front = node;
this.rear = node;
} else {
this.rear.next = node;
this.rear = node;
}
this.usedSize++;
}
//出队头元素
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
int val = this.front.data;
if(this.front.next == null) {
//只有一个结点
this.front = null;
this.rear = null;
} else {
this.front = this.front.next;
}
this.usedSize--;
return val;
}
//得到队头元素
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
return this.front.data;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
}3. 实现循环队列
MyCircularQueue.java
public class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int usedSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1];
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
this.elem[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear+1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
//出队
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.front = (this.front+1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
//得到对头元素
public int Front() {
if ((isEmpty())) {
return -1;
}
return this.elem[this.front];
}
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
if (this.rear == 0) {
return this.elem[this.elem.length-1];
}
return this.elem[this.rear-1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.front == this.rear) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isFull() {
if((this.rear+1) % this.elem.length == this.front) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}4. LeetCode习题
4.1 括号匹配问题
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:先判断是否为空、s.length()是否为0或奇数。
然后变量字符串,如果为左括号,则push进栈,如果为右括号,则与pop栈中的对比。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return true;
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if(ch == '{' ||ch == '(' ||ch == '[' ) {
stack.push(ch);
} else {
if (stack.empty()) return false;
//栈不为空
char tmp = stack.peek();
if(ch == '}' && tmp == '{' ||ch == ')' && tmp == '(' ||ch == ']' && tmp == '[') {
stack.pop();
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
if (!stack.empty()) return false;
return true;
}
}4.2 用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
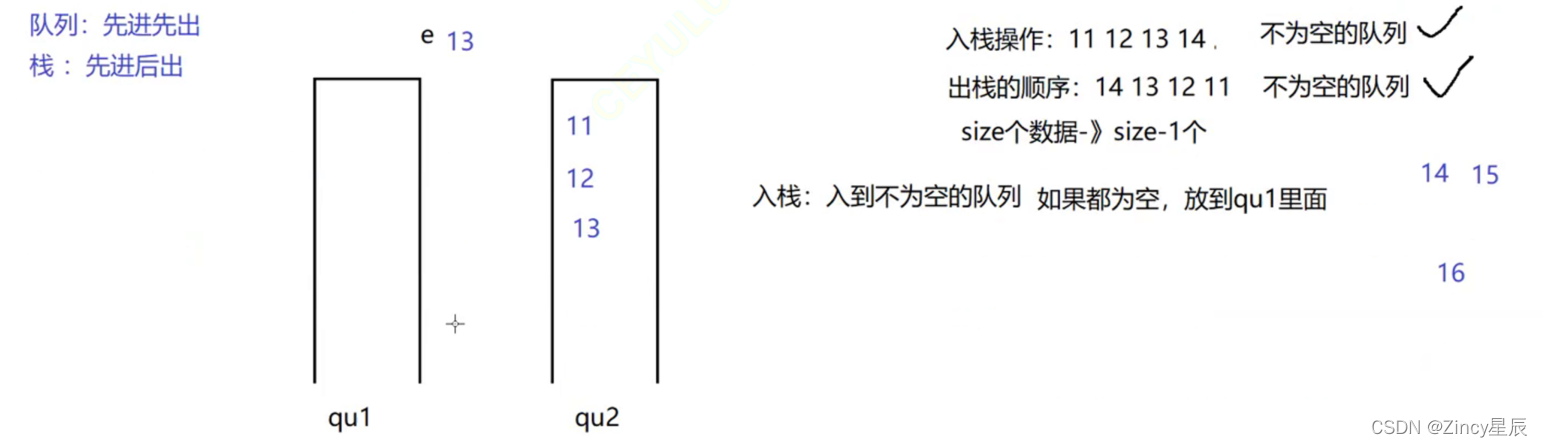
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
private Queue<Integer> qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
public MyStack() {
}
//入栈
public void push(int x) {
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
} else if (!qu2.isEmpty()){
qu2.offer(x);
} else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
if(empty()) return -1;
int e = -1;
if (!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size -1; i++) {
e = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(e);
}
e = qu1.poll();
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size -1; i++) {
e = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(e);
}
e = qu2.poll();
}
return e;
}
//得到栈顶元素,不删除
public int top() {
if(empty()) return -1;
int e = -1;
if (!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
e = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(e);
}
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
e = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(e);
}
}
return e;
}
//是否为空
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}4.3?用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
一个栈用来入,另一个栈用来出
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x); //指定push到第一个栈
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()) return -1;
if (s2.empty()) {
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (empty()) return -1;
if (s2.empty()) {
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
}4.4 实现一个最小栈
155. 最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
两个栈,一个正常栈,另一个栈存储最小值
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
public MinStack() {
}
public void push(int val) {
s1.push(val);
if (s2.empty() || val <= s2.peek()) {
s2.push(val);
}
}
public void pop() {
int val = s1.pop();
if(!s2.empty() && s2.peek()==val) {
s2.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
if(!s1.empty()) {
return s1.peek();
}
return 0;
}
public int getMin() {
if(!s2.empty()) {
return s2.peek();
}
return 0;
}
}