目录
1、先说什么是树?
树是什么?简单来说,它是一种数据结构,就如单链表来说,每个节点都至少有这几个点;数值、后继节点指针、(有时候会有前驱结点指针);对于树来说,也是每个节点按照不同于链表连接方式连接;
首先看一张图,也就是下面所要讲解所有代码都要用的例子;

这个图可以看出一个最基本的二叉树节点,至少含有;一个值、一个左孩子、一个右孩子;其他的树比如,T树、红黑树、B+树、B-树、等也就是对该节点的扩充,但是重要的是整体模型还是如此;对于树的来说,就是对树节点的连接不同;
2、对于一个二叉树书上还有很多概念(需要掌握);
树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n(n>=0)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做树是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
根结点:根节点没有前驱结点。
除根节点外,其余结点被分成是一棵结构与树类似的子树。每棵子树的根结点有且只有一个前驱,可以有0个或多个后继。因此,树是递归定义的。
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度;?
叶节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点;?
非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点;
双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;?
兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;?
树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度;
节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次;
堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;
节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;
子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。
森林:由m棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林
?
3、设计一个二叉树的节点
有了二叉树的概念,设计出一个二叉树首先得设计一个树的节点;用结构体变量来定义一个节点。
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BtNode
{
ElemType val;
struct BtNode* Leftchild;;
struct BtNode* Rightchild;
}BtNode,*BinaryNode;4、设计一个二叉树;
有了节点,设计一个二叉树,就是怎样连接的问题了;
?(1)顺序存储
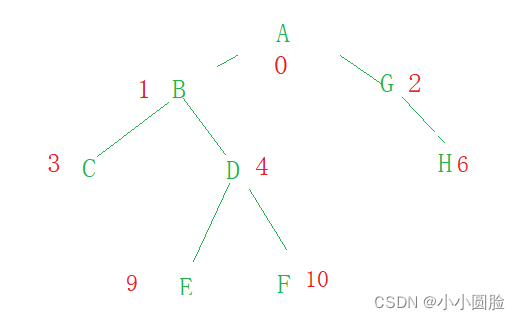
?以该图表示 也就是按照二叉树表示,每个下标都表示出来,也就是下标和树每个节点对相对应:
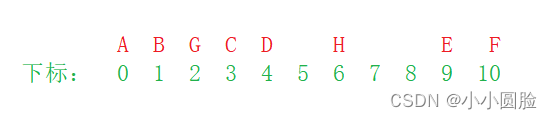
?(2)链式存储

?用代码表示:
为了后续代码遍历:先写出一个购买节点的函数
BtNode* Buynode()
{
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (nullptr == s) exit(1);
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));
}
BtNode* CBTree()
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
ElemType elem;
cin >> elem;
if (elem != '#')
{
s = Buynode();
s->val = elem;
s->Leftchild = CBTree();
s->Rightchild = CBTree();
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
BinaryNode ubuntu= CBTree();//ABC##DE##F##G#H##
return 0;
}5、有了二叉树表示,应该怎样表示出来(打印)
? 对于二叉树来说,有三种顺序遍历打印;也有递归和非递归来区分,对于递归来说很简单;对于非递归来说;可以用栈来表示;
(1)前序遍历打印(递归)
void PrOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
cout << p->val <<" ";
PrOrder(p->Leftchild);
PrOrder(p->Rightchild);
}
}(1)前序遍历打印(非递归)
? ? ? 使用栈来实现前序遍历的非递归;
void NicePreOreder(BtNode* ptr)//非递归先序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
std::stack<BtNode*>st;
while (ptr != NULL || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);
cout << ptr->val;
ptr = ptr->Leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
ptr = ptr->Rightchild;
}
cout << endl;
}(2)中序遍历打印(递归)
void InOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
InOrder(p->Leftchild);
cout << p->val << " ";
InOrder(p->Rightchild);
}
}(2)中序遍历打印(非递归)
void NiceInOreder(BtNode* ptr)//非递归中序遍历
{
if (ptr == nullptr) return ;
stack<BtNode* > st;
while (ptr != nullptr || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->Leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->val << " ";
ptr = ptr->Rightchild;
}
}(3)后续遍历打印(递归)
void PaOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
PaOrder(p->Leftchild);
PaOrder(p->Rightchild);
cout << p->val << " ";
}
}(3)后续遍历打印(非递归)
void LastInOrder(BtNode* ptr)//后续非递归
{
if (ptr == nullptr) return;
stack<BtNode*>st;
BtNode * tmp = nullptr;
while (ptr != nullptr || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->Leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();
if (ptr->Rightchild == nullptr || ptr->Rightchild == tmp)
{
tmp = ptr;
cout << ptr->val << " ";
st.pop();
ptr = nullptr;
}
else
{
ptr = ptr->Rightchild;
}
}
}5、常见的二叉树构建问题
? ? char ps[] = { "ABCDEFGH" };//前
?? ?char is[] = { "CBEDFAGH" };//中
?? ?char ls[] = { "CEFDBHGA" };//后
(1)已知前序后续构建二叉树
BtNode* CreatePI(const char* ps, const char* is, int n)//前中构建
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n >= 1)
{
s = Buynode();
s->val = ps[0];
int pos = FindIs(is, n, ps[0]);
if (pos == -1) exit(1);
s->Leftchild = CreatePI(ps + 1, is, pos);
s->Rightchild = CreatePI(ps + pos + 1, is + pos + 1, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}(2)已知后续中序构建二叉树
BtNode* CreateIL(const char* is, const char* ls, int n)//后中建立
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n >= 1)
{
s = Buynode();
s->val = ls[n - 1];
int pos = FindIs(is, n, ls[n-1]);
if (pos == -1) exit(1);
s->Leftchild = CreateIL(is, ls, pos);
s->Rightchild = CreateIL(is + pos + 1, ls + pos, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}6、常见的二叉树打印问题
(1)Z字型打印
void ZLevelOder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) return;
stack<BtNode*>st1;
stack<BtNode*>st2;
st1.push(ptr);
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty())
{
while (!st1.empty())
{
ptr = st1.top(); st1.pop();
cout << ptr->val << " ";
if (ptr->Leftchild != nullptr)
{
st2.push(ptr->Leftchild);
}
if (ptr->Rightchild != nullptr)
{
st2.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
while (!st2.empty())
{
ptr = st2.top(); st2.pop();
cout << ptr->val << " ";
if (ptr->Rightchild != nullptr)
{
st1.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
if (ptr->Leftchild != nullptr)
{
st1.push(ptr->Leftchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}(2)水平打印二叉树
void LevelOder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) return;
queue<BtNode*> qu;
queue<BtNode*> qu1;
qu.push(ptr);
while (!qu.empty() || !qu1.empty())
{
while (!qu.empty())
{
ptr = qu.front(); qu.pop();
cout << ptr->val << " ";
if (ptr->Leftchild != nullptr)
{
qu1.push(ptr->Leftchild);
}
if (ptr->Rightchild != nullptr)
{
qu1.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
while (!qu1.empty())
{
ptr = qu1.front(); qu1.pop();
cout << ptr->val << " ";
if (ptr->Leftchild != nullptr)
{
qu.push(ptr->Leftchild);
}
if (ptr->Rightchild != nullptr)
{
qu.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}7、判断是否是满二叉树
bool Is_FullBinaryTree(BtNode* ptr)
{
bool tag = true;
if (ptr == NULL)return tag;
queue<BtNode*>aqu;
queue<BtNode*>bqu;
int s = 1;
aqu.push(ptr);
while (!aqu.empty() || !bqu.empty())
{
if (s != aqu.size())
{
tag = false;
break;
}
while (!aqu.empty())
{
ptr = aqu.front(); aqu.pop();
if (ptr->Leftchild != NULL)bqu.push(ptr->Leftchild);
if (ptr->Rightchild != NULL)bqu.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
s += s;
if (s != bqu.size())
{
tag = false;
break;
}
while (!bqu.empty())
{
ptr = bqu.front(); bqu.pop();
if (ptr->Leftchild != NULL)aqu.push(ptr->Leftchild);
if (ptr->Rightchild != NULL)aqu.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
s += s;
}
return tag;
}8、判断是否是完全二叉树
bool Is_CompBinaryTree(BtNode* ptr)
{
bool tag = true;
if (ptr == nullptr) return tag;
queue<BtNode*>qu;
qu.push(ptr);
while (!qu.empty())
{
ptr = qu.front(); qu.pop();
if (ptr == nullptr) break;
qu.push(ptr->Leftchild);
qu.push(ptr->Rightchild);
}
while (!qu.empty())
{
if (qu.front() != nullptr)
{
tag = false;
break;
}
qu.pop();
}
}