417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
2022.4.27 每日一题
题目描述
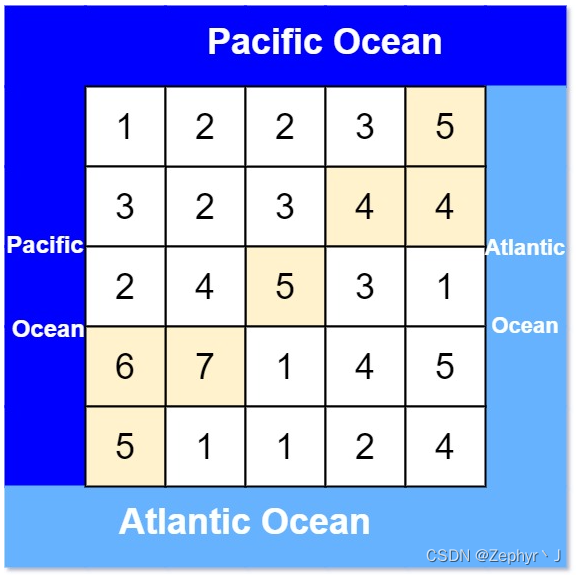
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回 网格坐标 result 的 2D列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水可以从单元格 (ri, ci) 流向 太平洋和大西洋 。
示例 1:
输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
示例 2:
输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
m == heights.length
n == heights[r].length
1 <= m, n <= 200
0 <= heights[r][c] <= 10^5
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
多源bfs
class Solution {
int[][] dirs = {{1,0}, {-1,0}, {0,1}, {0,-1}};
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
//这个题的意思是说,必须得既能流向太平洋,又能流向大西洋才行
//也就是说西北有一个能流过去,东南也有一个能流过去
//这样将能流进太平洋的放一个set,流进大西洋的放一个set
//例如太平洋的,先将边界放在queue中,如果周围有比它高的,就放在set中,说明可以流进太平洋
//多源bfs
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> pacific = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> atlantic = new HashSet<>();
boolean[][] used = new boolean[m][n];
//先处理太平洋
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
queue.add(new int[]{i, 0});
//used[i][0] = true;
}
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
queue.add(new int[]{0, j});
//used[0][j] = true;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] top = queue.poll();
pacific.add(top[0] * 201 + top[1]);
for(int[] dir : dirs){
int x = top[0] + dir[0];
int y = top[1] + dir[1];
if(x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || used[x][y])
continue;
if(heights[x][y] >= heights[top[0]][top[1]]){
queue.add(new int[]{x, y});
used[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
used = new boolean[m][n];
//处理大西洋
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
queue.add(new int[]{i, n - 1});
//used[i][0] = true;
}
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
queue.add(new int[]{m - 1, j});
//used[0][j] = true;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] top = queue.poll();
atlantic.add(top[0] * 201 + top[1]);
for(int[] dir : dirs){
int x = top[0] + dir[0];
int y = top[1] + dir[1];
if(x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || used[x][y])
continue;
if(heights[x][y] >= heights[top[0]][top[1]]){
queue.add(new int[]{x, y});
used[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int t : pacific){
if(atlantic.contains(t)){
int x = t / 201;
int y = t % 201;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(x);
list.add(y);
res.add(list);
}
}
return res;
}
}
905. 按奇偶排序数组
2022.4.28 每日一题
题目描述
给你一个整数数组 nums,将 nums 中的的所有偶数元素移动到数组的前面,后跟所有奇数元素。
返回满足此条件的 任一数组 作为答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,1,2,4]
输出:[2,4,3,1]
解释:[4,2,3,1]、[2,4,1,3] 和 [4,2,1,3] 也会被视作正确答案。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000
0 <= nums[i] <= 5000
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-array-by-parity
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
我第一时间想到的是双指针交换
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] nums) {
int l = nums.length;
int left = 0;
int right = l - 1;
while(left < right){
while(left < right && nums[left] % 2 == 0)
left++;
while(left < right && nums[right] % 2 == 1)
right--;
if(left == right)
break;
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
return nums;
}
}
class Solution:
def sortArrayByParity(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
return [n for n in nums if not n % 2] + [n for n in nums if n % 2]
使用额外空间的双指针
class Solution:
def sortArrayByParity(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
l = len(nums)
left = 0
right = l - 1
res = l * [0]
for n in nums:
if not n % 2:
res[left] = n
left += 1
else:
res[right] = n
right -= 1
return res
427. 建立四叉树
2022.4.29 每日一题
题目描述
给你一个 n * n 矩阵 grid ,矩阵由若干 0 和 1 组成。请你用四叉树表示该矩阵 grid 。
你需要返回能表示矩阵的 四叉树 的根结点。
注意,当 isLeaf 为 False 时,你可以把 True 或者 False 赋值给节点,两种值都会被判题机制 接受 。
四叉树数据结构中,每个内部节点只有四个子节点。此外,每个节点都有两个属性:
- val:储存叶子结点所代表的区域的值。1 对应 True,0 对应 False;
- isLeaf: 当这个节点是一个叶子结点时为 True,如果它有 4 个子节点则为 False 。
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
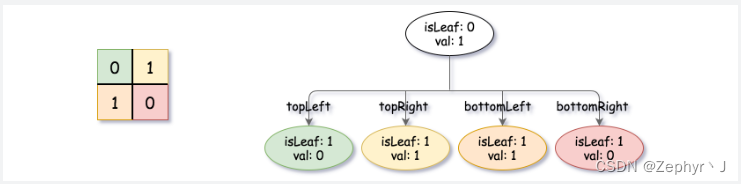
我们可以按以下步骤为二维区域构建四叉树:
- 如果当前网格的值相同(即,全为 0 或者全为 1),将 isLeaf 设为 True ,将 val 设为网格相应的值,并将四个子节点都设为 Null 然后停止。
- 如果当前网格的值不同,将 isLeaf 设为 False, 将 val 设为任意值,然后如下图所示,将当前网格划分为四个子网格。
- 使用适当的子网格递归每个子节点。

如果你想了解更多关于四叉树的内容,可以参考 wiki 。
四叉树格式:
输出为使用层序遍历后四叉树的序列化形式,其中 null 表示路径终止符,其下面不存在节点。
它与二叉树的序列化非常相似。唯一的区别是节点以列表形式表示 [isLeaf, val] 。
如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 True ,则表示它在列表 [isLeaf, val] 中的值为 1 ;如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 False ,则表示值为 0 。
示例 1:
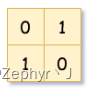
输入:grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]]
解释:此示例的解释如下:
请注意,在下面四叉树的图示中,0 表示 false,1 表示 True 。
示例 2:
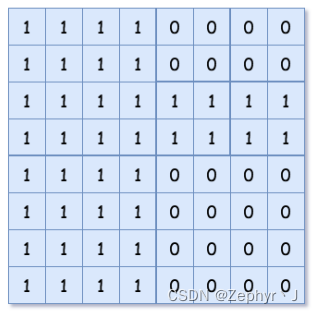
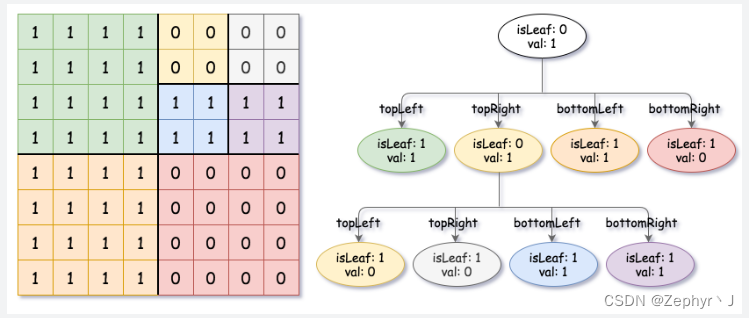
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]]
解释:网格中的所有值都不相同。我们将网格划分为四个子网格。
topLeft,bottomLeft 和 bottomRight 均具有相同的值。
topRight 具有不同的值,因此我们将其再分为 4 个子网格,这样每个子网格都具有相同的值。
解释如下图所示:
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[1,1],[1,1]]
输出:[[1,1]]
示例 4:
输入:grid = [[0]]
输出:[[1,0]]
示例 5:
输入:grid = [[1,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0],[0,0,1,1],[0,0,1,1]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length
n == 2^x 其中 0 <= x <= 6
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-quad-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
dfs分别判断四个部分的情况,如果有某些部分不是所有值都相同,再dfs细分
/*
// Definition for a QuadTree node.
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
public Node() {
this.val = false;
this.isLeaf = false;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf, Node topLeft, Node topRight, Node bottomLeft, Node bottomRight) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = topLeft;
this.topRight = topRight;
this.bottomLeft = bottomLeft;
this.bottomRight = bottomRight;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
//先得搞清楚这个题是什么意思,就是将所给的网格划分为四部分,如果某些部分所有元素都相同,那么就是叶子结点
//如果不相同,那么将这个部分继续划分
//怎么写呢
int n;
int[][] grid;
public Node construct(int[][] grid) {
n = grid.length;
this.grid = grid;
//默认构造的都是叶子结点
Node root = new Node(grid[0][0] == 1 ? true : false, true);
dfs(root, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
return root;
}
public void dfs(Node father, int left, int right, int up, int down){
if(left >= right || up >= down)
return;
int colmid = (right + left) / 2;
int rowmid = (down + up) / 2;
//左上
int leftup = grid[up][left];
Node lu = new Node(leftup == 1 ? true : false, true);
for(int i = left; i <= colmid; i++){
for(int j = up; j <= rowmid; j++){
//如果这个区域内的值不相同,那么dfs,并且将这个区域内的点
if(grid[j][i] != leftup){
leftup = -1;
lu.isLeaf = false;
lu.val = true;
dfs(lu, left, colmid, up, rowmid);
break;
}
}
}
//右上
int rightup = grid[up][right];
Node ru = new Node(rightup == 1 ? true : false, true);
for(int i = colmid + 1; i <= right; i++){
for(int j = up; j <= rowmid; j++){
//如果这个区域内的值不相同,那么dfs,并且将这个区域内的点
if(grid[j][i] != rightup){
rightup = -1;
ru.isLeaf = false;
ru.val = true;
dfs(ru, colmid + 1, right, up, rowmid);
break;
}
}
}
//左下
int leftdown = grid[down][left];
Node ld = new Node(leftdown == 1 ? true : false, true);
for(int i = left; i <= colmid; i++){
for(int j = rowmid + 1; j <= down; j++){
//如果这个区域内的值不相同,那么dfs,并且将这个区域内的点
if(grid[j][i] != leftdown){
leftdown = -1;
ld.isLeaf = false;
ld.val = true;
dfs(ld, left, colmid, rowmid + 1, down);
break;
}
}
}
//右下
int rightdown = grid[down][right];
Node rd = new Node(rightdown == 1 ? true : false, true);
for(int i = colmid + 1; i <= right; i++){
for(int j = rowmid + 1; j <= down; j++){
//如果这个区域内的值不相同,那么dfs,并且将这个区域内的点
if(grid[j][i] != rightdown){
rightdown = -1;
rd.isLeaf = false;
rd.val = true;
dfs(rd, colmid + 1, right, rowmid + 1, down);
break;
}
}
}
//如果四个部分都相同,那么直接返回
if(leftup != -1 && leftup == rightup && leftup == leftdown && leftup == rightdown){
//father.val = leftup == 0 ? false : true;
return;
}
//如果有不同的话,就是连接到新的结点
father.isLeaf = false;
father.val = true;
father.topLeft = lu;
father.topRight = ru;
father.bottomLeft = ld;
father.bottomRight = rd;
}
}
简化代码,并且用二维前缀和
/*
// Definition for a QuadTree node.
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
public Node() {
this.val = false;
this.isLeaf = false;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf, Node topLeft, Node topRight, Node bottomLeft, Node bottomRight) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = topLeft;
this.topRight = topRight;
this.bottomLeft = bottomLeft;
this.bottomRight = bottomRight;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
//用前缀和,并且简化一下代码
int n;
int[][] grid;
int[][] pre;
public Node construct(int[][] grid) {
n = grid.length;
this.grid = grid;
pre = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
pre[i + 1][j + 1] = pre[i][j + 1] + pre[i + 1][j] - pre[i][j] + grid[i][j];
}
}
return dfs(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
public Node dfs(int left, int right, int up, int down){
int colmid = (right + left) / 2;
int rowmid = (down + up) / 2;
int total = pre[down + 1][right + 1] - pre[up][right + 1] - pre[down + 1][left] + pre[up][left];
if(total == 0)
return new Node(false, true);
if(total == (down - up + 1) * (right - left + 1))
return new Node(true, true);
//如果能分,那么继续分
Node leftup = dfs(left, colmid, up, rowmid);
Node leftdown = dfs(left, colmid, rowmid + 1, down);
Node rightup = dfs(colmid + 1, right, up, rowmid);
Node rightdown = dfs(colmid + 1, right, rowmid + 1, down);
return new Node(true, false, leftup, rightup, leftdown, rightdown);
}
}