1.栈和队列常见方法
(1)栈:
stack.push()//压栈
stack.pop()//弹栈
stack.empty()==true//栈为空
stack.peek()//返回栈顶元素(只返回不删除)(2)队列:
queue.add():往队尾添加元素
queue.remove():删除队头元素(并且返回队头元素)
queue.peek():返回队头元素(只返回不删除)
Queue queue=new LinkedList();
queue.add(1)
queue.add(2)
queue.add(3)
queue.add(4)
queue.add(5)
int size=queue.szie();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
Systerm.out.println(queue.remove());
//得到1,2,3,4,5
}
双端队列:
(1)队列只能在队尾添加元素,在队头删除元素,而双端队列在队头队尾都可以进行添加和删除操作
(2)双端队列Deque的常见方法:(在队列的add,peek,remove方法基础上进行改造)
//创建双端队列
Deque queue=new LinkedList();
//First表示队首,Last表示队尾
//在队首添加元素
queue.addFirst();
//在队尾增加元素
queue.addLast();
//获取队首元素
queue.peekFirst();
//获取队尾元素
queue.peekLast();
//移除并且返回队首元素
queue.removeFirst();
queue.removeLast();2.用两个栈实现队列:力扣(剑指offer09)
把栈和队列都想象成一个黑箱子
将1,2,3依次输入到这个黑箱子,如果这个黑箱子是栈,就依次返回3,2,1
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?如果这个黑箱子是队列,就依次返回1,2,3
加入元素的时候直接加入到stack1里面就行
主要是弹出元素时:弹出元素肯定是弹出stack2中的元素
如果stack2中有元素,就直接stack2.pop()
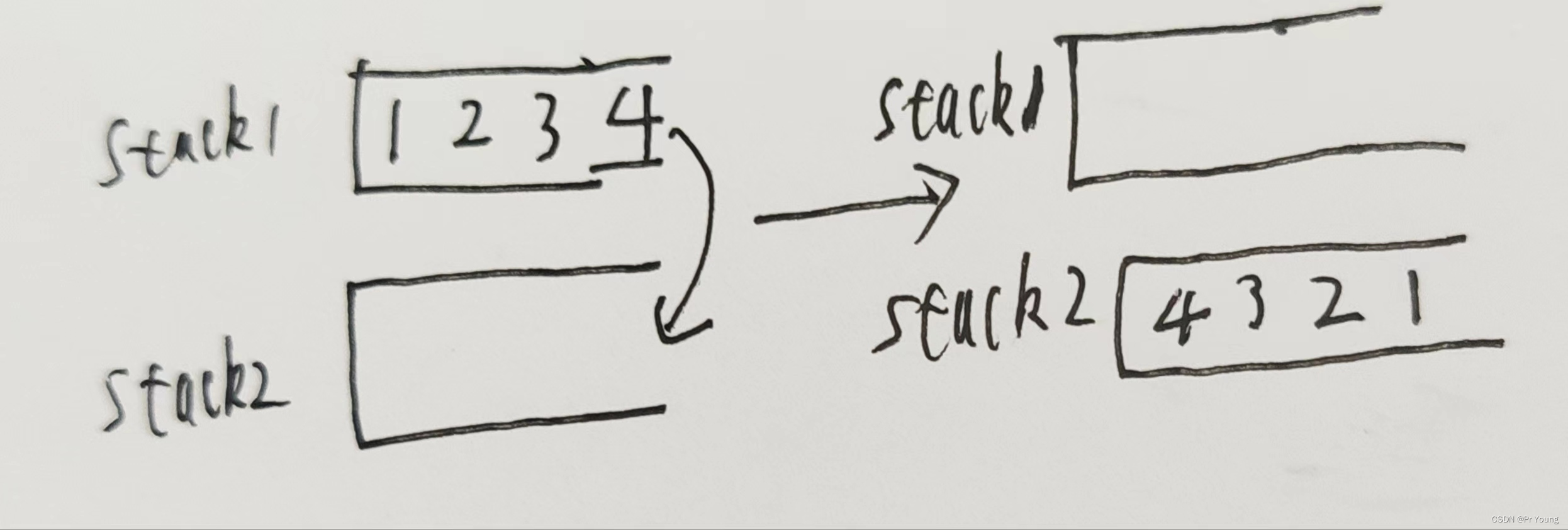
stack2为空的时候(即stack2中没有元素可以弹出的时候),把stack1中的元素全部转移到stack2中,然后再stack2.pop()
?将stack1内的元素全部转移到stack2内 :
class CQueue
{
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue()
{
stack1=new Stack();
stack2=new Stack();
}
//往你创建的队列中添加元素
public void appendTail(int value)
{
stack1.push(value);
}
//往你创建的队列中弹出元素
public int deleteHead()
{
//要弹出元素,肯定是弹出stack2这个栈里面的栈顶元素
//如果stack2栈内元素为空,stack1内也没元素,那就返回-1
//如果stack2栈内元素为空,stack1内有元素,就把stack1内所有元素转移到stack2里面去
/*比如stack1里面添加了四个元素1,2,3,4,现在显然是想要打印出1,2,3,4
所以要把1,2,3,4全部从stack1中压入stack2中,这样不断stack2.pop()才能得到1,2,3,4*/
if(stack2.empty()==true)
{
if(stack1.empty()==true) return -1;
else//如果stack1不为空
{
while(stack1.empty()==false)
{
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
//创建队列(调用构造方法)
CQueue obj = new CQueue();
//添加一个元素进队列队尾
obj.appendTail(value);
//删除队头元素并且返回这个队头元素
int param_2 = obj.deleteHead();另外一道跟这个也很相似力扣(leetcode232)
class MyQueue
{
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
//调用构造方法创建两个栈
public MyQueue()
{
stack1=new Stack();
stack2=new Stack();
}
public void push(int x)
{
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop()
{
//肯定是弹出stack2中的元素
//stack2为空的时候(即stack2中没有元素可以弹出的时候),把stack1中的元素全部转移到stack2中
if(stack2.empty()==true)
{
while(stack1.empty()==false)
{
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek()
{
if(stack2.empty()==true)
{
while(stack1.empty()==false)
{
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty()
{
if(stack1.empty()==true&&stack2.empty()==true)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
}3.用两个队列实现栈
力扣225
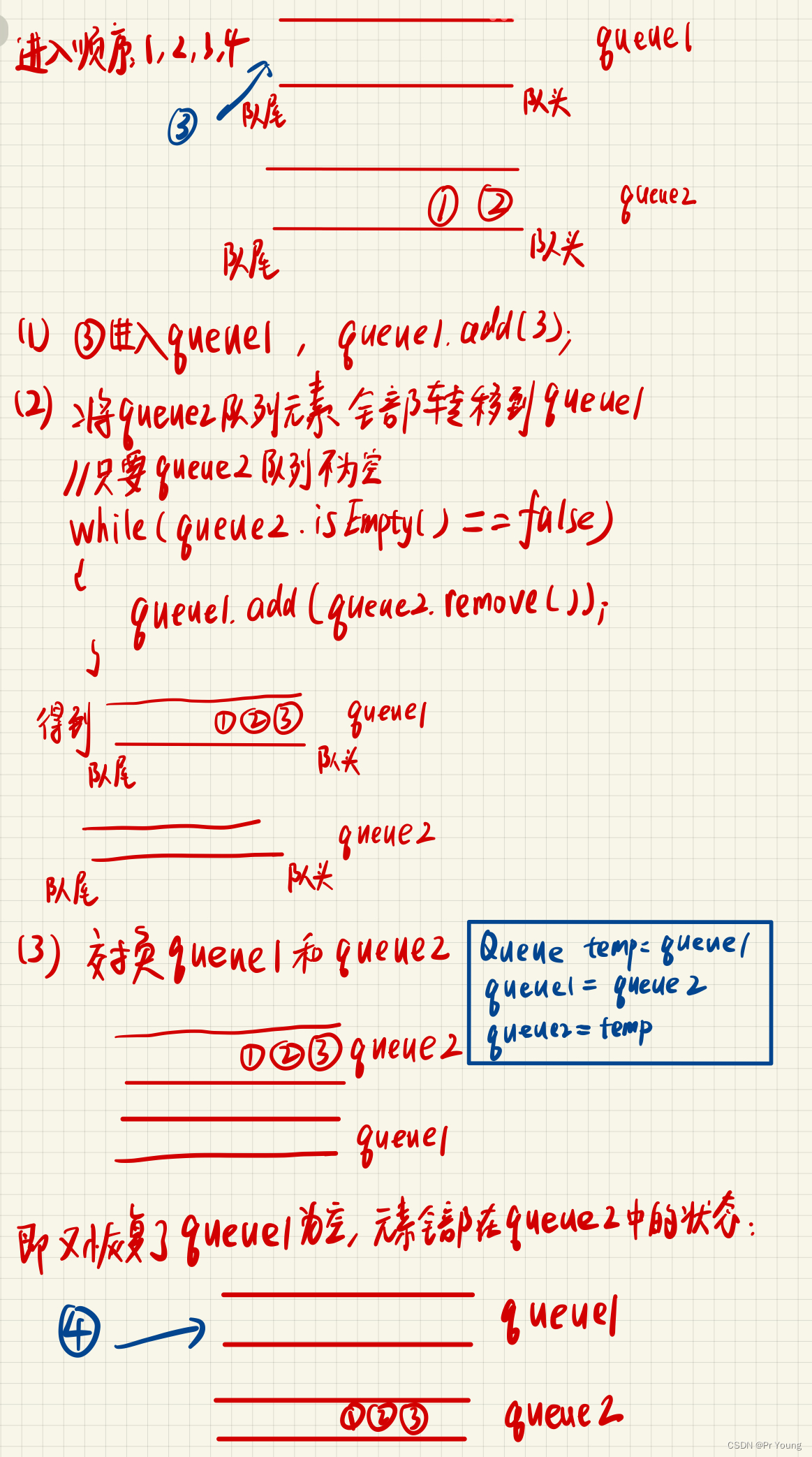
定义两个队列,其中queue1队列用来加入元素,queue2队列用来peek和pop弹出元素
?
class MyStack
{
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack()
{
queue1=new LinkedList();
queue2=new LinkedList();
}
public void push(int x)
{
//step1:先把元素添加到queue1里面
queue1.add(x);
//step2:只要队列queue2里面还有元素,就要把它转移到队列queue1里面
while(queue2.size()!=0)
{
queue1.add(queue2.remove());
}
//step3:此时元素就全部在队列queue1里面了,再交换queue1和queue2即可
Queue temp=queue1;
queue1=queue2;
queue2=temp;
}
public int pop()
{
return queue2.remove();
}
public int top()
{
return queue2.peek();
}
public boolean empty()
{
return queue2.size()==0;
}
}
4.最小栈
力扣155
最小栈其实就是在栈的基础上多了一个获取最小元素的功能
这道题进行测试时
minStack minstack=new MinStack();
minstack(-2);
minstack(0);
ninstack(-3);
//先压三个元素进栈
//然后调用getMin()方法来获取栈内最小元素是多少
minstack.getMin();
?暴力方法:
class MinStack
{
Stack<Integer>stack;
public MinStack()
{
stack=new Stack();
}
public void push(int val)
{
stack.push(val);
}
public void pop()
{
stack.pop();
}
public int top()
{
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin()
{
ArrayList<Integer> a=new ArrayList();
for(int i:stack)
{
a.add(i);
}
int temp=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int j:a)
{
temp=Math.min(temp,j);
}
return temp;
}
显然暴力法时间复杂度为O(n),因为遍历栈的时间复杂度为O(n)
题目规定要用常数时间内找到最小元素肯定是满足不了的
双栈法:用两个栈,一个栈是正常的栈,元素进栈和出栈都是正常的
另一个栈是特殊的栈,一个元素要想进这个栈必须小于这个栈的栈顶元素,
当正常栈弹出栈顶元素时,特殊栈要不要也弹出栈顶元素呢?当正常栈要弹出的栈顶元素等于特殊栈的栈顶元素时,特殊栈的栈顶元素也要弹出,不相等时,特殊栈的栈顶元素就不用弹出
class MinStack
{
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MinStack()//初始化两个栈,一个正常栈,一个特殊栈
{
stack1=new Stack();
stack2=new Stack();
}
public void push(int x)
{
//stack1正常栈,入栈时正常入栈就行
stack1.push(x);
if(stack2.empty()) stack2.push(x);
else
{
if(x<=stack2.peek()) stack2.push(x);
}
}
public void pop()
{
int temp=stack1.peek();
stack1.pop();
if(!stack2.empty()&&stack2.peek()==temp) stack2.pop();
}
public int top()
{
return stack1.peek();
}
public int getMin()
{
return stack2.peek();
}
}