配套视频https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PT4y13767?p=2&vd_source=3558fd85254f40ca0361146cc92d2cce
一、归并排序
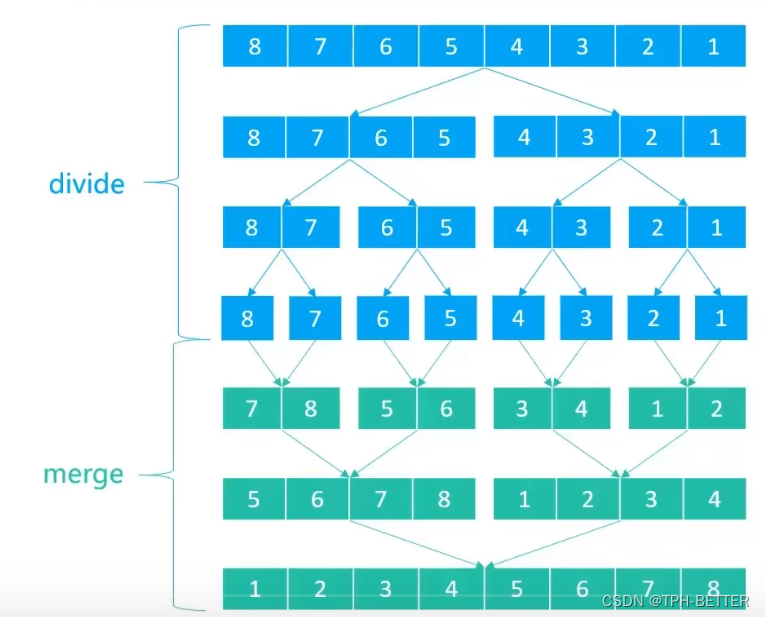
1. 归并排序原理
执行流程
- 不断地将当前序列平均分割成2个子序列,直到不能再分割(序列中只剩一个元素)
- 不断地将子序列合并成一个有序序列,直到最终只剩下一个有序序列
2. 归并排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void mergeSort(int [] array,int start,int end){
if(end-start<2) {
return;
}
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
mergeSort(array, start, mid);
mergeSort(array, mid, end);
//归并
merge(array,start,mid,end);
}
public static void merge(int [] array,int start,int mid,int end){
int[] leftArray=new int[mid-start];
//复制数组左边部分到新数组
System.arraycopy(array,start,leftArray,0,mid-start);
int arrayIndex=start;
int lIndex=0;
int lEnd=leftArray.length;
int rIndex=mid;
int rEnd=end;
while(lIndex<lEnd) {
if (rIndex<rEnd) {
if (leftArray[lIndex] < array[rIndex]) {
array[arrayIndex++] = leftArray[lIndex++];
} else {
array[arrayIndex++] = array[rIndex++];
}
}else{
array[arrayIndex++] = leftArray[lIndex++];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={3,2,1};
mergeSort(array,0,array.length);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
二、快速排序
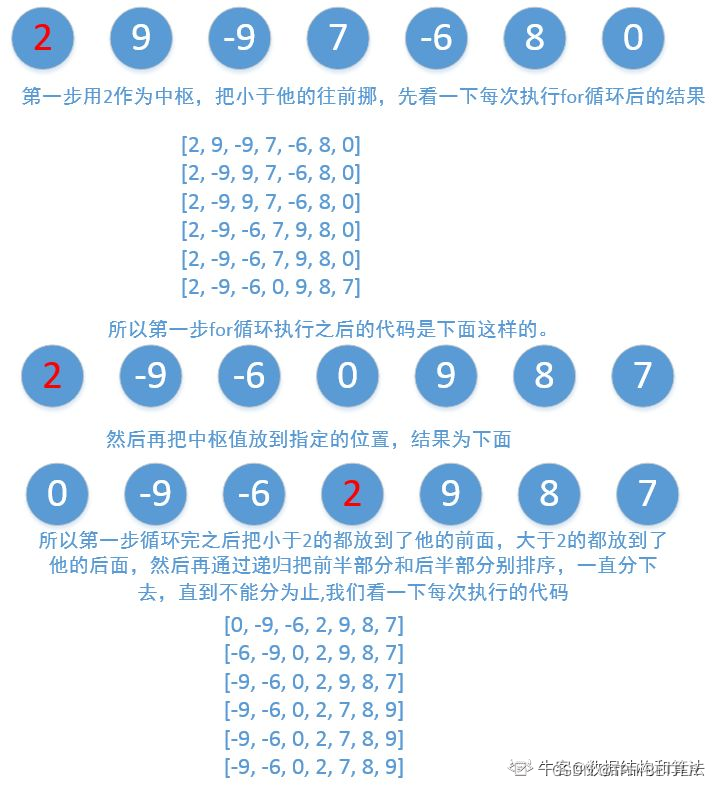
1. 快速排序原理
快速排序原理是首先要找到一个中枢,把小于中枢的值放到他前面,大于中枢的值放到他的右边,然后再以此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序。
这里是先用待排数组的第一个作为中枢,把数组划分两部分,小于他的往前挪,那大于他的自然就在后面了,然后再把中枢值放到大于和小于他之间的位置。
2. 快速排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void quickSort(int [] array,int start,int end){
if (end-start<2){
return;
}
int j=start;
int key=array[start];
for (int i = start+1; i < end; i++) {
if (key>array[i]){
j++;
swap(array,j,i);
}
}
swap(array,j,start);
quickSort(array,start,j);
quickSort(array,j+1,end);
}
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={7};
quickSort(array,0,array.length);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
三、冒泡排序
1. 冒泡排序原理
将第一个元素和第二个元素比较,若前者大于后者,则交换两者的位置,再将第二个元素与第三个元素比较,若前者大于后者则交换两者位置,以此类推直到倒数第二个元素与最后一个元素比较,若前者大于后者,则交换两者位置。这样一轮比较下来将会把序列中最大的元素移至序列末尾,这样就安排好了最大数的位置,接下来只需对剩下的(n-1)个元素,重复上述操作即可。
2. 冒泡排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
private static void bubbleSort(int[] array){
for (int j=array.length-1;j>0;j--){
for (int i=0;i<j;i++){
if (array[i]>array[i+1]){
swap(array,i,i+1);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={999999998,999999996};
bubbleSort(array);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
四、选择排序
1. 选择排序原理
执行流程
- 从序列中找出最大的那个元素,然后与最末尾的元素交换位置(执行完一轮后,最末尾的那个元素就是最大的元素)
- 忽略1中曾经找到的最大元素,重复执行步骤1
2. 选择排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
public static void selectionSort(int []arr){
for (int j=arr.length;j>1;j--){
int maxIndex=0;
for (int i=1;i<j;i++){
if (arr[maxIndex]<arr[i]){
maxIndex=i;
}
}
swap(arr,maxIndex,j-1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={2,4,1};
selectionSort(array);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
五、插入排序
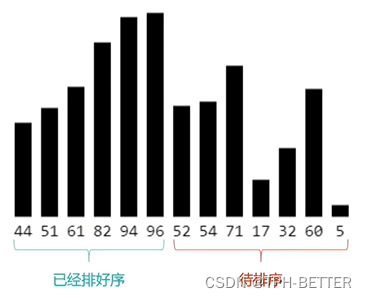
1. 插入排序原理
插入排序非常类似于扑克牌的排序
 执行流程
执行流程
- 在执行过程中,插入排序会将序列分为2部分(头部是已经排好序的,尾部是待排序的)
- 从头开始扫描每一个元素(每当扫描到一个元素,就将它插入到头部合适的位置,使得头部数据依然保持有序)
2. 插入排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
//第一种方式(优先)
public static void insertionSort(int []array){
for (int begin=1;begin<array.length;begin++){
int cur=begin;
while (cur>0 && array[cur]<array[cur-1]){
swap(array,cur,cur-1);
cur--;
}
}
}
//第二种方式
//用的插入扑克牌的方式写的
public static void insertionSort(int []array){
int j=0;
for (int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
int end=j;
while (j>=0){
if (array[j] < array[i]) {
break;
}
if (j-1>=0) {
if (array[j] > array[i] && array[i] > array[j - 1]) {
int tmp=array[i];
System.arraycopy(array, j, array, j + 1, end - j + 1);
array[j]=tmp;
break;
}
}
if(j==0) {
int tmp=array[i];
System.arraycopy(array, j, array, j + 1, end - j + 1);
array[j] = tmp;
break;
}
j--;
}
j=end+1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={5,2,1,4};
insertionSort(array);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
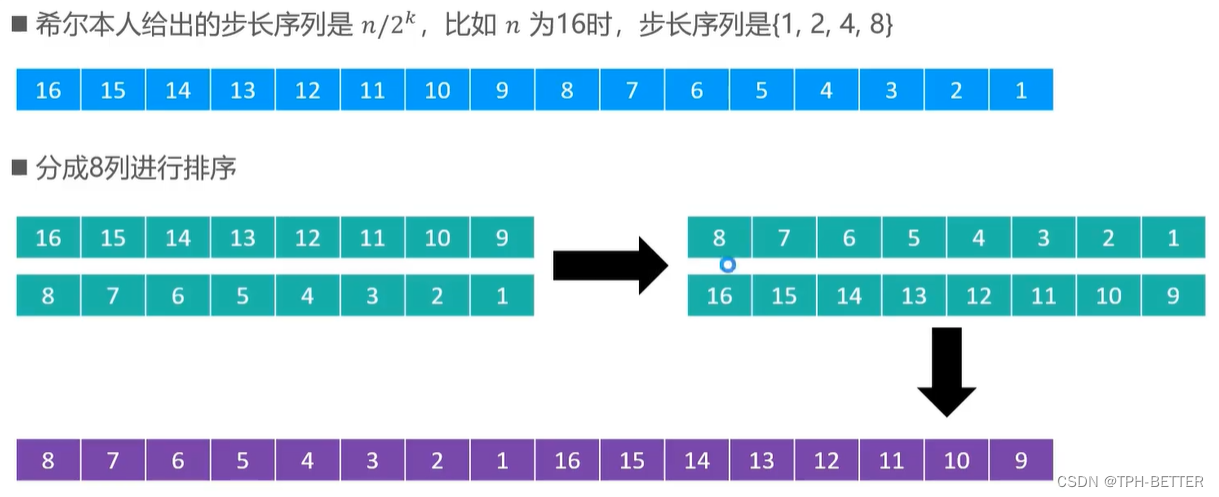
希尔排序
1. 希尔排序原理
2. 希尔排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
public static void shellSort(int array[]){
List<Integer> stepList=new ArrayList();
stepList=shellStepSequence(array);
for (int step:stepList){
for (int col = 0; col < step; col++) {
for (int i = col+step ; i < array.length ; i+=step) {
for (int cur=i;cur>=col+step;cur-=step) {
if (array[cur] < array[cur - step]) {
swap(array, cur, cur - step);
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static List shellStepSequence(int [] array){
List stepList=new ArrayList();
int step=array.length;
while ((step>>=1)>=1){
stepList.add(step);
}
return stepList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={5,2,3,1,4};
shellSort(array);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}
希尔排序
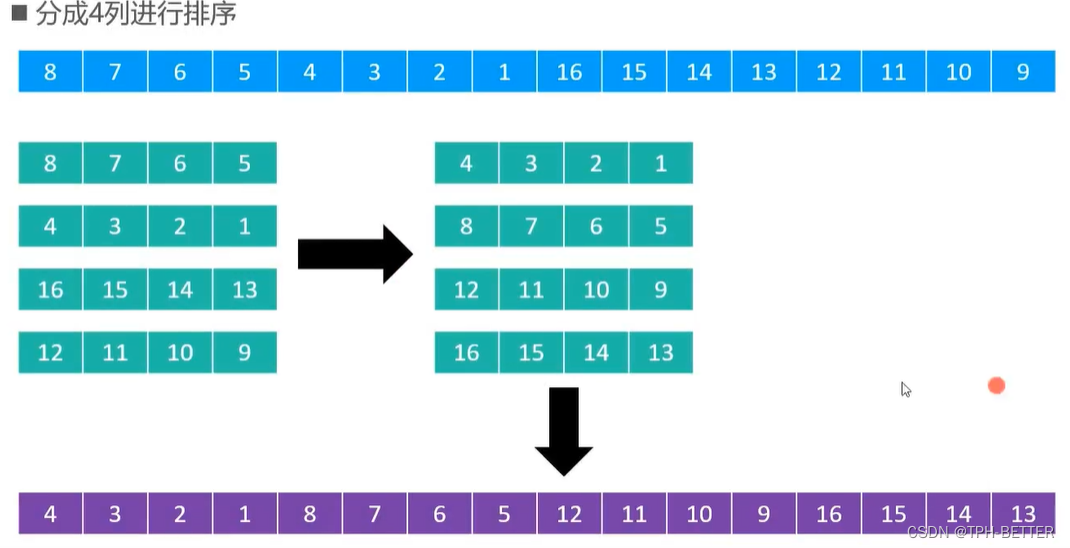
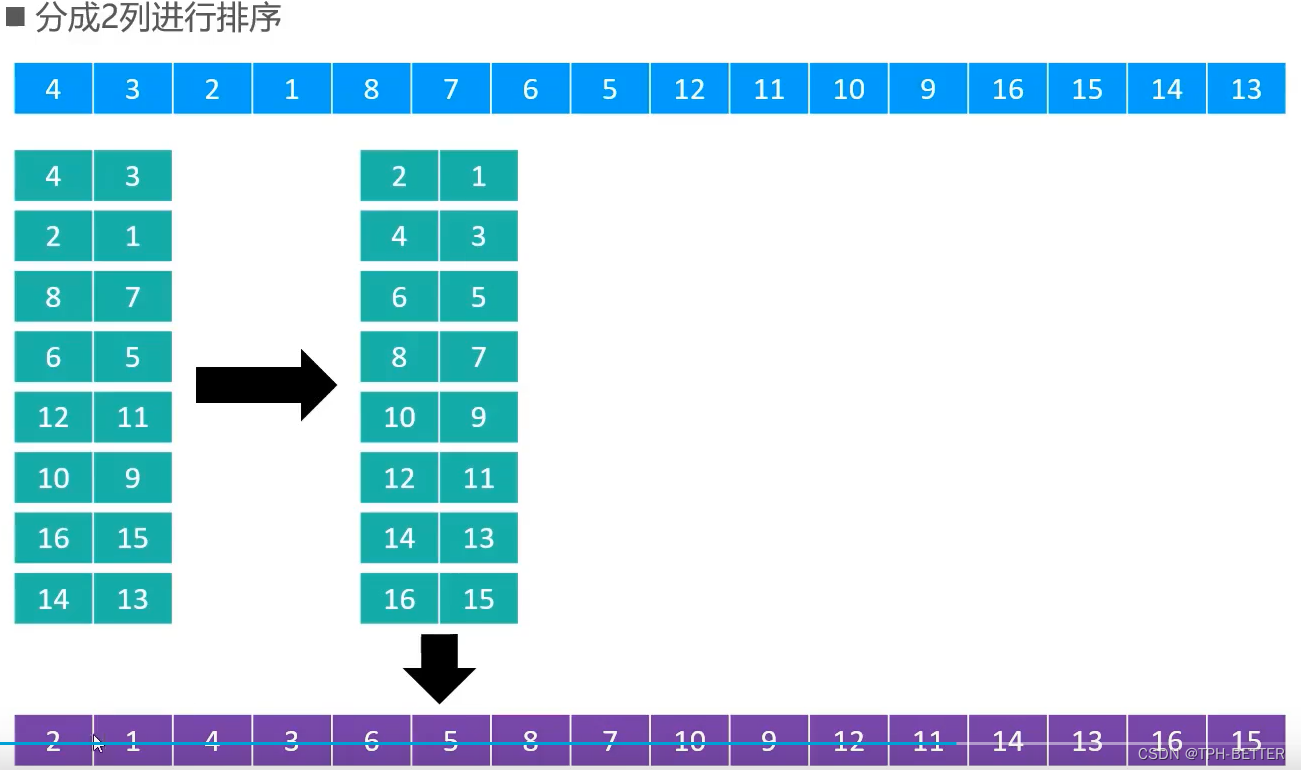
希尔排序把序列看做是一个矩阵,分成m列,逐列进行排序
- m从某个整数逐渐减为1
- 当m为1时,整个序列将完全有序
矩阵的列数取决于步长序列
- 比如,如果步长序列为{1,5,19,41,109},就代表依次分成109列,41列,19列,5列,1列。
- 不同的步长序列,执行效率也不同。
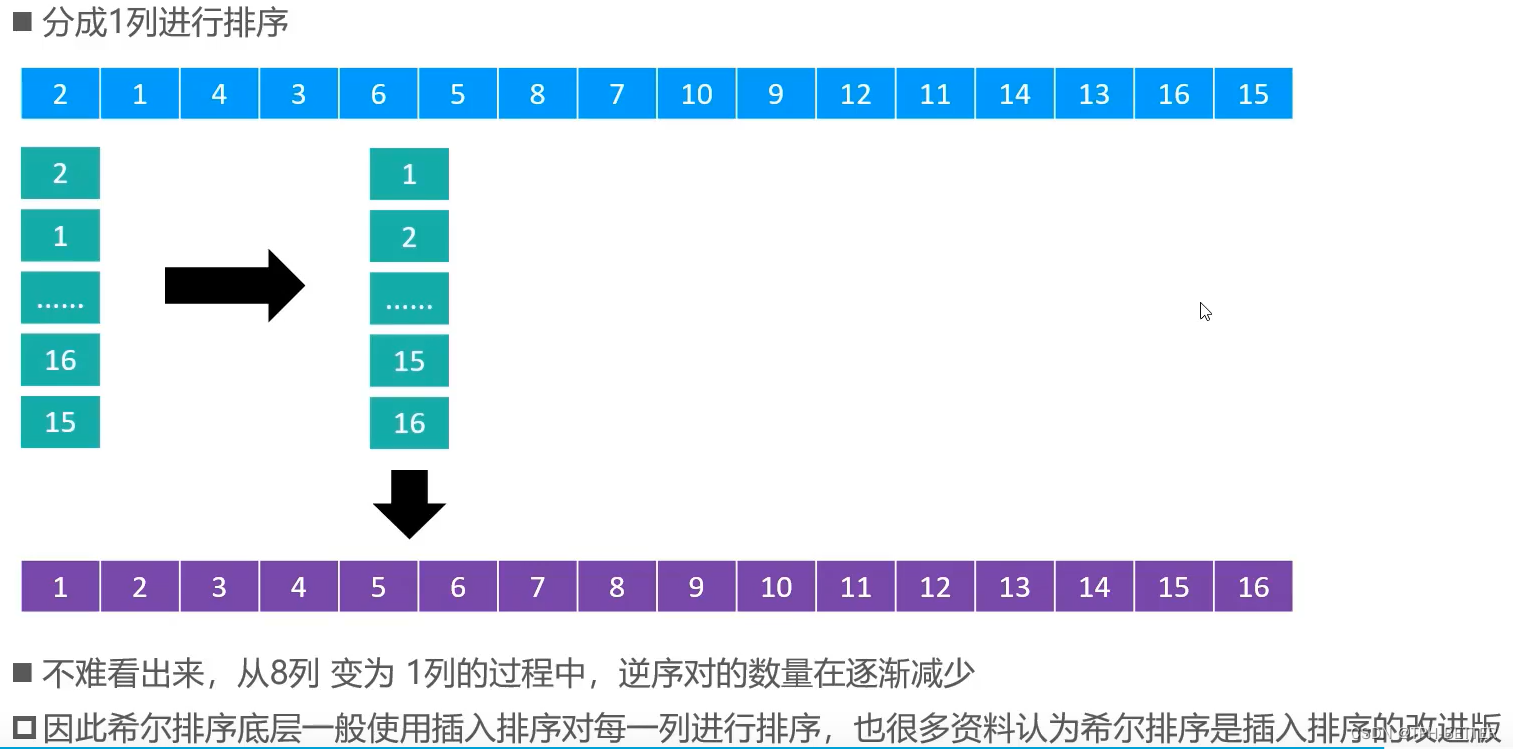 插入排序的时间复杂度与逆序对的数量成正比关系,逆序对的数量越多,插入排序的时间复杂度越高。
插入排序的时间复杂度与逆序对的数量成正比关系,逆序对的数量越多,插入排序的时间复杂度越高。
七、计数排序
1. 计数排序原理
冒泡、选择、插入、归并、快速、希尔、堆排序都是基于比较的排序,平均时间复杂度目前最低是O(nlogn)
计数排序、桶排序、基数排序都不是基于比较的排序,它们是典型的空间换时间,在某些时候,平均复杂度可以比O(nlogn)更低。
计数排序适合一定范围内的整数进行排序
计数排序的核心思想统计每个整数在序列中出现的次数,进而推导出每个整数在有序序列中的索引。
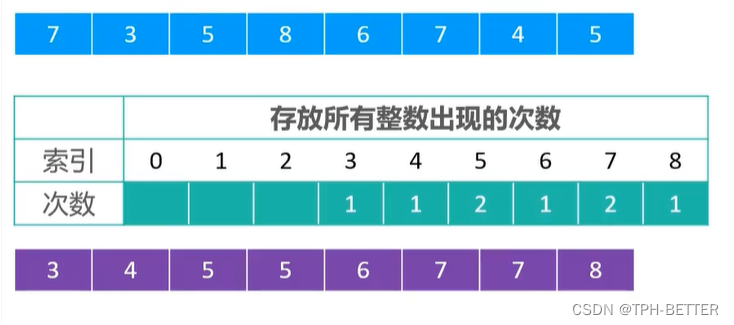
2. 计数排序代码实现
public class Test {
public static void swap(int []array,int j,int i){
int tmp=array[j];
array[j]=array[i];
array[i]=tmp;
}
public static void countSort(int arr[]){
int max=arr[0];
for (int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){
if (max<arr[i]){
max=arr[i];
}
}
int []countArr=new int[max+1];
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
countArr[arr[i]]++;
}
int i=0;
for(int index=0;index<countArr.length;index++){
while (countArr[index]-->0){
arr[i++]=index;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] array={1,2};
countSort(array);
for (int num:array) {
System.out.print(num +"\t");
}
}
}