目录
- 单链表的实现
- ArrayList的缺陷和与单链表的区别
1.单链表的实现
首先我们和ArrayList一样,将MySingleList单独定义为一个Java文件,然后每一个结点我们将它定义成一个静态内部类,这样就方便我们访问结点的成员,,还是和ArrayList一样,我们再定义一个Test类用来测试我们的单链表,写一个函数可以测试一下,这样在最后就不会眼麻手乱了,,
无头单向非循环链表的实现:
1.1MySingleList的大概实现框架
public class MySingleList {
static class ListNode {
public int value;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//简单的创建单链表
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(22);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(23);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
this.head = listNode1;
}
public ListNode head;
public void addFirst(int data){}
public void addLast(int data){}
public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
public boolean contains(int key){return false;}
public void remove(int key){}
public void removeAllKey(int key){}
public int size(){return -1;}
public void display(){}
public void clear(){}
}?addFirst--头插
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}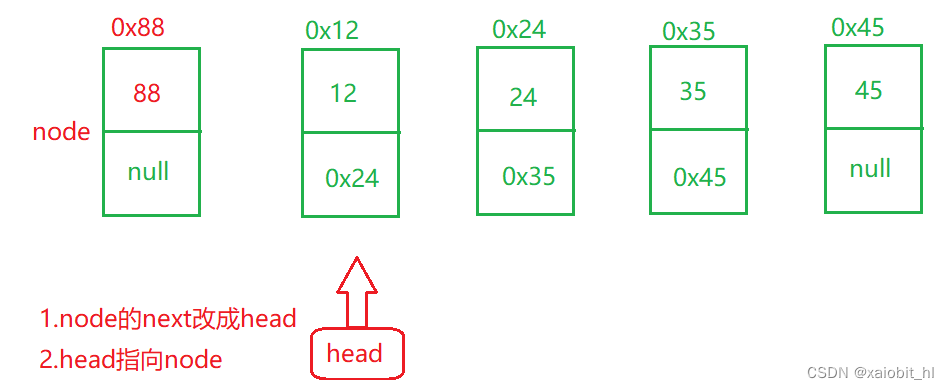
?头插没啥细节点,以上图做辅助理解,我就不多赘述了,,
?addLast--尾插
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//1.链表为空
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}
//2.链表不为空
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}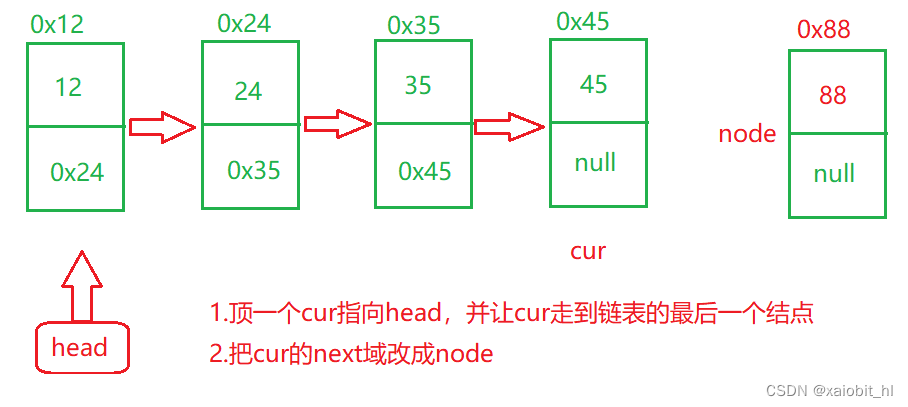
?这里要注意链表为空的时候,只需要将head指向node即可;
addIndex--任意位置插
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws MySingleListIndexOutOfException{
//1.先检查插入位置是否合法
checkAddIndex(index);
//2.分两种情况:1.头插 2.中间位置和尾插
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findAddIndexSubOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private void checkAddIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > this.size()) {
throw new MySingleListIndexOutOfException("任意位置插入时,index不合法!");
}
}
//找到待插入位置的前一个结点
private ListNode findAddIndexSubOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
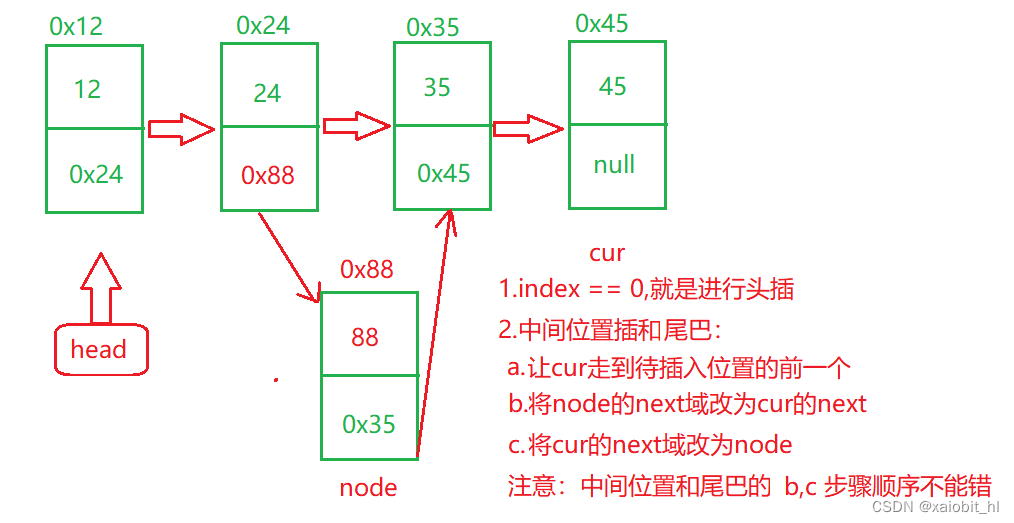
?任意位置插的注意事项:1.先要判断下标是否合法;2.要分两种情况。
contains--查找
public boolean contains(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return false;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.value == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}remove--删除第一次出现的key
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
//1.判断有无结点
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
//2.删第一个
if(this.head.value == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
//3.删后面的
ListNode cur = this.head;
cur = removeSubOne(key,cur);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("链表中没有这个元素!");
return;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
private ListNode removeSubOne(int key, ListNode cur) {
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.value == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}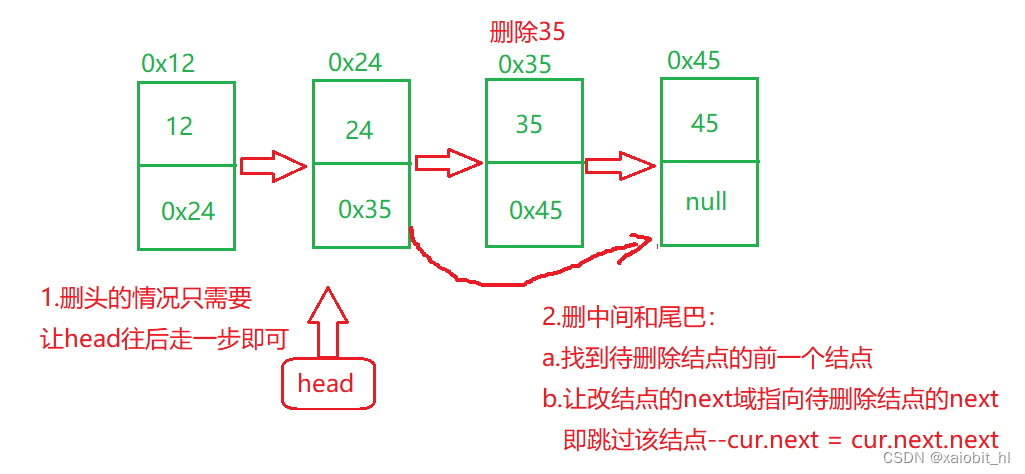
?
删除函数的注意事项:1.判空? 2.分两种情况:删头和删剩下的,,
?removeAllkey--删除所有key
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
//1.判断有无结点
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
//处理中间和尾巴
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
//removeSubOne函数在上一个删除方法里头
cur = removeSubOne(key,cur);
if(cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
}
//处理头
if(this.head.value == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}这里的辅助图,跟remove函数类似,,,?
注意事项:(判空和分情况我就不多赘述了)
1.如果先处理头,则需要写成循环,因为当链表所有结点都是待删除的情况时,一个if条件语句处? ? ?理不了
2.while循环里面的条件不能写成cur.next == null,因为removeSubOne函数如果没找到待删除? ? ? ?的结点,它返回的是一个null,如果写成cur.next != null,则可能会报空指针异常
接下来就是几个简单的函数,也很重要,大家都能看得懂:
1.求单链表的长度;2.打印单链表;3.清除单链表
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear() {
this.head = null;
}这里说说清除函数,我这种方式是比较暴力,也可以用温柔的方式:
用cur结点保存head的next,然后将head的val和next不断置为0或空,然后两个"指针"不断往后走
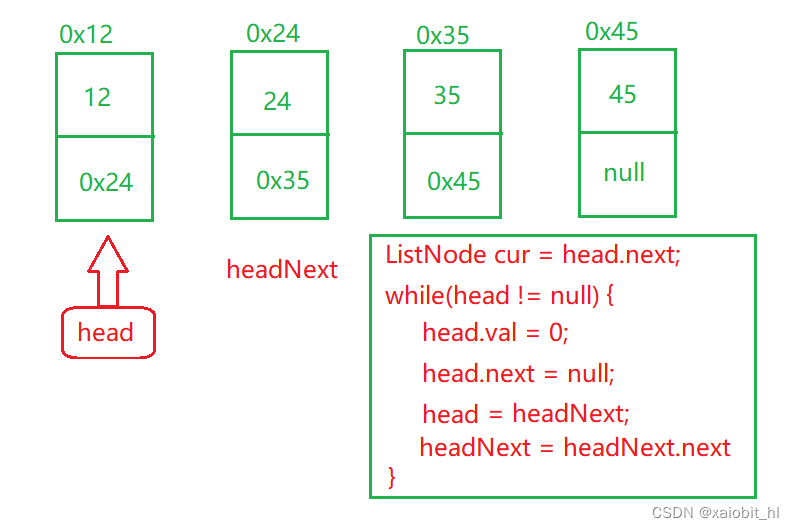
?
2.缺陷与区别(ArrayList&LinkedList)
我们之前学了顺序表,但是在某些方面,它存在着许多不足,由于其底层是一段连续的空间,当ArrayList任意位置插入或删除元素的时候,就需要将后续元素整体往前或者往后移动,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入删除比较多的场景,而这些问题链表都可以解决。
区别:
| 不同点 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上连续 | 逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持O(N) |
| 头插 | 需要移动元素,效率低O(N) | 只需要修改引用的指向O(1) |
| 插入 | 空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 频繁访问+随机存取 | 任意位置插入+频繁删除 |
