凡老师:写程序就是打游戏,很快乐。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?行业定律:时间、加钱、质量不可兼得。
用链表实现多项式加法:其本质就是用结点表示出一项的系数与幂,按幂的次方顺序由小到大排列即可。两个多项式相加时,对分别两项次方数进行比较,然后或连接,或删除,或相加。
难度不大!!!耐心分析情况即可,感受数据结构的乐趣罢了。
(我们直接考虑输入的顺序就是由小到大,同样也可以添加一个排序函数将链表进行重新连接按次方顺序排列,本文暂不考虑!)
两个多项式的创建就是两个单链表的创建:可以理解为只包括初始化与添加项式:
结构体的选择:两个数据与一个指针域
typedef struct node{
int coe;
int exp;
struct node* next;
}Node,*NodePtr;? ?初始化与插入结点:(就是单链表的常规操作)
NodePtr Initialize() {
NodePtr head = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->coe = 0;
head->exp = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void AppendNode(NodePtr head,int coe,int exp) {
NodePtr q = head;
NodePtr p = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->coe = coe;
p->exp = exp;
p->next = NULL;
while (q->next) {
q = q->next;
}
q->next = p;
}?打印:精致打印,细节加号
void Print(NodePtr head) {
NodePtr p = head->next;
while (p) {
if (p->coe > 0) {
printf(" %d * 10^%d ", p->coe, p->exp);
}
else {
printf(" (%d) * 10^%d ", p->coe, p->exp);
}
p = p->next;
if (p) {
putchar('+');
}
}
}?将两链表相加:典型的双指针问题,p、q分别在L1,L2上移动,r记录上一结点便于插入,s1、s2是为了便于删除结点
此处是将L2合并到L1上:(建议亲自用手模拟便于方便理解)
? ? ? ? 1.跳过虚拟头结点
? ? ? ? 2.while循环,终止条件为p或q为NULL,既L1或L2到了表尾
? ? ? ? 3.如果p>q ,则按顺序r应该下一个接q,q后移
? ? ? ? 4.如果p<q,则按顺序r下一个接p,p后移
? ? ? ? 5.如果p=q,则p+=q即可,同时删除s2(q的备份),r接p,p、q同时后移,如果相加后p=0,则删除p、q,r不变。
? ? ? ? 6.如果p或q有衣服到尾部,则直接接上即可
void Add_Two_L(NodePtr L1, NodePtr L2) {
NodePtr p = L1->next, q = L2->next, r=L1;
NodePtr s1, s2;
while (p && q) {
if (p->exp > q->exp) {
r->next = q;
r = q;
q = q->next;
}
else if (p->exp < q->exp) {
r->next=p;
r = p;
p = p->next;
}
else {
if (p->coe + q->coe == 0) {
s1 = p;
s2 = q;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
free(s1);
free(s2);
}
else {
p->coe += q->coe;
r = p;
p = p->next;
s2 = q;
q = q->next;
free(s2);
}
}
}
if (p == NULL) {
r->next = q;
}
else {
r->next = p;
}
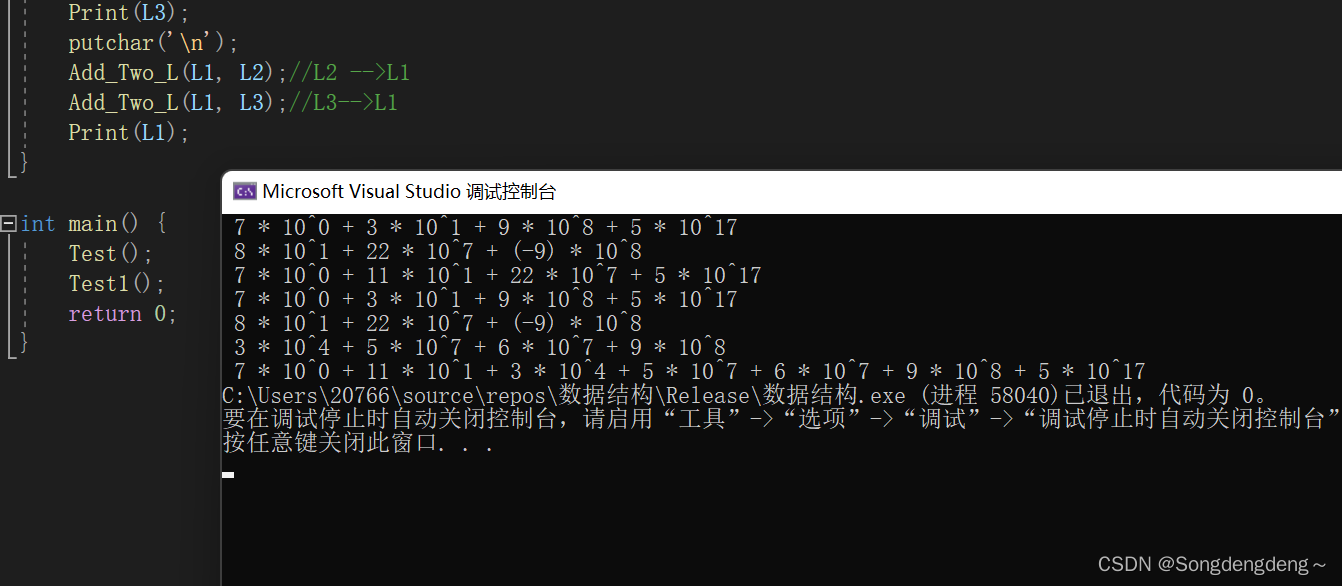
}运行截图:
????????我写了两个测试文件,一个就是两项相加,一个是三项相加
完整代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct node{
int coe;
int exp;
struct node* next;
}Node,*NodePtr;
NodePtr Initialize() {
NodePtr head = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->coe = 0;
head->exp = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void Print(NodePtr head) {
NodePtr p = head->next;
while (p) {
if (p->coe > 0) {
printf(" %d * 10^%d ", p->coe, p->exp);
}
else {
printf(" (%d) * 10^%d ", p->coe, p->exp);
}
p = p->next;
if (p) {
putchar('+');
}
}
}
void AppendNode(NodePtr head,int coe,int exp) {
NodePtr q = head;
NodePtr p = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->coe = coe;
p->exp = exp;
p->next = NULL;
while (q->next) {
q = q->next;
}
q->next = p;
}
void Add_Two_L(NodePtr L1, NodePtr L2) {
NodePtr p = L1->next, q = L2->next, r=L1;
NodePtr s1, s2;
while (p && q) {
if (p->exp > q->exp) {
r->next = q;
r = q;
q = q->next;
}
else if (p->exp < q->exp) {
r->next=p;
r = p;
p = p->next;
}
else {
if (p->coe + q->coe == 0) {
s1 = p;
s2 = q;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
free(s1);
free(s2);
}
else {
p->coe += q->coe;
r = p;
p = p->next;
s2 = q;
q = q->next;
free(s2);
}
}
}
if (p == NULL) {
r->next = q;
}
else {
r->next = p;
}
}
void Test() {
NodePtr L1 = Initialize();
AppendNode(L1, 7, 0);
AppendNode(L1, 3, 1);
AppendNode(L1, 9, 8);
AppendNode(L1, 5, 17);
Print(L1);
putchar('\n');
NodePtr L2 = Initialize();
AppendNode(L2, 8, 1);
AppendNode(L2, 22, 7);
AppendNode(L2, -9, 8);
Print(L2);
putchar('\n');
Add_Two_L(L1, L2);
Print(L1);
}
void Test1() {
putchar('\n');
NodePtr L1 = Initialize();
AppendNode(L1, 7, 0);
AppendNode(L1, 3, 1);
AppendNode(L1, 9, 8);
AppendNode(L1, 5, 17);
Print(L1);
putchar('\n');
NodePtr L2 = Initialize();
AppendNode(L2, 8, 1);
AppendNode(L2, 22, 7);
AppendNode(L2, -9, 8);
Print(L2);
putchar('\n');
NodePtr L3 = Initialize();
AppendNode(L3, 3, 4);
AppendNode(L3, 5, 7);
AppendNode(L3, 6, 7);
AppendNode(L3, 9, 8);
Print(L3);
putchar('\n');
Add_Two_L(L1, L2);//L2 -->L1
Add_Two_L(L1, L3);//L3-->L1
Print(L1);
}
int main() {
Test();
Test1();
return 0;
}凡老师代码:数据结构 C 代码 2.5: 多项式的加法_闵帆的博客-CSDN博客
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/**
* Linked list of integers. The key is data. The key is sorted in non-descending order.
*/
typedef struct LinkNode{
int coefficient;
int exponent;
struct LinkNode *next;
} *LinkList, *NodePtr;
/**
* Initialize the list with a header.
* @return The pointer to the header.
*/
LinkList initLinkList(){
LinkList tempHeader = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
tempHeader->coefficient = 0;
tempHeader->exponent = 0;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}// Of initLinkList
/**
* Print the list.
* @param paraHeader The header of the list.
*/
void printList(LinkList paraHeader){
NodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d * 10^%d + ", p->coefficient, p->exponent);
p = p->next;
}// Of while
printf("\r\n");
}// Of printList
/**
* Print one node for testing.
* @param paraPtr The pointer to the node.
* @param paraChar The name of the node.
*/
void printNode(NodePtr paraPtr, char paraChar){
if (paraPtr == NULL) {
printf("NULL\r\n");
} else {
printf("The element of %c is (%d * 10^%d)\r\n", paraChar, paraPtr->coefficient, paraPtr->exponent);
}// Of while
}// Of printNode
/**
* Add an element to the tail.
* @param paraCoefficient The coefficient of the new element.
* @param paraExponent The exponent of the new element.
*/
void appendElement(LinkList paraHeader, int paraCoefficient, int paraExponent){
NodePtr p, q;
// Step 1. Construct a new node.
q = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
q->coefficient = paraCoefficient;
q->exponent = paraExponent;
q->next = NULL;
// Step 2. Search to the tail.
p = paraHeader;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}// Of while
// Step 3. Now add/link.
p->next = q;
}// Of appendElement
/**
* Polynomial addition.
* @param paraList1 The first list.
* @param paraList2 The second list.
*/
void add(NodePtr paraList1, NodePtr paraList2){
NodePtr p, q, r, s;
// Step 1. Search to the position.
p = paraList1->next;
printNode(p, 'p');
q = paraList2->next;
printNode(q, 'q');
r = paraList1; // Previous pointer for inserting.
printNode(r, 'r');
free(paraList2); // The second list is destroyed.
while ((p != NULL) && (q != NULL)) {
if (p->exponent < q->exponent) {
//Link the current node of the first list.
printf("case 1\r\n");
r = p;
printNode(r, 'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p, 'p');
} else if ((p->exponent > q->exponent)) {
//Link the current node of the second list.
printf("case 2\r\n");
r->next = q;
r = q;
printNode(r, 'r');
q = q->next;
printNode(q, 'q');
} else {
printf("case 3\r\n");
//Change the current node of the first list.
p->coefficient = p->coefficient + q->coefficient;
printf("The coefficient is: %d.\r\n", p->coefficient);
if (p->coefficient == 0) {
printf("case 3.1\r\n");
s = p;
p = p->next;
printNode(p, 'p');
// free(s);
} else {
printf("case 3.2\r\n");
r = p;
printNode(r, 'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p, 'p');
}// Of if
s = q;
q = q->next;
//printf("q is pointing to (%d, %d)\r\n", q->coefficient, q->exponent);
free(s);
}// Of if
printf("p = %ld, q = %ld \r\n", p, q);
} // Of while
printf("End of while.\r\n");
if (p == NULL) {
r->next = q;
} else {
r->next = p;
} // Of if
printf("Addition ends.\r\n");
}// Of add
/**
* Unit test.
*/
void additionTest(){
// Step 1. Initialize the first polynomial.
LinkList tempList1 = initLinkList();
appendElement(tempList1, 7, 0);
appendElement(tempList1, 3, 1);
appendElement(tempList1, 9, 8);
appendElement(tempList1, 5, 17);
printList(tempList1);
// Step 2. Initialize the second polynomial.
LinkList tempList2 = initLinkList();
appendElement(tempList2, 8, 1);
appendElement(tempList2, 22, 7);
appendElement(tempList2, -9, 8);
printList(tempList2);
// Step 3. Add them to the first.
add(tempList1, tempList2);
printList(tempList1);
}// Of additionTest
/**
* The entrance.
*/
void main(){
additionTest();
printf("Finish.\r\n");
}// Of main
