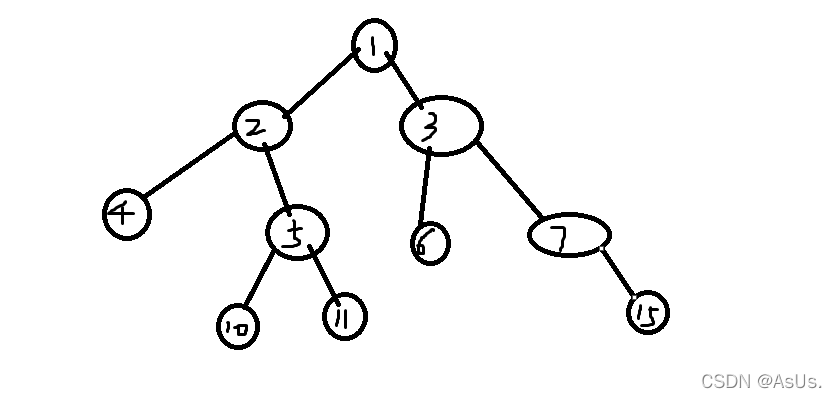
借用一下dalao的题干

输入样例:
8
6 8 7 4 5 1 3 2
8 5 4 7 6 3 2 1
输出样例:
R: 1 2 3 4 5
L: 1 6 7 8 5
根据后续和中序正常建树,然后维护每一层的编号最大值和最小值,左边看就是输出每一层最小的那个节点,右边看就是每一层输出最大的那个节点
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=110;
int n;
int in[N],post[N];
int two[30];
map<int,int>tree;
map<int,int>l,r;
void creat(int l1,int r1,int l2,int r2,int id){
if(l1<=r1&&l2<=r2){
int p=post[r2];
int i;
tree[id]=p;
for(i=l1;i<=r1;i++){
if(in[i]==p) break;
}
creat(l1,i-1,l2,l2+i-l1-1,id*2);
creat(i+1,r1,r2-(r1-i),r2-1,id*2+1);
}
}
int main(){
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) two[i]=(1<<i)-1;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>in[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>post[i];
creat(1,n,1,n,1);
int pos=1;
for(auto it:tree){
int i1=it.first;
while(i1>two[pos]) pos++;
if(l[pos]==0) l[pos]=i1;
else l[pos]=min(l[pos],i1);
r[pos]=max(r[pos],i1);
}
cout<<"R: ";
int i=1;
for(auto it:r){
if(i==1) cout<<tree[it.second];
else cout<<" "<<tree[it.second];
i++;
}
puts("");
cout<<"L: ";
i=1;
for(auto it:l){
if(i==1) cout<<tree[it.second];
else cout<<" "<<tree[it.second];
i++;
}
return 0;
}