1 算法流程
本算法适用领域为以某种方式细化后的图像。
算法的主要思路就是将所有分支与毛刺都看成不同长度的分支,如果分支长度过短小于一定长度就认为是毛刺被去掉。每一个分支的结尾点都是一个端点。算法具体流程:
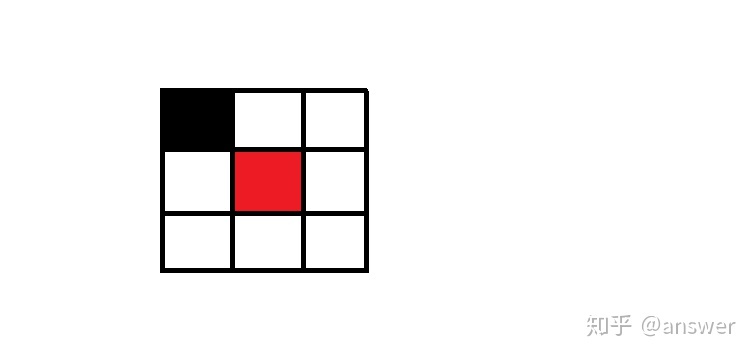
1)遍历所有连通区所有点,找到所有端点,端点的定义为其8邻域点只有一个像素点,如下图红色像素点八邻域内只有黑色点一个像素点,那么判断红色点为端点。
2)遍历每一个端点,直到遍历到该分支的起始点也就是分岔点,分岔点定义为:经过细化后,8邻域的像素点个数大于等于3的点,统计每个分支的长度,长度小于阈值T的分支被认为是毛刺分支。
3)将毛刺分支擦除。
2 代码
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//找8邻域点
int Get8NeighborPt(cv::Mat mSrc, cv::Point point, std::vector<cv::Point> &vPoint)
{
if (0 == mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point.y)[point.x])
{
return 0;
}
vPoint.clear();
cv::Point point1, point2, point3, point4, point5, point6, point7, point8;
point1.x = point.x - 1;
point1.y = point.y - 1;
int nValuePt1 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point1.y)[point1.x];
point2.x = point.x;
point2.y = point.y - 1;
int nValuePt2 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point2.y)[point2.x];
point3.x = point.x + 1;
point3.y = point.y - 1;
int nValuePt3 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point3.y)[point3.x];
point4.x = point.x - 1;
point4.y = point.y;
int nValuePt4 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point4.y)[point4.x];
point5.x = point.x + 1;
point5.y = point.y;
int nValuePt5 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point5.y)[point5.x];
point6.x = point.x - 1;
point6.y = point.y + 1;
int nValuePt6 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point6.y)[point6.x];
point7.x = point.x;
point7.y = point.y + 1;
int nValuePt7 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point7.y)[point7.x];
point8.x = point.x + 1;
point8.y = point.y + 1;
int nValuePt8 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(point8.y)[point8.x];
if (255 == nValuePt1)
{
vPoint.push_back(point1);
}
if (255 == nValuePt2)
{
vPoint.push_back(point2);
}
if (255 == nValuePt3)
{
vPoint.push_back(point3);
}
if (255 == nValuePt4)
{
vPoint.push_back(point4);
}
if (255 == nValuePt5)
{
vPoint.push_back(point5);
}
if (255 == nValuePt6)
{
vPoint.push_back(point6);
}
if (255 == nValuePt7)
{
vPoint.push_back(point7);
}
if (255 == nValuePt8)
{
vPoint.push_back(point8);
}
int nFlagEdgePt = vPoint.size();
return nFlagEdgePt;
}
//找端点
void FindTerminalPt(cv::Mat mSrc, std::vector<cv::Point> &vTerminalPt)
{
int nWidth, nHeight;
for (nHeight = 1; nHeight < mSrc.rows - 1; nHeight++)
{
for (nWidth = 1; nWidth < mSrc.cols - 1; nWidth++)
{
uchar nValuePt1 = mSrc.ptr<uchar>(nHeight)[nWidth];
cv::Point point;
point.x = nWidth;
point.y = nHeight;
std::vector<cv::Point> vPoint;
if (1 == Get8NeighborPt(mSrc, point, vPoint))
{
vTerminalPt.push_back(point);
}
}
}
}
//去毛刺统计每个分支的长度,小于阈值nTBurr的分支被认为是毛刺分支。
void RemoveBurr(cv::Mat mSrc, cv::Mat &mDst, int nTBurr = 20)
{
mDst = mSrc.clone();
std::vector<cv::Point> vTerminalPt;
FindTerminalPt(mSrc, vTerminalPt);
cv::Point LastPt, NextPt;
int nLenthBranch = 0;
bool bFlagEnd = true;
for (int nIndex = 0; nIndex < vTerminalPt.size(); nIndex++)
{
LastPt = vTerminalPt[nIndex];
NextPt = vTerminalPt[nIndex];
nLenthBranch = 0;
bFlagEnd = true;
std::vector<cv::Point> vBurrPt;
while (bFlagEnd)
{
std::vector<cv::Point> vPoint;
if (1 == Get8NeighborPt(mSrc, NextPt, vPoint))
{
vBurrPt.push_back(NextPt);
LastPt = NextPt;
NextPt = vPoint[0];
nLenthBranch++;
}
else if (2 == Get8NeighborPt(mSrc, NextPt, vPoint))
{
vBurrPt.push_back(NextPt);
if (LastPt != vPoint[0])
{
LastPt = NextPt;
NextPt = vPoint[0];
}
else
{
LastPt = NextPt;
NextPt = vPoint[1];
}
nLenthBranch++;
}
else if (3 <= Get8NeighborPt(mSrc, NextPt, vPoint))
{
bFlagEnd = false;
}
if (nLenthBranch > nTBurr)
{
bFlagEnd = false;
}
}
if (nLenthBranch < nTBurr)
{
int nIndexBurr = 0;
for (nIndexBurr = 0; nIndexBurr < vBurrPt.size(); nIndexBurr++)
{
mDst.ptr<uchar>(vBurrPt[nIndexBurr].y)[vBurrPt[nIndexBurr].x] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
cv::Mat src_bin = imread("毛刺.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
threshold(src_bin, src_bin, 120,255, THRESH_BINARY);
cv::imshow("src_bin", src_bin);
cv::Mat result;
RemoveBurr(src_bin, result);
cv::imshow("result", result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
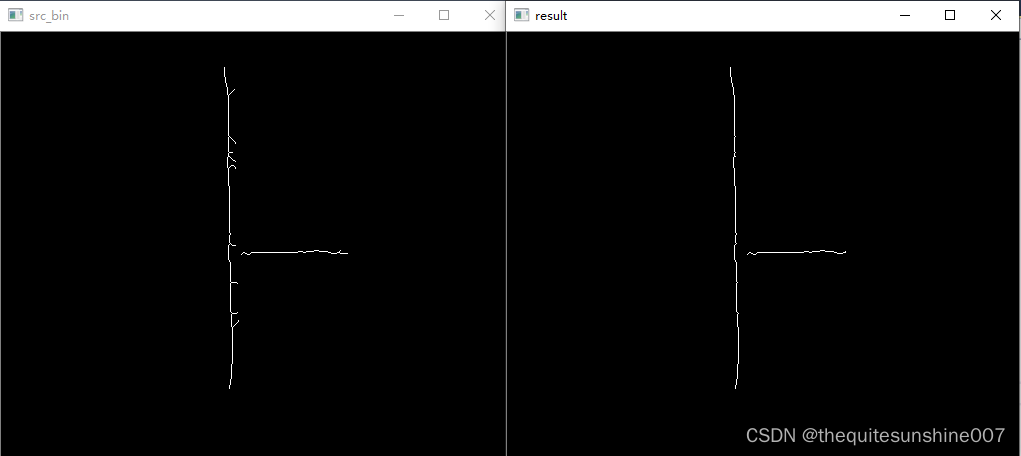
3 效果
?