【数据结构】之顺序表(C语言版)
目录
1.线性表的定义
线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列,线性表是一种在实际生活中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表有:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
2.什么是顺序表
顺序表即是线性表的顺序存储,他是用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的数据元素,从而使得逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻。
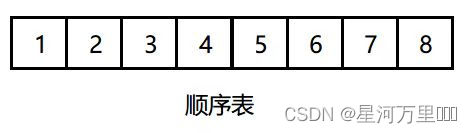
顺序表的定义
typedef int SLDataType;//类型重命名
//动态顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;//指向动态开辟的数组
int size;//表示数组中存储了多少个数据
int capacity;//数组实际能存储的空间是多大
}SL;
3.顺序表的接口实现
需要分装三个部分实现:Seqlist.h、Seqlist.c、test.c。
【Seqlist.h】里面用来写相关头文件的引用、接口函数的声明和结构体的类型定义。
【Seqlist.c】里面用来实现所有的接口函数。
【test.c】里面用来测试接口函数以及功能菜单的实现
【Seqlist.h】头文件以及相关代码如下:
#pragma once//防止头文件倍二次引用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;//类型重命名
//动态顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;//指向动态开辟的数组
int size;//表示数组中存储了多少个数据
int capacity;//数组实际能存储的空间是多大
}SL;
//初始化顺序表
void SeqListInit(SL* ps);
//顺序表尾插入
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps);
//顺序表尾删除
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps);
//顺序表头插入
void SeqListPusFront(SL* ps);
//顺序表头删除
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps);
//顺序表检测增容问题
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
//顺序表查找指定值
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//顺序表指定下标位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps);
//删除pos位置的数据
void SeqListErase(SL* ps);
//打印顺序表
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps);
//销毁顺序表
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps);
//顺序表修改指定元素数值
void SeqListModify(SL* ps);
【test.c】文件中菜单的实现如下:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Seqlist.h"
void menu()
{
printf(" 顺序表操作 \n");
printf("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
printf(" 1.尾插入 2.尾删除 \n");
printf(" 3.头插入 4.头删除 \n");
printf(" 5.指定下标位置插入 6.打印顺序表 \n");
printf(" 7.删除指定位置数据 8.修改指定数值 \n");
printf("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~0.退出程序~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
SL s1;
SeqListInit(&s1);//初始化顺序表
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
SeqListPushBack(&s1);//尾插
break;
case 2:
SeqListPopBack(&s1);//尾删
break;
case 3:
SeqListPusFront(&s1);//头插
break;
case 4:
SeqListPopFront(&s1);//头删
break;
case 5:
SeqListInsert(&s1);//指定下标位置插入
break;
case 6:
SeqListPrint(&s1);//打印顺序表
break;
case 7:
SeqListErase(&s1);//删除指定位置数据
break;
case 8:
SeqListModify(&s1);//修改指定数值
break;
case 0:
SeqListDestory(&s1);//销毁顺序表
printf("退出程序\n");
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,请重新选择\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
(1)初始化顺序表
void SeqListInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;//初始化顺序表为空
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;//初始化数据个数和数组实际存储的空间为空
}
(2)顺序表检测增容问题
为避免频繁增容,我们一次性去增容上一次空间大小的两倍,在这里需要注意的是当传给realloc的指针为空时,realloc的用法等同于malloc。
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//如果是第一次开辟空间,先开辟四个字节大小的存储空间
//之后就以原空间二倍的大小去增加容量
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a,
newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);//如果内存开辟失败,直接退出程序
}
ps->a = tmp;//将数组指向新开辟的动态存储空间
ps->capacity = newcapacity;//将容量指向新开辟的大小
}
}
(3)顺序表尾插
在这里我们使用while循环可以一次性插入多个数据。
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps)
{
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//插入数据之前,先检测容量是否已满
SLDataType x;
printf("请输入您要插入的元素:");
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x!= EOF)
{
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;//数据个数+1
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//检测容量是否已满
scanf("%d", &x);
}
}
函数功能测试
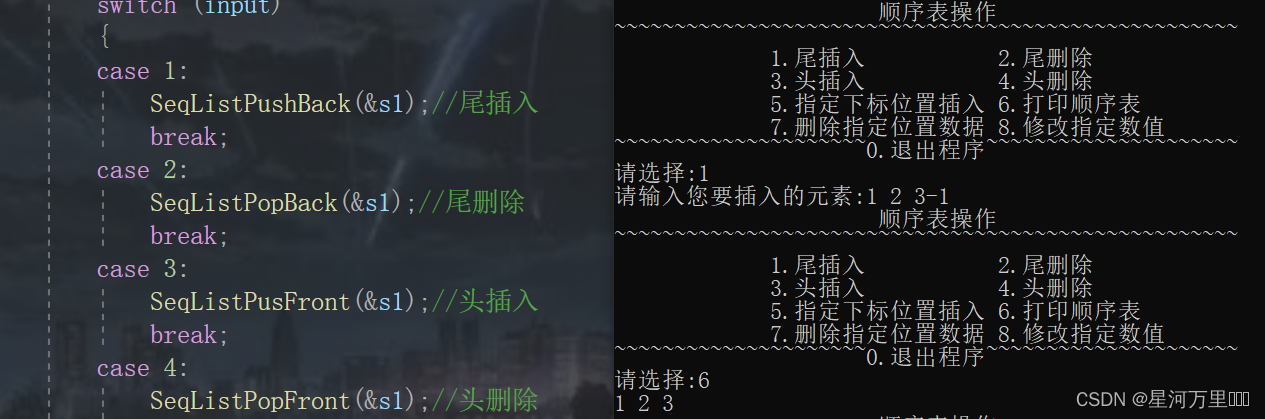
(4)顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size);//先断言顺序表是否为空
if (ps->size > 0)
{
ps->size--;//只需将有效数据个数减一即可
printf("尾删成功\n");
}
}
函数功能测试
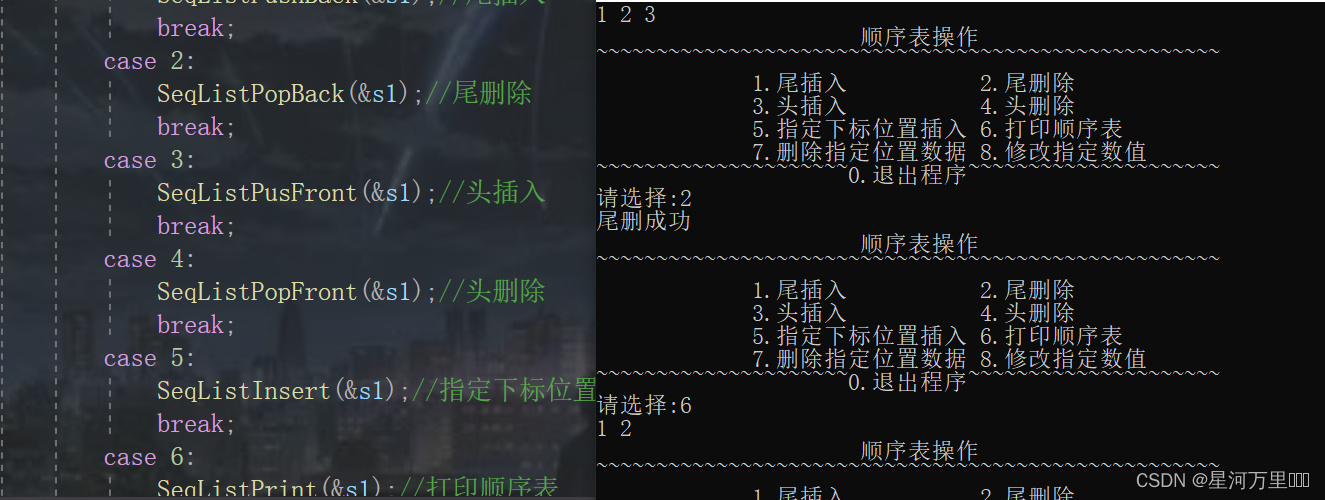
(5)顺序表头插
和尾插一样,在这里我们可以使用循环一次性插入多个数据
void SeqListPusFront(SL* ps)
{
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//头插之前先检测是否需要增容
SLDataType x;
printf("请输入您要头插的元素:");
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x != EOF)
{
int i = 0;
//遍历数组,使得头部数据到尾部数据依次向后挪动一位
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//每插入一个元素,都需要检测容量
scanf("%d", &x);
}
}
函数功能测试
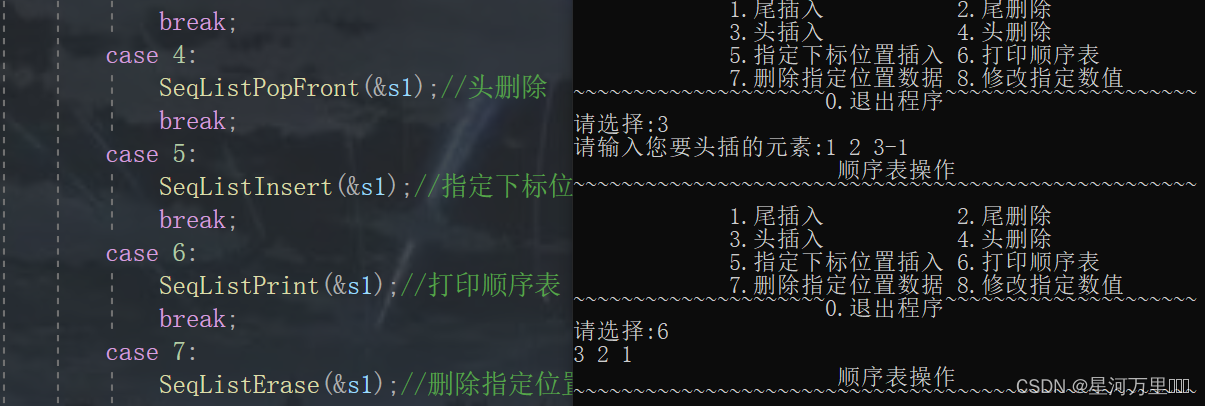
(6)顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size);//先判断顺序表数据个数是否为空
if (ps->size > 0)
{
int i = 0;
//遍历数组,将头元素之后的元素依次向前挪动一位
for (i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;//有效数据个数减一
printf("头删成功\n");
}
函数功能测试
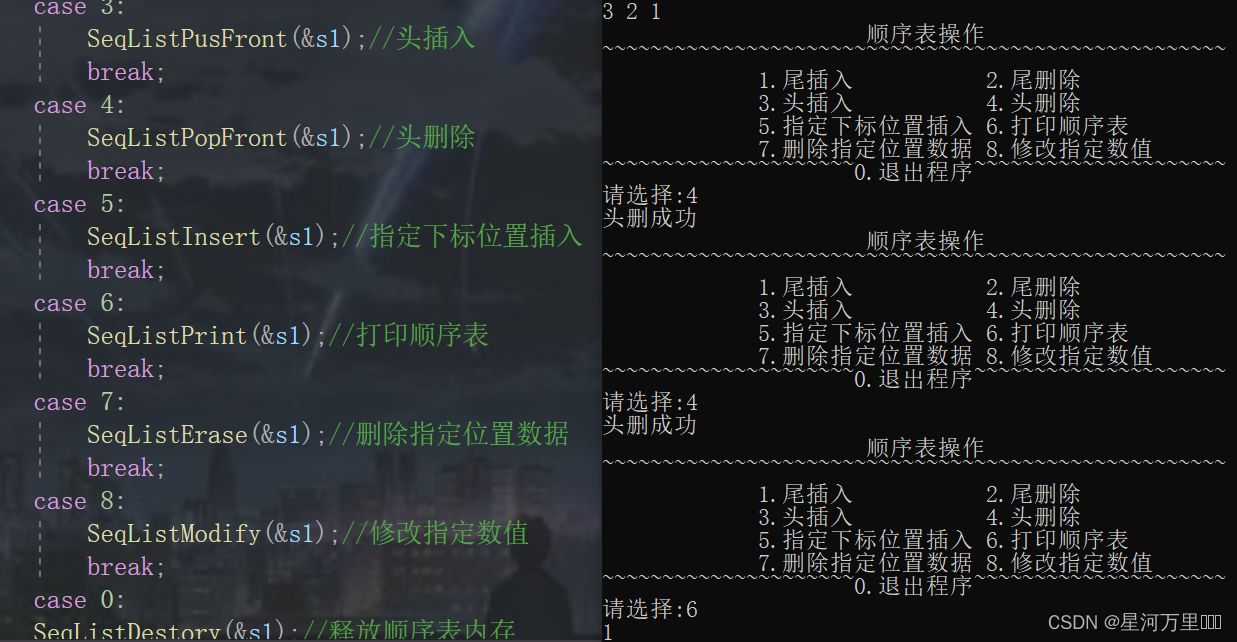
(7)顺序表查找指定值
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps->size);//顺序表元素个数是不能为空
int i = 0;
//遍历数组,将所有元素与所需查找的指定元素一一对比
while (i < ps->size)
{
//若能找到,返回元素下标
if (ps->a[i] == x)
return i;
i++;
}
return -1;//找不到,则返回-1
}
(8)顺序表指定下标位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps)
{
int pos = 0;
SLDataType x;
printf("请输入下标和需要插入的数据");
scanf("%d%d", &pos, &x);
//判断指定下标是否超出有效范围,超出范围,则重新输入
while (pos<0||pos > ps->size)
{
printf("下标位置超出范围,请重新输入:");
scanf("%d", &pos);
}
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//检测顺序表容量是否已满
for (size_t i = ps->size - 1; i >= pos; i--)
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];
ps->a[pos] = x;//插入数据
ps->size++;//有效数据个数+1
printf("插入成功\n");
}
函数功能测试
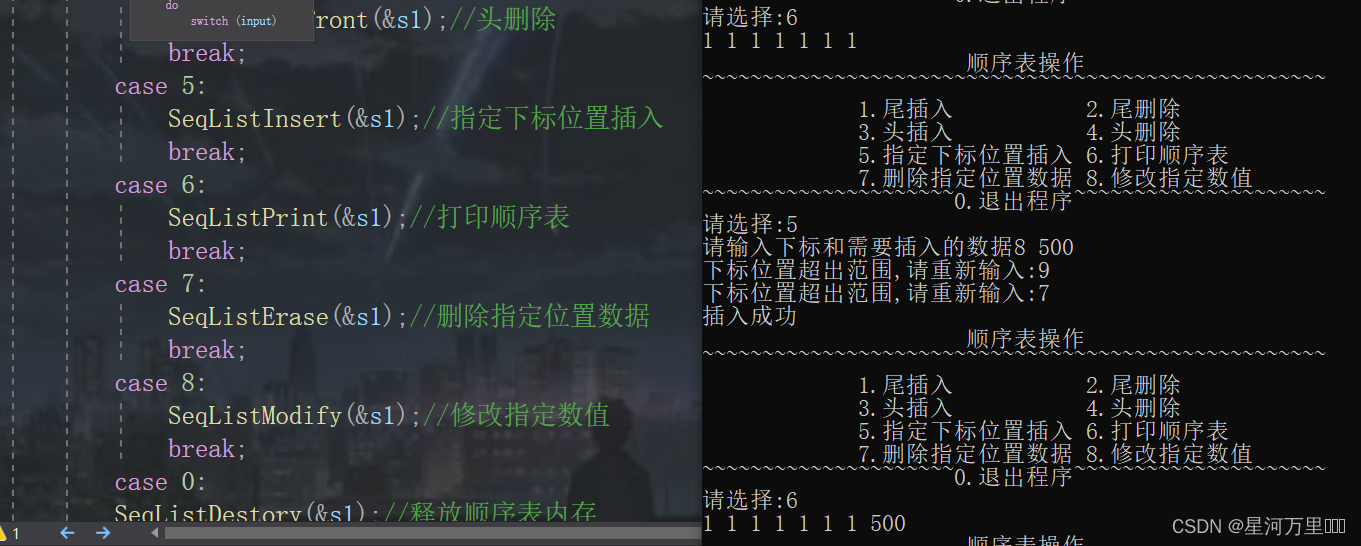
(9)删除指定位置的数据
在这里我们需要注意的是指定pos的范围是大于size-1,而上面的指定插入的pos的范围是大于size。这是因为数组的插入可以在最后一个元素的后面插入,而删除只能是删除最后一个元素。
void SeqListErase(SL * ps)
{
assert(ps->size);
int pos = 0;
printf("请输入所需删除的数值下标");
scanf("%d", &pos);
//判断指定位置下表是否超出有效范围
while (pos<0 || pos>ps->size - 1)
{
printf("pos invalid,请重新输入下标:");//超出范围,重新输入
scanf("%d", &pos);
}
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size; i++)
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
ps->size--;//有效数据个数-1
printf("删除成功\n");
}
函数功能测试
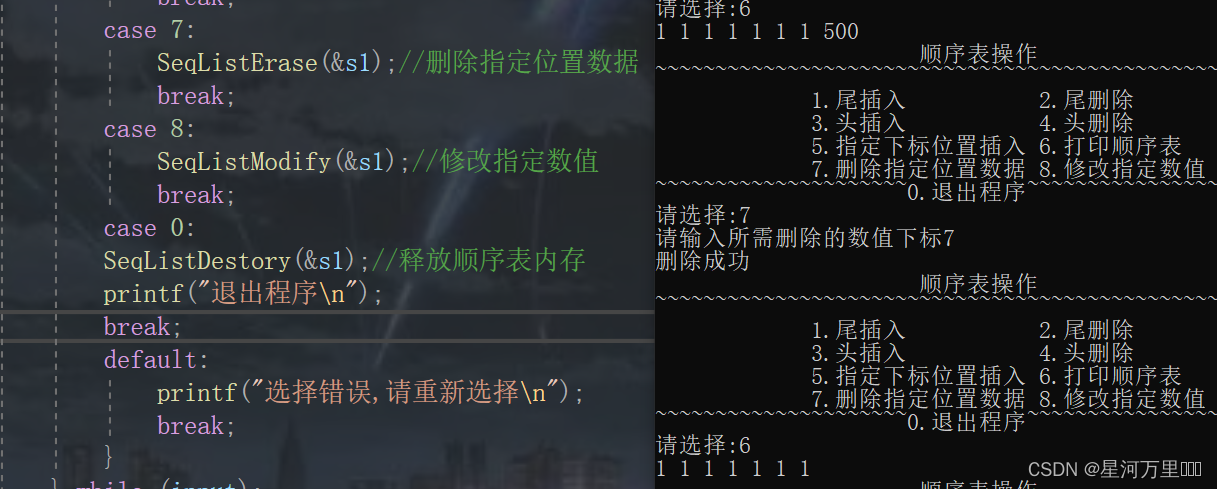
(10)打印数据表
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size);//断言,元素个数不能为0
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);//遍历数组,打印出每一个元素
printf("\n");
}
(11)顺序表修改指定数值
这里我们需要用到“顺序表查找指定值”这个函数,用一个整型变量来接收所需要修改元素的下标,最后再修改。
void SeqListModify(SL* ps)
{
SLDataType value, x ;//x为所需要修改的元素,value为该元素修改后的值
printf("请输入所需要修改的元素:");
scanf("%d", &x);
int tmp = SeqListFind(ps, x);
while (tmp == -1)
{
printf("该元素不存在,请重新输入:");
scanf("%d", &x);//重新输入所需要修改的元素
tmp = SeqListFind(ps, x);//重新接受新输入元素的下标
}
if (tmp != -1)
{
printf("请输入修改后的值:");
scanf("%d", &value);
ps->a[tmp] = value;//将该元素修改为value
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}
函数功能测试
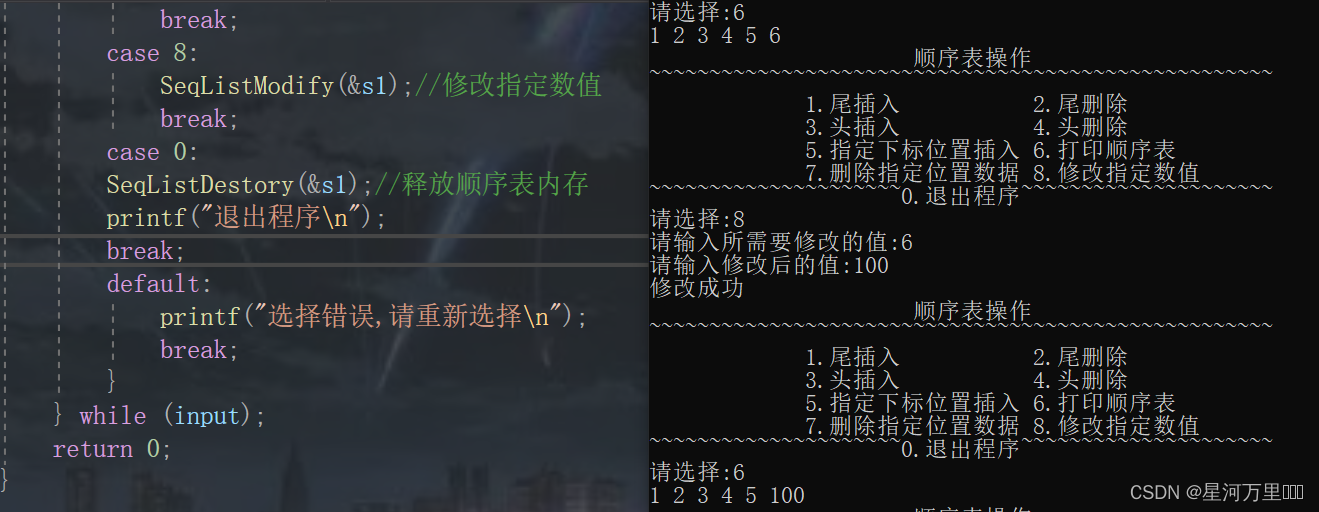
(12)销毁顺序表
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a)//释放开辟的空间
ps->a=NULL;
ps->size = 0;//数据个数置为0
ps->capacity = 0;//空间容量置为0
}
总节
好了,以上就是顺序表的详解了,各位小伙伴们如果觉得不错的话可以支持一下哦!