Given the?root?of a binary tree, split the binary tree into two subtrees by removing one edge such that the product of the sums of the subtrees is maximized.
Return?the maximum product of the sums of the two subtrees. Since the answer may be too large, return it?modulo?109?+ 7.
Note?that you need to maximize the answer before taking the mod and not after taking it.
Example 1:
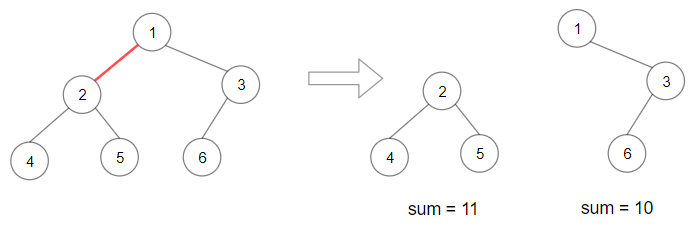
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 110 Explanation: Remove the red edge and get 2 binary trees with sum 11 and 10. Their product is 110 (11*10)
Example 2:
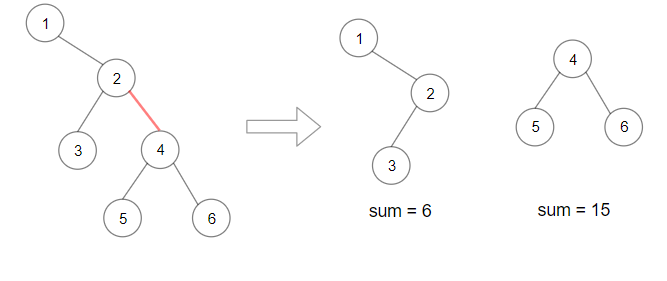
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,null,null,5,6] Output: 90 Explanation: Remove the red edge and get 2 binary trees with sum 15 and 6.Their product is 90 (15*6)
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range?
[2, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^4
题目给定一棵二叉树,要求移除树中的一条边变成两棵子树并且这两棵子树和的乘积最大。返回该最大乘积。
由于移除树中的任意一条边都将变成两棵子树,因此最直观的做法就是移除每条边算出两棵子树的和,再计算它们的乘积,从中找出乘积最大值。但是每移除一条边再计算两棵子树和,将有很大计算量,有很多的重复计算。
如果知道整棵树的和以及其中一棵子树的和,那么它们的差就是另外一棵子树的和。因此只要计算一棵子树的和,但要是每次从子树的根节点开始遍历计算子树和还是有很多重复计算。我们常用的二叉树求和是利用前序或后序遍历从底向上求得的。其实对于一个节点,把它和它的父节点的边断开,就把树分成了两棵子树,另外当前序遍历递归返回到该节点时,以该节点为根的子树和就已经计算出来了,这样把整棵树和减去该子树和就是另外一棵子树的和了。由于会遍历到树中的每个节点,也自然会包含树中的每条边。因此通过一次遍历求得整棵树的和,再通过一次遍历就可以求得所有双子树的和的乘积。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def helper(node):
if not node:
return 0
return node.val + helper(node.left) + helper(node.right)
total = helper(root)
res = 0
def helper1(node):
if not node:
return 0
nonlocal res
subSum = node.val + helper1(node.left) + helper1(node.right)
res = max(res, subSum * (total - subSum))
return subSum
helper1(root)
return res % (10 ** 9 + 7)