单向链表示意图:
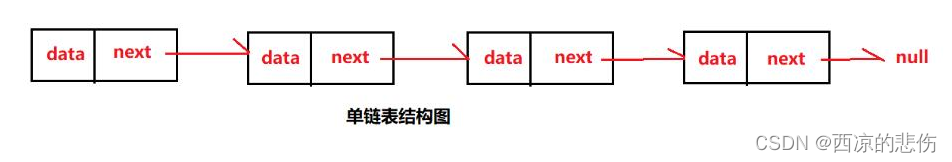
以下是单链表相对于双链表的优缺点。
优点
(1) 只有一个指向下一个节点的指针。
(2) 单向链表增加删除节点简单。遍历时候不会死循环。
缺点
(1) 只能从头到尾遍历。只能找到后继,无法找到前驱,也就是只能前进。
单向链表实现代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Spliterator;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class SingleLinkedList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
/**
* 链表长度
*/
public int size;
/**
* 头节点
*/
private Node head = null;
/**
* 尾节点
*/
private Node tail = null;
private class Node {
public T value;
public Node nexNode;
public Node(T value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.nexNode = next;
}
}
public SingleLinkedList() {
this.size = 0;
}
public SingleLinkedList(T value) {
this.head = new Node(value, null);
this.tail = head;
size++;
}
/**
* 默认插入数据到尾部
*/
public void add(T value) {
if (size != 0) {
Node node = new Node(value, null);
tail.nexNode = node;
tail = tail.nexNode;
} else {
this.head = new Node(value, null);
this.tail = head;
}
size++;
}
/**
* 插入数据到头部
*/
public void addToHead(T value) {
if (size != 0) {
Node node = new Node(value, head);
head = node;
} else {
this.head = new Node(value, null);
this.tail = head;
}
size++;
}
/**
* 插入数据到尾部
*/
public void addToTail(T value) {
add(value);
}
/**
* 根据索引返回其节点的数据
*/
public T get(int index) {
return getIndexNode(index).value;
}
/**
* 根据索引位置插入节点
*/
public void insert(int index, T value) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引越界");
}
if (index == 0) {
addToHead(value);
} else if (index == size - 1) {
addToTail(value);
} else {
Node beforeNode = getIndexNode(index - 1);
Node afterNode = getIndexNode(index);
Node insertNode = new Node(value, afterNode);
beforeNode.nexNode = insertNode;
size++;
}
}
/**
* 清空链表
*/
public void clear() {
//每一个结点的value和指向的前结点和后结点都置为null,防止内存溢出,有益GC回收
for (Node x = head; x != null; ) {
Node next = x.nexNode;
x.value = null;
x.nexNode = null;
x = next;
}
// 将底层数组所有元素赋为null
head = tail = null;
size = 0;
}
/**
* 删除指定位置的节点
*/
public void remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引越界");
}
if (index == 0) {
head.nexNode = null;
Node afterNode = getIndexNode(index + 1);
} else if (index == size - 1) {
Node beforeNode = getIndexNode(index - 1);
beforeNode.nexNode = null;
} else {
Node beforeNode = getIndexNode(index - 1);
Node afterNode = getIndexNode(index + 1);
Node removetNode = getIndexNode(index);
removetNode.nexNode = null;
beforeNode.nexNode = afterNode;
}
size--;
}
/**
* 判断是否包含
*/
public boolean contains(T value) {
if (null == value) {
return false;
}
Node currentNode = head;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (value.equals(currentNode.value)) {
return true;
}
currentNode = currentNode.nexNode;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 根据索引返回其节点
*/
public Node getIndexNode(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引越界");
}
//根据index大小来确定从头部查还是尾部查,以增加查询速度
Node currentNode = head;
for (int i = 0; i < size && currentNode != null; i++) {
if (i == index) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.nexNode;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String[] array = new String[size];
Node currentNode = head;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = String.valueOf(currentNode.value);
currentNode = currentNode.nexNode;
}
return Arrays.toString(array);
}
//此内部类用于实现迭代器,使得DoublieLinkedList能够通过Iterator来遍历
class SingleLinkedListIterator implements Iterator<T> {
Node cuerrentNode;
public SingleLinkedListIterator(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
cuerrentNode = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cuerrentNode != null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
if (cuerrentNode == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Node node = cuerrentNode;
cuerrentNode = node.nexNode;
return node.value;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new SingleLinkedListIterator(head);
}
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {
Iterable.super.forEach(action);
}
@Override
public Spliterator<T> spliterator() {
return Iterable.super.spliterator();
}
}
测试:
SingleLinkedList<Integer> d = new SingleLinkedList<>();
d.add(1);
d.add(2);
d.add(3);
d.add(4);
d.add(5);
d.add(6);
//指定位置插入
d.insert(2, 222);
//头部插入
d.addToHead(111);
//尾部插入
d.addToTail(999);
System.out.println("链表:" + d.toString());
//获取大小
System.out.println("链表长度:" + d.size);
//判断是否包含
System.out.println("判断是否包含222:" + d.contains(222));
//获取指定位置的元素
System.out.println("获取index是3的列表元素:" + d.get(3));
//删除指定位置的数据
d.remove(3);
System.out.println("删除index是3后的链表:" + d.toString());
System.out.println("链表长度:" + d.size);
System.out.println("遍历链表:");
for (Integer v : d) {
System.out.println(v);
}
//清空链表
d.clear();
System.out.println("清空链表后长度:" + d.size);
结果:
链表:[111, 1, 2, 222, 3, 4, 5, 6, 999]
链表长度:9
判断是否包含222:true
获取index是3的列表元素:222
删除index是3后的链表:[111, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 999]
链表长度:8
遍历链表:
111
1
2
3
4
5
6
999
清空链表后长度:0
