欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
给定平面内三角网格进行最优delauney三角化
空圆性
如果一个三角网格中任意一对三角形满足空圆性,则该三角网格为delauney三角化网格。
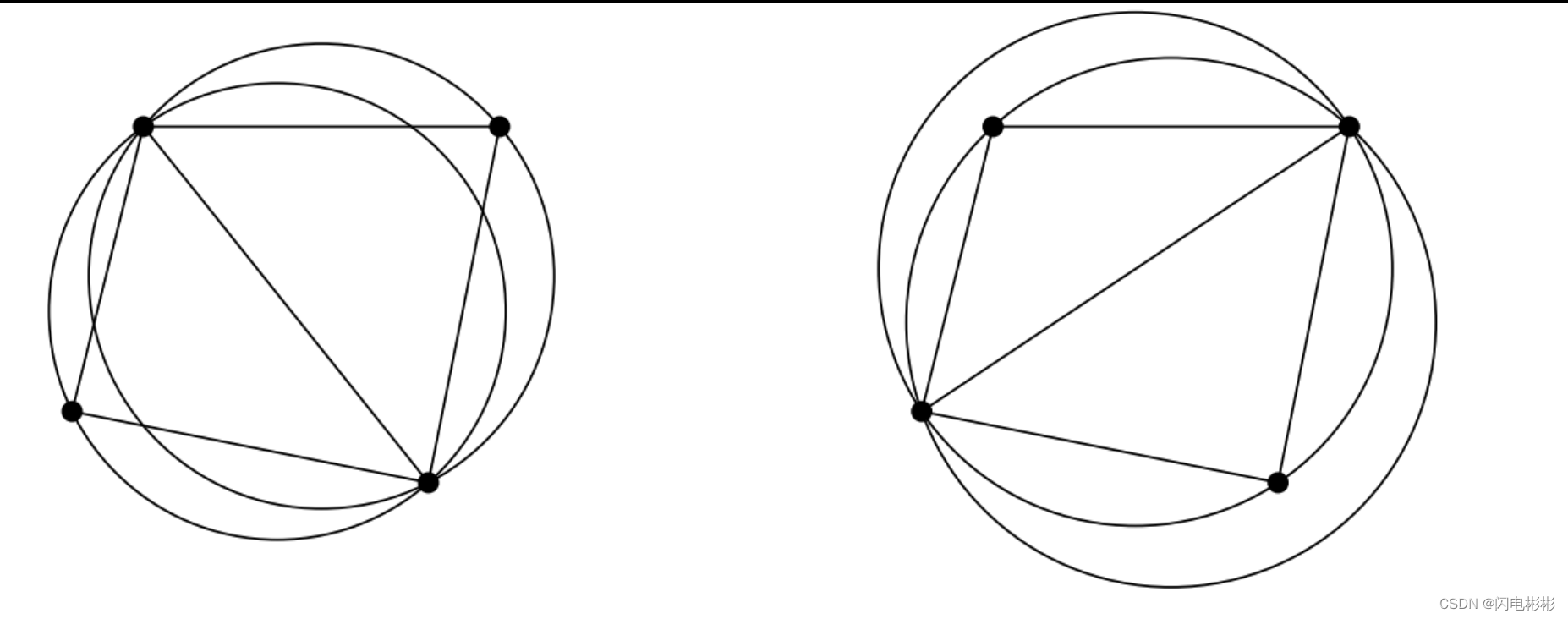
对其中一个三角形作外接圆,如果圆没有第4个点,则满足空圆。否则不满足。如果一对三角形不满足空圆性,则只要调整中间的分隔边即可。
如上图,右边是不满足空圆性的,调整中间的边,变成左边的图就满足了。
可以证明,如果所有局部满足空圆性,则全局也满足空圆性。
空圆性判断
按照定义可以对三角形作外接圆进行判断,此种方法比较麻烦。
还有一种简便方法。
可 以 计 算 边 e 的 2 个 对 角 α 1 , α 2 , 如 果 α 1 + α 2 > π , 则 不 满 足 空 圆 性 。 可以计算边e的2个对角\alpha_1, \alpha_2, 如果\alpha_1+\alpha_2>\pi, 则不满足空圆性。 可以计算边e的2个对角α1?,α2?,如果α1?+α2?>π,则不满足空圆性。
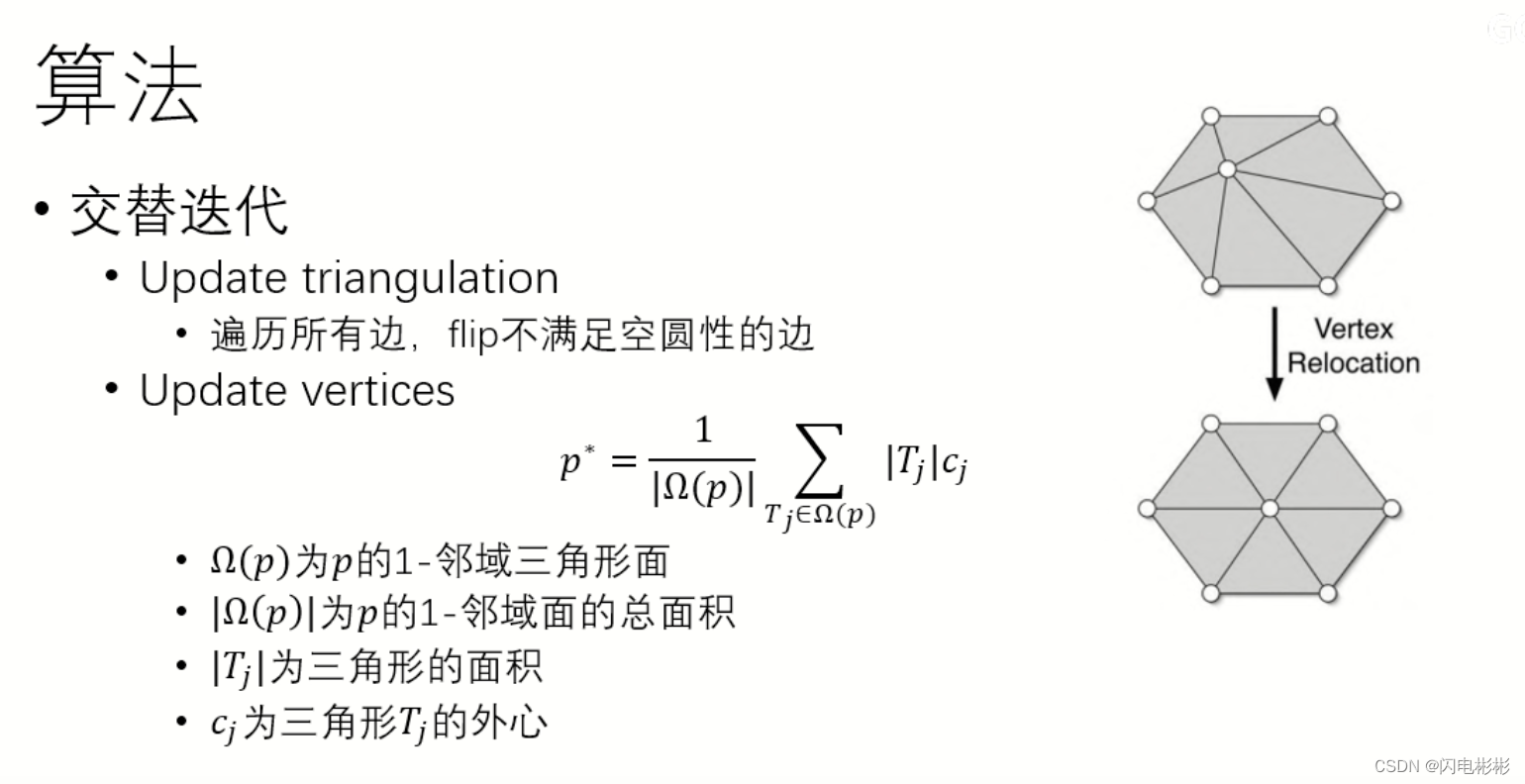
顶点最优化
上述只能保证是一外delauney三角网格,但是网格的分布还不是很均匀。
想要得到均匀的网格,需要对顶点位置进行优化。优化公式如下。
算法实现

代码库:https://github.com/LightningBilly/ACMAlgorithms/tree/master/图形学算法/三角网格算法/MeshWork/src/hw12/
#include "../../PolyMesh/IOManager.h"
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace acamcad;
using namespace polymesh;
PolyMesh* mesh12;
double get_TriFace_Area(MPolyFace* f)
{
MHalfedge* he = f->halfEdge();
MPoint3 v0 = he->fromVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v1 = he->toVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v2 = he->next()->toVertex()->position();
return 0.5 * ((v1 - v0) % (v2 - v0)).norm();
}
MPoint3 get_TriFace_Circumcenter(MPolyFace* f)
{
MHalfedge* he = f->halfEdge();
MPoint3 v0 = he->fromVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v1 = he->toVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v2 = he->next()->toVertex()->position();
double x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3;
x1 = v0[0]; y1 = v0[1];
x2 = v1[0]; y2 = v1[1];
x3 = v2[0]; y3 = v2[1];
double a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2;
a1 = 2 * (x2 - x1); a2 = 2 * (x3 - x2); c1 = x2 * x2 + y2 * y2 - x1 * x1 - y1 * y1;
b1 = 2 * (y2 - y1); b2 = 2 * (y3 - y2); c2 = x3 * x3 + y3 * y3 - x2 * x2 - y2 * y2;
MPoint3 circumcenter(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
circumcenter[0] = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2) / (a1 * b2 - a2 * b1);
circumcenter[1] = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1) / (a1 * b2 - a2 * b1);
circumcenter[2] = 0;
return circumcenter;
}
void Optimal_Delaunay_Trianglation(int iter_num)
{
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < iter_num; i++)
{
// flip
for (EdgeIter e_it = mesh12->edges_begin(); e_it != mesh12->edges_end(); ++e_it)
{
if (mesh12->isBoundary(*e_it) || !mesh12->is_flip_ok_Triangle(*e_it)) continue;
MHalfedge* he1 = (*e_it)->halfEdge();
MHalfedge* he2 = (*e_it)->halfEdge()->next();
MHalfedge* he3 = (*e_it)->halfEdge()->pair()->next();
MPoint3 v1 = he1->fromVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v2 = he1->toVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v3 = he2->toVertex()->position();
MPoint3 v4 = he3->toVertex()->position();
double alpha(0.0), alpha1(0.0), alpha2(0.0);
alpha1 = acos((pow((v1 - v3).norm(), 2) + pow((v2 - v3).norm(), 2)
- pow((v1 - v2).norm(), 2)) / (2 * (v1 - v3).norm() * (v2 - v3).norm()));
alpha2 = acos((pow((v1 - v4).norm(), 2) + pow((v2 - v4).norm(), 2)
- pow((v1 - v2).norm(), 2)) / (2 * (v1 - v4).norm() * (v2 - v4).norm()));
alpha = alpha1 + alpha2;
if (alpha > M_PI) mesh12->flipEdgeTriangle(*e_it);
}
// update vertex position
for (VertexIter v_it = mesh12->vertices_begin(); v_it != mesh12->vertices_end(); ++v_it)
{
if (mesh12->isBoundary(*v_it)) continue;
MPoint3 tmp(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
double area(0.0), sum_area(0.0);
for (VertexFaceIter vf_it = mesh12->vf_iter(*v_it); vf_it.isValid(); ++vf_it)
{
area = get_TriFace_Area(*vf_it);
sum_area += area;
MPoint3 center = get_TriFace_Circumcenter(*vf_it);
tmp = tmp + area * center;
}
(*v_it)->setPosition(tmp / sum_area);
}
}
}
void delaunay_trianglation(){
mesh12 = new PolyMesh();
char buffer[500];
getcwd(buffer, 500);
printf("The current directory is: %s/../\n", buffer);
string mesh_path = buffer;
mesh_path += "/../src/hw12/leaf.obj";
loadMesh(mesh_path, mesh12);
std::string out_path = "leaf-tri.obj";
//loadMesh("rectangle.obj", mesh);
int iter_num = 1000; // iterative number
Optimal_Delaunay_Trianglation(iter_num);
writeMesh(out_path, mesh12);
}
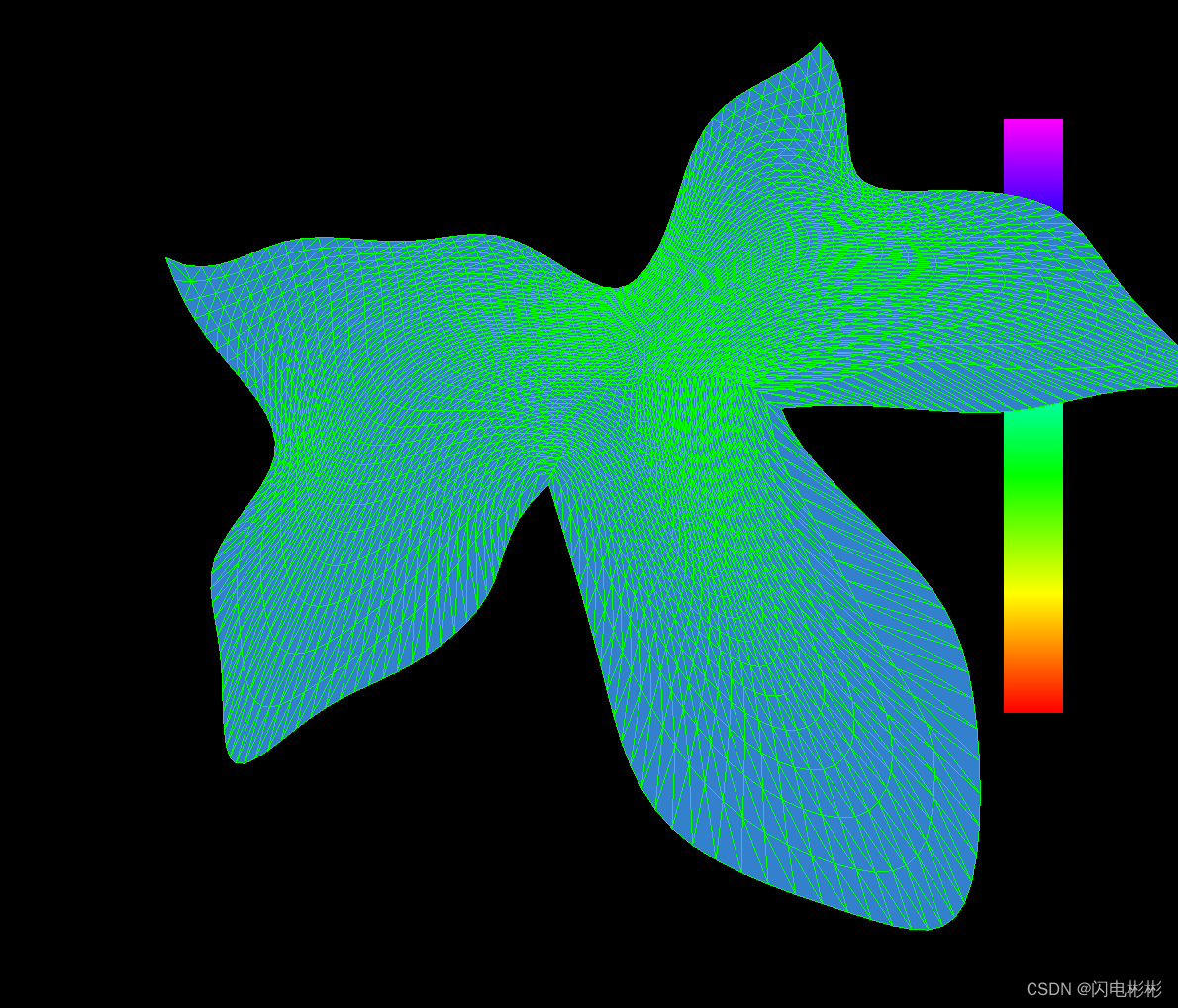
效果展示
优化前
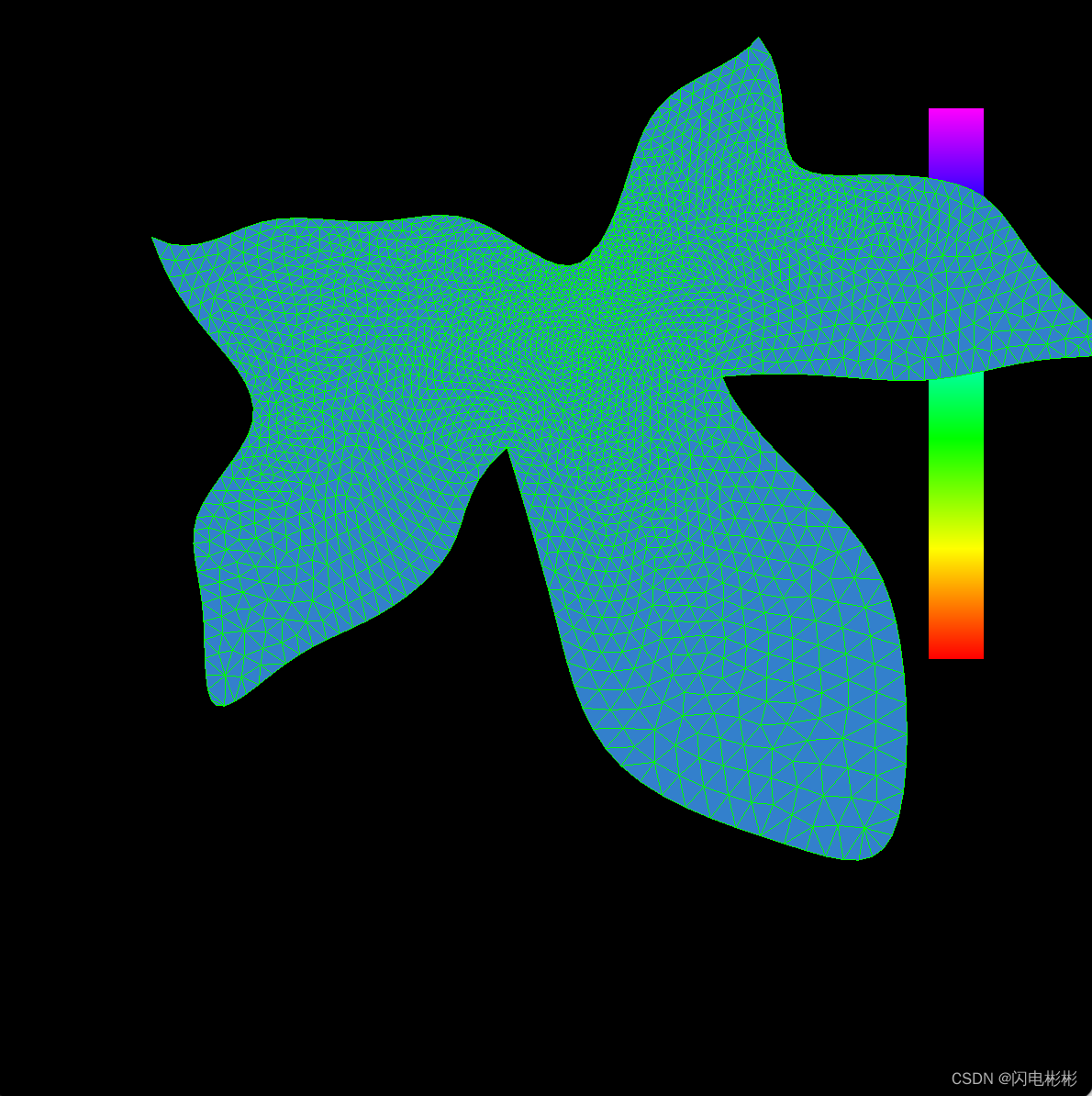
优化后
迭代10次
迭代100次
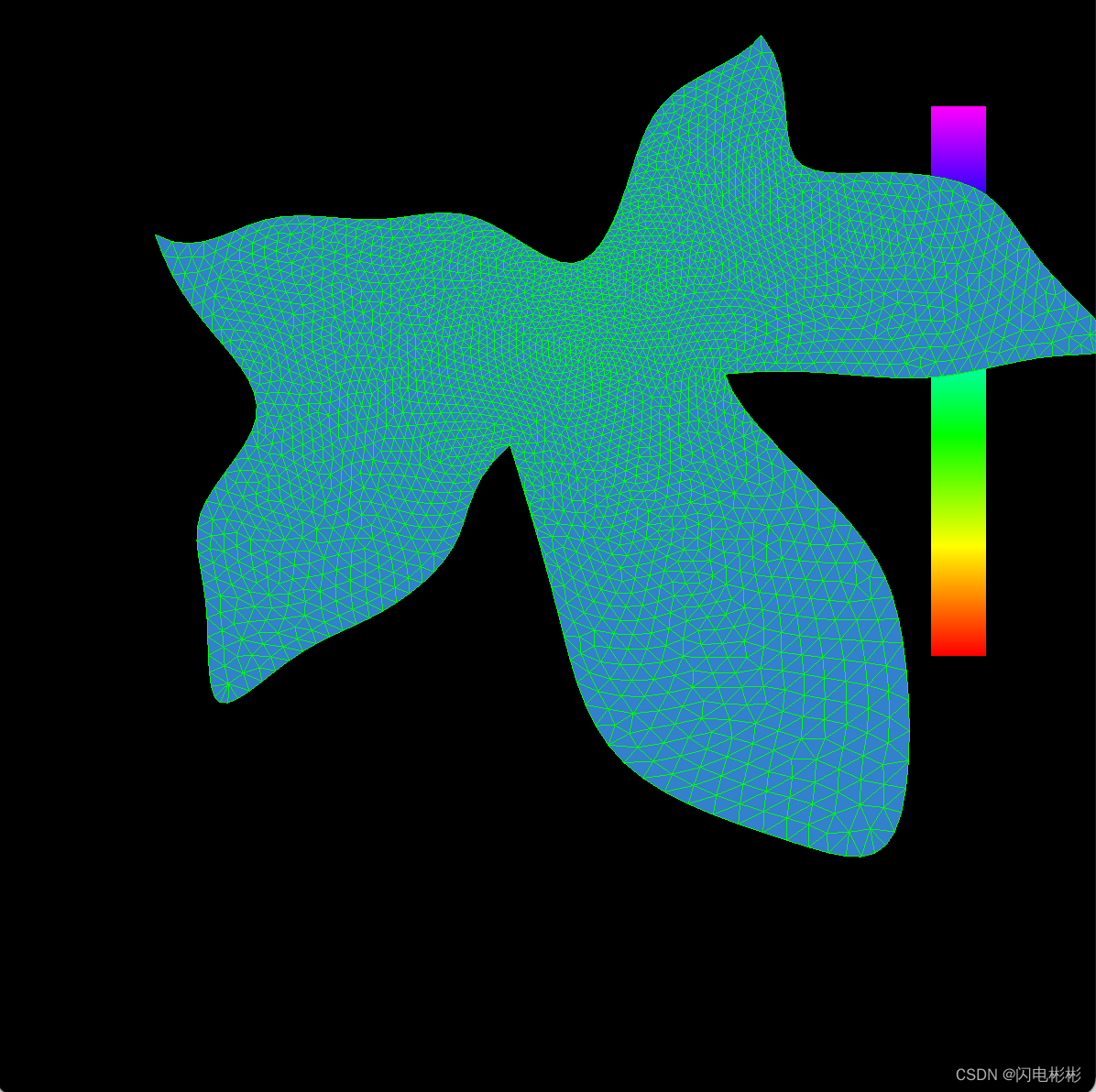
迭代200次
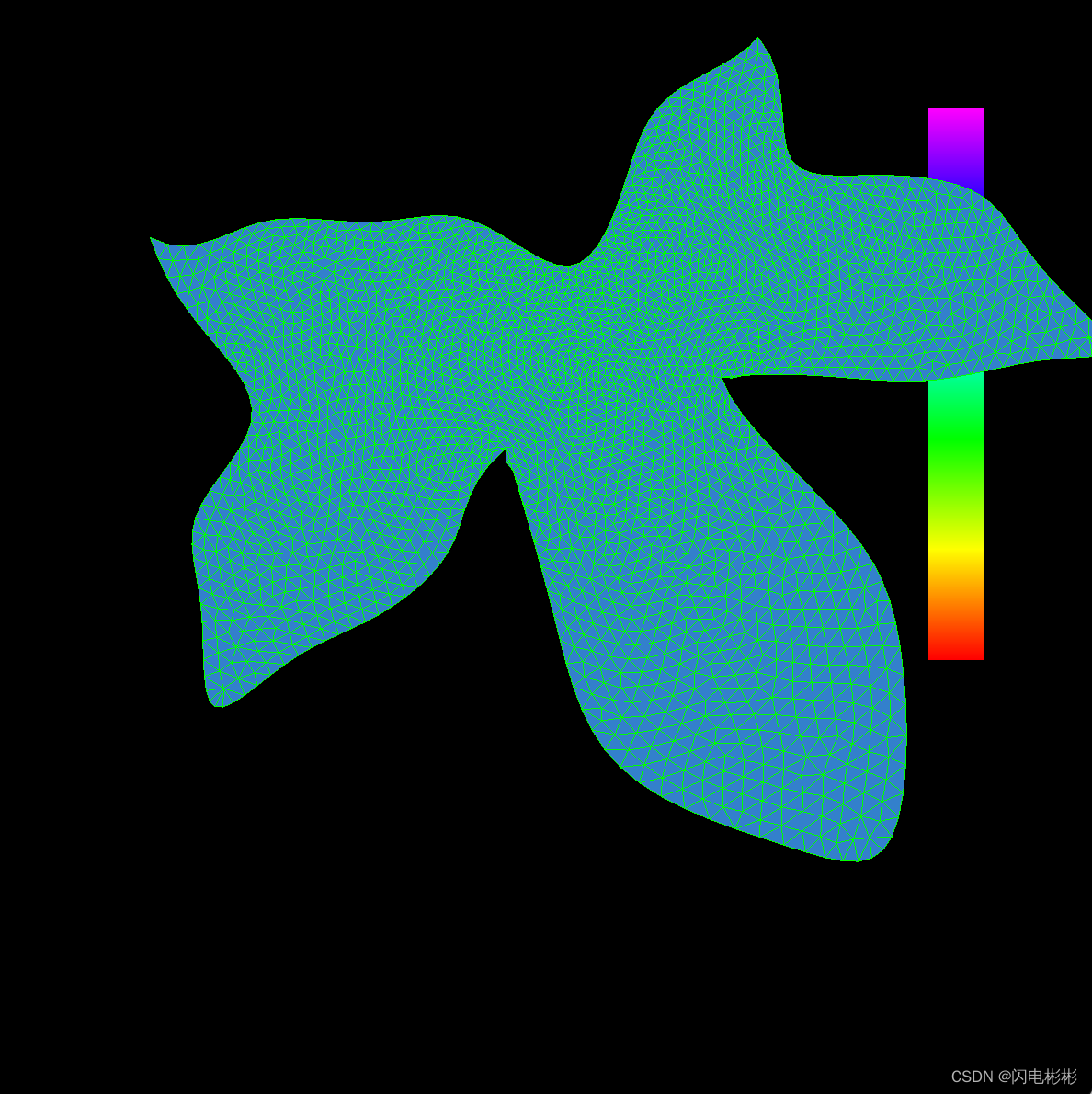
迭代500次
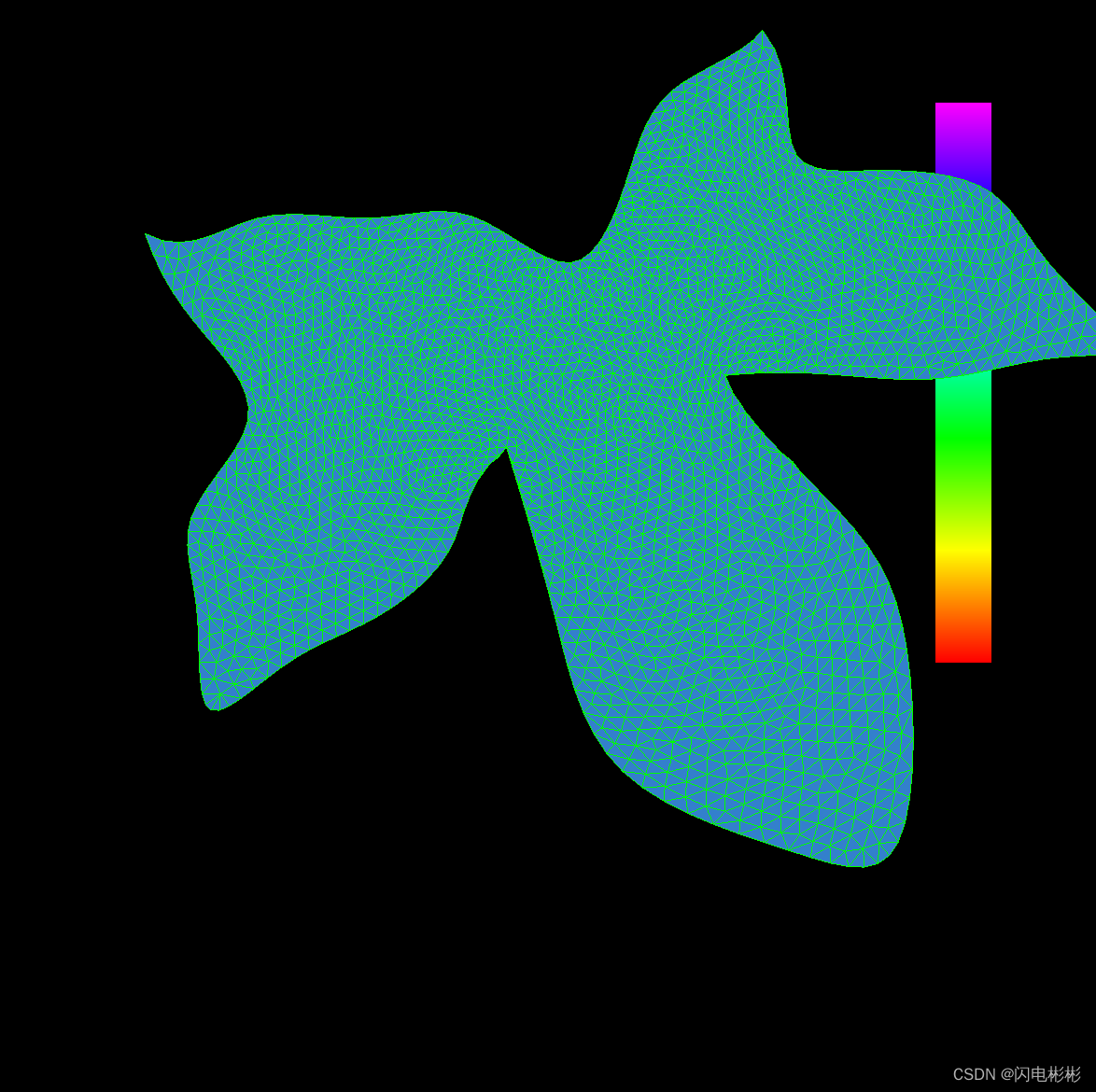
迭代700次
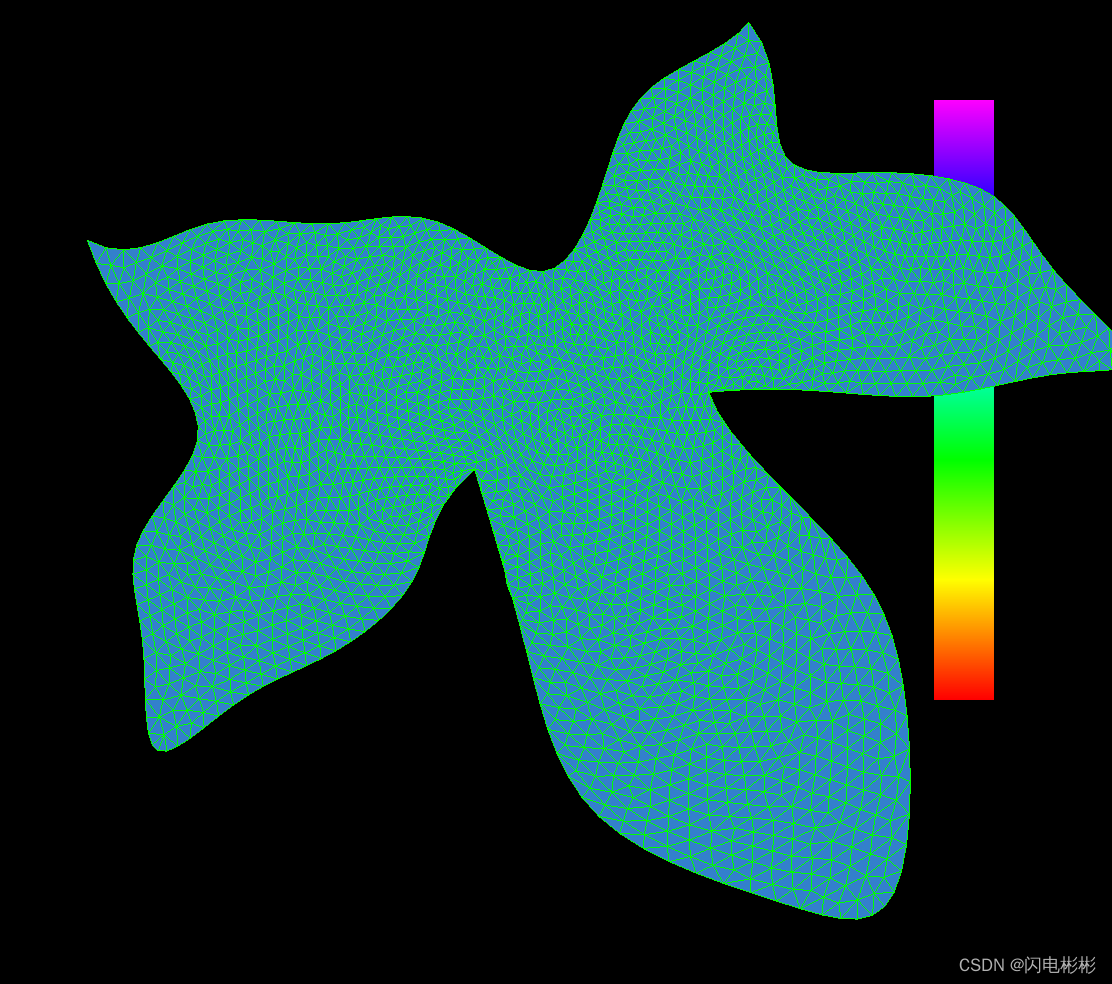
迭代1000次
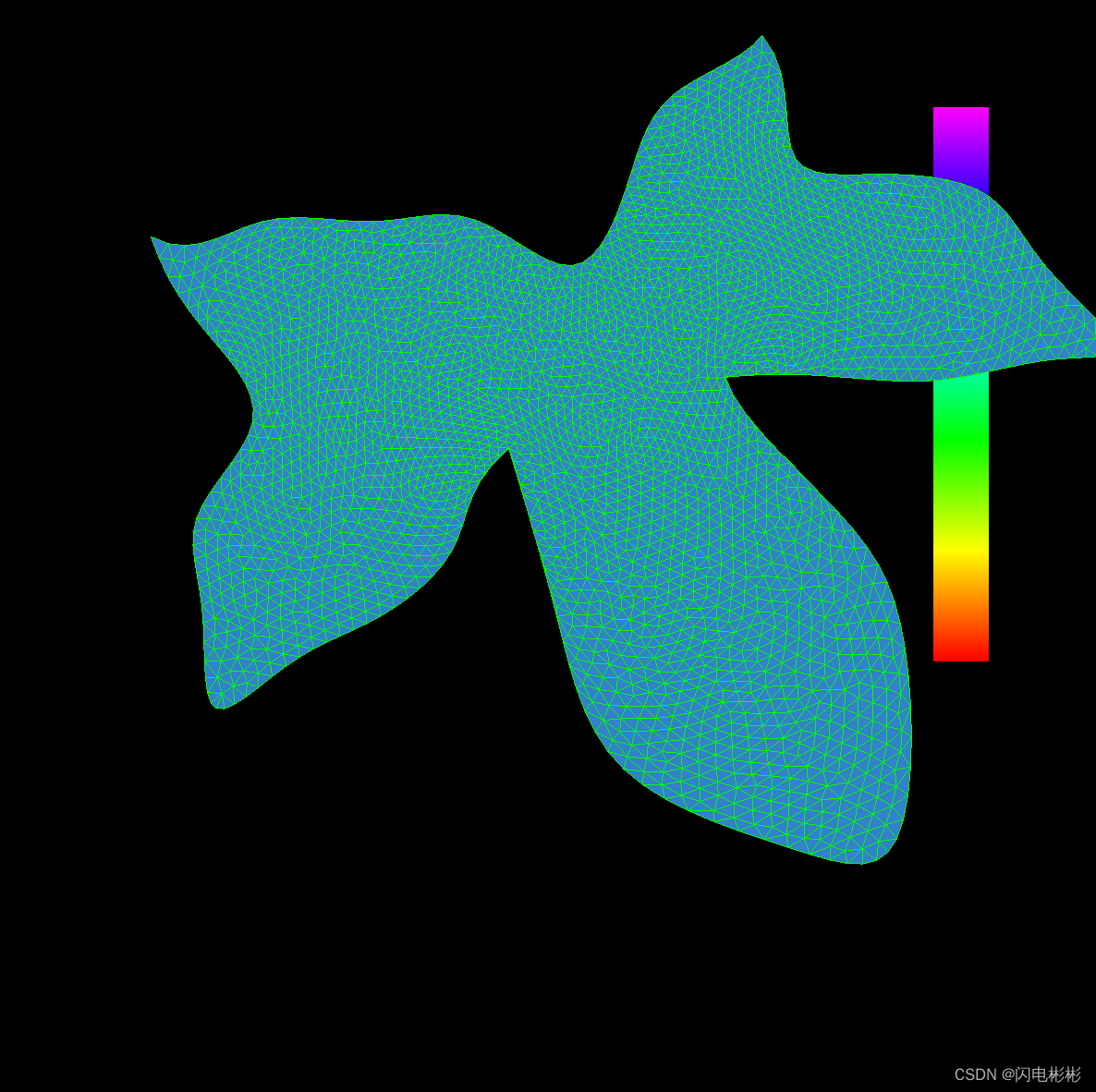
可以看出随着迭代次数增加三角形越来越均匀。
迭代效果取决于网格初始的质量,以及迭代次数。
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。

