哈希表、集合、映射
哈希表的原理与实现
哈希表
哈希表(Hash table)又称散列表,是一种可以通过"关键码” (key) 直接进行访问的数据结构。
哈希表由两部分组成
- 一个数据结构,通常是链表、数组
- Hash函数,输入“关键码” (key) ,返回数据结构的索引
对外表现为可以通过关键码直接访问: hash_ table[key] = value
实际上是在数据结构的hash(key)位置处存储了value: data_ structure[hash(key)] = value
最简单的例子,关键码是整数,定义hash(key) = key
那这个哈希表其实就是一一个数组了,key 自己就是下标
当然,一般情况下,关键码key是一个比较复杂的信息,比如很大的数、字符串
这时候key就不能直接作为数据结构的下标了
此时就需要设计一个Hash函数,把复杂信息映射到一个较小的值域内,作为索引
一个简单的hash _table[“ies”]= 233的例子,以各字符ASCII码相加mod 20为Hash函数
哈希碰撞
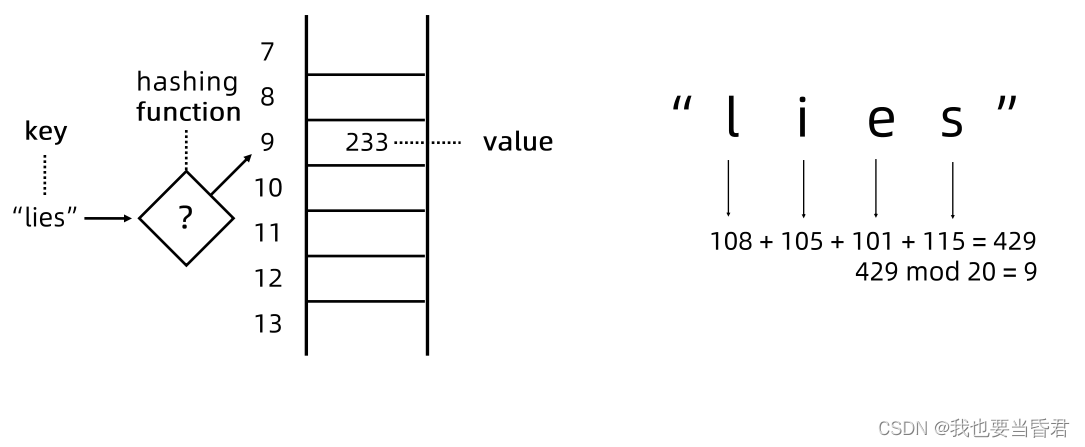
哈希碰撞(Collisions) 指的是两个不同的key被计算出同样的Hash结果
把复杂信息映射到小的值域,发生碰撞是不可避免的
好的Hash函数可以减少碰撞发生的几率,让数据尽可能地均衡分布
开散列是最常见的碰撞解决方案
- Hash函数依然用于计算数组下标
- 数组的每个位置存储一个链表的表头指针(我们称它为表头数组)
- 每个链表保存具有同样 Hash值的数据
形象描述:“挂链” 一表头数组每个位置 “挂”着一个链表
哈希碰撞 + 开散列
工程应用
- 电话号码簿
- 用户信息表
- 缓存(LRUCache)
- 键值对存储(Redis)
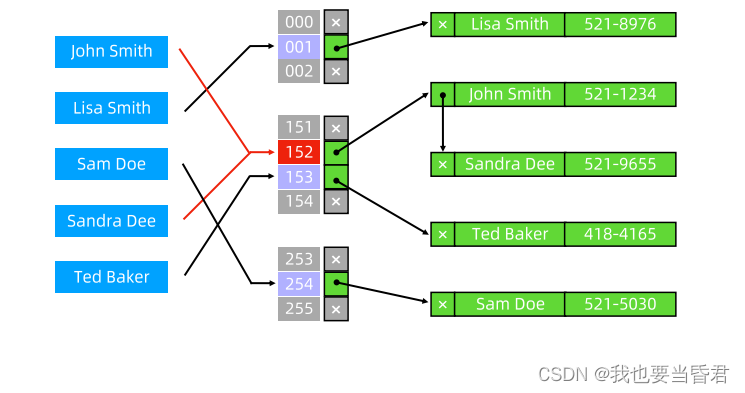
完整结构图
时间复杂度
- 期望:插入、查询、删除0(1)
- 数据分布比较均衡时 - 最坏:插入、查询、删除0(n)
- 数据全部被映射为相同的Hash值时
无序集合、映射的实现与应用
集合与映射
集合(set) 存储不重复的元素
- 有序集合, 遍历时按元素大小排列,一般用平衡二叉搜索树实现, 0(logN)
- 无序集合,一般用hash实现,0(1)
映射(map)存储关键码(key) 不重复的键值对(key-value pair)
- 有序集合, 遍历时按照key大小排列,一般用平衡二叉搜索树实现, O(logN)
- 无序集合,一般用哈希表实现,0(1)
对于语言内置的类型(int, string) ,已经有默认的优秀的hash函数,可以直接放进set/map
里使用
C++ code
set与unordered_ set
- unordered_ set S;
- insert, find, erase, clear等方法
- multiset
map与unordered_ map
- unordered_map<string, int> h;
- h[key] = value
- find(key), erase(key), clear等方法
- multimap
Java code
Set:不重复元素的集合
- HashSet<…> set = new HashSet<>()
- set.add(value)
- set.contains(value)
- set.remove(value)
Map: key-value对, key不重复
- HashMape<…,…> map = new HashMap<>()
- map.put(key, value)
- map.get(key)
- map.remove(key)
- map.clear()
Python code
list_ a= list([1,2,3, 4])
集合
set_ a = {‘jack’, ‘selina’, ‘Andy’}
set_ b= set(list_ _a)
字典
map_ a= {
‘Jack’: 100,
‘张三’: 80,
‘Candela’: 90,
}
实战
1.两数之和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/
基本思路:枚举一个数x, 找它前面有没有target-x
所以建立一个数值到下标的hash map就可以了
对于每个数x,先查询target-x,再插入x
时间复杂度0(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
for(int i = 0;i < nums.size(); i++){
if(h.find(target - nums[i]) != h.end()) {
return {h[target - nums[i]],i };
}
h[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
}
private:
unordered_map<int,int> h;
};
874.模拟行走的机器人
https://leetcode.cn/problems/walking-robot-simulation/
可以用set或者map存储障碍物,从而快速判断一个格子里有没有障碍
可以利用方向数组简化实现(代替if)
class Solution {
public:
int robotSim(vector<int>& commands, vector<vector<int>>& obstacles) {
unordered_set<long long> obstacles_set;
for(auto obstacle : obstacles){
obstacles_set.insert(callHash(obstacle));
}
int ans = 0;
int dir=0;
int x=0;
int y=0;
int dx[4] = {0 ,1, 0, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
for(int i=0; i < commands.size() ;i++){
if(commands[i] == -2){
dir = (dir + 3) % 4;
}else if(commands[i] == -1){
dir = (dir + 1) % 4;
}else{
for(int step = 0;step < commands[i]; step++){
int nx = x + dx[dir];
int ny = y + dy[dir];
if( obstacles_set.find(callHash({nx , ny})) != obstacles_set.end()){
break;
}
x = nx;
y = ny;
ans = max(ans,x * x + y * y);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private:
long long callHash(vector<int> obstacle){
return (obstacle[0] + 30000) *60000ll +(obstacle[1] + 30000);
}
};
49.字母异位词分组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/group-anagrams/
对字符串分组,其实就是进行Hash
让同一组的字符串具有相同的Hash函数值,不同组的字符串具有不同的Hash函数值
然后就可以用hash map分组了
方案一: 把每个字符串中的字母排序,排序后的串作为hash map的key
map<string, group>
方案二:统计每个字符串中各字母出现次数,把长度为26的计数数组作为key
map<array<26, int>, group> (C++ std::array, Python tuple)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {
for(string& s : strs) {
string copy = s;
sort(copy.begin(), copy.end());
groups[copy].push_back(s);
}
vector<vector<string>> ans;
for(const pair<string, vector<string>> & group : groups) {
ans.push_back(group.second);
}
return ans;
}
private:
unordered_map<string, vector<string>> groups;
};
30.串联所有单词的子串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words/
遇到难题,先分解
不会求解,可以先想想判定:
给出一个s的子串、words,判定这个子串是不是words的串联?
把子串划分以后,其实就是比较两个Hash map是否相等
“barfoothefoobarman” mapA= {“bar”: 1, “foo”: 1}
[“oo”,“bar”] mapB ={“bar”: 1, “foo”: 1}
mapA ?= mapB
回到原问题:
枚举子串的所有起始位置, 0(length of s * total length of words)
barfoothefoobarman→barfoothefoobarman >…
枚举部分起始位置+滑动窗口,O(length of s * length of one word)
barfoothefoobarman→barfoothefoobarman→…
barfoothefoobarman→barfoothefoobarman→…
…
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string &s, vector<string> &words) {
vector<int> res;
int m = words.size(), n = words[0].size(), ls = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n && i + m * n <= ls; ++i) {
unordered_map<string, int> differ;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
++differ[s.substr(i + j * n, n)];
}
for (string &word: words) {
if (--differ[word] == 0) {
differ.erase(word);
}
}
for (int start = i; start < ls - m * n + 1; start += n) {
if (start != i) {
string word = s.substr(start + (m - 1) * n, n);
if (++differ[word] == 0) {
differ.erase(word);
}
word = s.substr(start - n, n);
if (--differ[word] == 0) {
differ.erase(word);
}
}
if (differ.empty()) {
res.emplace_back(start);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
vector<int> ans;
int tot =0;
for(string& word:words){
tot+=word.length();
wordsMap[word]++;
}
for(int i=0;i+tot<=s.length();i++){
if(valid(s.substr(i,tot),words)){
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
private:
//怎么看两个数组含有一样的元素,字符排序,字符串比较有问题,统计次数,hash
bool valid(string str, vector<string>& words){
//分解是不是好点,不是n阶乘
int k = words[0].length();
//vector<string> splitWords;
unordered_map<string,int> splitWordsMap;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i+=k){
//splitWords.push_back(str.substr(i,k));
splitWordsMap[str.substr(i,k)]++;
}
return equalsMap(splitWordsMap,wordsMap);
}
bool equalsMap(unordered_map<string,int> &a,unordered_map<string,int> &b){
for(auto& key_and_value : a){
const string &key=key_and_value.first;
int value = key_and_value.second;
if(b.find(key) == b.end() || b[key] != value) return false;
}
for(auto& key_and_value : b){//严谨
const string &key=key_and_value.first;
int value = key_and_value.second;
if(a.find(key) == a.end() || a[key] != value) return false;
}
return true;
}
unordered_map<string,int> wordsMap;
};
推荐一个零声学院免费公开课程,个人觉得老师讲得不错,分享给大家:Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK等技术内容,立即学习