1. 双向链表
与单链表相比,双向链表有两个指针域,既可以保存右边节点的地址(后继),也可以保存左边的节点地址(前驱)。
2. 双向链表图
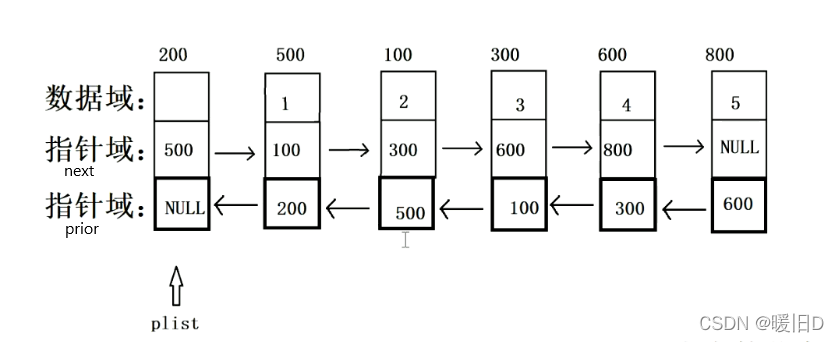
其中:next指针域,保存下一个节点的地址(后继), prior指针域, 保存上一个节点的地址(前驱)
3. 双向链表可执行函数
注意:头插:① 插入新节点时,一般情况下,需要修改4给我指针域:自身的next和prior;上一个节点的next;下一个节点的prior;如
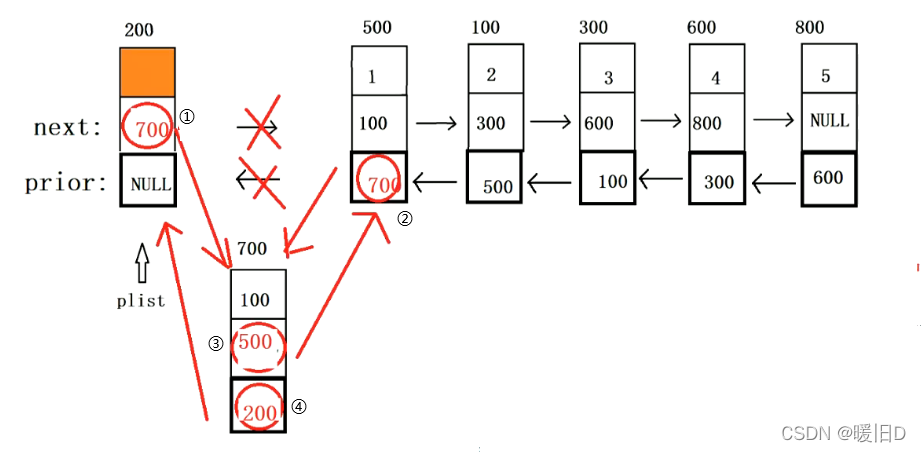
?调整规则:③④②①
第一次:先修改pnewnode自身的next域和prior域
第二次:再修改后一个节点的前驱
第三次:最后修改前一个节点的后继
代码为:
pnewnode->next=plist->next;
pnewnode->prior=plist;
plist->next->prior=pnewnode;
plist->next=pnewnode;
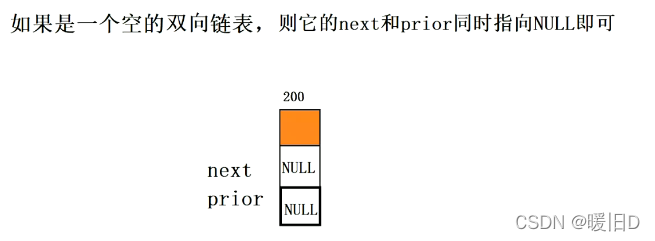
注意:如果是给空的双向链表进行头插,那么上述第三行代码不一定能实现,要特殊处理、
4. 代码
Dlist.h文件
#pragma once
//双向链表结构体设计
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
typedef struct Dlist
{
ELEM_TYPE data; //数据域 保存有效值
struct Dlist* next; //指针域 保存下一个节点的地址(后继)
struct Dlist* prior; //指针域 保存上一个节点的地址(前驱)
}Dlist,*PDlist;
//双向链表可执行函数声明
//初始化
void Init_dlist(struct Dlist* plist);
//购买新节点
struct Dlist* Buynewnode(ELEM_TYPE val);
//头插
bool Insert_head(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//尾插
bool Insert_tail(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PDlist plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val);
//头删
bool Del_head(PDlist plist );
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PDlist plist);
//按位置删除
bool Del_pos(PDlist plist, int pos);
//按值删
bool Del_val(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//查找 (如果值重复,返回第一个值的下标)
struct Dlist* Search(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PDlist plist);
//判满(链表不用,因为要用malloc)
//获取有效长度
int GetLength(PDlist plist);
//清空
void Clear(PDlist plist);//链表里面的清空直接调用销毁就可以
//销毁1
void Destroy(PDlist plist);
//销毁2
void Destroy2(PDlist plist);
//打印
void Show(PDlist plist);
Dlist.cpp文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"Dlist.h"
//初始化
void Init_dlist(struct Dlist* plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return;
}
plist->next = NULL;
plist->prior = NULL;
}
//购买新节点
struct Dlist* Buynewnode(ELEM_TYPE val)
{
assert(val != NULL);
struct Dlist* pnewnode = (struct Dlist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Dlist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
if (pnewnode == NULL)//购买失败
{
return NULL;
}
pnewnode->data = val;
pnewnode->next = NULL;
pnewnode->prior = NULL;
return pnewnode;
}
//头插
bool Insert_head(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//1.购买新节点、
struct Dlist* pnewnode = (struct Dlist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Dlist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
if (pnewnode == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pnewnode->data = val;
pnewnode->next = NULL;
pnewnode->prior = NULL;
//2.找到合适的插入位置
// 头插不用找,因为plist就指向插入位置的上一个节点
//3.插入
pnewnode->next = plist->next;
pnewnode->prior = plist;
if (plist->next != NULL)
{
pnewnode->next->prior = pnewnode;//为空的话,pnewnode->next->prior 没有,这条代码失败
}
plist->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//尾插 尾插的话,下一个节点肯定不存在,所以下一个节点的前驱这根线,不用写
bool Insert_tail(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//购买新节点
struct Dlist* pnewnode = (struct Dlist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Dlist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
if (pnewnode == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pnewnode->data = val;
pnewnode->next = NULL;
pnewnode->prior = NULL;
//找到合适的插入位置(找一个指针p指向尾节点)
struct Dlist* p = plist;
for (p; p->next != NULL; p = p->next);
//此时,for循环结束,p指向尾节点
//插入3421,这块2不用写,因为后面的节点不存在
pnewnode->next = p->next;
pnewnode->prior = p;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PDlist plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= GetLength(plist));//pos = 0,头插,pos = GetLength(plist),尾插
if (pos == 0)
{
return Insert_head(plist, val);
}
else if (pos == GetLength(plist))
{
return Insert_tail(plist, val);
}
//购买新节点
struct Dlist* pnewnode = (struct Dlist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Dlist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
if (pnewnode == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pnewnode->data = val;
pnewnode->next = NULL;
pnewnode->prior = NULL;
//找到合适插入位置 pos=(),指针p从头结点开始向后跑()
struct Dlist* p = plist;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
{
p = p->next;
}
//插入
pnewnode->next = p->next;
pnewnode->prior = p;
p->next->prior = pnewnode;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//头删
bool Del_head(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//插入不需要判满,但是删除一定记得判空
if (IsEmpty(plist))
{
return false;
}
//找个指针p指向待删除节点
struct Dlist* p = plist ->next;
//找个指针q指向待删除节点的是上一个节点
//跨越指向+释放内存
plist->next = p->next;
if (p->next != NULL)//代表不仅仅只有一个有效节点
{
p->next->prior = plist;
}
free(p);
return true;
}
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
struct Dlist* q = plist;
for (q; q->next->next != NULL; q = q->next);
//此时,for循环结束,q指向倒数第二个节点
struct Dlist* p = q->next;
//跨越指向+内存释放
q->next = p->next;//让上一个节点指向下一个节点
//让下一个节点指向上一个节点(因为是尾删,所以待删除节点后面没有加点了)
free(p);//释放待删除节点
return true;
}
//按位置删除 (一般来说,头和尾得注意,一开始处理掉)
bool Del_pos(PDlist plist, int pos)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= GetLength(plist));//pos = 0,头删,pos = GetLength(plist),尾删
if (pos == 0)
{
return Del_head( plist );
}
else if (pos == GetLength(plist)-1)
{
return Del_tail(plist );
}
//先找q再找p
struct Dlist* q = plist;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
struct Dlist* p = q->next;
q->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = q;
free(p);
return true;
}
//按值删
bool Del_val(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{
struct Dlist* p = Search(plist, val);
if (IsEmpty(p))
{
return false;
}
//再申请一个指针q,指向p的前一个节点
struct Dlist* q = plist;
for (q; q->next != p; q = q->next);
//此时,q在p的前面
//跨越指向+释放内存
q->next = p->next;
if (p->next != NULL)
{
p->next->prior = q;
}
free(p);
return true;
}
//查找 (如果值重复,返回第一个值的下标)
struct Dlist* Search(PDlist plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
for (struct Dlist* p = plist->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
if (p->data == val)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PDlist plist)
{
return plist->next == NULL;
}
//判满(链表不用,因为要用malloc)
//获取有效长度
int GetLength(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
int count = 0;
for (struct Dlist* p = plist->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
count ++;
}
return count;
}
//清空
void Clear(PDlist plist)//链表里面的清空直接调用销毁就可以
{
Destroy(plist);
}
//销毁1
void Destroy(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return ;
}
while (plist->next != NULL)
{
struct Dlist* p = plist->next;
plist->next = plist;
free(p);
}
plist->next = plist->prior = NULL;
}
//销毁2
void Destroy2(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct Dlist* p = plist->next;
struct Dlist* q = NULL;
plist->next = plist->prior = NULL;
while (p != NULL)
{
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
//打印
void Show(PDlist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return ;
}
for (struct Dlist* p = plist->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
}
printf("\n");
}主函数运行结果代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Dlist.h"
int main()
{
struct Dlist head;
Init_dlist(&head);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
Insert_pos(&head, i, i + 1);
}
Show(&head);
printf("length=%d\n", GetLength(&head));
Insert_head(&head, 100);
Insert_tail(&head, 200);
Show(&head);
printf("length=%d\n", GetLength(&head));
Del_head(&head);
Del_tail(&head);
Show(&head);
printf("length=%d\n", GetLength(&head));
Del_pos(&head,4);
Del_val(&head,14);
Show(&head);
printf("length=%d\n", GetLength(&head));
Destroy(&head);
return 0;
}
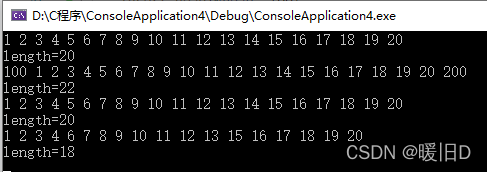
运行后如下的结果:
?