一. 二叉树的简单介绍
????????二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。二叉树特点是每个节点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分 。
? ? ? ? 其中,满二叉树和完全二叉树是其中比较特殊的类型。如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的节点和度为2的节点,并且度为0的节点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树。深度为k,有n个节点的二叉树当且仅当其每一个节点都与深度为k的满二叉树中编号从1到n的节点一一对应时,称为完全二叉树,完全二叉树的特点是叶子节点只可能出现在层序最大的两层上,即缺失的叶子节点只能在最后一层的叶子节点上。
二. 二叉树的典型代码实现
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}三. 二叉树的遍历
? ? ? ? 二叉树的遍历一般有三种方式,递归方式,使用栈和Morris 遍历。递归的方式实现较为简单,栈则是显示维护一个空间,Morris 遍历的核心思想是利用树的大量空闲指针,实现空间开销的极限缩减。
前序遍历
递归
class Solution {
List<Integer> list= new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return list;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
list.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}栈?
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
res.add(node.val);
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
return res;
}
}
?Morris 遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
TreeNode p1 = root, p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1) {
p2 = p2.right;
}
if (p2.right == null) {
res.add(p1.val);
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
} else {
p2.right = null;
}
} else {
res.add(p1.val);
}
p1 = p1.right;
}
return res;
}
}
中序遍历
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
}
栈/迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
}?Morris
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
TreeNode predecessor = null;
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != root) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
res.add(root.val);
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
后序遍历
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, res);
postorder(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
}
}
栈/迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode prev = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.right == null || root.right == prev) {
res.add(root.val);
prev = root;
root = null;
} else {
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}?Morris
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
TreeNode p1 = root, p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1) {
p2 = p2.right;
}
if (p2.right == null) {
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
} else {
p2.right = null;
addPath(res, p1.left);
}
}
p1 = p1.right;
}
addPath(res, root);
return res;
}
public void addPath(List<Integer> res, TreeNode node) {
int count = 0;
while (node != null) {
++count;
res.add(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
int left = res.size() - count, right = res.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int temp = res.get(left);
res.set(left, res.get(right));
res.set(right, temp);
left++;
right--;
}
}
}四. leetcode实战
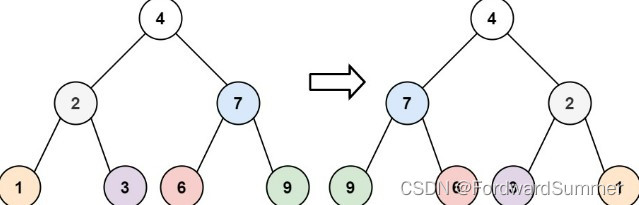
1. leetcode226 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//递归函数的终止条件,节点为空时返回
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
//下面三句是将当前节点的左右子树交换
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = tmp;
//递归交换当前节点的 左子树
invertTree(root.left);
//递归交换当前节点的 右子树
invertTree(root.right);
//函数返回时就表示当前这个节点,以及它的左右子树
//都已经交换完了
return root;
}
}
本题小结(1)先在一棵树上操作交换,典型的交换的思想
? ? ? ? ? ? ??(2)然后递归左子树和右子树
2. leetcode104 & leetcode111 二叉树的最大/小深度
????????给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
最大深度
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}最小深度
错误的版本:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}else{
int leftL = minDepth(root.left);
int rightL = minDepth(root.right);
return Math.min(leftL,rightL)+1;
}
}
}正确版本:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
//这道题递归条件里分为三种情况
//1.左孩子和有孩子都为空的情况,说明到达了叶子节点,直接返回1即可
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
//2.如果左孩子和由孩子其中一个为空,那么需要返回比较大的那个孩子的深度
int m1 = minDepth(root.left);
int m2 = minDepth(root.right);
//这里其中一个节点为空,说明m1和m2有一个必然为0,所以可以返回m1 + m2 + 1;
if(root.left == null || root.right == null) return m1 + m2 + 1;
//3.最后一种情况,也就是左右孩子都不为空,返回最小深度+1即可
return Math.min(m1,m2) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int rightdeep = minDepth(root.right);
int leftdeep = minDepth(root.left);
if(root.left == null || root.right == null) return rightdeep+leftdeep+1;
return Math.min(rightdeep,leftdeep)+1;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
else if (root.left == null) return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
else if (root.right == null) return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
else return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}?本题小结:(1)这题和求最大值不一样,最大的区别在于若左右节点有一个为空怎么办
参考来源:
【1】leetcode 官方解题 二叉树的前序遍历
【2】leetcode wang_ni_ma 动画演示 两种实现 226. 翻转二叉树?
【3】leetcode?房建斌学算法?二叉树的最小深度-理解递归结束条件
【4】百度百科 二叉树??