题面
1
?
s
?????
512
?
m
b
_{_{\rm1\,s~~~~~512\,mb}}
1s?????512mb??



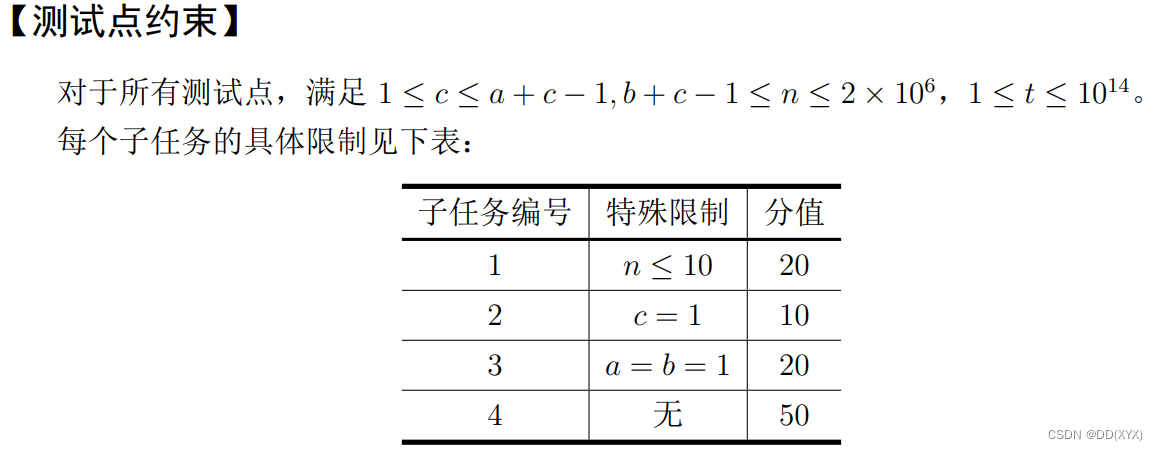
题解
我们会发现,任何时刻魔眼阈值最小的都是方阵的四个角之一,因此我们只需要考虑四个角上的魔眼就可以了。
判断是否有解可以贪心判断。
得到字典序最小的方案,可以每一步尝试向右+贪心判断是否有解。
那么怎么贪心判断呢?
注:以下为判断是否有解的贪心策略,并非最终输出的答案。
我们可以先把整个网格图分区:五芒星阵为魔眼区
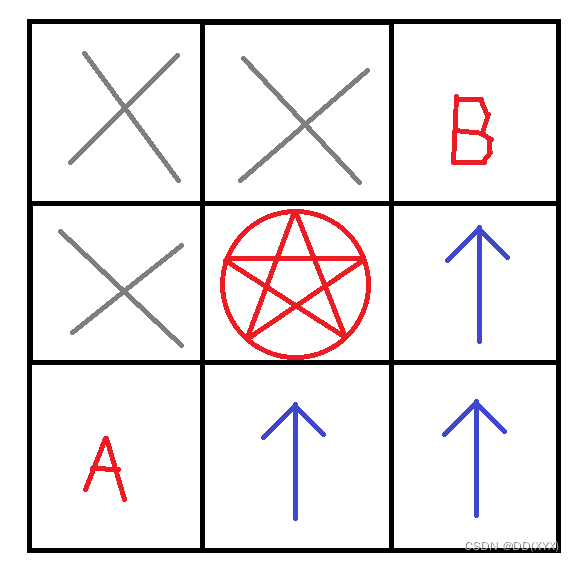
由于魔眼每次减小的阈值等于曼哈顿距离,因此大方向肯定是越靠近魔眼区越好。
在 A 区域时,贪心地一路走到魔眼区左下角,中途怎么走随意,对魔眼区的影响相同。
在蓝色箭头区域,本着越靠近越好的原则,肯定是无脑往上走。
在 B 区域时,怎么走都无所谓了,对魔眼区的影响相同。
当你进入魔眼区的时候,就要麻烦点,
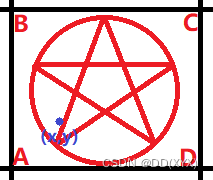
假设当前在魔眼区
(
x
,
y
)
(x,y)
(x,y) ,中途走出魔眼区肯定是不优的,所以肯定是一路走到
C
C
C 点,这一路对
A
,
C
A,C
A,C 的影响是相同的。出了
C
C
C 点之后就是随便走了,因此我们要尽量让
B
,
D
B,D
B,D 的阈值最小值最大。
左边的方案是对
B
B
B 最有利的、对
D
D
D 最有害的方案,右边的方案相反:
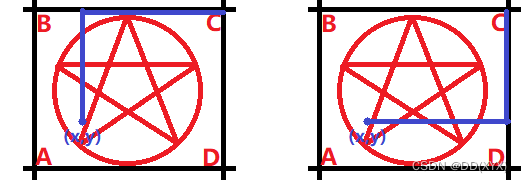
我们考虑调整法,从左边的方案调整到右边的方案,每次将一个“上右”变成“右上”,会刚好让
B
B
B 的阈值减少 2,
D
D
D 的阈值增加 2 。所以,不论什么方案,对
B
,
D
B,D
B,D 的阈值贡献和是相等的,边界就是上述两种情况。我们可以
O
(
1
)
O(1)
O(1) 贪心分配,使得最终
B
,
D
B,D
B,D 的阈值尽量平均。
代码实现算是一道模拟题了。
时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 。既然是模拟,常数可以往大的写。
CODE
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<random>
#include<bitset>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define MAXN (1<<16|5)
#define LL long long
#define ULL unsigned long long
#define ENDL putchar('\n')
#define DB double
#define lowbit(x) (-(x) & (x))
#define FI first
#define SE second
#define PR pair<int,int>
#define UIN unsigned int
int xchar() {
static const int maxn = 1000000;
static char b[maxn];
static int pos = 0,len = 0;
if(pos == len) pos = 0,len = fread(b,1,maxn,stdin);
if(pos == len) return -1;
return b[pos ++];
}
// #define getchar() xchar()
LL read() {
LL f = 1,x = 0;int s = getchar();
while(s < '0' || s > '9') {if(s<0)return -1;if(s=='-')f=-f;s = getchar();}
while(s >= '0' && s <= '9') {x = (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (s^48);s = getchar();}
return f*x;
}
void putpos(LL x) {if(!x)return ;putpos(x/10);putchar((x%10)^48);}
void putnum(LL x) {
if(!x) {putchar('0');return ;}
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
return putpos(x);
}
void AIput(LL x,int c) {putnum(x);putchar(c);}
int n,m,s,o,k;
int a,b,c;
LL A_,B_,L_,R_,t;
int Abs(int x) {return x<0 ? -x:x;}
int dis(int x,int y,int a,int b) {
return Abs(a-x) + Abs(b-y);
}
LL sm(int l,int r) {return (l+r) *1ll* (r-l+1) / 2;}
bool check(int x,int y,LL A,LL B,LL L,LL R) {
if(A > t || B > t || L > t || R > t) return 0;
if(x == n+1 && y == n) return 1;
if(x < a)
return check(a,b,A+sm(1,dis(x,y,a,b)),B+sm(c+c+1,dis(x,y,a+c,b+c)),
L+sm(c+1,dis(x,y,a,b+c)),R+sm(c+1,dis(x,y,a+c,b)));
if(x >= a+c && y >= b+c)
return check(n+1,n,A+sm(x-a+y-b,n-a+n-b),B+sm(x-a-c+y-b-c,n-a-c+n-b-c),
L+sm(x+y-a-b-c,n+n-a-b-c),R+sm(x+y-a-b-c,n+n-a-b-c));
if(x <= a+c && y < b)
return check(x,b,A+sm(x-a+1,dis(x,y,a,b)),B+sm(a+c-x+c+1,dis(x,y,a+c,b+c)),
L+sm(dis(x,b-1,a,b+c),dis(x,y,a,b+c)),R+sm(a+c-x+1,dis(x,y,a+c,b)));
if(x > a+c && y < b)
return check(x,b,A+sm(x-a+1,dis(x,y,a,b)),B+sm(x-a+1,dis(x,y,a,b)),
L+sm(dis(x,b-1,a,b+c),dis(x,y,a,b+c)),R+sm(x-a-c+1,dis(x,y,a+c,b)));
if(x > a+c && y < b+c)
return check(x,b+c,A+sm(dis(x,y,a,b),dis(x,b+c-1,a,b)),B+sm(dis(x,b+c-1,a+c,b+c),dis(x,y,a+c,b+c)),
L+sm(dis(x,b+c-1,a,b+c),dis(x,y,a,b+c)),R+sm(dis(x,y,a+c,b),dis(x,b+c-1,a+c,b)));
A += sm(dis(x,y,a,b),c+c); B += sm(0,dis(x,y,a+c,b+c));
LL sl = sm(x-a,dis(x,y,a,b+c)) + sm(x-a+1,c);
L += sl; R += sm(y-b,dis(x,y,a+c,b)) + sm(y-b+1,c);
LL ad = sm(dis(x,y,a,b+c),dis(a+c,y,a,b+c)) + sm(c,dis(a+c,y,a,b+c)-1) - sl;
if(L+ad <= R+2) L += ad;
else if(R+ad <= L+2) R += ad;
else {
if(L > R) swap(L,R);
LL nb = R-L - ((R-L)&1); L += nb; ad -= nb;
if(ad & 3) ad -= 2,L += 2;
L += ad>>1; R += ad>>1;
}
return check(a+c+1,b+c,A,B,L,R);
}
int main() {
freopen("elis.in","r",stdin);
freopen("elis.out","w",stdout);
n = read(); t = read();
a = read(); b = read(); c = read()-1;
int x = 1,y = 1;
if(!check(x+1,y,0,0,0,0) && !check(x,y+1,0,0,0,0)) return printf("Again\n"),0;
while(x < n || y < n) {
if(x < n && check(x+1,y,A_,B_,L_,R_)) x ++,putchar('R');
else y ++,putchar('U');
A_ += dis(x,y,a,b); B_ += dis(x,y,a+c,b+c);
L_ += dis(x,y,a,b+c); R_ += dis(x,y,a+c,b);
} ENDL;
return 0;
}
这好像是几年前的题了吧🤔