目录
leetcode每日一题
417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
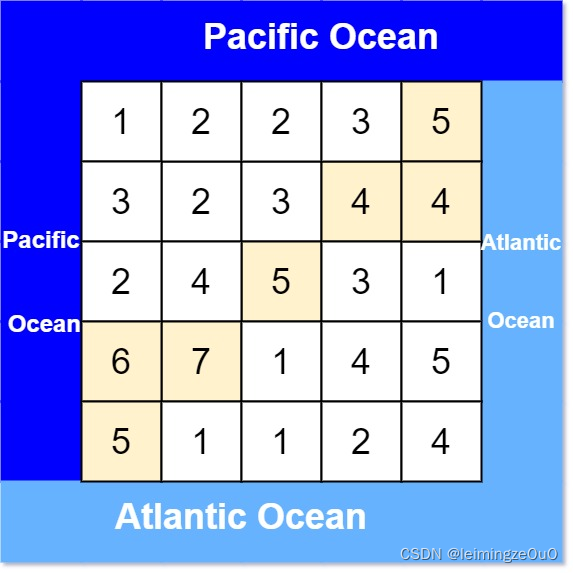
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回 网格坐标 result 的 2D列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水可以从单元格 (ri, ci) 流向 太平洋和大西洋 。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>>heights;
int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0};
int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
void dfs(int x,int y,vector<vector<bool>>&ocean)
{
ocean[x][y]=true;
int m=ocean.size();
int n=ocean[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int a=dx[i]+x,b=dy[i]+y;
if(a<0||a>=m||b<0||b>=n)continue;
if(ocean[a][b])continue;
if(heights[a][b]<heights[x][y])continue;
ocean[a][b]=true;
dfs(a,b,ocean);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
this->heights=heights;
int m=heights.size();
int n=heights[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>>pacific(m,vector<bool>(n,false)),atlantic(m,vector<bool>(n,false));
vector<vector<int>>res;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)dfs(i,0,pacific);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)dfs(0,i,pacific);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)dfs(i,n-1,atlantic);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)dfs(m-1,i,atlantic);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(pacific[i][j]&&atlantic[i][j])
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(i),v.push_back(j);
res.push_back(v);
}
return res;
}
};
Codeforces Round #783 (Div. 2)
A. Direction Change
You are given a grid with n rows and m columns. Rows and columns are numbered from 1 to n, and from 1 to m. The intersection of the a-th row and b-th column is denoted by (a,b).
Initially, you are standing in the top left corner (1,1). Your goal is to reach the bottom right corner (n,m).
You can move in four directions from (a,b): up to (a?1,b), down to (a+1,b), left to (a,b?1) or right to (a,b+1).
You cannot move in the same direction in two consecutive moves, and you cannot leave the grid. What is the minimum number of moves to reach (n,m)?
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤103) — the number of the test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n and m (1≤n,m≤109) — the size of the grid.
Output
For each test case, print a single integer: ?1 if it is impossible to reach (n,m) under the given conditions, otherwise the minimum number of moves.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int _;
int n,m;
void solve()
{
cin>>n>>m;
if(n<m)swap(n,m);
if(m==1&&n>=3)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
}
else
{
if((n+m)%2==0)
{
cout<<2*(m-1)+2*(n-m)<<endl;
}
else cout<<2*(m-1)+2*(n-m-1)+1<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>_;
while(_--)solve();
return 0;
}
B. Social Distance
m chairs are arranged in a circle sequentially. The chairs are numbered from 0 to m?1. n people want to sit in these chairs. The i-th of them wants at least a[i] empty chairs both on his right and left side.
More formally, if the i-th person sits in the j-th chair, then no one else should sit in the following chairs: (j?a[i])modm, (j?a[i]+1)modm, … (j+a[i]?1)modm, (j+a[i])modm.
Decide if it is possible to sit down for all of them, under the given limitations.
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤5?104) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n and m (2≤n≤105, 1≤m≤109) — the number of people and the number of chairs.
The next line contains n integers, a1, a2, … an (1≤ai≤109) — the minimum number of empty chairs, on both sides of the i-th person.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases will not exceed 105.
Output
For each test case print “YES” (without quotes) if it is possible for everyone to sit down and fulfil the restrictions, and “NO” (without quotes) otherwise.
You may print every letter in any case you want (so, for example, the strings “yEs”, “yes”, “Yes” and “YES” will all be recognized as positive answers).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int _;
int n,m;
void solve()
{
cin>>n>>m;
long long sum=0,maxv=0,minv=1e9;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
long long x;
cin>>x;
sum+=x;
minv=min(minv,x);
maxv=max(maxv,x);
}
if(n+sum+maxv-minv<=m)puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
int main()
{
cin>>_;
while(_--)solve();
return 0;
}
C. Make it Increasing
You are given an array a consisting of n positive integers, and an array b, with length n. Initially bi=0 for each 1≤i≤n.
In one move you can choose an integer i (1≤i≤n), and add ai to bi or subtract ai from bi. What is the minimum number of moves needed to make b increasing (that is, every element is strictly greater than every element before it)?
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (2≤n≤5000).
The second line contains n integers, a1, a2, …, an (1≤ai≤109) — the elements of the array a.
Output
Print a single integer, the minimum number of moves to make b increasing.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=5010;
int a[N];
int _;
int n;
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
long long res=1e18;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
long long pre=0,sum=0;
for(int j=i-1;j>=1;j--)
{
pre+=a[j]-pre%a[j];
sum+=pre/a[j];
}
pre=0;
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
{
pre+=a[j]-pre%a[j];
sum+=pre/a[j];
}
res=min(res,sum);
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
