一、位运算
● ^ 可理解为不进位相加
● a^a=0
● a^0=a
题目一
一组数中,只有一个数出现的次数是奇数,其他数字出现的次数都为偶数,找出这个出现次数为奇数的数。
public static void printOddTimesNum1(int[] arr) {
int eor = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
eor ^= i;
}
System.out.println(eor);
}
题目二
一组数中,只有两个数出现的次数是奇数,其他数字出现的次数都为偶数,找出这两个出现次数为奇数的数。
因为两个数的值不同,所以两个数一定存在二进制的某一位不同,所以这两个值的异或结果的二进制中这个不同的位为1(比如说两个数第8位二进制不同,那么异或后的值的第8位为1),从而可以将数字分成两组,该位为1和不为1。
可以将所有的数分为该位为1和该位不为1的两组,这两个出现次数为奇数的数一定分别在两个组中。
public static void printOddTimesNum2(int[] arr) {
int eor = 0;
for (int cur : arr) {
eor ^= a;// 两个不同的奇数次的数异或最后得到 eor = a ^ b != 0
}
int rightOne = med & (~med + 1);// 取出 eor 二进制最右边为1(必存在,因为不同值)
int eor1 = 0;
for (int cur : arr) {
// 将对应位为 1 的值取出进行异或 最后得到对应位为1的某个奇数次数
// (cur & rightOne)== 0 得到对应位为0
if ((cur & rightOne) == rightOne) {
eor1 ^= cur;
}
}
System.out.println(eor1);// 其中一个数 a/b
System.out.println(eor ^ eor1);// 另一个数 a^b^a 或者 a^b^b
}
二、排序算法
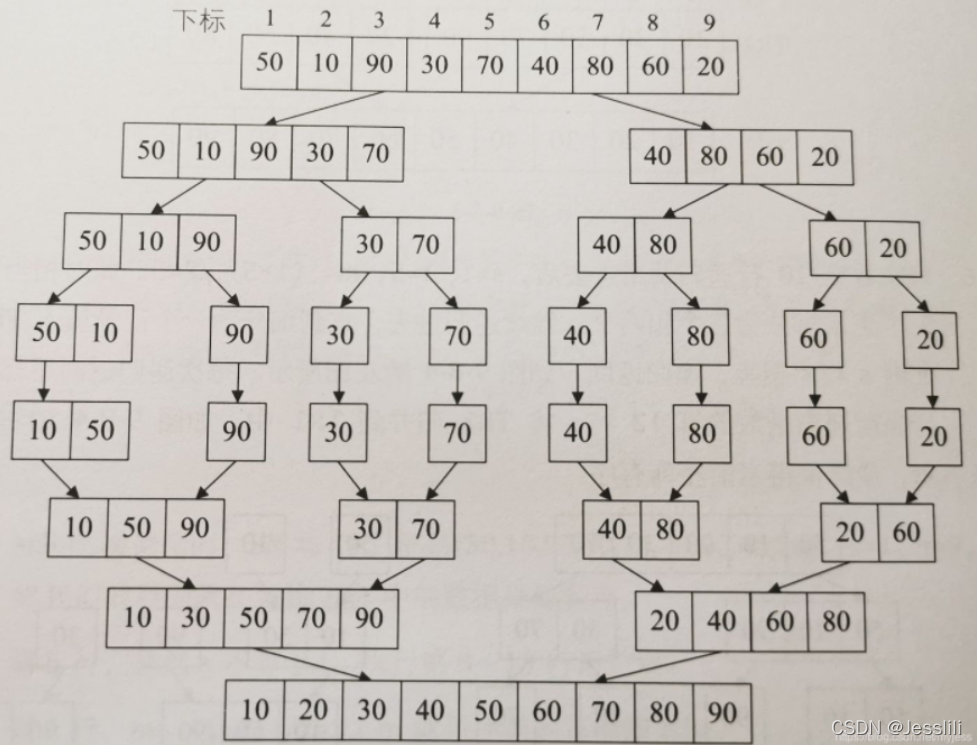
1. 归并排序
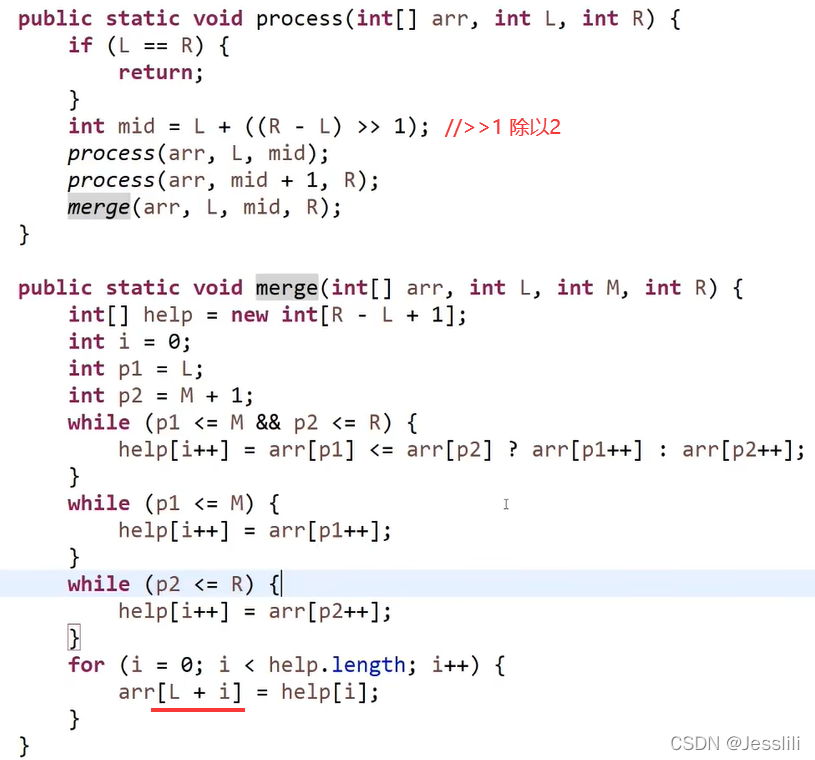
递归理解:
归并拓展题目
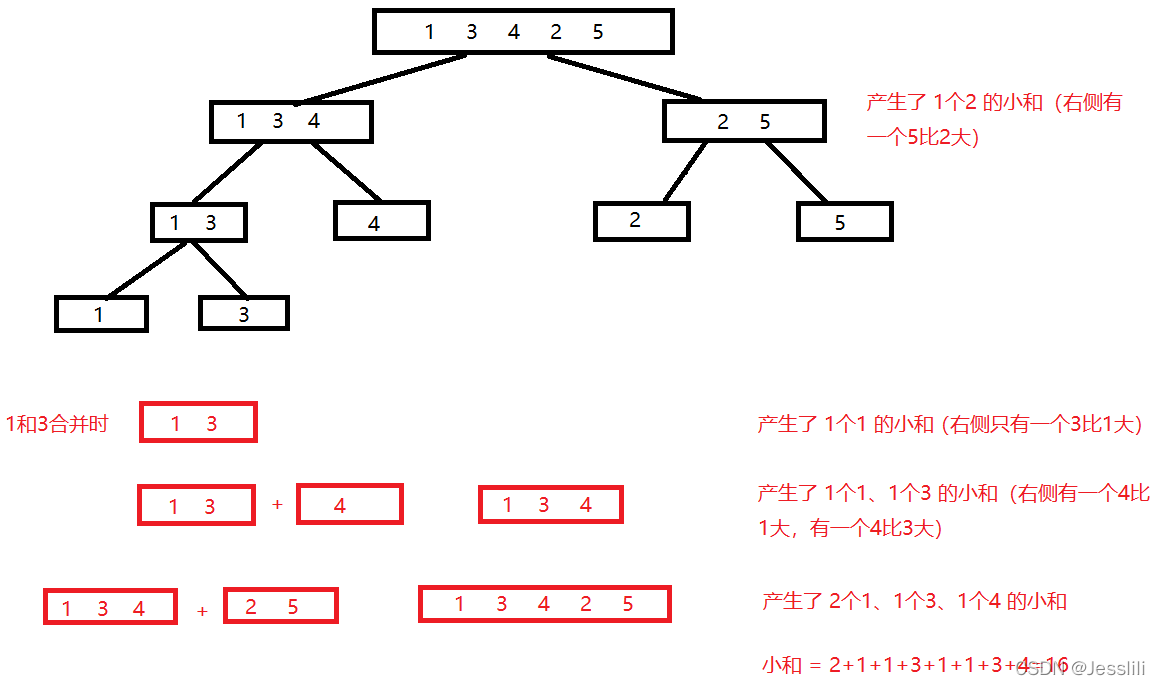
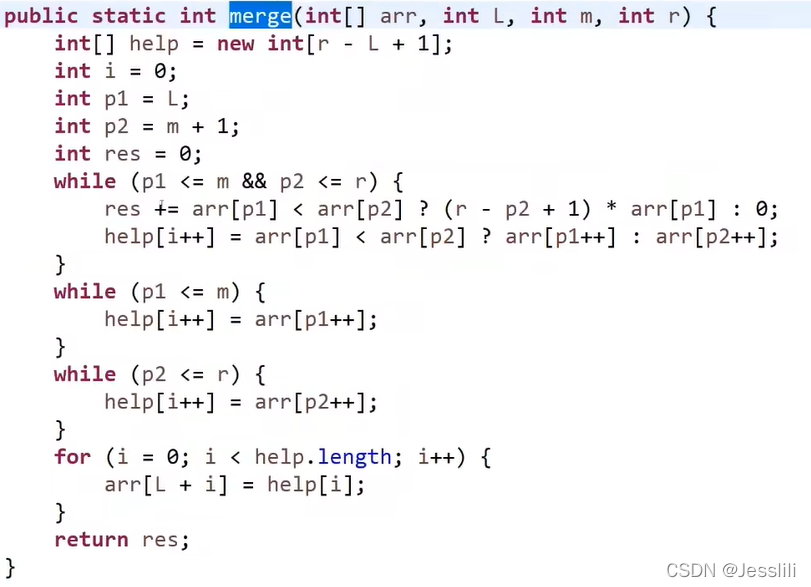
1. 小和问题

上述问题可以理解为—右边有多少个数比该数大,最后算出的小和是相同的。而求右边有多少个数比该数大的过程就可以使用归并排序。
算法思路流程:
注意:在递归时有个细节与传统归并不太一样

如果先拷贝了左边的1,就不知道右边有几个数比1大了。
代码实现:


2. 逆序对问题
在一个数组中,如果左边的数比右边的数大,则这两个数构成一个逆序对,求逆序对的个数。
例:对于[3,2,4,5,0]有[3,2]、[3,0]、[2,0]、[4,0]、[5,0]共5个逆序对。
上述问题可以理解为—右边有多少个数比该数小
2. 快速排序
-
问题1
给定一个数组 arr,和一个数num,请把小于等于num的数放在数组的左边,大于num的数放在数组的右边。要求额外空间复杂度0(1),时间复杂度O(N)。
运用了快排的思想(不是排序,不要求左边和右边的数有序)
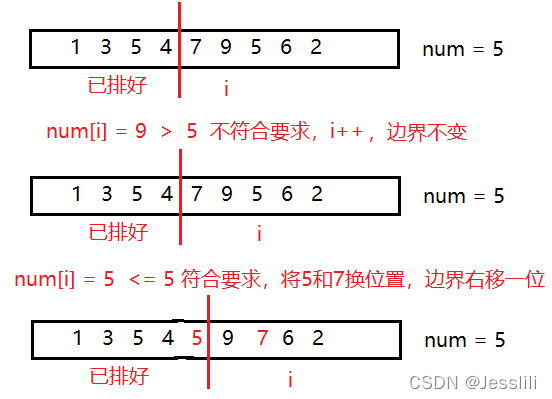
-
问题2(荷兰国旗问题)
给定一个数组 arr,和一个数num,请把小于num的数放在数组的左边,等于num的数放在中间,大于num的数放在数组的右边。要求额外空间复杂度0(1),时间复杂度O(N)。
比问题1多一个右边界,右边界>num,左边界<num
- arr[i] < num,arr[i]和小于区下一个交换,i++,小于区右扩
- arr[i] == num,i++
- arr[i] > num,arr[i]和大于区前一个交换,i 不变(当前的arr[i]值未知,需要进行比较),大于区左扩
- 当大于区和 i 撞上的时候,停止
快速排序:
● 随机任取一个元素(如:第一个)为中心
● 所有比它小的元素一律前放,比它大的一律后放,形成左右两个子表
● 对各子表重新选择中心元素并依此规则调整
● 直到每个子表的元素只剩一个
代码实现:


3. 堆排序
堆结构就是用数组实现的完全二叉树。
当前节点下标为 i,则父节点下标为 (i-1)/2、左孩子下标2i+1、右孩子下标2i+2
大顶堆:每个结点的值都大于或等于其左右孩子结点的值
小顶堆:每个结点的值都小于或等于其左右孩子结点的值
大顶堆结构示例
节点向上移动,例如:插入一个节点

节点向下移动,例如:消除值最大的节点
- 记录根节点的值(最大值)。
- 将最后一个结点a转移到根节点的位置上,heapsize - 1。
- 调整堆:从根节点a开始,在左右孩子中选出一个最大值,若最大值>根结点的值,该孩子节点交换到根结点的位子上,节点a换到孩子节点上。若a结点还有孩子节点则继续重复该操作,当a结点不在有孩子结点或者孩子结点的值<a节点时,调整完毕。

堆排序:

例题
已知一个几乎有序的数组,几乎有序是指,如果把数组排好顺序的话,每个元素移动的距离可以不超过k,并且k相对于数组来说比较小。请选择一个合适的排序算法针对这个数据进行排序。
准备一个小根堆,遍历数组。若k = 6,先遍历前7个数(0~6)建立小根堆,因为每个元素移动的距离不超过6,所以之后的数字不会出现在0的位置上,就可以知道小根堆的最小值了。取出最小值,然后再把第8个数放进小根堆,重复操作。
在 java 中,优先级队列底层就是堆结构,默认小根堆:PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();

4. 桶排序(基数排序)
先按照个位数排序,再按照十位数排序,最后按照百位数字排序。
相关博客
5. 排序总结
同样值的个体之间,如果不因为排序而改变相对次序,就是这个排序是有稳定性的;否则就没有。
● 不具备稳定性的排序:
选择排序、快速排序、堆排序
● 具备稳定性的排序:
冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序、一切桶排序思想下的排序
目前没有找到时间复杂度0(N*logN),额外空间复杂度0(1),又稳定的排序。
三、链表
1. 判断链表是否是回文结构

笔试:遍历单链表,将单链表结点放入栈中。重新遍历单链表,每次遍历一个结点就从栈中弹出一个结点,判断二者是否相等,若存在不相等的结点那就不是回文单链表。
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node tail = header;
while (tail != null) {
stack.push(tail);
tail = tail.next;
}
tail = header;
while (tail != null) {
if (stack.pop().value != tail.value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
面试(省空间):只把单链表右边的结点放进栈中,遍历左边的结点进行比对。(快慢指针)
快慢指针:快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走完链表时,慢指针走到链表中间。
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Node slow = header;
Node quick = header;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (quick.next != null && quick.next.next != null) {
stack.push(slow);
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
}
// 此时若整个链表为双数,slow指向上一半的最后一个,需要入栈slow
// 若为单数,指向中间元素,不需要入栈slow
// 单双数的判断由quick的终止条件确定
if (quick.next!=null) {
stack.push(slow);
}
slow = slow.next;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (slow.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
面试(不需要额外空间):使用快慢指针,当慢指针到中间时,将后半部分链表转向,从两头向中间进行比较,比较完后将链表还原。
public static boolean process(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return false;
}
Node slow = header;
Node quick = header;
while (quick.next != null && quick.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
}
slow=slow.next;
Node preNode=null;
Node postNode=null;
// 后半段反转
while (slow!=null) {
preNode=slow.next;
slow.next=postNode;
postNode=slow;
slow=preNode;
}
Node tailLeft=header;
Node tailRight=postNode;
boolean flag=true;
// 两边向中间判断
while (tailRight!=null) {
if (tailLeft.value!=tailRight.value) {
flag=false;
break;
}
tailLeft=tailLeft.next;
tailRight=tailRight.next;
}
Node tailNode=null;
// 后半段链表恢复
while (postNode!=null) {
preNode=postNode.next; i
postNode.next=tailNode;
tailNode=postNode;
postNode=preNode;
}
return flag;
} .
public static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
}
2. 复制含有随机指针的单链表
剑指offer 35题
笔试:使用一个hashmap结构,首先遍历链表,map的key存放原链表的节点,value存放新节点。之后再次遍历原链表,原节点的next和random指向的节点和新节点指向相同,可以通过getValue获得。
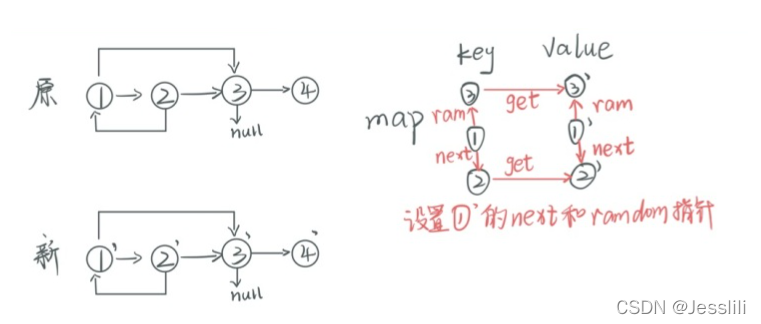
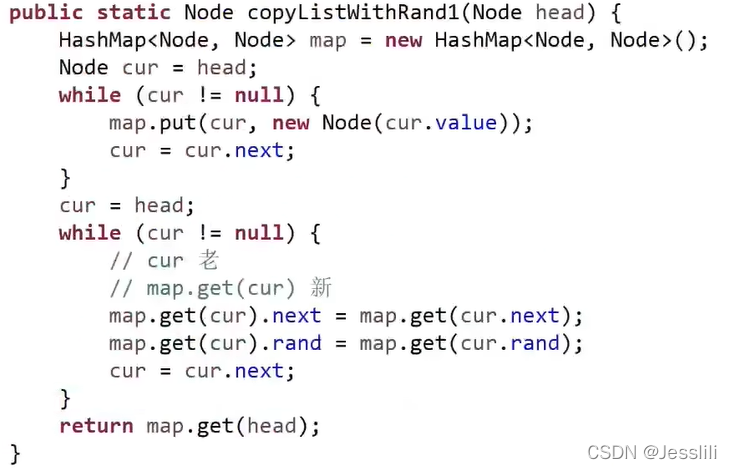
面试:遍历链表,将新节点直接添加在原节点后面,然后一对一对的取出来。新节点random指针指向的节点为原节点random指针指向节点的新节点。
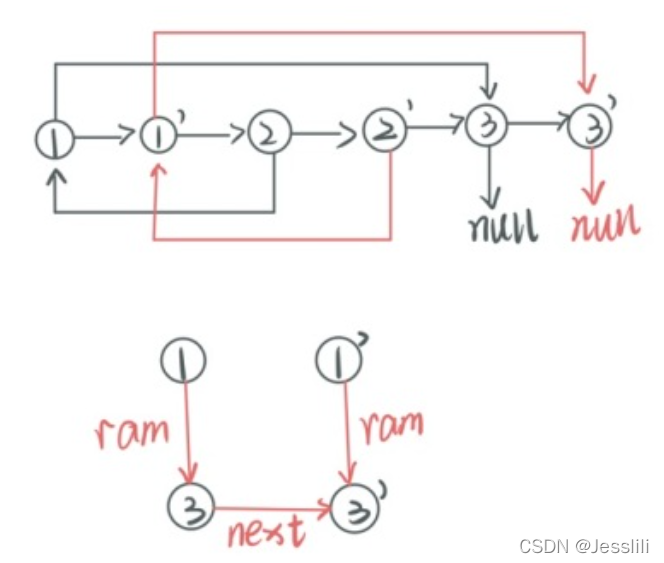
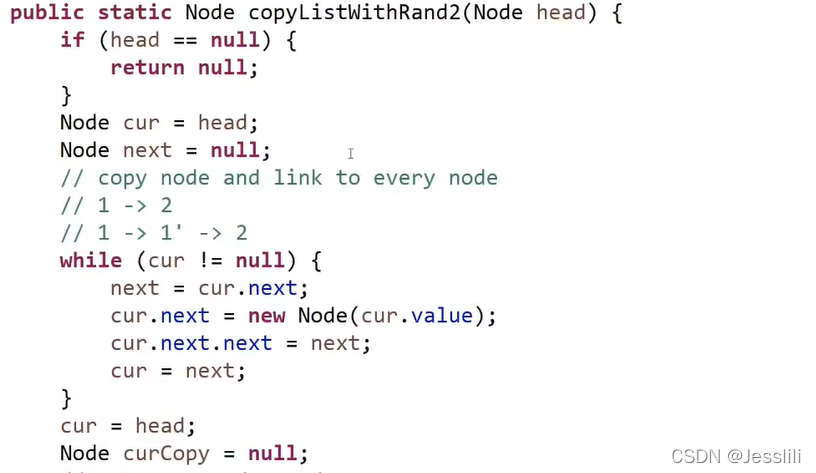
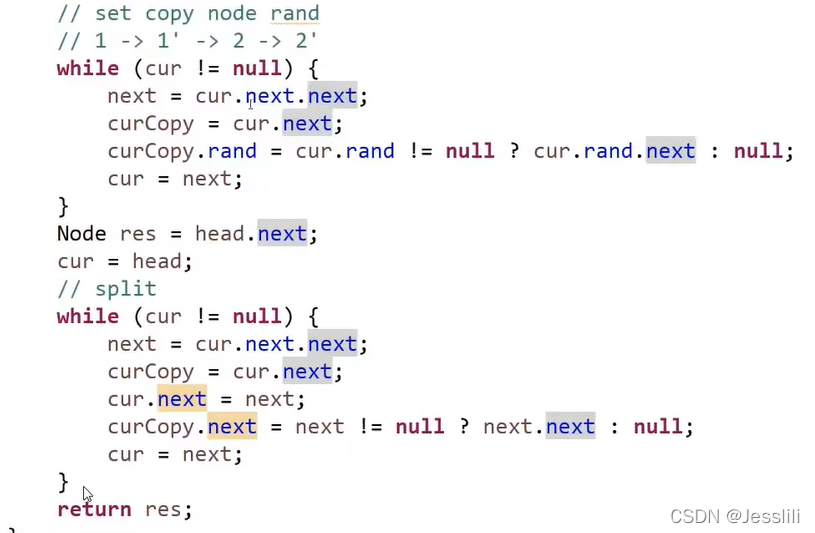
3. 两个链表相交有关问题

前置问题:判断一个链表是否有环
方法一:使用一个额外hashSet结构,遍历链表将结点添加进set中即可知道有无环
public ListNode getLoopNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos = head;
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (pos != null) {
if (visited.contains(pos)) {
return pos;
} else {
visited.add(pos);
}
pos = pos.next;
}
return null;
}
方法二:快慢指针。快指针一次两步,慢指针一次一步。当快慢指针第一次相遇时,慢指针不动,快指针回到链表头,接下来两个指针每次都走一步,再一次相遇的节点就是入环点。
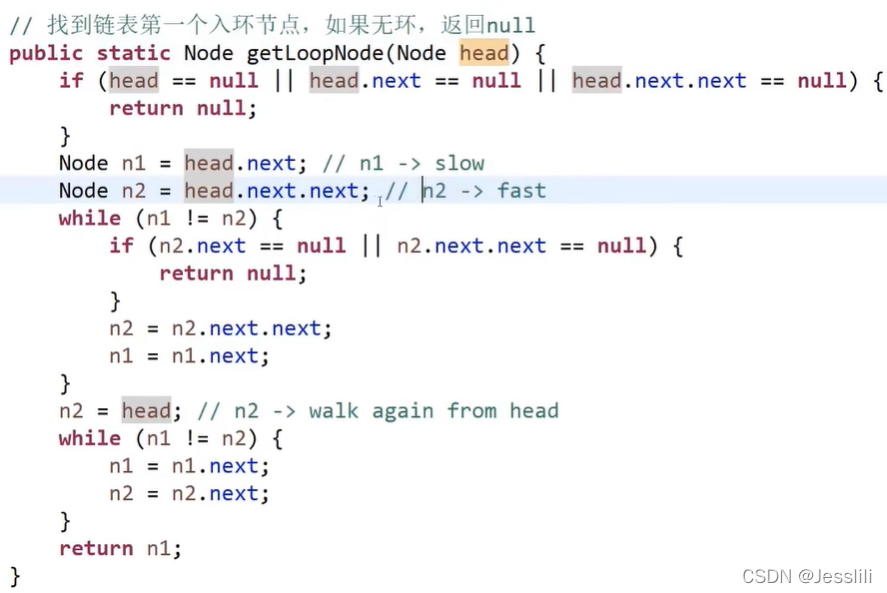
问题解析
将两个链表分别调用getLoopNode函数就,分别求出两个链表的入环节点。
- 若两个链表都无环。
- 一个有环一个无环(不可能相交)
- 两个链表都有环

//如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交,返回null
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
//计算链表长度差值
while (cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
//尾结点地址不同
if (cur1 != cur2) {
return null;
}
//谁长,谁的头为cur1
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
//谁短,谁的头为cur2
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
//长的走到和短的长度同位置
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//判断是否有相同节点,若无就会走到最后返回null
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
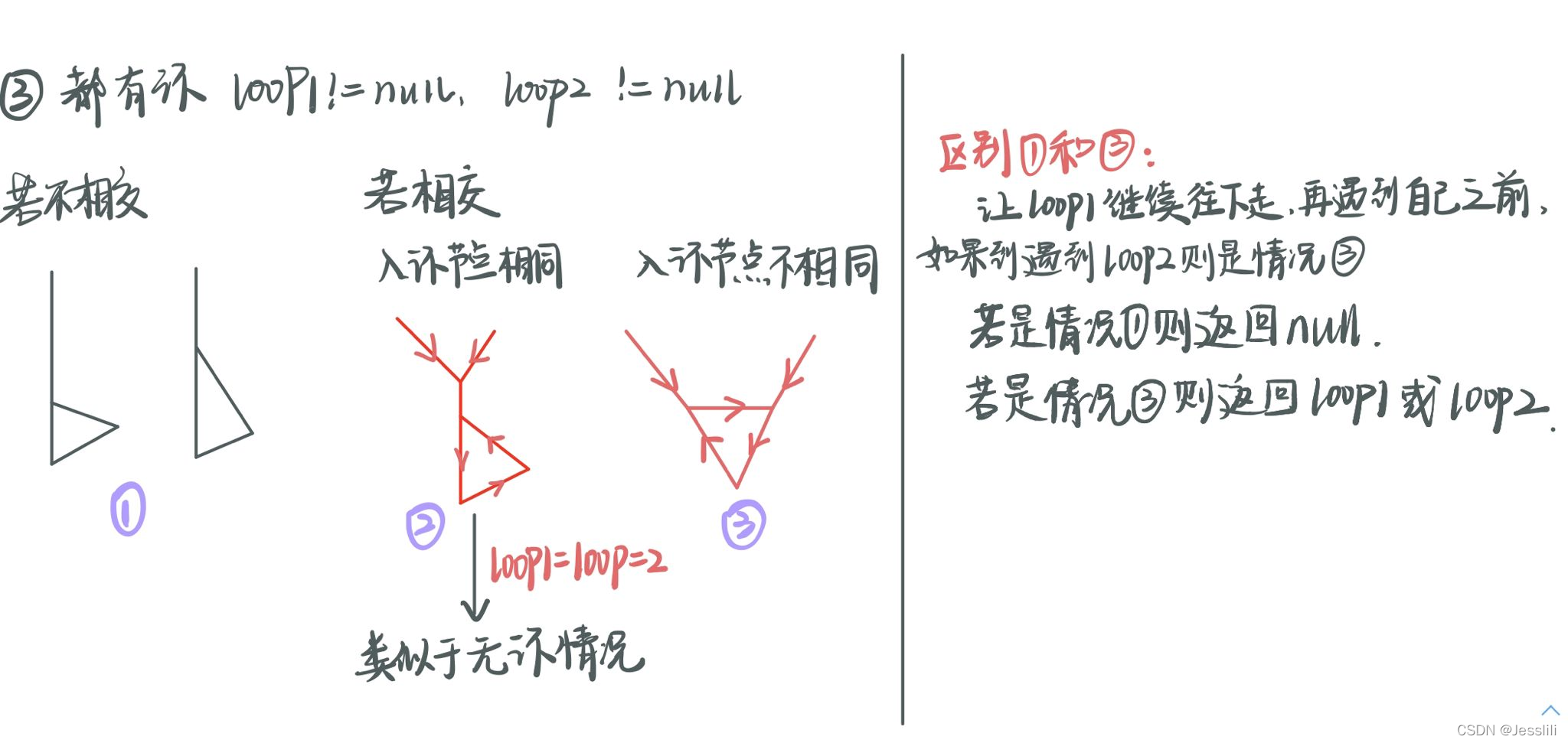
//两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不相交返回null
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
//情况2
if (loop1 == loop2) {
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
} else {
cur1 = loop1.next;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
if (cur1 == loop2) {
return loop1;//环内相交 情况3
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;//不相交 情况1
}
}
主函数:
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node loop1 = hasCircle(head1);
Node loop2 = hasCircle(head2);
if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2);//无环,判断是否为链式相交或不相交
}
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);//有环,返回相交节点
}
return null;//一有环,一无环必定不相交
}
四、二叉树
1. 非递归遍历
- 先序遍历
● 先将头结点入栈
● 每次从栈中弹出一个结点cur,处理cur。
● 先把cur的右孩子入栈,再将cur的左孩子入栈(先弹出左节点)。
● 重复操作。
public static void preOrder(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = stack.pop();
System.out.println(popNode.value);
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.rightNode);
}
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.leftNode);
}
}
}
- 中序遍历
● 先将头结点入栈
● 整棵树的左边界进栈
● 依次弹出节点并处理节点,并对弹出节点的右树重复操作
public static void inOrder(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {// 一直向左进行入栈
stack.push(head);
head = head.leftNode;
} else {// 对于每一个删除的元素要向该节点的右侧进行节点寻找遍历
head = stack.pop();
System.out.println(head.value);
head = head.rightNode;
}
}
}
- 后序遍历
● 准备两个栈。(当前栈和收集栈)
● 先将头结点入当前栈。
● 每次从当前栈中弹出一个结点cur并加入收集栈。
● 把cur的左孩子入栈,再将cur的右孩子入栈。
● 重复操作。
● 最后,收集栈全部弹出,即为后序遍历。
先右后左的先序遍历的反向就是先左后右的后序遍历。
public static void postOrder(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> postStack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 先右后左的先序遍历的反向就是先左后右的后序遍历
Node popNode = stack.pop();
postStack.push(popNode);
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.leftNode);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
stack.push(popNode.rightNode);
}
}
while (!postStack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(postStack.pop().value);
}
}
- 层序遍历
● 将头节点放入队列
● 头节点出队列并处理,将左节点入队列,再将右节点入队列。
● 重复
public static void wedthOrder(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = queue.poll();
System.out.println(popNode.value);
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
queue.add(popNode.leftNode);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
queue.add(popNode.rightNode);
}
}
}
2. 求二叉树的最大宽度
即求二叉树每一层的节点个数取最大值(在层序遍历的基础上加一个计数器)
LeetCode 其他相关题目
public static int floorMaxNodeNum(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int thisFloorNum = 0;// 该层节点个数记录
int thisFloor = 1;// 这是第几层
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
HashMap<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
queue.add(head);
map.put(head, thisFloor);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node popNode = deque.poll();
if (map.get(popNode) == thisFloor) {// 若是该层元素
thisFloorNum++;
} else {// 若已经进入下一层中的节点
max = Math.max(max, thisFloorNum);
thisFloor++;
thisFloorNum = 1;
}
// 每次添加都要在map中记录节点层数
if (popNode.leftNode != null) {
queue.add(popNode.leftNode);
map.put(popNode.leftNode, thisFloor + 1);
}
if (popNode.rightNode != null) {
queue.add(popNode.rightNode);
map.put(popNode.rightNode, thisFloor + 1);
}
}
// 这一这里还是取最大值,最后一层没有和max比较过
return Math.max(max, thisFloorNum);
}
3. 常见套路问题
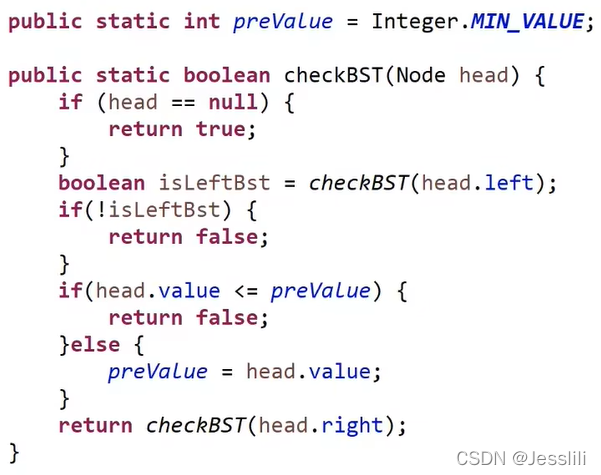
1. 判断一棵树是不是搜索二叉树
中序遍历这棵树,如果结果是升序的,则是搜索二叉树。

动态代码实现:
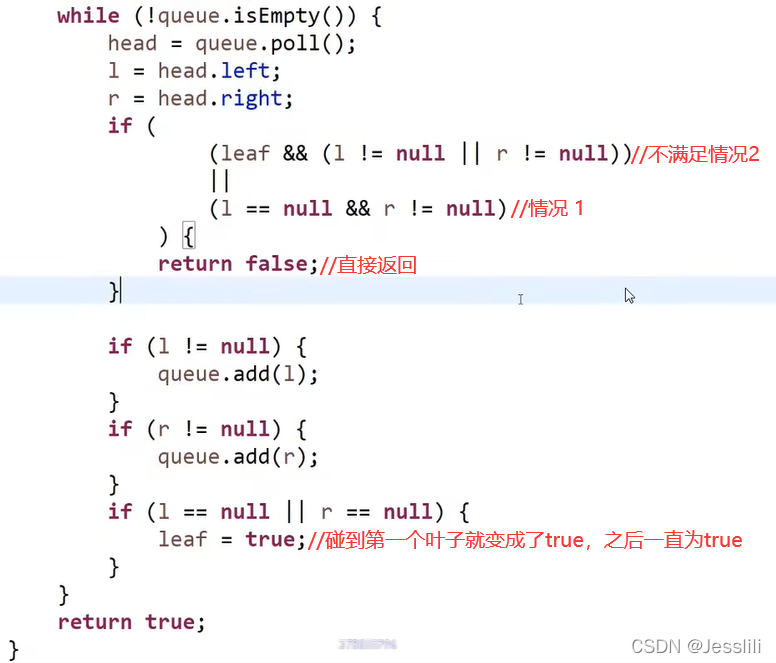
2. 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
二叉树层序遍历:
- 如果出现 一个节点有右孩子但是没有左孩子直接返回false。
- 在满足第一个条件的情况下,如果遇到第一个左右两个孩子没有同时存在的情况(即只有左孩子),那么接下来遇到的所有节点都必须是叶子节点。

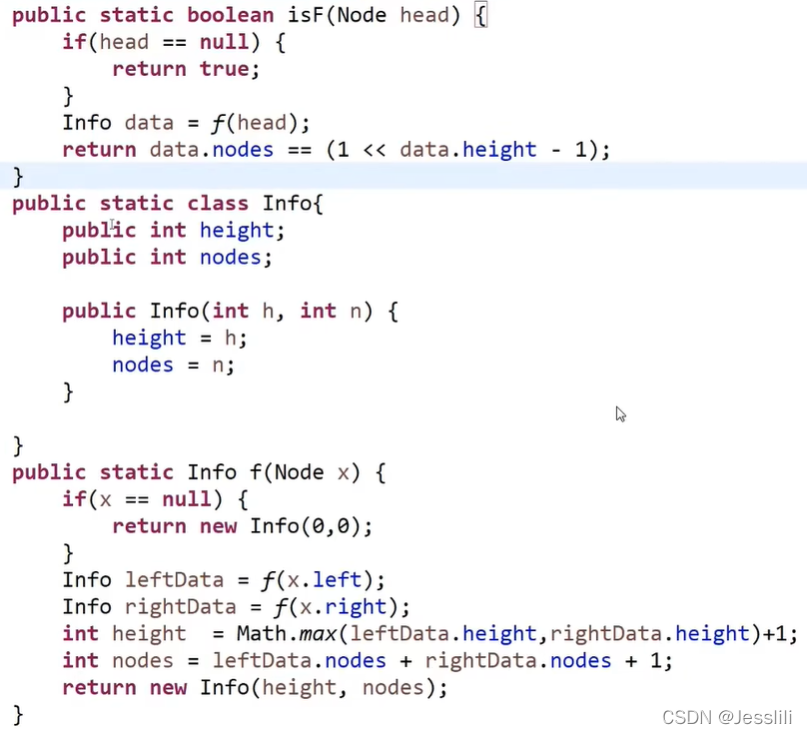
3. 判断一棵树是不是满二叉树
树形DP套路解答。(树形DP:可以通过向左右孩子获取信息来解答的问题)
满二叉树:节点个数 N 和最大深度 L 满足 N = 2 ^ L - 1
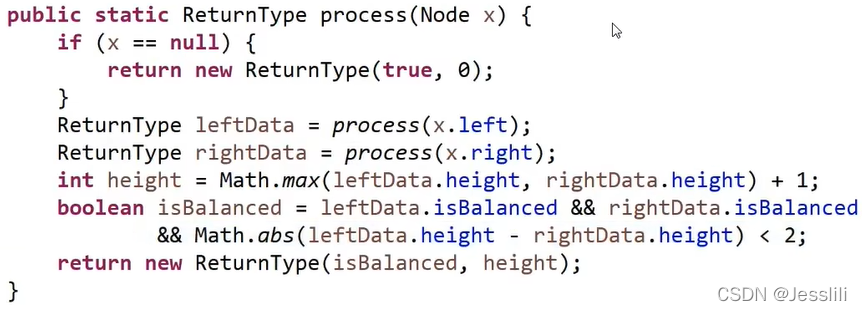
- 判断一棵树是不是平衡二叉树
- 左子树和右子树都是平衡二叉树
- |左子树高 - 右子树高| <= 1

4. 最低公共祖先节点
(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)
Leetcode 题目
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null; //如果树为空,直接返回null
// 如果p和q中有等于root的,那么它们的最近公共祖先即为root(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)
if(root == p || root == q) return root;
// 递归遍历左子树,只要在左子树中找到了p或q,则先找到谁就返回谁
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
// 递归遍历右子树,只要在右子树中找到了p或q,则先找到谁就返回谁
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
/*如果在左子树中p和q都找不到,则p和q一定都在右子树中,
右子树中先遍历到的那个就是最近公共祖先(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)*/
if(left == null) {
return right;
}
/*如果left不为空,在左子树中有找到节点(p或q),这时候要再判断一下右子树中的情况,
如果在右子树中,p和q都找不到,则p和q一定都在左子树中,
左子树中先遍历到的那个就是最近公共祖先(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)*/
else if(right == null) {
return left;
}
else {//当left和right均不为空时,说明p、q节点分别在root异侧, 最近公共祖先即为root
return root;
}
}
5. 二叉树的序列化和反序列化二叉树
Leetcode 题目
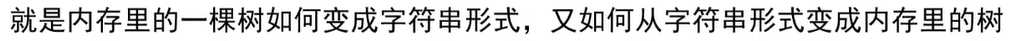
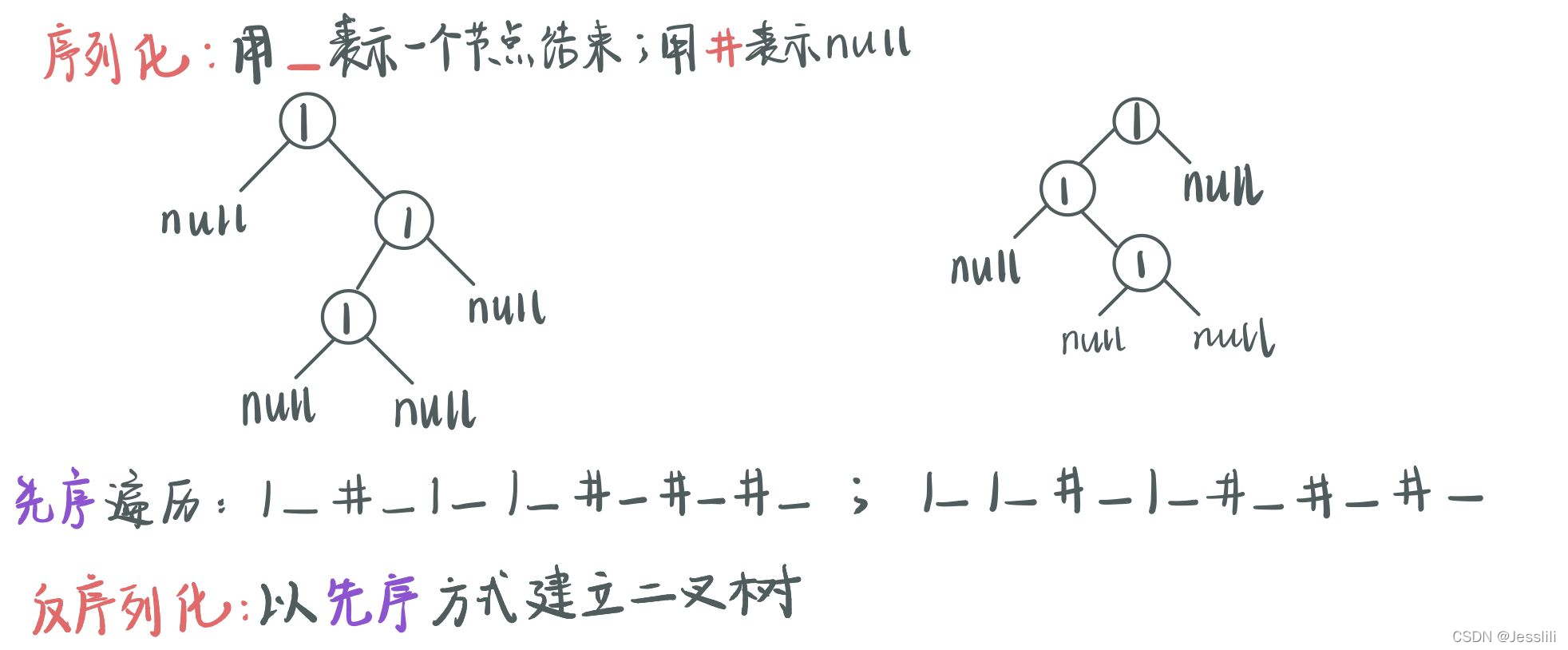
先序序列化

先序反序列化


6. 折纸问题

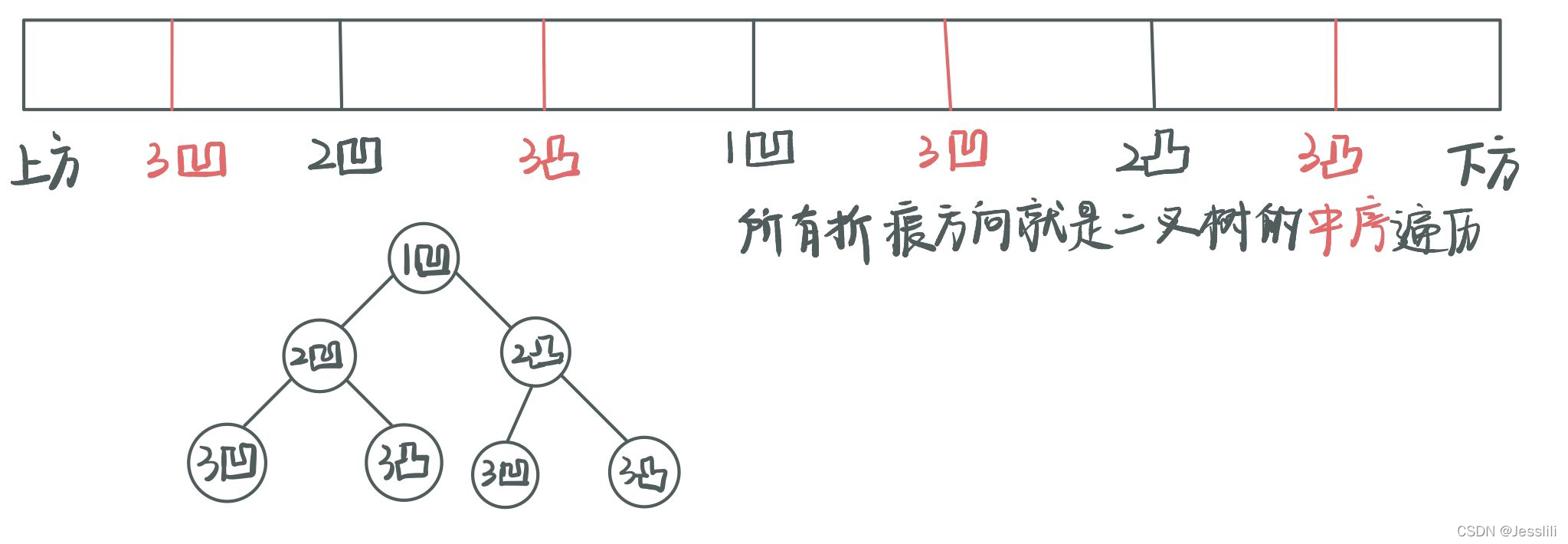
这是一颗根节点为凹节点,每一颗左子树的根节点为凹节点,每一颗右子树的根节点为凸节点的二叉树。

五、贪心算法
在某一个标准下,优先考虑最满足标准的样本,最后考虑最不满足标准的样本,最终得到一个答案的算法,叫作贪心算法。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,所做出的是在某种意义上的局部最优解。

不要纠结贪心策略的证明
1. 题目1

先安排结束时间早的会议,安排完后把不能进行的会议删除掉。剩下的会议里再安排结束时间早的会议安排完后把不能进行的会议删除掉。重复上述操作。



2. 题目2


六、暴力递归
1. 汉诺塔问题
如下图所示,从左到右有A、B、C三根柱子,其中A柱子上面有从小叠到大的n个圆盘,现要求将A柱子上的圆盘移到C柱子上去,期间只有一个原则:一次只能移动一个盘子且大盘子不能在小盘子上面,求移动的步骤和移动的次数。



2. 字符串的子序列
字符串的一个 子序列 是指,通过删除一些(也可以不删除)字符且不干扰剩余字符相对位置所组成的新字符串。(例如,“ACE” 是 “ABCDE” 的一个子序列,而 “AEC” 不是)

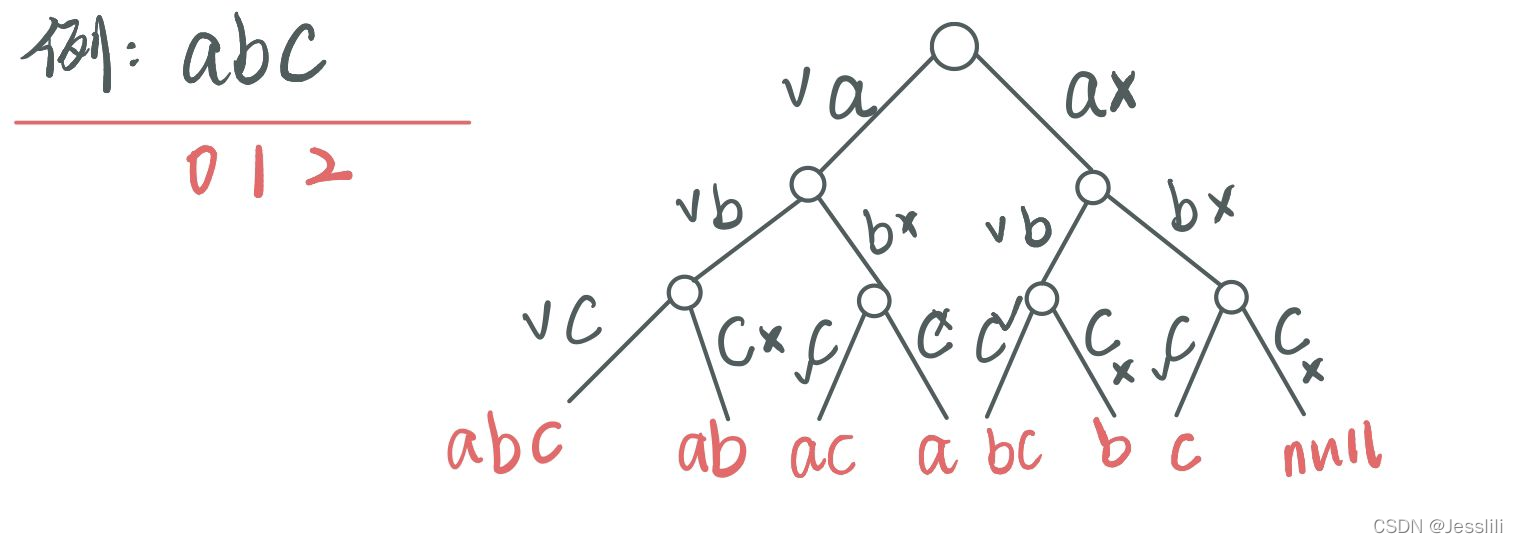
实现一

实现二
3. 字符串的全排列*(回溯)
输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。
你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组,但里面不能有重复元素。
class Solution {
List<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
char[] c;
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();
dfs(0);
return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
}
//x 当前固定位
void dfs(int x) {
if(x == c.length - 1) {
res.add(String.valueOf(c)); // 添加排列方案
return;
}
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();//防止同一层递归出现重复元素
for(int i = x; i < c.length; i++) {
if(set.contains(c[i])) continue; // 发生剪枝,当包含这个元素的时候,直接跳过
set.add(c[i]);
swap(i, x); // 交换,将 c[i] 固定在第 x 位
dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
swap(i, x); // 恢复交换
}
}
void swap(int a, int b) {
char tmp = c[a];
c[a] = c[b];
c[b] = tmp;
}
}
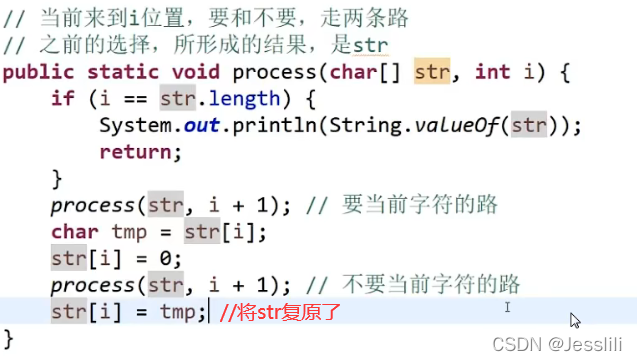
4. 01背包问题

0号要/不要两种情况展开,1号要/不要两种情况展开……
public class Main {
private static int maxBag;
private static int[] weights;
private static int[] values;
public static int process(int[] weights, int[] values, int maxBag) {
Main.maxBag = maxBag;
Main.weights = weights;
Main.values = values;
return process(maxBag, 0);
}
/**
* @param w 剩余空间
* @param i 当前已经判断到那个物品了
* @return 最大价值
*/
private static int process(int w, int i) {
if (i == weights.length) {//选完了返回0
return 0;
}
if (w < weights[i]) {
return process(w, i + 1);
}
//不要i号 //要i号
return Math.max(process(w, i + 1), process(w - weights[i], i + 1) + values[i]);
}
}
动态规划
dp[i][j]表示将前 i 件物品装进限重为 j 的背包可以获得的最大价值, 0<=i<=N, 0<=j<=bag
那么我们可以将dp[0][0…bag]初始化为0,表示将前0个物品(即没有物品)装入书包的最大价值为0。 那么当 i > 0
时dp[i][j]有两种情况:
- 不装入第 i 件物品,即dp[i?1][j];
- 装入第i件物品(前提是能装下),即dp[i?1][j?w[i]] + v[i]。 即状态转移方程为: dp[i][j] = max(dp[i?1][j], dp[i?1][j?w[i]]+v[i]) // j >= w[i]
由上述状态转移方程可知,dp[i][j]的值只与dp[i-1][0,…,j-1]有关。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] weights, int[] values, int maxBag) {
int[][] dp = new int[weights.length + 1][maxBag + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= weights.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= maxBag; j++) {
if (j < weights[i - 1]) {//超重了,不装入
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j],
dp[i - 1][j - weights[i]] + values[i]);
}
}
}
return dp[weights.length][maxBag];
}
}
5. N皇后问题

一行一行的放入皇后,只要放入的一行与前面几行的皇后不同列、不同斜线就符合要求。
比如说,放第二行皇后的时候只要是和第一行的皇后不同列不同斜线的位置都符合要求。
放第三行皇后的时候只要是和第一行与第二行的皇后不同列不同斜线的位置都符合要求。

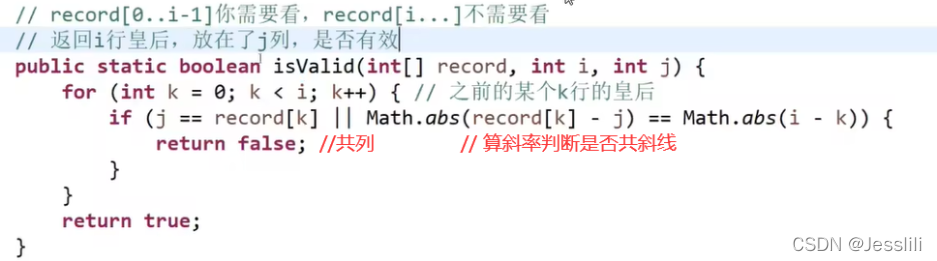
列相减的绝对值 == 行相减的绝对值(|y1-y2| = |x1-x2| -> |y1-y2|/|x1-x2|=1 -> 45°或135°)
七、动态规划
文章内容参考kuangshen教程
