目录
题目
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]?按?升序?排列lists[i].length?的总和不超过?10^4
分析
? ? ? ? 条件确认
? ? ? ? 在分析前,对于链表题目我们首先需要明确是否允许在原链表上操作,如果不允许,我们就要创建一个新的链表来返回结果(这里题目未作明确要求,我们默认允许在原链表上操作)。其次就是输入条件数组是否可能为空以及数组中的链表是否可能为空。
? ? ? ? 题目分析
? ? ? ? 图片来源《四种解法+多图演示 23. 合并K个排序链表》
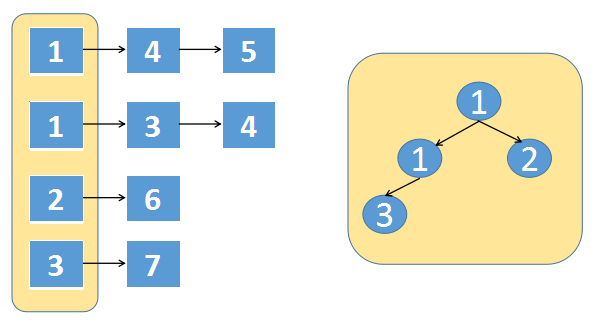
? ? ? ? 两两合并
? ? ? ? ?在以往的题目中,我们曾经做过这题的简化版《21. 合并两个有序链表》,本题将2个链表扩展成了K个链表,我们可以不断的合并两个链表直到所有链表合并完成。
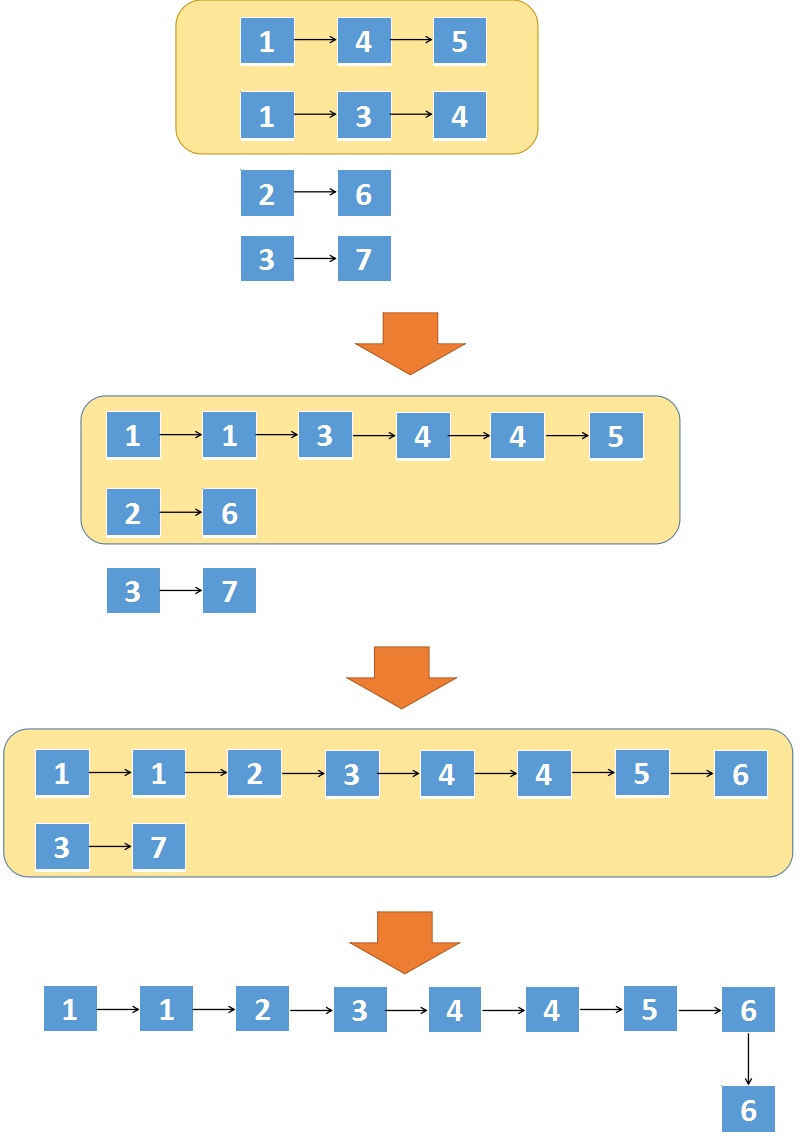
? ? ? ? 分治归并
? ? ? ? 我们可以将大的问题化解成小的问题,使用分治的方法,由底向上每次合并2个链表,直到所有链表合并完成。
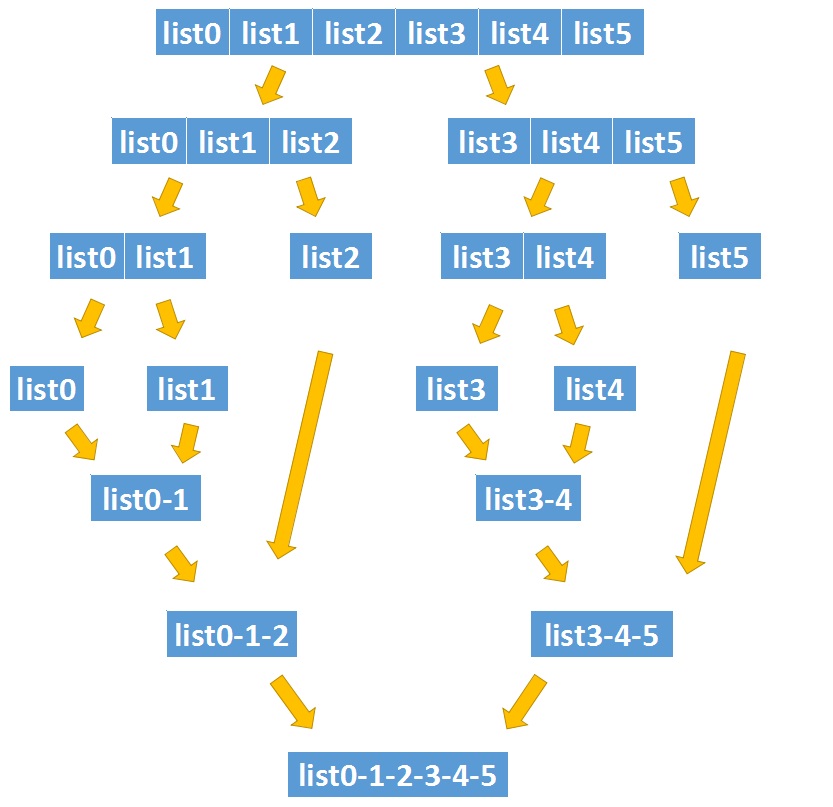
? ? ? ? 优先队列
? ? ? ? 暴力破解的方法需要不断的遍历数组中的所有元素,于是我们考虑使用额外的空间将当前遍历到的元素作为候选存储起来,这样就省去了不断遍历的时间。这里我们使用优先队列来辅助求解(在使用前最好沟通下是否允许API,如果不允许那么我们还要自己手动实现下小根堆)。
解答
????????简化分析
? ? ? ? 先来回忆下合并2个链表,我们可以使用迭代与递归2中方法求解:
? ? ? ? 迭代,2个指针同时遍历这两个边表,不断将最小值取出,同时将问题转化未list1.next与list2合并,这样不断递归下去直到结束。
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = list1 == null? list2: list1;
return dummyHead.next;
}? ? ? ? ?分治,比较当前2个元素的大小,并将问题转化为list1.next与list2的合并问题。
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}????????两两合并
? ? ? ? 一次遍历+合并2个升序链表即可完成,代码最简单,但是复杂度也最高。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode res = null;
for (ListNode list: lists) {
res = mergeTwoLists(res, list);
}
return res;
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = list1 == null? list2: list1;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}?????????我们知道合并2个链表的时间复杂度为O(a+b),a与b分别为这两个链表的长度,我们假设每个链表的平均长度为n,第1次到第K次合并的复杂度依次为2n,3n,,4n,...(k-1)n,由此可以得出总的复杂度为(1+k)*k*n/2。
? ? ? ? 因此时间复杂度为O((k^2)*n)。空间复杂度为O(1)。
????????分治归并
? ? ? ? 每次取2个链表,将这2个链表合并,然后不断扩大,合并4个元素,8个元素,直至全部合并。这里取出2个链表的方式有迭代与递归两种。
? ? ? ? 迭代
? ? ? ? 我们通过遍历的方式,每次取2个相邻位置的链表进行合并,并置入lists[index++]位置中,形成新的链表,这样,每一轮遍历完后,我们得到了index个两两合并后的新链表,再重复以上过程,直至最后合并为1个。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int size = lists.length;
// size=1时表明已全部汇总到了一个链表中
while(size>1){
int index = 0;
for(int i=0;i<size;i+=2){
// 可能存在最后的元素不满足两两合并的要求,因此独立为1个链表
if(i==size-1){
lists[index++] = lists[i];
}else{
lists[index++] = mergeTwoLists(lists[i],lists[i+1]);
}
}
// 更新本轮合并后的链表
size = index;
}
return lists[0];
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = list1 == null? list2: list1;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}? ? ? ? 结合之前的分析,我们每一轮迭代都是讲所有的链表进行了一次合并,因此每一轮的时间复杂度为n*K(链表个数为k,平均长度为n),迭代轮数为logK(每次合并2个,参考二分),因此最终的时间复杂度为O(n*K*logK),空间复杂度为O(1)。
????????递归
? ? ? ? 递归的做法是将链表数组无限二分直至只剩1个元素,然后向上返回递归时两两合并链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int size = lists.length;
return merge(lists,0,lists.length-1);
}
// 二分法递归至只有1个链表,再往上两两合并
public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists,int left,int right){
if(left==right){
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left+(right-left)/2;
// 这里递归的时候记得带上mid,不然会漏掉元素
ListNode list1 = merge(lists,left,mid);
ListNode list2 = merge(lists,mid+1,right);
// 二分出的2个子链表合并完后,在对这两个子链表合并
return mergeTwoLists(list1,list2);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = list1 == null? list2: list1;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}????????最终的时间复杂度为O(n*K*logK),空间复杂度为O(logK)。
????????优先队列
? ? ? ? 利用优先队列自动实现排序的效果,将所有元素逐个加入到队列中再依次取出当前最小值即可。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists==null || lists.length==0){
return null;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
// 定义优先队列,重写比较规则
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>((v1,v2)->(v1.val-v2.val));
for(ListNode node : lists){
if(node!=null){
queue.add(node);
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ListNode temp = queue.poll();
// 注意判空
if(temp.next!=null){
queue.add(temp.next);
}
curr.next = temp;
curr = curr.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}? ? ? ? 总元素个数为n*k,优先队列每次调整的时间为logK,因此时间复杂度为O(K*n*logK),空间复杂度为O(K)。
? ? ? ? 如果不允许使用优先队列的话我们需要手动实现一个小根堆。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists==null||lists.length==0){
return null ;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1) ;
ListNode cur = dummy ;
MyHeap minHeap = new MyHeap() ;
for(int i=0;i<lists.length;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null){
minHeap.offer(lists[i]);
}
}
while(!minHeap.isEmpty()){
ListNode temp = minHeap.poll() ;
cur.next = temp ;
cur=cur.next ;
if(temp.next!=null){
minHeap.offer(temp.next);
}
}
return dummy.next ;
}
class MyHeap {
private ArrayList<ListNode> list ;
public MyHeap (){
this.list = new ArrayList<>() ;
}
public int size(){
return list.size() ;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return list.size()==0 ;
}
//入队操作
public void offer(ListNode node){
if(list.size()==0){
list.add(node);
return ;
}
list.add(node);
floatUp(list.size()-1);
}
//出队操作
public ListNode poll (){
if(list.size()==0){
return null ;
}
if(list.size()==1){
ListNode res = list.get(0) ;
list.remove(0);
return res ;
}
ListNode res = list.get(0);
swap(0,list.size()-1);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
sinkDown(0);
return res ;
}
public ListNode peek(){
return list.get(0) ;
}
// 向上调整
public void floatUp (int index){
int size = list.size();
while(index>0){
int parent = index%2==0?index/2-1:index/2 ;
if(index%2==1&&index+1<size&&list.get(index).val>list.get(index+1).val){
index++;
}
if(list.get(index).val<list.get(parent).val){
swap(index,parent);
}else{
break ;
}
index=parent;
}
}
// 向下调整
public void sinkDown (int index){
int size = list.size() ;
while(index*2+1<size){
int son = 2*index+1 ;
if(son+1<size&&list.get(son).val>list.get(son+1).val){
son++;
}
if(list.get(son).val<list.get(index).val){
swap(son,index);
}else{
break;
}
index = son ;
}
}
public void swap (int i ,int j){
Collections.swap(list,i,j);
}
}
}
