This blog will cover as below :
- The K-mens clustering algorithm(K-均值聚类算法)
- Cluster postprocessing (对聚类得到的簇进行后处理)
- Bisecting k-means(二分K-均值聚类算法)
Clustering is a type of unsupervised learning that automatically forms clusters of similar things.It's like automatic classification. In this blog, we're going to study one type of clustering algorithm called k-means.It's called k-means because it finds k unique clusters, and the center of each cluster is the mean of the value in that cluster. Clustering is sometimes called unsupervised classification because it produces the same result as classification but without having predefined classes.The notion of similarity depends on a similarity measurement. The type of similarity measure used depend on the application.
We’ll build the k-means algorithm and see it in action. We’ll next discuss some drawbacks of the simple k-means algorithm. To improve some of these problems, we can apply postprocessing to produce better clusters. Next, you’ll see a more efficient version of k-means called bisecting k-means. Finally, you’ll see an example where we’ll use bisecting k-means to find optimal parking locations while visiting multiple nightlife hotspots
10.1 The k-means clustering algorithm(k-均值聚类算法)


?k-means is an algorithm that will find k clusters for a given dataset. (k-均值是发现给定数据集的k个簇的算法)The number of clusters k is user defined .Each cluster is descirbed by a single point known as the centroid .(簇个数k是用户给定的,每一个簇通过其质心 (centroid),即簇中所有点的中心来描述。)Centroid means it's at the center of all the points in the cluster.(每个簇的质心更新为该簇所有点的平均值)
The k-means algorithm works like this:
- the k centroids are randomly assigned to a point
- each point in the dataset is assigned to a cluster. The assignment is done by finding the closest centroid and assigning the point to that cluster.
- the centroids are all updated by taking the mean value of the points in that cluster.

?
?
'''
Author: Maxwell Pan
Date: 2022-04-29 04:56:43
LastEditTime: 2022-04-29 05:56:03
FilePath: \cp010\kMeans.py
Description: Grouping unlabeled items using k-means clustering
利用K-均值聚类算法对未标注数据分组
Software:VSCode,env:
'''
# k-means support functions
import readline
import numpy as np
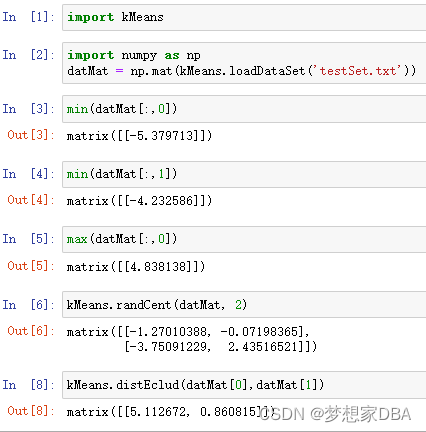
def loadDataSet(fileName):
dataMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')
fltLine = np.map(float,curLine)
dataMat.append(fltLine)
return dataMat
# calculates the Euclidean distance between two vectors.
def distEclud(vecA,vecB):
return np.sqrt(sum(np.power(vecA - vecB, 2)))
# randCent(), which creates a set of k random centroids for a given dataset.This is accomplished by finding the minimum and maximum values of each dimension in the dataset.
def randCent(dataSet, k):
n = np.shape(dataSet)[1]
centroids = np.mat(np.zeros((k,n)))
for j in range(n):
minJ = min(dataSet[:,j])
rangeJ = float(max(dataSet[:,j]) - minJ)
centroids[:,j] = minJ + rangeJ * np.random.rand(k,1)
return centroids
?
def kMeans(dataSet,k,disMeas=distEclud,createCent=randCent):
m = np.shape(dataSet)[0]
# the cluster assignment matrix
clusterAssment = np.mat(np.zeros(m,2))
centroids = createCent(dataSet,k)
# create a flag called clusterChanged,if this is True you continue iterating.
clusterChanged = True
# the iteration is handled by a while loop.
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged = False
for i in range(m):
minDist = np.inf
minIndex = -1
for j in range(m):
distJI = np.distMeas(centroids[j,:],dataSet[i,:])
if distJI < minDist:
minDist = distJI
minIndex = j
if clusterAssment[i,0] != minIndex:
clusterChanged = True
clusterAssment[i,0] = minIndex,minDist**2
print(centroids)
for cent in range(k):
ptsInClust = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A==cent)[0]]
centroids[cent,:] = np.mean(ptsInClust,axis=0)
return centroids,clusterAssment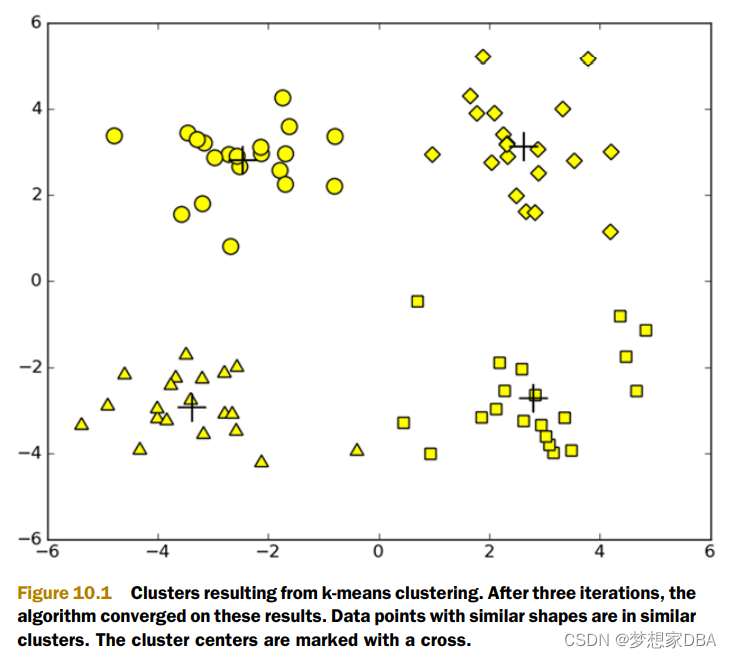
?
10.2 Improving cluster performance with postprocessing?
10.3 Bisecting k-means
To overcome the problem of poor clusters because of k-means getting caught in local minimum, another algorithm has been developed.

?
'''
Author: Maxwell Pan
Date: 2022-04-29 04:56:43
LastEditTime: 2022-04-30 07:39:35
FilePath: \cp010\kMeans.py
Description: Grouping unlabeled items using k-means clustering
利用K-均值聚类算法对未标注数据分组
Software:VSCode,env:
'''
# k-means support functions
import numpy as np
"""
def loadDataSet(fileName):
dataMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')
fltLine = list(map(float,curLine)) # map all elements to float()
dataMat.append(fltLine)
return dataMat
# calculates the Euclidean distance between two vectors.
def distEclud(vecA,vecB):
return np.sqrt(sum(np.power(vecA - vecB, 2)))
# randCent(), which creates a set of k random centroids for a given dataset.This is accomplished by finding the minimum and maximum values of each dimension in the dataset.
def randCent(dataSet, k):
n = np.shape(dataSet)[1]
centroids = np.mat(np.zeros((k,n)))
for j in range(n):
minJ = min(dataSet[:,j]) # create cluster centroids
maxJ = max(dataSet[:,j])
rangeJ = float(maxJ - minJ)
# Create an array of the given shape and populate it with samples from a uniform distribution over (0,1)
centroids[:,j] = minJ + rangeJ * np.random.rand(k,1)
return centroids
def kMeans(dataSet,k,distMeas=distEclud,createCent=randCent):
m = np.shape(dataSet)[0]
# the cluster assignment matrix
clusterAssment = np.mat(np.zeros((m,2)))
centroids = createCent(dataSet,k)
# create a flag called clusterChanged,if this is True you continue iterating.
clusterChanged = True
# the iteration is handled by a while loop.
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged = False
for i in range(m):
minDist = np.inf #pay attention
minIndex = -1
for j in range(k):
distJI = distMeas(centroids[j,:],dataSet[i,:])
if distJI < minDist:
minDist = distJI
minIndex = j
if clusterAssment[i,0] != minIndex:
clusterChanged = True
clusterAssment[i,:] = minIndex,minDist**2
print(centroids)
for cent in range(k):
ptsInClust = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A==cent)[0]]
centroids[cent,:] = np.mean(ptsInClust,axis=0)
return centroids,clusterAssment
def biKmeans(dataSet,k,distMeas=distEclud):
m = np.shape(dataSet)[0]
clusterAssment = np.mat(np.zeros((m,2)))
centroid0 = np.mean(dataSet, axis=0).tolist()[0]
centList = [centroid0]
for j in range(m):
clusterAssment[j,1] = distMeas(np.mat(centroid0), dataSet[j,:])**2
while (len(centList) < k):
lowestSSE = np.inf
for i in range(len(centList)):
ptsInCurrCluster = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A==i)[0],:]
centroidMat,splitClustAss = kMeans(ptsInCurrCluster,2,distMeas)
sseSplit = sum(splitClustAss[:,1])
sseNotSplit = sum(clusterAssment[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A !=i)[0],1])
print("sseSplit, and notSplit: ",sseSplit,sseNotSplit)
if(sseSplit + sseNotSplit) < lowestSSE:
bestCentToSplit = i
bestNewCents = centroidMat
bestClustAss = splitClustAss.copy()
lowestSSE = sseSplit + sseNotSplit
bestClustAss[np.nonzero(bestClustAss[:,0].A == 1)[0],0] = len(centList)
bestClustAss[np.nonzero(bestClustAss[:,0].A == 0)[0],0] = bestCentToSplit
print("the bestCentToSplit is: ", len(bestClustAss))
print("the len of bestClusterAss is: ",len(bestClustAss))
centList[bestCentToSplit] = bestNewCents[0,:].tolist()[0]
centList.append(bestNewCents[1,:].tolist()[0])
clusterAssment[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A == bestCentToSplit)[0],:] = bestClustAss
return np.mat(centList), clusterAssment
"""
def loadDataSet(fileName): #general function to parse tab -delimited floats
dataMat = [] #assume last column is target value
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')
fltLine = list(map(float,curLine)) #map all elements to float()
dataMat.append(fltLine)
return dataMat
def distEclud(vecA, vecB):
return np.sqrt(sum(np.power(vecA - vecB, 2))) #la.norm(vecA-vecB)
def randCent(dataSet, k):
n = np.shape(dataSet)[1]
centroids = np.mat(np.zeros((k,n)))#create centroid mat
for j in range(n):#create random cluster centers, within bounds of each dimension
minJ = min(dataSet[:,j])
rangeJ = float(max(dataSet[:,j]) - minJ)
centroids[:,j] = np.mat(minJ + rangeJ * np.random.rand(k,1))
return centroids
def kMeans(dataSet, k, distMeas=distEclud, createCent=randCent):
m = np.shape(dataSet)[0]
clusterAssment = np.mat(np.zeros((m,2)))#create mat to assign data points
#to a centroid, also holds SE of each point
centroids = createCent(dataSet, k)
clusterChanged = True
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged = False
for i in range(m):#for each data point assign it to the closest centroid
minDist = np.inf; minIndex = -1
for j in range(k):
distJI = distMeas(centroids[j,:],dataSet[i,:])
if distJI < minDist:
minDist = distJI; minIndex = j
if clusterAssment[i,0] != minIndex: clusterChanged = True
clusterAssment[i,:] = minIndex,minDist**2
print(centroids)
for cent in range(k):#recalculate centroids
ptsInClust = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A==cent)[0]]#get all the point in this cluster
centroids[cent,:] = np.mean(ptsInClust, axis=0) #assign centroid to mean
return centroids, clusterAssment
def biKmeans(dataSet, k, distMeas=distEclud):
m = np.shape(dataSet)[0]
clusterAssment = np.mat(np.zeros((m,2)))
centroid0 = np.mean(dataSet, axis=0).tolist()[0]
centList =[centroid0] #create a list with one centroid
for j in range(m):#calc initial Error
clusterAssment[j,1] = distMeas(np.mat(centroid0), dataSet[j,:])**2
while (len(centList) < k):
lowestSSE = np.inf
for i in range(len(centList)):
ptsInCurrCluster = dataSet[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A==i)[0],:]#get the data points currently in cluster i
centroidMat, splitClustAss = kMeans(ptsInCurrCluster, 2, distMeas)
sseSplit = sum(splitClustAss[:,1])#compare the SSE to the currrent minimum
sseNotSplit = sum(clusterAssment[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A!=i)[0],1])
print("sseSplit, and notSplit: ",sseSplit,sseNotSplit)
if (sseSplit + sseNotSplit) < lowestSSE:
bestCentToSplit = i
bestNewCents = centroidMat
bestClustAss = splitClustAss.copy()
lowestSSE = sseSplit + sseNotSplit
bestClustAss[np.nonzero(bestClustAss[:,0].A == 1)[0],0] = len(centList) #change 1 to 3,4, or whatever
bestClustAss[np.nonzero(bestClustAss[:,0].A == 0)[0],0] = bestCentToSplit
print('the bestCentToSplit is: ',bestCentToSplit)
print('the len of bestClustAss is: ', len(bestClustAss))
centList[bestCentToSplit] = bestNewCents[0,:].tolist()[0]#replace a centroid with two best centroids
centList.append(bestNewCents[1,:].tolist()[0])
clusterAssment[np.nonzero(clusterAssment[:,0].A == bestCentToSplit)[0],:]= bestClustAss#reassign new clusters, and SSE
return np.mat(centList), clusterAssment
import urllib
import json
def geoGrab(stAddress, city):
apiStem = 'http://where.yahooapis.com/geocode?' #create a dict and constants for the goecoder
params = {}
params['flags'] = 'J'#JSON return type
params['appid'] = 'aaa0VN6k'
params['location'] = '%s %s' % (stAddress, city)
url_params = urllib.parse.urlencode(params)
yahooApi = apiStem + url_params #print url_params
print(yahooApi)
c=urllib.request.urlopen(yahooApi)
return json.loads(c.read())
from time import sleep
def massPlaceFind(fileName):
fw = open('places.txt', 'w')
for line in open(fileName).readlines():
line = line.strip()
lineArr = line.split('\t')
retDict = geoGrab(lineArr[1], lineArr[2])
if retDict['ResultSet']['Error'] == 0:
lat = float(retDict['ResultSet']['Results'][0]['latitude'])
lng = float(retDict['ResultSet']['Results'][0]['longitude'])
print("%s\t%f\t%f" % (lineArr[0], lat, lng))
fw.write('%s\t%f\t%f\n' % (line, lat, lng))
else: print("error fetching")
sleep(1)
fw.close()
def distSLC(vecA, vecB):#Spherical Law of Cosines
a = np.sin(vecA[0,1]*np.pi/180) * np.sin(vecB[0,1]*np.pi/180)
b = np.cos(vecA[0,1]*np.pi/180) * np.cos(vecB[0,1]*np.pi/180) * \
np.cos(np.pi * (vecB[0,0]-vecA[0,0]) /180)
return np.arccos(a + b)*6371.0 #pi is imported with numpy
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def clusterClubs(numClust=5):
datList = []
for line in open('places.txt').readlines():
lineArr = line.split('\t')
datList.append([float(lineArr[4]), float(lineArr[3])])
datMat = np.mat(datList)
myCentroids, clustAssing = biKmeans(datMat, numClust, distMeas=distSLC)
fig = plt.figure()
rect=[0.1,0.1,0.8,0.8]
scatterMarkers=['s', 'o', '^', '8', 'p', \
'd', 'v', 'h', '>', '<']
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
ax0=fig.add_axes(rect, label='ax0', **axprops)
imgP = plt.imread('Portland.png')
ax0.imshow(imgP)
ax1=fig.add_axes(rect, label='ax1', frameon=False)
for i in range(numClust):
ptsInCurrCluster = datMat[np.nonzero(clustAssing[:,0].A==i)[0],:]
markerStyle = scatterMarkers[i % len(scatterMarkers)]
ax1.scatter(ptsInCurrCluster[:,0].flatten().A[0], ptsInCurrCluster[:,1].flatten().A[0], marker=markerStyle, s=90)
ax1.scatter(myCentroids[:,0].flatten().A[0], myCentroids[:,1].flatten().A[0], marker='+', s=300)
plt.show()10.5 Summary:
Clustering is a technique used in unsupervised learning.Clustering groups data points together, with similar data points in one cluster and dissimilar points in a different group. A number of different measurements can be used to measure similarity.
One widely used clustering algorithm is k-means, where k is a user-specified number of clusters to create. The k-means clustering algorithm starts with k-random cluster centers known as centroids. Next, the algorithm computes the distance from every point to the cluster centers. Each point is assigned to the closest cluster center
k-means and its derivatives aren’t the only clustering algorithms. Another type of clustering, known as hierarchical clustering, is also a widely used clustering algorithm. In the next chapter, we’ll examine the Apriori algorithm for finding association rules in a dataset.
