判断链表是否为回文结构
给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构
思路
1. 额外空间占用为O(n)的,使用额外空间
2. 额外空间占用为O(1)的,不使用额外空间

代码实现
import java.util.Stack;
public class Code02_IsPalindromeList {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
// need n extra space
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node node) {
Stack<Node> nodes = new Stack<>();
Node cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
nodes.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value != nodes.pop().value) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return true;
}
// need n/2 extra space
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node node) {
if (node == null || node.next == null) {
return true;
}
Node right = node.next;
Node cur = node;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
right = right.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (right != null) {
stack.push(right);
right = right.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (node.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
node = node.next;
}
return true;
}
// need O(1) extra space
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node node) {
if (node == null || node.next == null) {
return true;
}
Node n1 = node;
Node n2 = node;
while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}
// slow 为中点
n2 = n1.next;
n1.next = null;
Node n3 = null;
// 中点后指针反转
while (n2 != null) {
n3 = n2.next;
n2.next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
// 循环结束之后 slow指向最后一个节点,fast指向null
// 两边向中间验证
n3 = n1; // 指向最后一个节点
n2 = node;
// slow 为最后一个节点, fast为头结点
while (n1 != null && n2 != null) {
if (n1.value != n2.value) {
return false;
}
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
// 还原原链表
n1 = n3.next; // 倒数第二个节点
n3.next = null; // 最后一个节点next指向null
while (n1 != null) {
n2 = n1.next;
n1.next = n3;
n3 = n1;
n1 = n2;
}
return true;
}
public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
}
}
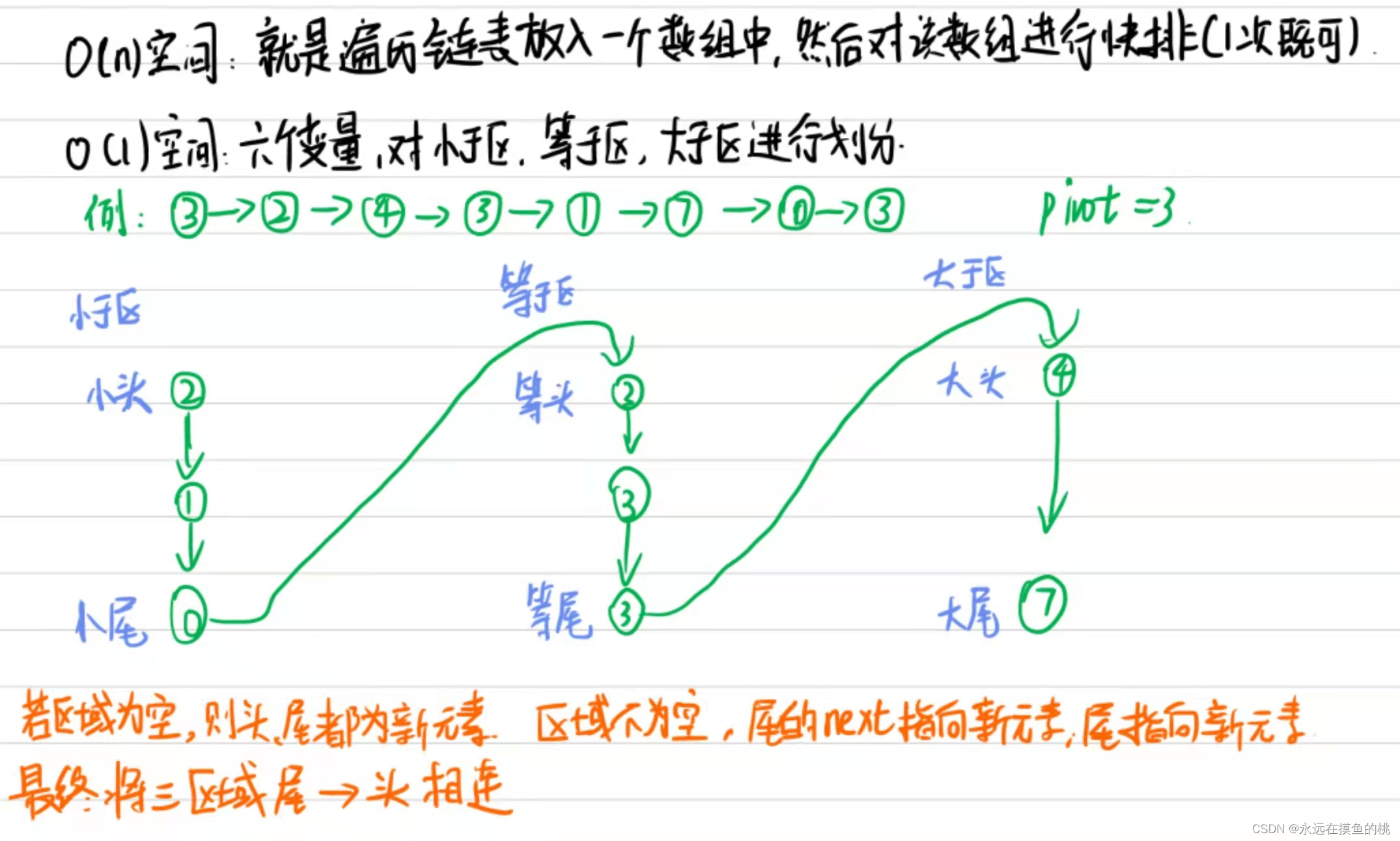
将链表按n划分成左边<n、中间==n、右边>n
给定一个单链表的头节点head,给定一个整数n,将链表按n划分成左边<n、中间==n、右边>n
思路
1. 额外空间占用为O(n)的,使用额外空间
2. 额外空间占用为O(1)的,不使用额外空间
代码实现
public class Code03_SmallerEqualBigger {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
// need n extra space
public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr, int a, int b) {
Node tmp = nodeArr[a];
nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b];
nodeArr[b] = tmp;
}
public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int i = 0;
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
i++;
cur = cur.next;
}
Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i];
cur = head;
// 将节点存入到数组中
for (i = 0; i <nodeArr.length; i++) {
nodeArr[i] = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 快排
arrPartition(nodeArr, pivot);
// 将排好序的数组各个节点连接起来
for (i = 1; i < nodeArr.length; i++) {
nodeArr[i - 1].next = nodeArr[i];
}
nodeArr[i - 1].next = null;
return nodeArr[0];
}
private static void arrPartition(Node[] nodeArr, int pivot) {
int small = -1; // 小于边界
int big = nodeArr.length; // 大于边界
int index = 0; // 遍历下标
while (index != big) {
if (nodeArr[index].value < pivot) {
swap(nodeArr, ++small, index++);
} else if (nodeArr[index].value == pivot) {
index++;
} else {
swap(nodeArr, --big, index);
}
}
}
// need 1 extra space
public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot) {
Node sH = null; // small head
Node sT = null; // small tail
Node eH = null; // equal head
Node eT = null; // equal tail
Node mH = null; // big head
Node mT = null; // big tail
Node next = null; // save next node
// 按照小区、等区、大区划分
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = null;
if (head.value < pivot) {
if (sH == null) {
sH = head;
sT = head;
} else {
sT.next = head;
sT = head;
}
} else if (head.value == pivot) {
if (eH == null) {
eH = head;
eT = head;
} else {
eT.next = head;
eT = head;
}
} else {
if (mH == null) {
mH = head;
mT = head;
} else {
mT.next = head;
mT = head;
}
}
head = next;
}
// 将三个区域相连
// 小于区域的尾巴,连等于区域的头,等于区域的尾巴连大于区域的头
if (sH != null) {
sT.next = eH; // 小尾指向等头
eT = eT == null ? sT : eT; // 看等区是否为空,如果为空则eT就等于sT
}
// 下一步,一定是需要用eT 去接 大于区域的头
// 有等于区域,eT -> 等于区域的尾结点
// 无等于区域,eT -> 小于区域的尾结点
// eT 尽量不为空的尾巴节点
if (eT != null) {
eT.next = mH;
}
return sH != null ? sH : (eH != null ? eH : mH);
}
public static void printLinkedList(Node node) {
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
printLinkedList(head1);
// head1 = listPartition1(head1, 4);
head1 = listPartition2(head1, 5);
printLinkedList(head1);
}
}
复制一个特殊结构的单链表
一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int value; // 节点值
Node next; // 节点的下一个节点
Node rand; // 节点指向的一个随机节点
Node(int val) { value = val; }
}
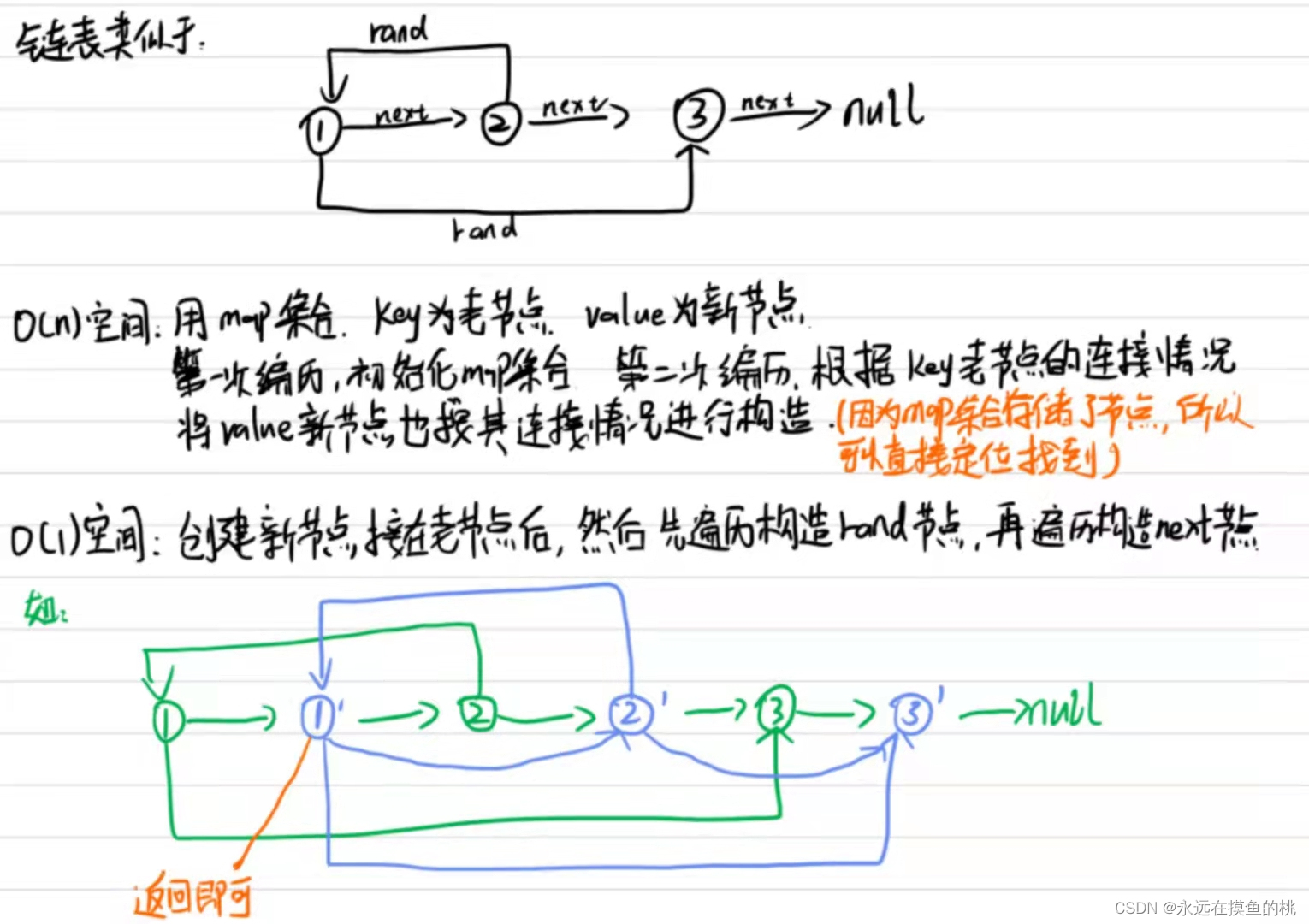
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null
给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制
返回复制的新链表的头节点,要求时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
思路
1. 额外空间占用为O(n)的,使用额外空间
2. 额外空间占用为O(1)的,不使用额外空间
代码实现
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Code04_CopyListWithRandom {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node rand;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
// need n extra space
public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head) {
// key 老节点 value 新节点
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
// 遍历原链表,按照原链表中的节点next和rand在map中进行查找,复制
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
// need 1 extra space
public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Node next = null;
// 创建新节点插入原节点之后
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = new Node(cur.value);
cur.next.next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
Node curCopy = null;
// 先完成rand的连接
while (cur != null) {
// cur 老
// cur.next 新 copy
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
// 新节点的rand指向新节点,即原节点之后的那个节点
curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;
cur = next;
}
// 再完成next的连接
Node res = head.next; // 赋值出来的新的头结点
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
cur.next = next; // 还原原链表的next关系
curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null;
cur = next;
}
return res;
}
public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
System.out.print("order: ");
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
cur = head;
System.out.print("rand: ");
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
Node res1 = null;
Node res2 = null;
printRandLinkedList(head);
res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);
printRandLinkedList(res1);
res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);
printRandLinkedList(res2);
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6
head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6
head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5
head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3
head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> null
head.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4
System.out.println("原始链表:");
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);
System.out.println("方法一的拷贝链表:");
printRandLinkedList(res1);
System.out.println("=========================");
res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);
System.out.println("方法二的拷贝链表:");
printRandLinkedList(res2);
System.out.println("=========================");
System.out.println("经历方法二拷贝之后的原始链表:");
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
}
}
链表相交的问题
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2
请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点。如果不相交返回null
要求如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)
思路
首先判断两个链表有无环的情况
- 两个链表都无环
两个链表都无环的情况,对两个链表进行遍历并统计长度,计算两链表长度的差值,让较长的链表先走差值步,然后两个链表同时前进,相遇的那个节点一定是第一个相交节点 - 两个链表一个有环一个无环
两个链表一个有环一个无环,这种情况不可能相交,因为链表的next只有一个,如果一个链表出现了环,而另一个链表无环,next指针一定会指出两个,这种情况是不可能出现的 - 两个链表都有环
这种情况下,会出现三种情况,两个链表各自有环,不想交;两个链表先相交,然后共用同一个环;两个链表直接同时共用同一个环。只有第二三两种情况会相交,第二种情况就是以入环节点为结尾走第一种情况的流程,第三种情况两个链表的入环节点都是相交节点,返回一个即可
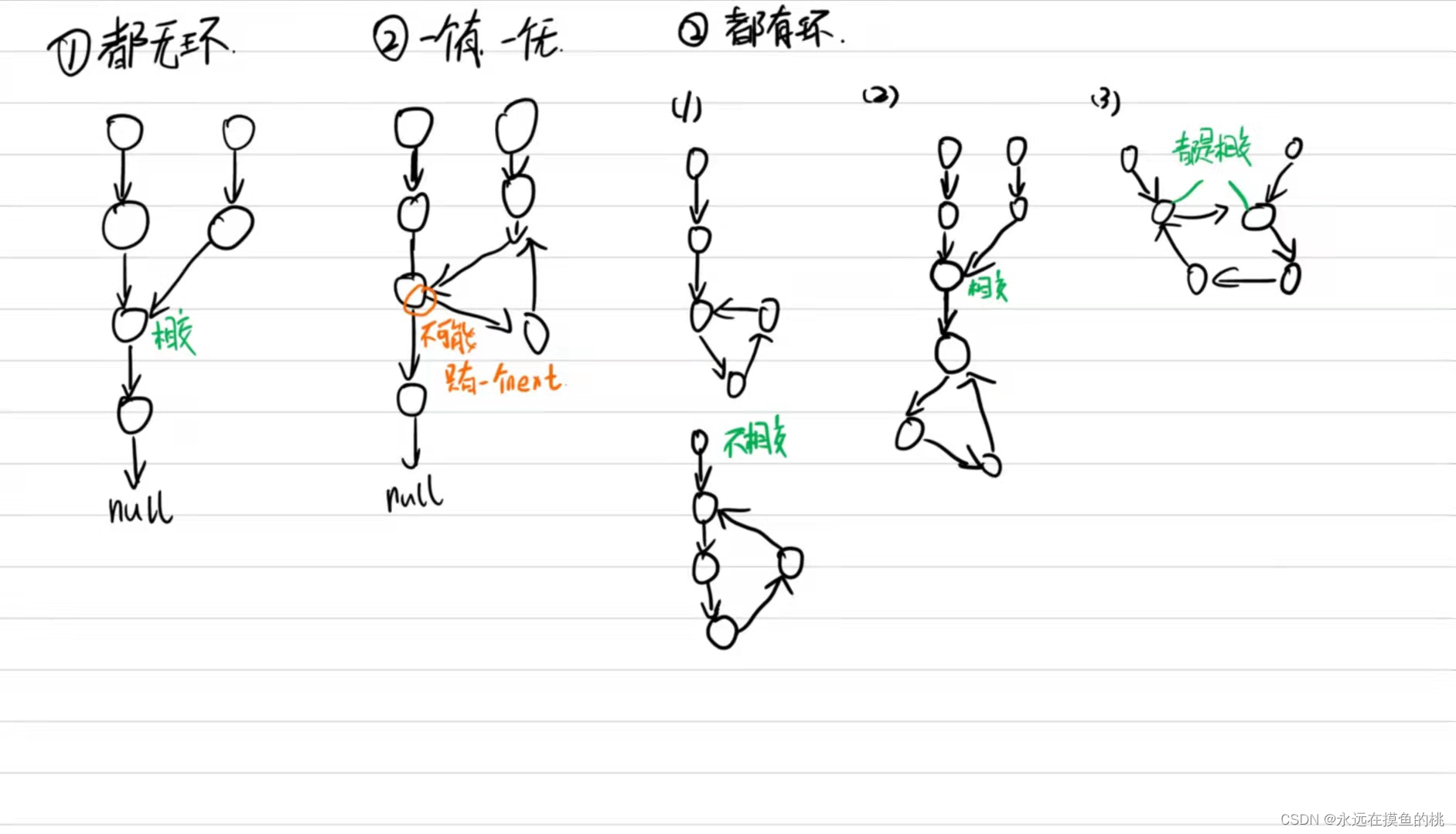
这里需要补充这么求链表的入环节点
代码实现
public class Code01_FindFirstIntersectNode {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
// 获取相交节点
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
// 两链表都无环
if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {
return noLoop(head1, head2);
}
// 两链表都有环
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
}
// 两链表一个有环一个无环直接返回null
return null;
}
// 找到链表第一个入环节点,如果无环,返回null
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node slow = head.next;
Node fast = head.next.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
fast = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交,返回null
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) return null;
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
// 首先计算两个链表长度的差值
while (cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
// 此时 n 就是两个链表长度的差值
// 将较长的链表赋值给cur1,较短的赋值给cur2
// 长链表先走差值步,然后两链表一起前进,相遇的节点为相交节点
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
// 两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回null
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
// 共用一个环,用环的起点作为结束,进行无环逻辑即可
if (loop1 == loop2) {
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1 != loop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
} else {
cur1 = loop1.next;
// 判断是否是公用一个环,但起点不一致
while (cur1 != loop1) {
if (cur1 == loop2) {
// 如果是,则返回任意一个环起点,就是相交节点
return loop1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
// 如果都不是,说明就是两个单独的有环链表,返回null
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
}
}
