一、特性及常用操作
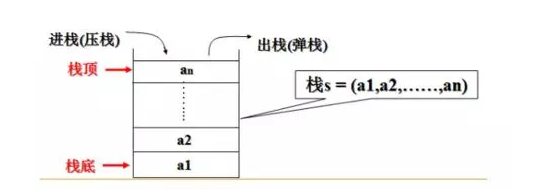
????????栈是一个动态集合,作为数据结构中的一种基本数据类型,其实现了一种后进先出(last-in,firtst-out,缩写LIFO)的策略。
????????作用与栈上的insert操作常称为入栈(push),无参数的delete操作常称为出栈(pop)。栈结构类似于我们生活中厨房存放的盘子,最后放入(push)的盘子则在一层层盘子的最顶端。当我们需要使用盘子时,第一个取出(pop)也是放在最顶端位置的盘子。
二、两种实现
1,使用数组实现
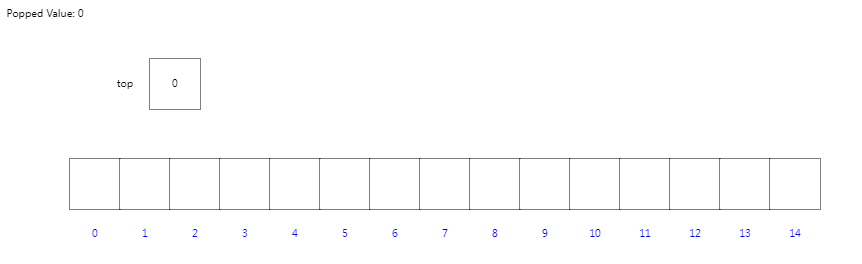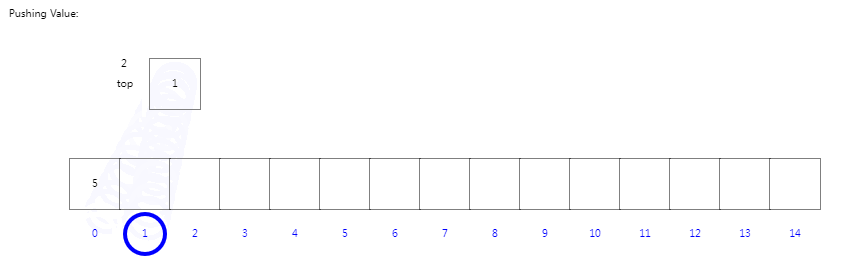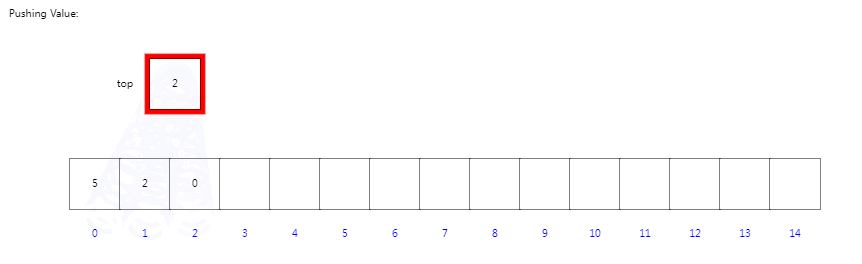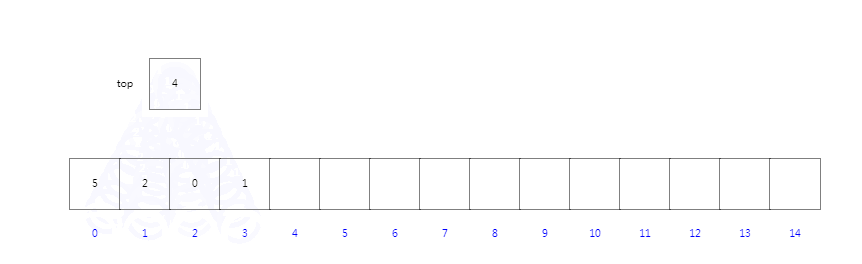
????????我们定义一个容器大小为15的数组,并定义一个指向下一个入栈位置的索引top,初次索引位置为0。当我们入栈操作时,将入栈对象放置在top指向位置,完成后top索引进行+1。当我我们依次入栈5201后top为第五个位置角标4;
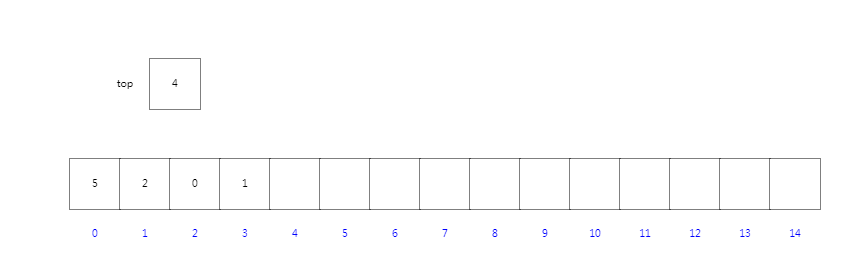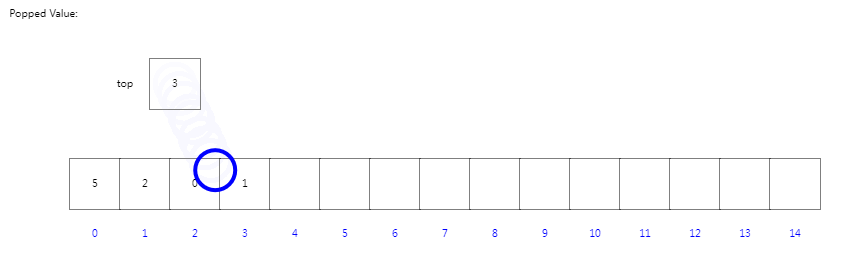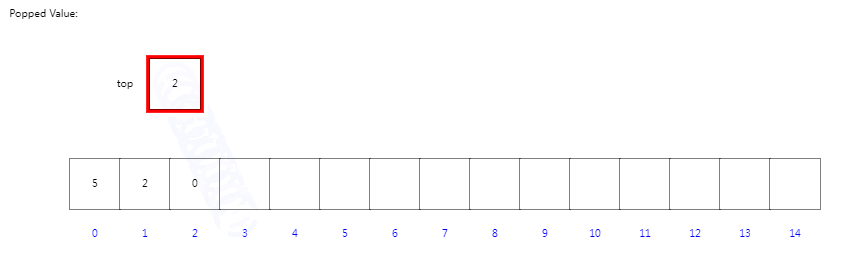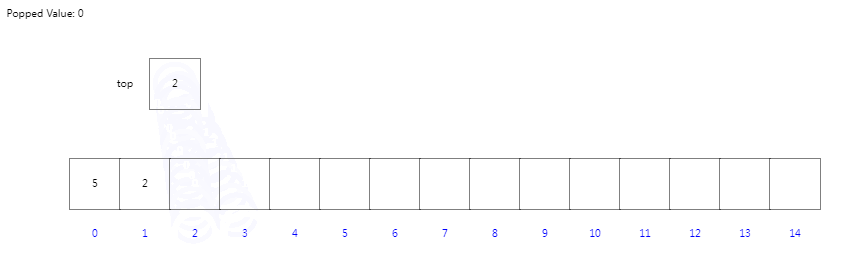
当我们进行出栈时,索引top先进行-1后指向当前栈顶元素,然后返回当前栈顶元素。
入栈操作
出栈操作
代码实现(不考虑容器溢出问题)
自定义栈实现类 MyStackUseArray
package com.xiaohui.basics.stack.array;
/**
* 自定义栈,array实现(不考虑角标越界问题)
* @author huizi
*/
public class MyStackUseArray{
/**
* 当前栈顶下一个位置角标
*/
private int index = 0;
/**
* 默认的栈容器大小
*/
private Integer[] array = new Integer[15];
/**
* 进栈操作
*
* @param val 进栈对象
* @return 进栈对象
*/
public Integer push(Integer val){
array[index++] = val;
return val;
}
/**
* 出栈操作
*
* @return Integer 栈顶元素
*/
public Integer pop(){
Integer popVal = array[--index];
array[index] = null;
return popVal;
}
}
测试类
package com.xiaohui.basics.stack;
import com.xiaohui.basics.stack.array.MyStackUseArray;
import com.xiaohui.basics.stack.linked.Node;
/**
* 自定义栈演示
*
* @author huizi
*/
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
stackArrayTest();
}
private static void stackArrayTest() {
MyStackUseArray stackUseArray = new MyStackUseArray();
stackUseArray.push(5);
stackUseArray.push(2);
stackUseArray.push(0);
stackUseArray.push(1);
Integer pop = stackUseArray.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
Integer pop2 = stackUseArray.pop();
System.out.println(pop2);
Integer pop3 = stackUseArray.pop();
System.out.println(pop3);
}
}
控制台输出:
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_131\bin\java.exe ...
1
0
2
Process finished with exit code 02,使用链表实现
? ? ? ? 使用链表结构实现则不需要指定容器大小,链表由一个个节点(包含存储值对象以及该节点的下一个节点的指针引用两部分组成)依次链接组成。根据栈的特性我们知道需要有一个记录当前栈顶元素的引用(即指针)指向当前栈顶元素top。每当入栈时我们需要将当前入栈对象的下一节点的指针修改为当前记录栈顶元素top所指向的对象。并将top指向新入栈对象。当出栈时,我们先返回top所指向对象,并将top修改为所返回对象的下一个节点指向对象。
入栈操作:

出栈操作:

代码实现
定义节点信息 Node:
package com.xiaohui.basics.stack.linked;
/**
* 节点元素对象
*
* @author huizi
*/
public class Node {
/**
* 下一个节点
*/
private Node next;
/**
* 当前节点值
*/
private Integer value;
public Node(Node next, Integer value) {
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Integer getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
?自定义栈实现:
package com.xiaohui.basics.stack.linked;
/**
* 栈使用链表实现
*
* @author huizi
*/
public class MyStackUserLinked {
/**
* 指向栈顶元素的引用
*/
private Node top = new Node(null,null);
public Node push(Node val){
// 获取当前栈顶对象,并这设置为进栈对象的下一个节点
Node next = top.getNext();
val.setNext(next);
// 将栈顶引用指向进栈对象
top.setNext(val);
return val;
}
public Node pop(){
// 获取当前栈顶元素
Node topNode = top.getNext();
// 设置新的栈顶元素
Node newTopNode = topNode.getNext();
top.setNext(newTopNode);
return topNode;
}
}
测试代码
package com.xiaohui.basics.stack;
import com.xiaohui.basics.stack.linked.MyStackUserLinked;
import com.xiaohui.basics.stack.linked.Node;
/**
* 自定义栈演示
*
* @author huizi
*/
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
stackLinkedTest();
}
private static void stackLinkedTest() {
MyStackUserLinked linkedStack = new MyStackUserLinked();
linkedStack.push(new Node(null,5));
linkedStack.push(new Node(null,2));
linkedStack.push(new Node(null,0));
linkedStack.push(new Node(null,1));
Node pop = linkedStack.pop();
System.out.println(pop.getValue());
Node pop2 = linkedStack.pop();
System.out.println(pop2.getValue());
Node pop3 = linkedStack.pop();
System.out.println(pop3.getValue());
}
}
?打印输出:
D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_131\bin\java.exe ...
1
0
2
Process finished with exit code 0