一,用二个栈实现队列
用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数 appendTail 和 deleteHead ,分别完成在队列尾部插入整数和在队列头部删除整数的功能。(若队列中没有元素,deleteHead?操作返回 -1 )
示例 1:
输入:
["CQueue","appendTail","deleteHead","deleteHead"]
[[],[3],[],[]]
输出:[null,null,3,-1]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/yong-liang-ge-zhan-shi-xian-dui-lie-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
栈(stack):简单来说就是先进后出(先进入的元素,最后出来,比如给手枪压子弹的过程(先到的子弹最后打出))
使用方法:增加元素:push()? 抛出元素:pop()? 检查是否为空:isEmpty()
队列:先进先出(先进入的元素,先出来:比如排队一样(谁在前面,谁就先走))
class CQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack();
stack2 = new Stack();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.push(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if(!stack2.isEmpty()){
return stack2.pop();
}else{
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack2.pop();
}
}
}
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue obj = new CQueue();
* obj.appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj.deleteHead();
*/
二,包含main函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
使用方法:增加元素:push()? 抛出元素:pop()? ?检查是否为空:isEmpty() 查看栈顶元素:peek()
class MinStack {
Deque<Integer> stack;
Deque<Integer> minStack;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
stack = new LinkedList();
minStack = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(minStack.isEmpty() || x < minStack.peek() ){
minStack.push(x);
}else{
minStack.push(minStack.peek());
}
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.min();
*/三,从头到尾打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
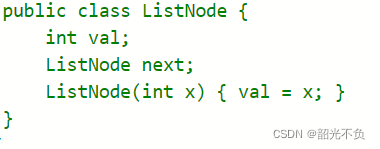
首先我们需要清楚什么是链表,链表存在一种叫节点的结构ListNode,有单项链表与双向链表.下图就是节点的属性
?当我们需要一个从头进末尾返回的结构时!我们应当考虑栈这个结构!(先进后出),还需要一个数组用来返回结果!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
//定义指针
ListNode corNode = head;
//定义一个栈
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack();
//进栈
while(corNode != null){
stack.push(corNode);
corNode = corNode.next; //!!!指针向下移动
}
int len = stack.size();
//定义数组
int[] arr = new int[len];
for(int i = 0;i < len ;i++){
arr[i] = stack.pop().val; //出栈,进入数组
}
return arr;
}
}
四,反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
递归方法:让next发生反向
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if ( head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode val = reverseList(head.next); //递归
head.next.next = head; //next指向发生反向
head.next = null; //原来指向断开
return val;
}
}五,复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fu-za-lian-biao-de-fu-zhi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
Map<Node,Node> map = new HashMap();
while(cur != null){
Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);
map.put(cur,newNode);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur= head;
while(cur != null){
Node valcur = map.get(cur);
Node nextcul = cur.next;
Node randomcul = map.get(nextcul);
valcur.next = randomcul;
Node randomkey = cur.random;
Node keyrandom = map.get(randomkey);
valcur.random = keyrandom;
cur=cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
?
六,替换空格
请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成"%20"。
示例 1:
输入:s = "We are happy."
输出:"We%20are%20happy."
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
int len = s.length();
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++ ){
if(s.charAt(i) == ' '){
count++;
}
}
int newLen = len + count*2;
char arr[] = new char[newLen];
for(int i = len-1; i >= 0 ; i--){
if(s.charAt(i) == ' '){
arr[--newLen] = '0';
arr[--newLen] = '2';
arr[--newLen] = '%';
len--;
}else{
arr[--newLen] = s.charAt(--len);
}
}
return new String(arr);
}
}七,左旋转字符串
字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。比如,输入字符串"abcdefg"和数字2,该函数将返回左旋转两位得到的结果"cdefgab"。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcdefg", k = 2
输出:?"cdefgab"
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zuo-xuan-zhuan-zi-fu-chuan-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
切换为数组进行拼接(小编第一时间想到方法):
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
int len = s.length();
char [] arr = new char[len];
int val = 0;
for(int j = n ; j < len ; j++ ){
arr[val] = s.charAt(j);
val++;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
arr[val] = s.charAt(i);
val++;
}
return new String(arr);
}
}
内置方法进行拼接:(大神方法!)
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
String start = s.substring(0,n);
String end = s.substring(n);
return end + start;
}
}
指针方法:(小编第二想到方法,效果最差)
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
String str = "";
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (i > n-1){
str+=c;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (i < n){
str+=c;
}
}
return str;
}
}
八,数组中重复的数子
找出数组中重复的数字。
在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0~n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
示例 1:
输入:
[2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3]
输出:2 或 3?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-zhong-fu-de-shu-zi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
小编第一个想到的是这个使用位运算:使用一些
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int val = 0 ;
int tmp = 0;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int len = nums.length-1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= len ; i++ ){
if(0 == (nums[tmp]^nums[i]) ){
val = nums[i];
break;
}else{
tmp++;
}
}
return val;
}
}看大神使用的是引用变量,确实比小编强!
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int val = -1;
int len = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if (nums[i] == val ){
val = nums[i];
break;
}else {
val = nums[i];
}
}
return val;
}
}小编突然想到如果二个方法和为一个方法,效率会不会提高许多呢!(效果并不理想)
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int val = -1;
int len = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if ( 0 == (nums[i] ^ val) ){
val = nums[i];
break;
}else {
val = nums[i];
}
}
return val;
}
}十,在二维数组中查找数值
在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
[
? [1, ? 4, ?7, 11, 15],
? [2, ? 5, ?8, 12, 19],
? [3, ? 6, ?9, 16, 22],
? [10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
? [18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-wei-shu-zu-zhong-de-cha-zhao-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
首先记住:二个for循环解决一个二维数组!!!
//行与列的表示
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][4];
int line = arr.length; //行
int column = arr[0].length; //列
System.out.println("行:"+line+" 列:"+column);
}
}
?好了,我们来看看题目在二维数组中查找一个元素,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序(从下面二维数组中就可以看见我们可以查找每一列的末尾元素(15,19,22,24,30),当末尾元素小于查找元素时(比如23,就直接找末尾二行就行),就能证明该行没有查找元素(从右上角开始和右下脚开始都行),大大提高查找速度!!!)
[
? [1, ? 4, ?7, 11, 15],
? [2, ? 5, ?8, 12, 19],
? [3, ? 6, ?9, 16, 22],
? [10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
? [18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0){
//考虑特殊情况
return false;
}
int line = matrix.length; //行
int column = matrix[0].length; //列
//创建查找的指针,从左上角开始查找(第一行末尾开始)
int findLine = 0;
int findColumn = column-1;
while(line-1 >= findLine && findColumn >= 0){
//开始循环遍历
if(target == matrix[findLine][findColumn]){
return true;
}else if(target > matrix[findLine][findColumn]){
//目标比查找值末尾还大,向下一行前进
findLine ++;
}else{
//目标比查找值末尾还小,可能存在,列向前进
findColumn--;
}
}
//没有找到。返回false
return false;
}
}使用二个for循环解决
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0){
//考虑特殊情况
return false;
}
int line = matrix.length ; //行
int column = matrix[0].length; //列
//二个for循环解决问题
for(int i = 0; i < line ;i++){
for(int j = column -1 ; j >= 0 ; j--){
if(target == matrix[i][j]){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
十一,在排列数组中查找数值1
统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
输出: 2
示例?2:
输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
输出: 0
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zai-pai-xu-shu-zu-zhong-cha-zhao-shu-zi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
遍历方式:(小编第一想到方式)
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int len = nums.length;
int count = 0; //统计次数
for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++){
if(target == nums[i]){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}二分法:(提高效率方式)
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] <= target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int right = i;
// 若数组中无 target ,则提前返回
if(j >= 0 && nums[j] != target) return 0;
// 搜索左边界 right
i = 0; j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] < target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int left = j;
return right - left - 1;
}
}十二,0~n中缺失的数子
一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0~n-1之内。在范围0~n-1内的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。
示例 1:
输入: [0,1,3]
输出: 2
示例?2:
输入: [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9]
输出: 8
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/que-shi-de-shu-zi-lcof
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
位运算:(将缺少数数组+不少数的数组相结合,相同异或(^)为0,并且异或存在交换定理,0与任何数异或为它本身!)
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int len1 = nums.length;
int val = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int [] arr = new int[(2*len1)+1];
int len2 = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len2 ; i++) {
if (i < len1){
arr[i] = nums[i];
}else {
arr[i] = tmp;
tmp++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < len2 ; i++) {
val =val^arr[i];
}
return val;
}
}