目录
前言:
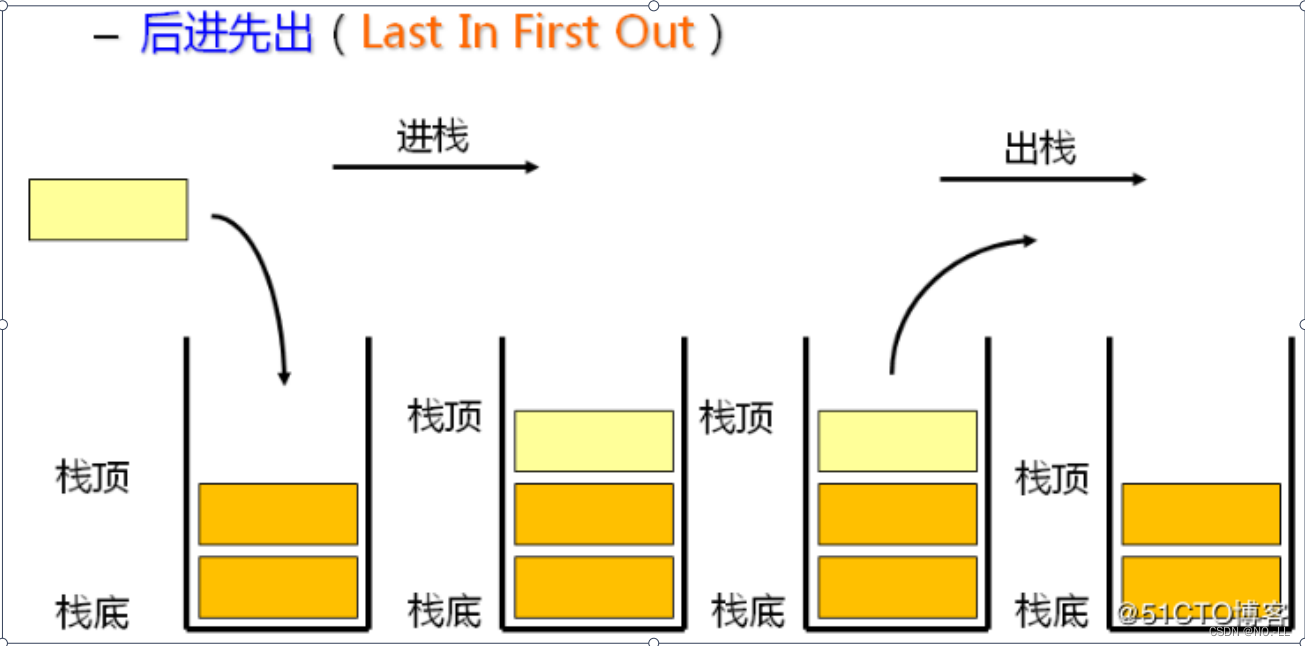
- 栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)原则。
- 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
- 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
栈的实现方式讨论
实现栈无非就两种结构:数组结构?和?链式结构;
相对而言数组的结构实现更优,尾插尾删的效率高,缓存利用率高,它的唯一缺点只是增容,但是增容1次扩2倍对栈来说本身就比较合理,是无伤大雅的。而链式栈虽然不会空间浪费,用一个 malloc 申请一个,但是链式栈存在一个致命的缺点:单链表不好出数据,必须要实现双向链表,否则尾上删除数据将会异常麻烦。
总结:
栈的实现一般可以使用 数组或者链表实现 ,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
栈的实现
栈的定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶的位置
int capacity; // 容量
}ST;接口函数
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);接口函数实现
1、初始化栈(StackInit)
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0; //个数
ps->capacity = 0; //容量
}????????初始化和顺序表几乎没有什么区别。首先通过结构体指针(我们定义的Stack)?ps?指向?array,将数组为空。因为是初始化,所以将有效数据个数和数组时即能存数据的空间容量一并置为0。
2、销毁(StackDestroy)
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}首先把栈?free?掉,为了防止野指针我们手动把它置为空指针(好习惯)
3、入栈(StackPush)
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity* sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}4、出栈(StackPop)
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}5、返回栈顶数据(StackTop)
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}6、计算栈的大小(StackSize)
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}7、判断栈是否为空(StackIfEmpty)
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top > 0)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}*/
return ps->top == 0;
}完整代码:
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
//struct Stack
//{
// int a[N];
// int top; // 栈顶的位置
//};
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶的位置
int capacity; // 容量
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);Stack.c?
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity* sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top > 0)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}*/
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}OJ练习:

为了演示代码,我这边直接复制粘贴上文,有许多代码是“没用的”,所以看起来非常长
思路:
首先将所给的字符串进行遍历,如果是左括号就将它压入栈中,根据栈后进先出的特性,然后逐个取出栈中的左括号与后面剩下的右括号进行逐对进行匹配,如果不匹配就返回false,如果都匹配了就返回true。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶的位置
int capacity; // 容量
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity* sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top > 0)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}*/
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//表演开始了
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s=='['||*s=='('||*s=='{')
{
StackPush(&st,*s);
s++;
}
else
{
if(StackEmpty(&st))
return false;
char top=StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if(*s==']'&&top!='['
||*s==')'&&top!='('
||*s=='}'&&top!='{')
{
StackDestory(&st);
return false;
}
else
{
s++;
}
}
}
bool ret=StackEmpty(&st); // 栈为空声明所以左括号匹配
StackDestory(&st);
return ret;
}