目录
🍔关于LinkedList
LinkedList的底层是用一个双向链表实现的,即一个结点中除了有一个引用指向下一个结点的地址,还有一个引用指向前一个结点的地址
LinkedList还有三个成员变量:
🍂size,表示该链表中结点的个数
🍂first,指向链表首结点
🍂last,指向链表尾结点
🍿模拟实现LinkedList
🍉准备工作
🍃创建静态内部类ListNode,后续创建结点都需要ListNode来创建新的结点
private static class ListNode<E> {
ListNode<E> pre; //指向前一个结点
ListNode<E> next; //指向下一个结点
E val; //结点的值
public ListNode(E val){
this.val = val;
}
}🍃创建成员变量:first,last,size
private ListNode<E> first; //指向链表首结点
private ListNode<E> last; //指向链表尾结点
private int size; //链表结点的个数🍃重写toString()方法,在进行测试方法的时候需要将链表打印出来
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
if(first == null){
sb.append("]");
}else {
ListNode<E> cur = first;
while(cur.next != null){
sb.append(cur.val);
sb.append(",");
cur = cur.next;
}
sb.append(cur.val);
sb.append("]");
}
return sb.toString();
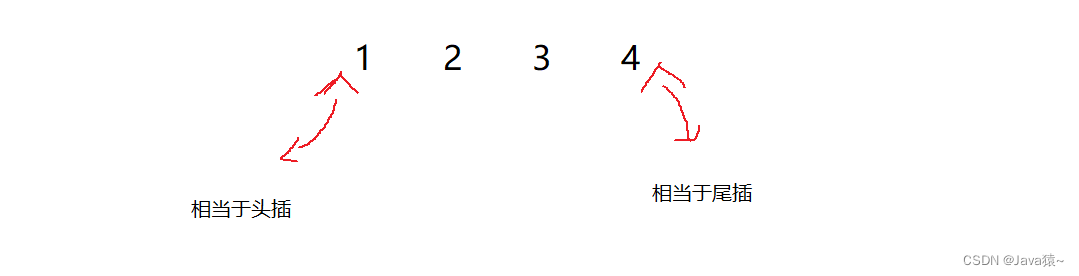
}🍊头插
🍀在链表的头部插入结点,这里分两种情况:链表为空,链表不为空
🍀链表为空:直接将first,last指向该结点,因为这个结点既是第一个结点,也是最后一个结点
🍀链表不为空:将first的pre执行该结点,再将该结点的next指向first,更新first位置🍀在结点头插完后,更新size的长度,进行size++
public void addFirst(E e){
ListNode<E> newNode = new ListNode<>(e);
if(first == null){
first = newNode;
last = newNode;
}else {
first.pre = newNode;
newNode.next = first;
first = newNode;
}
size++;
}🍂进行测试:依次头插入1,2,3,4,打印list
MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>(); list.addFirst(1); list.addFirst(2); list.addFirst(3); list.addFirst(4); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:因为是头插,所以打印4,3,2,1
🍋尾插
🍁在链表的尾部插入结点,分两种情况:链表为空,链表不为空
🍁链表为空:直接将first,last指向该结点,该结点既是链表的首结点,又是最后一个结点
🍁链表不为空:last的next执行该节点,该节点的pre指向last,更新last位置🍁在结点尾插完后,更新size的长度,进行size++
public void addLast(E e){
ListNode<E> newNode = new ListNode<>(e);
if(first == null){
first = newNode;
last = newNode;
}else {
last.next = newNode;
newNode.pre = last;
last = newNode;
}
size++;
}🍂进行测试:依次尾插入1,2,3,4,打印list
list.addLast(1); list.addLast(2); list.addLast(3); list.addLast(4); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:因为是尾插,所以打印1,2,3,4?
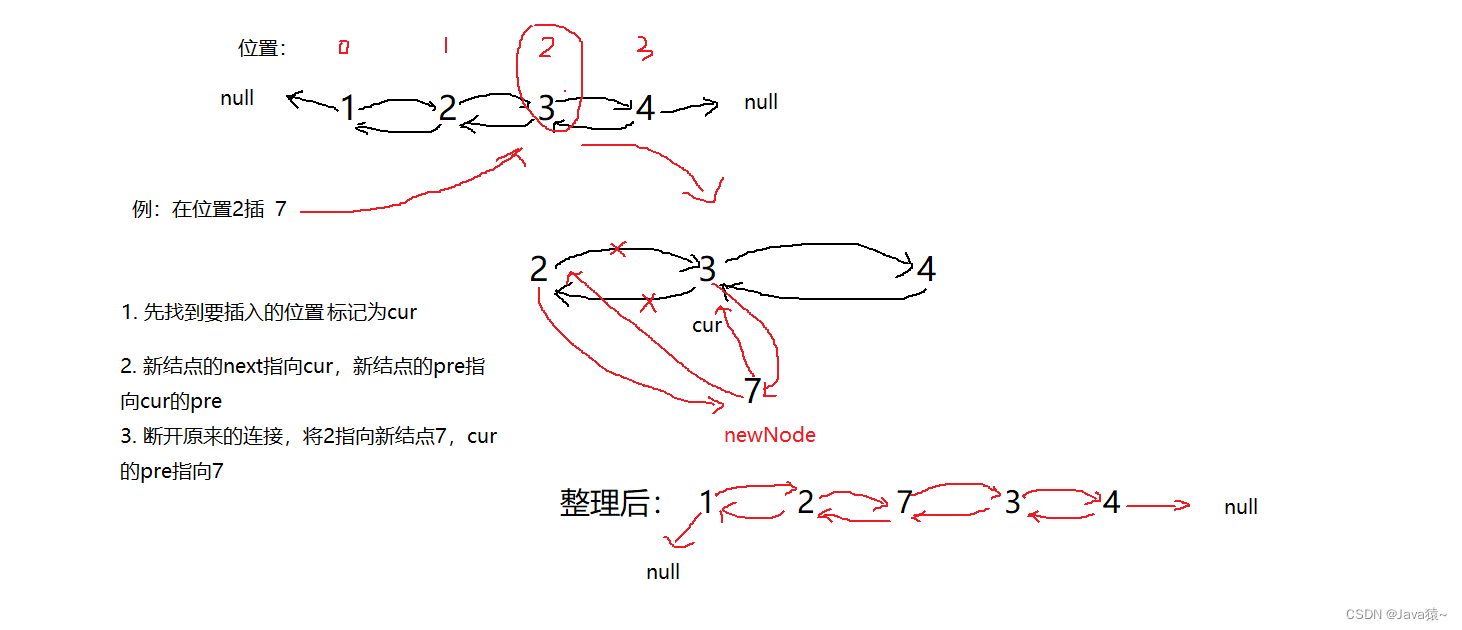
🍏在任意位置插入
这里分三种情况讨论:在第一个位置插入,在最后一个位置插入,在其他位置插入
🍂在第一个位置插入:相当于头插,调用addFirst()方法
🍂在最后一个位置插入:相当于尾插,调用addLast()方法
🍂在其他位置插入:看下图解析
public boolean addIndex(int index,E e){
ListNode<E> newNode = new ListNode<>(e);
if(index < 0 && index > size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("addIndex:下标越界");
}
if(index == size){
addLast(e);
}else if(index == 0){
addFirst(e);
}else {
ListNode<E> cur = first;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
newNode.pre = cur.pre;
newNode.next = cur;
newNode.pre.next = newNode;
cur.pre = newNode;
size++;
}
return true;
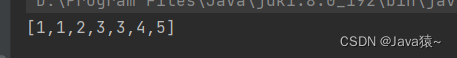
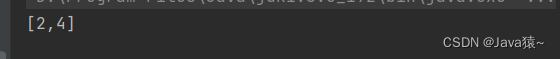
}🍂进行测试:原来链表为1,2,3,4,在位置0插入1,在位置5插入5,在位置3插入3?
list.addIndex(0,1); list.addIndex(4,5); list.addIndex(3,3); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:打印为1,1,2,3,3,4,5
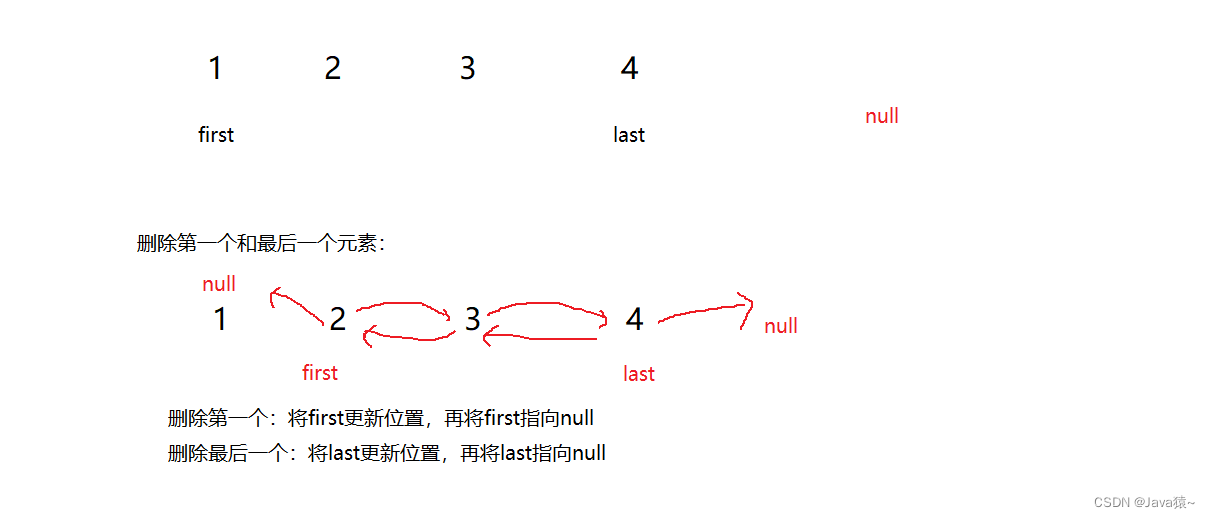
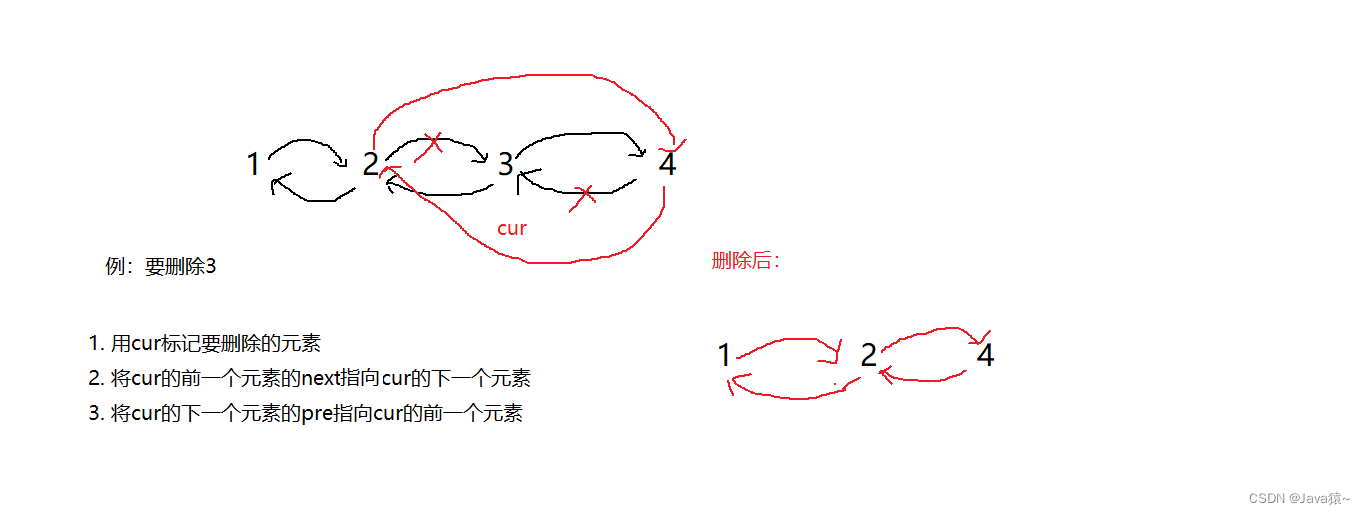
🍑删除remove
这里分为三种情况:删除的是第一个元素,删除的是最后一个元素,删除其他元素
🍃删除一个元素:将first指向first的next,再将first的pre指向null
🍃删除最后一个元素:将last更新为last的pre位置,再将last的next指向null
🍃删除其他位置元素:参照下图解析
🍃删除完后,进行size--操作?
public void remove(E e){
ListNode<E> cur = first;
while(cur != null){
if(e.equals(cur.val)){
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(cur == first){
first = first.next;
first.pre = null;
}else if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
}else {
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
}
size--;
}🍂进行测试:原链表为1,2,3,4,5,删除1,删除5,删除3
list.remove(1); list.remove(5); list.remove(3); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:打印2,4
🍒删除removeAll
这个与删除一次出现元素e的做法差不多,只是在找到第一次出现元素e时,将它删掉,继续遍历链表
public void removeAll(E e){
ListNode<E> cur = first;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val.equals(e)){
if(cur == first){
first = first.next;
first.pre = null;
}else if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
}else {
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
}
size--;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}🍂进行测试:链表为1,2,1,3,1,将所有的1全部删掉
list.removeAll(1); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:链表中的元素只剩下2,3?
🍐找元素下标indexOf
创建一个下标index,从0开始增加,每遍历一个元素进行index++,如果遍历的元素是要找的元素则返回index,当遍历完链表没有要找的元素时,返回-1
public int indexOf(E e){
ListNode<E> cur = first;
int index = 0;
while(cur != null){
if(e.equals(cur.val)){
return index;
}else {
index++;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return -1;
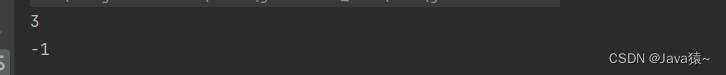
}🍂进行测试:链表为1,2,3,4,5,找3的位置和6的位置
System.out.println(list.indexOf(3)); System.out.println(list.indexOf(6));🍀打印结果:3在下标为2的位置,6不在该链表中,故返回-1
🍍找元素下标lastIndexOf
这个从链表尾部往前遍历,创建index值为size-1,当元素不为我们要找的元素时,index--,找到返回index,当遍历完整个链表都没有找到时,返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(E e){
ListNode<E> cur = last;
int index = size-1;
while(cur != null){
if(e.equals(cur.val)){
return index;
}else {
cur = cur.pre;
index--;
}
}
return -1;
}🍂进行测试:链表为1,2,3,3,4,5,找3的位置和6的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(3)); System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(6));?🍀打印结果:最后一个3的下标为3,6不在该链表中
🍅判断链表是否包含某个元素
这里可以调用indexOf方法,看返回的是不是-1,如果不是-1则说明链表包含该元素,如果返回的是-1,说明链表不包含该元素
public boolean contains(E e){
return -1 != indexOf(e);
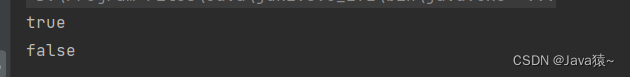
}🍂进行测试:链表为1,2,3,4,5,判断该链表是否包含2和6
boolean ret = list.contains(2); boolean ret1 = list.contains(6); System.out.println(ret); System.out.println(ret1);🍀输出结果:2在链表中,6不在链表中
🫐获得链表长度
直接返回size即可
public int size(){
return size;
}🍂进行测试:返回空链表的size,和有元素的size
list.clear(); System.out.println(list.size()); list.addFirst(1); System.out.println(list.size());?🍀打印结果:
🥝链表判空
判断链表为空有两种方式:判断size是否为0或者判断first是否指向null
public boolean isEmpty(){
//return size==0;
return first==null;
}🍂进行测试:看有元素的链表是否为空,和空链表是否为空
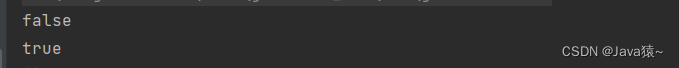
list.clear(); list.addFirst(1); boolean ret1 = list.isEmpty(); System.out.println(ret1); list.clear(); boolean ret2 = list.isEmpty(); System.out.println(ret2);🍀打印结果:
🥥清空链表
清空操作就是将first指向null,将last指向null,将size置0
public void clear(){
first = null;
last = null;
size = 0;
}🍂进行测试:执行清空操作,打印list
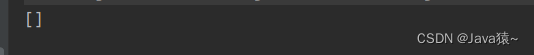
list.clear(); System.out.println(list);🍀打印结果:链表中没有元素