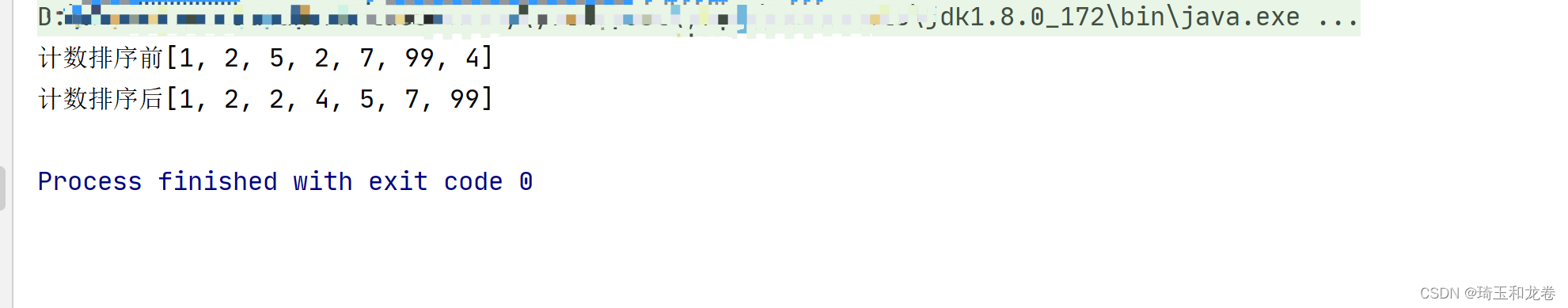目录
-
简单介绍计数排序
计数排序是一个非基于比较的排序算法,该算法于1954年由 Harold H. Seward 提出。它的优势在于在对一定范围内的整数排序时,它的复杂度为Ο(n+k)(其中k是整数的范围),快于任何比较排序算法。 [1] 当然这是一种牺牲空间换取时间的做法,而且当O(k)>O(nlog(n))的时候其效率反而不如基于比较的排序(基于比较的排序的时间复杂度在理论上的下限是O(nlog(n)), 如归并排序,堆排序)
-
代码
实现计数排序(非比较排序,牺牲空间弥补时间)
1. 优点:比较快,通常快于其它排序算法
2. 缺点:需要知道元素范围,并且元素的范围不能太大,否者失去优点
注:计数排序是需要获取数组的最大值和最小值,假如条件没给出,可能还需要自己写个循环,里面同时比较最大和最小,然后才能知道存储计数的数组的大小
注:我这里以0-100的数为例 max - min +1
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,5,2,7,99,4};
System.out.println("计数排序前" + Arrays.toString(arr));
countingSort(arr);
System.out.println("计数排序后" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void countingSort(int[] arr) {
int[] temp = new int[101];
// 计数
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp[arr[i]]++;
}
// 将临时数组中数据依次放回原数组
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
// 多个数的话,index++
while (temp[i]-- > 0) {
arr[index++] = i;
}
}
}
-
结果