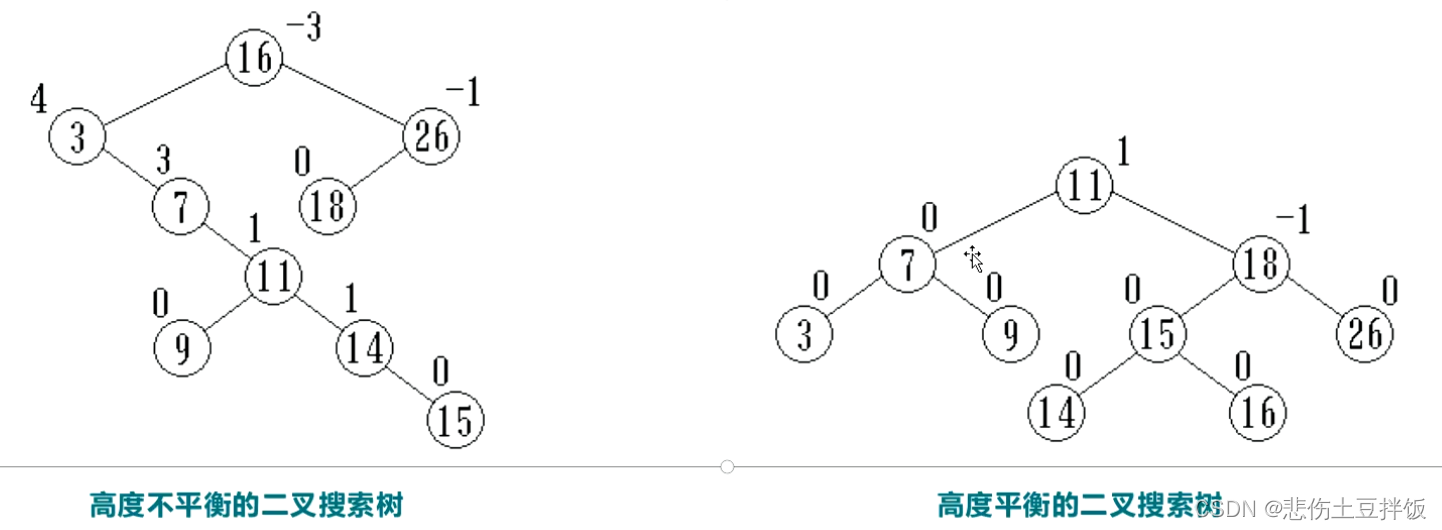
AVL树的定义
一颗AVL树或者是空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉搜索树:它的左子树和右子树都是AVL树,且左子树和右子树的高度只差绝对值不超过 1
结点的平衡因子 balance
- 每个结点附加一个数字,给出该结点右子树的高度减去左子树的高度所得的高度差,这个数字即为结点的平衡因子balance
- 根据AVL 树的定义,任一结点的平衡因子只能取 -1、0 和 1
- 如果一个结点的平衡因子的绝对值大于1,则这颗二叉搜索树就失去了平衡,不再是AVL树
- 如果一棵二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,它就成为AVL树,如果它有 n 个结点,其高度可保持在O(log2n),平均搜索长度也可保持在O(log2n)
AVL树的结构
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct AVLNode
{
KeyType key;
struct AVLNode* leftchild;
struct AVLNode* parent;
struct AVLNode* rightchild;
int balance; //-1 0 1
}AVLNode, * AVLTree;
AVL树的插入
在向一颗本来是高度平衡(0,1,-1)的AVL树中插入一个新结点和在BST树一样,区别是,如果树中某个结点的平衡因子的绝对值 [balance] > 1,则出现了不平衡,需要做平衡化处理,使得树中各结点重新平衡化
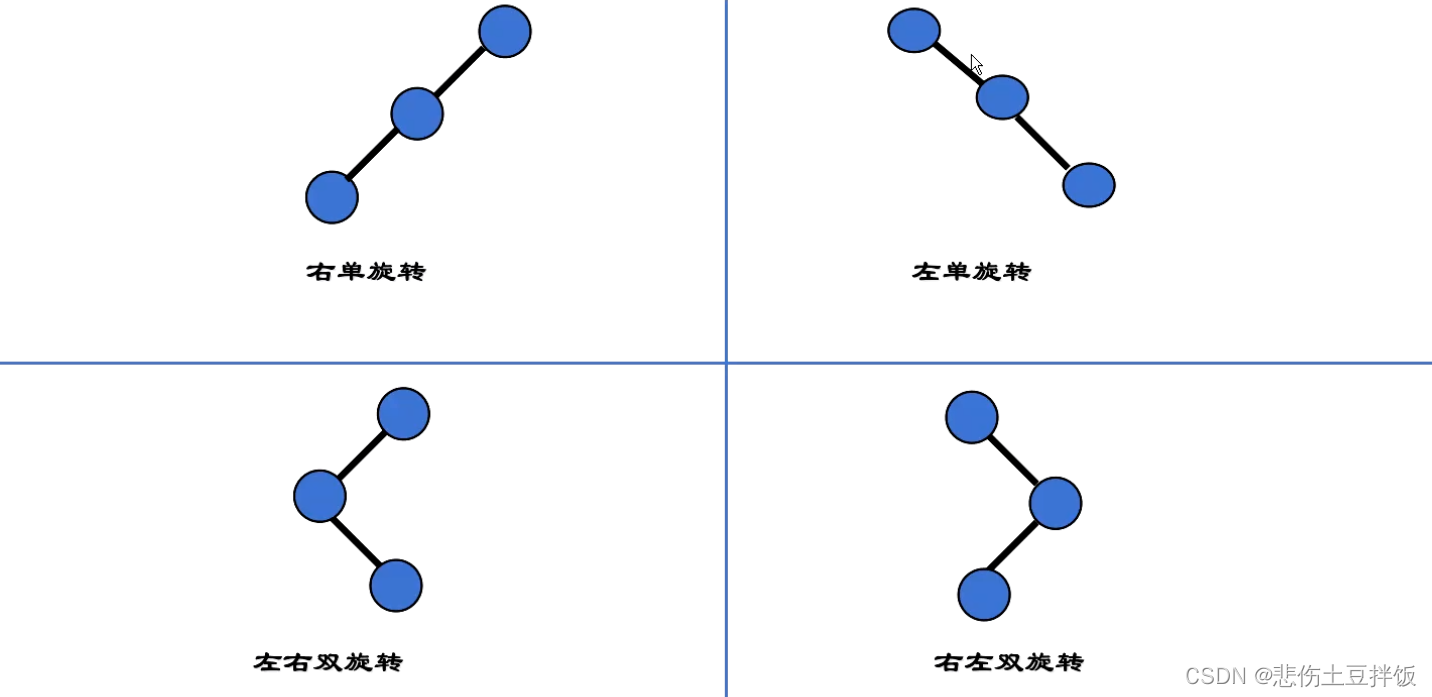
平衡化旋转
- 如果在一棵平衡的二叉搜索树中插入一个新结点,造成了不平衡。此时必须调整树的结构,使之平衡化
- 平衡化旋转有两类:
- 单旋转(左旋和右旋)
- 双旋转(左平衡和右平衡)
- 每插入一个新结点时,AVL树中相关结点的平衡状态会发生改变,因此,在插入一个新结点后,需要从插入位置沿通向根的路径回溯,检查各结点的平衡因子(左、右子树的高度差)
- 如果在某一结点发现高度不平衡,停止回溯
- 从发生不平衡的结点起,沿刚才回溯的路径取直接下两层的结点
- 如果在三个结点处于一条直线上,则采用单旋转进行平衡化,单旋转可按其方向分为左单旋转和右单旋转,其中一个是另一个的镜像,其方向与不平衡的形状相关
- 如果这三个结点处于一条折线上,则采用双旋转进行平衡化,双旋转分为先左后右和先右后左两类
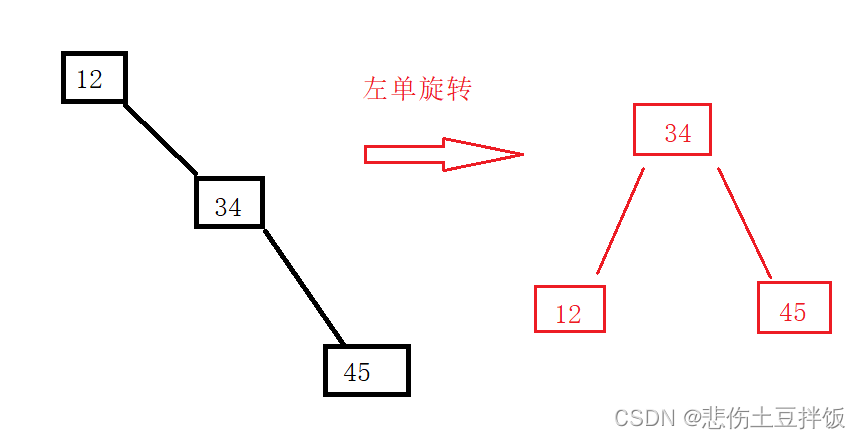
左单旋转
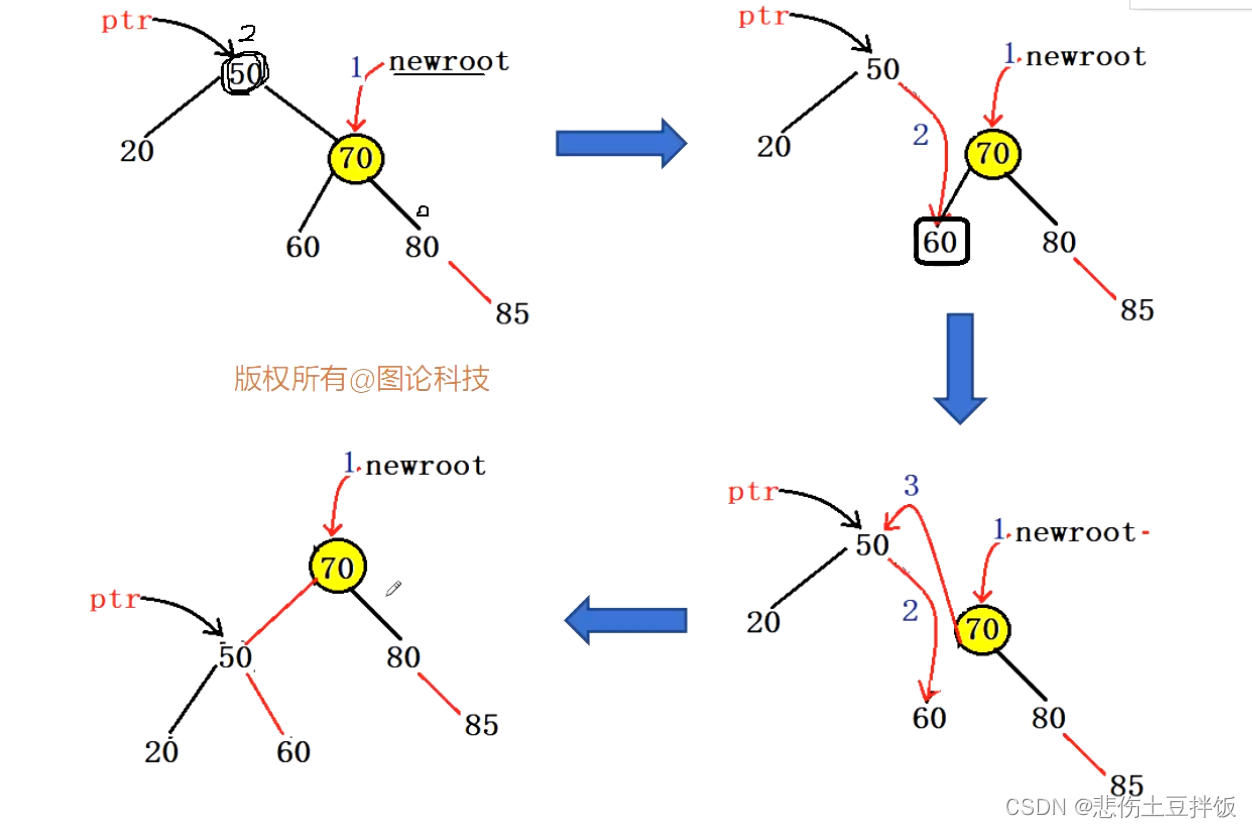
根据上图,当我们插入了结点85,70平衡因子变为1,50平衡因子变为2,失去平衡性;
- 那么将结点50作为ptr指针,将其进行旋转 ,使得ptr的右节点指向结点60,
- 令结点70的左子树指向结点50,继而规整成一个新的结点
void RotateLeft(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr)
{
AVLNode* newroot = ptr->rightchild; //a
newroot->parent = ptr->parent; //1 切换父节点
ptr->rightchild = newroot->leftchild;//b
if (newroot->leftchild != nullptr)
{
newroot->leftchild->parent = ptr;//2
}
newroot->leftchild = ptr; //c
if (ptr == tree)
{
tree = newroot;
}
else
{
if (ptr->parent->leftchild == ptr)
{
ptr->parent->leftchild = newroot;
}
else
{
ptr->parent->rightchild = newroot;
}
}
ptr->parent = newroot; //3
}
这三句代码分别对应:
结点50右子树指向结点70左子树结点60,接着将结点70左子树指向结点50
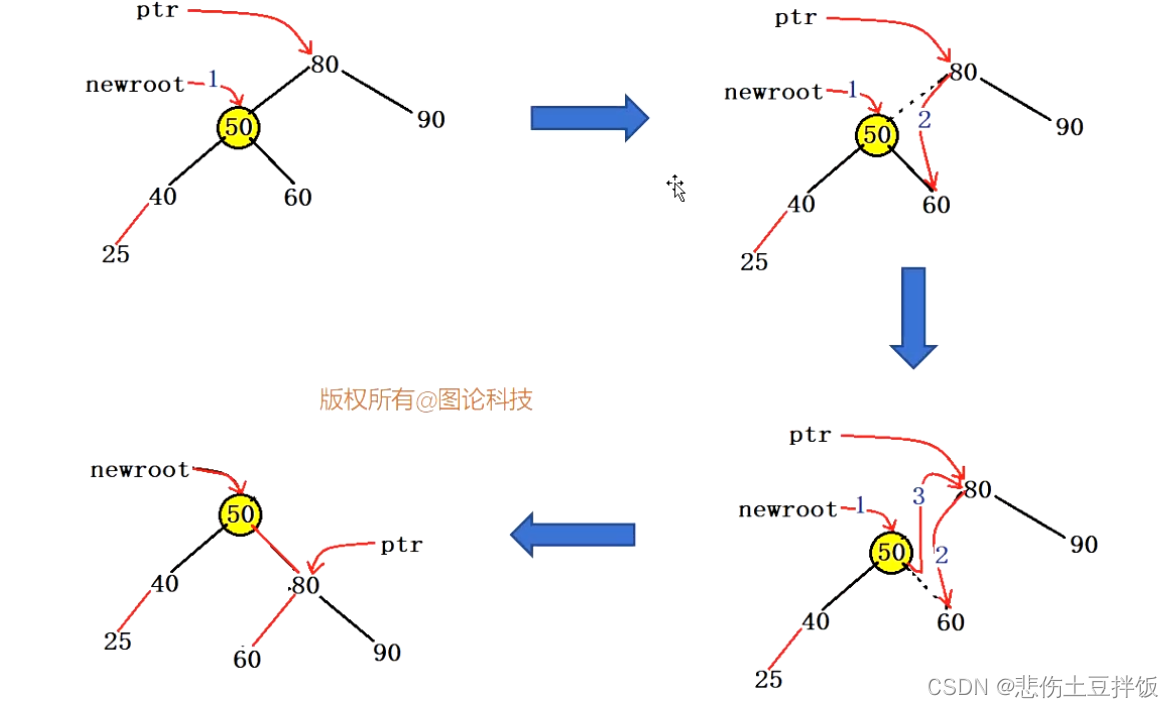
右单旋转
void RotateRight(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr)
{
AVLNode* newroot = ptr->leftchild;
newroot->parent = ptr->parent;
if (newroot->rightchild != nullptr)
{
newroot->rightchild->parent = ptr;
}
ptr->leftchild = newroot->rightchild;
newroot->rightchild = ptr;
if (ptr == tree)
{
tree = newroot;
}
else
{
if (ptr->parent->leftchild == ptr)
{
ptr->parent->leftchild = newroot;
}
else
{
ptr->parent->rightchild = newroot;
}
}
ptr->parent = newroot;
}
与左单旋转类似,仅需要对其进行相对变形
左双旋转
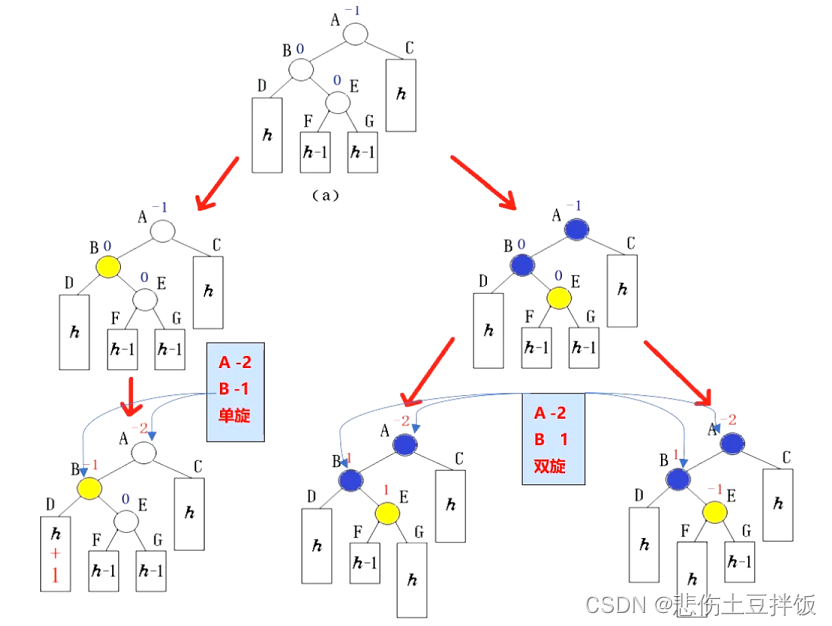
当我们在插入过程中,出现上面的情况,当我们新的结点插入F,或者G无论哪一个结点,出现了A->B->E 这样的一个折线,那么我们就需要进行双旋转进行二叉树的平衡
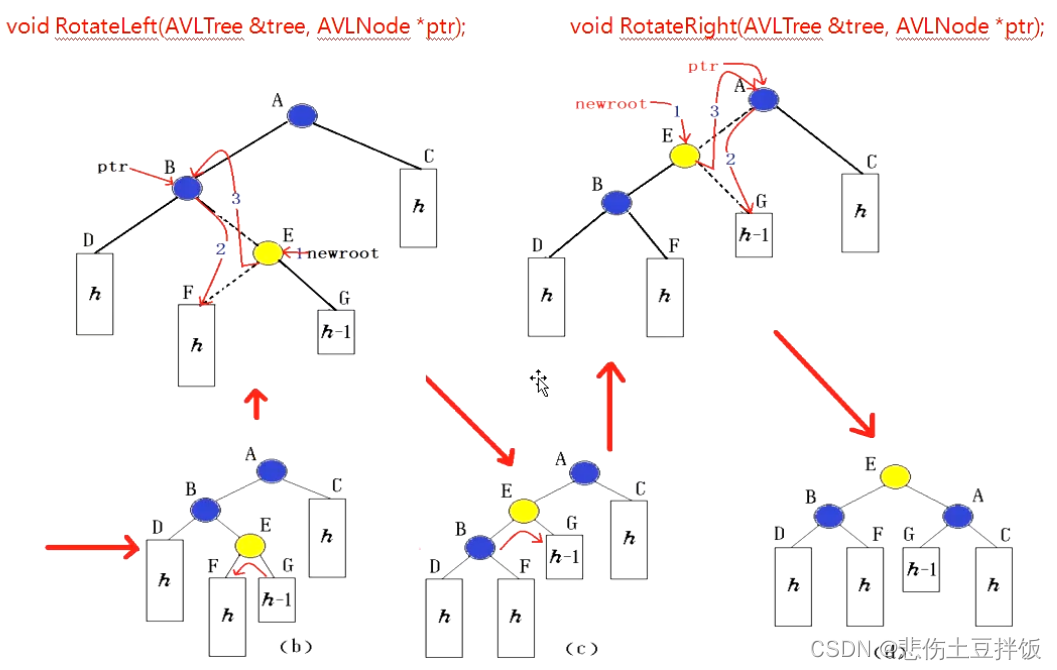
加入我们在F进行插入,E的平衡因子变为-1,B的平衡因子变为1,A的平衡因子变为-2,进行双旋转,首先以 B 作为 ptr 进行左单旋转,变为图(c ) 再将 A 作为 ptr E为旋转点进行右单旋转变为图(d)
插入 insert
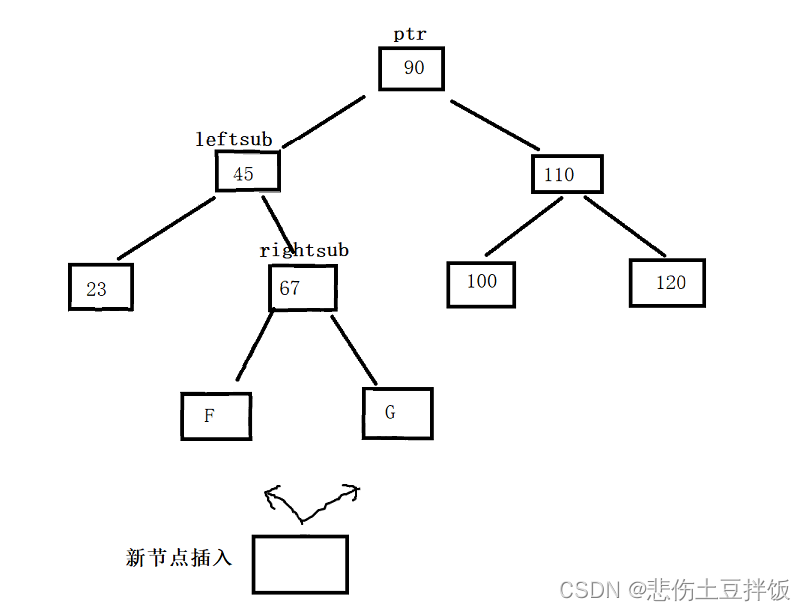
AVL树的插入与BST树的插入相似,但是需要进行高度平衡,继而要进行左右单旋转与左右双旋转,通过旋转还平衡二叉树,以及通过平衡因子的操作旋转,上图为左双旋转的实例,无论新节点插入F,或者G都需要进行左双旋转,因为ptr、leftsub、rightsub 组成了一个折线
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct AVLNode
{
KeyType key;
struct AVLNode* leftchild;
struct AVLNode* parent;
struct AVLNode* rightchild;
int balance; //-1 0 1
}AVLNode, * AVLTree;
AVLNode* Buynode(KeyType kx)
{
AVLNode* s = (AVLNode*)malloc(sizeof(AVLNode));
if (s == NULL) exit(1);
memset(s, 0, sizeof(AVLNode));
s->key = kx;
s->balance = 0;
return s;
}
AVLNode* MakeRoot(KeyType kx)
{
AVLNode* s = Buynode(kx);
s->key = kx;
return s;
}
void RotateLeft(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr)
{
AVLNode* newroot = ptr->rightchild;
newroot->parent = ptr->parent;
if (newroot->leftchild != nullptr)
{
newroot->leftchild->parent = ptr;
}
ptr->rightchild = newroot->leftchild;
newroot->leftchild = ptr;
if (ptr == tree)
{
tree = newroot;
}
else
{
if (ptr->parent->leftchild == ptr)
{
ptr->parent->leftchild = newroot;
}
else
{
ptr->parent->rightchild = newroot;
}
}
ptr->parent = newroot;
}
void RotateRight(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr)
{
AVLNode* newroot = ptr->leftchild;
newroot->parent = ptr->parent;
ptr->leftchild = newroot->rightchild;
if (newroot->rightchild != nullptr)
{
newroot->rightchild->parent = ptr;
}
newroot->rightchild = ptr;
if (ptr == tree)
{
tree = newroot;
}
else
{
if (ptr->parent->leftchild == ptr)
{
ptr->parent->leftchild = newroot;
}
else
{
ptr->parent->rightchild = newroot;
}
}
ptr->parent = newroot;
}
void RightBalance(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr) //右双旋转 左双旋的镜像
{
AVLNode* rightsub = ptr->rightchild, * leftsub = nullptr;
switch (rightsub->balance)
{
case 0: cout << "right balance" << endl; break;
case 1:
ptr->balance = 0;
rightsub->balance = 0;
RotateLeft(tree, ptr);//左上右下的一条斜线 进行左单旋 下面左双旋的时候同理
break;
case -1:
leftsub = rightsub->leftchild;
switch (leftsub->balance)
{
case -1:
rightsub->balance = 1 ;
ptr->balance = 0;
break;
case 1:
rightsub->balance = 0;
ptr->balance = -1;
break;
case 0:
rightsub->balance = 0;
ptr->balance = 0;
break;
}
leftsub->balance = 0;
RotateRight(tree, rightsub);
RotateLeft(tree, ptr);
break;
}
}
void LeftBalance(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* ptr)
{
//传入的ptr是平衡因子为-2的结点
AVLNode* leftsub = ptr->leftchild, * rightsub = nullptr;
// 根节点的左边 折线的中间节点
switch (leftsub->balance)
{
case 0: cout << "left balance" << endl; break;
case -1: //向左延申的直线
ptr->balance = 0;
leftsub->balance = 0;
RotateRight(tree, ptr);
break;
case 1: //一条折线 左双旋转
rightsub = leftsub->rightchild;
//根节点左边的右边,折线的下面节点
switch (rightsub->balance)
{
case -1: //插入在左边
leftsub->balance = 0; //原本ptr的左孩子 现在也是ptr的左孩子
ptr->balance = 1; //ptr做双旋后变为了右孩子
break;
case 1: //插入在右边
leftsub->balance = -1;
ptr->balance = 0;
break;
case 0: //左双旋转后为0
leftsub->balance = 0;
ptr->balance = 0;
break;
}
rightsub->balance = 0; //最终作根的结点,树两边高度相同
RotateLeft(tree, leftsub);//左单旋转 ptr(最上面节点)是折线中间节点
RotateRight(tree, ptr); //右单旋转 ptr 是折线上面节点
break;
}
}
void PassBalance(AVLTree& tree, AVLNode* p)
{
AVLNode* pa = p->parent;
bool tall = true; //判断高度是否变化
for (; pa != nullptr && tall;)
{
if (pa->leftchild == p) //判断左孩子或右孩子
{
switch (pa->balance)
{
case 0: pa->balance = -1; break;
case 1: pa->balance = 0; tall = false; break;
case -1:
LeftBalance(tree, pa);
tall = false;
break;
}
}
else
{
switch (pa->balance)
{
case 0: pa->balance = 1; break;
case -1: pa->balance = 0; tall = false; break;
case 1:
RightBalance(tree, pa);
tall = false;
break;
}
}
p = pa;
pa = p->parent;
}
}
bool Insert(AVLNode*& tree, KeyType kx)
{
if (tree == nullptr)
{
tree = MakeRoot(kx);
return true;
}
AVLNode* pa = nullptr;
AVLNode* p = tree;
while (p != nullptr && p->key != kx)
{
pa = p;
p = kx < p->key ? p->leftchild : p->rightchild;
}
if (p != nullptr && p->key == kx) return false;
p = Buynode(kx);
p->parent = pa;
if (kx < pa->key)
{
pa->leftchild = p;
}
else
{
pa->rightchild = p;
}
PassBalance(tree, p); //回溯
return true;
}
void InOrder(AVLNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
InOrder(ptr->leftchild);
cout << ptr->key << " " << ptr->balance << endl;
InOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
int main()
{
int ar[] = { 12,23,34,45,56,67,78,89,90,100 };
AVLTree root = nullptr;
for (auto& x : ar)
{
cout << Insert(root, x) << endl;
}
InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
AVL 树的删除
如果被删除的节点 x 最多只有一个子女,那么问题比较简单,如果被删除节点 x 右两个子女,首先搜索 x 在中序次序下的直接前驱 y (同样可以找直接后继);再把节点 y 的内容传送给结点 x ,现在问题转移到删除结点 y ,把结点 y 当作被删除的结点 x
将结点 x 从树中删去,因为结点 x 最多右一个子女,那么我们可以简单地把 x 的双亲结点中原来指向 x 的指针改指到这个子女结点;如果结点 x 没有子女,x 双亲结点的相应指针置为 NULL,然后将原来以结点 x 为根的子树的高度减 1
- 必须沿 x 通过向根路径反向追踪高度的变化对路经上各个结点的影响
- 用一个布尔遍历 shorter 来指向子树的高度是否被缩短,在每个结点上要做的操作取决于 shorter 的值和结点的 balance 有时还要依赖子女的 balance
- 布尔变量 shorter 的值初始化为 True,然后对于从 x 的双亲到根的路径上的各个结点 p,在shorter 保持为 True 时执行下面的操作,如果 shorter 变成 False,算法终止
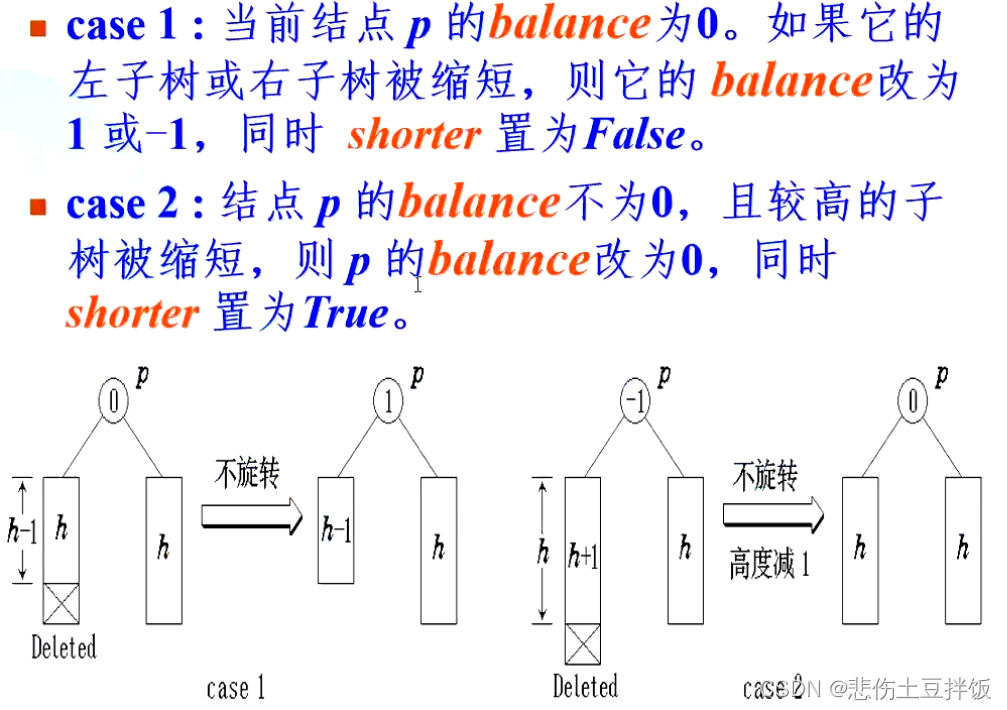
case 1:虽然删掉节点使得p的平衡因子变为了1,但是对于树的总体高度没有变化,依旧为h
case 2:当删掉节点后,p的平衡因子变为0,但是该树的总体高度由h+1变为了h,使得其父亲结点的平衡因子也会随之变化,那么就需要进行回溯

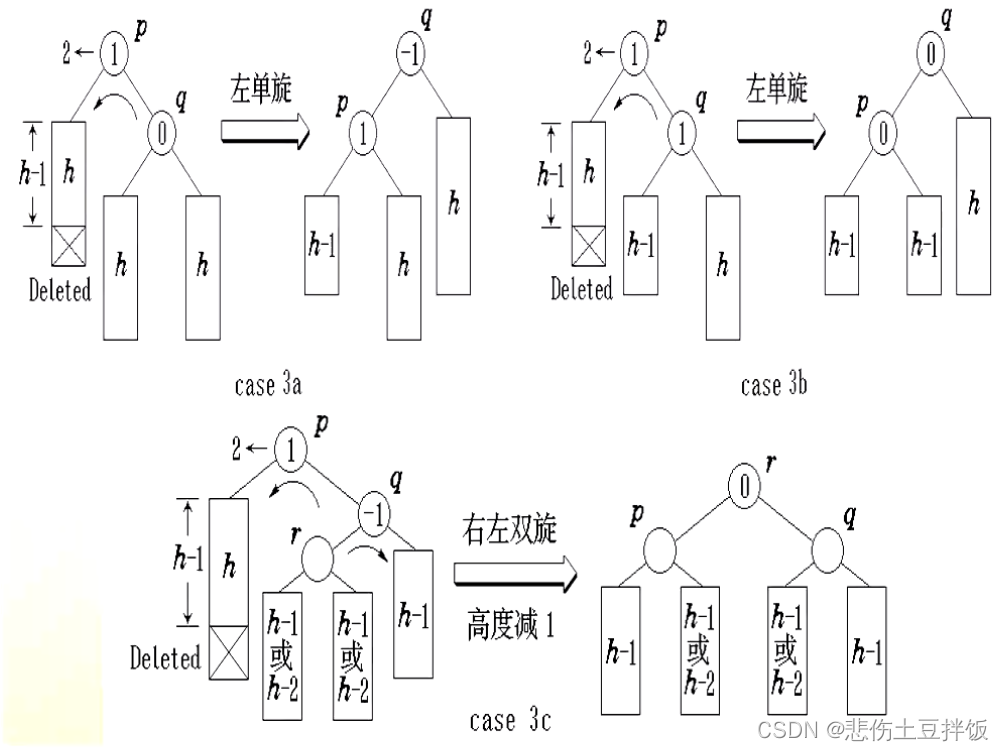

总结来说,就是要分析在平衡树的过程中是否对树的总体高度进行了影响,如果影响到了就需要进行回溯
