目录
一、概念
在顺序结构以及平衡树中,因为元素与存储位置之间没有对应的关系。因此在查找一个数据时,需要经过多次的比较。
理想的搜索方法:不经过任何比较。一次性从表中得到要搜索的数据。
解决方案:哈希表
通过某种函数使得元素和元素的存储位置建立一一映射的关系。
在插入元素时:根据元素和函数,计算出存储的位置进行存储
查找元素:根据元素和函数,求出存储的位置
这种方法,不是十全十美,会存在哈希冲突问题。
二、哈希冲突
哈希冲突:两个元素通过哈希函数计算得到相同的哈希地址
哈希冲突是没有办法避免的。能做的是降低冲突率。
解决思路有两种:
- 尽可能的避免哈希冲突:设计合适的哈希函数、负载因子
- 冲突发生后尽可能的解决冲突:闭散列、哈希桶
三、避免冲突-哈希函数
3.1 哈希函数设计原则
- 哈希函数的定义域必须包含要存储的全部关键码
- 哈希函数计算出来的地址能均匀分布在整个空间中
- 哈希函数比较简单
3.2 常见的哈希函数
3.2.1 直接定制法
取关键字的某个线性函数为地址: Hash (Key) = A*Key+B
优点:简单、均匀
缺点:需要事先知道关键字的分布情况
使用场景:适合查找比较小且连续的情况
3.2.2 除留余数法
设散列表中允许的地址数为m,取一个不大于m,但最接近或者等于m的质数p作为除数,按照哈希函数:Hash(key) = key% p(p<=m),将关键码转换成哈希地址。
3.2.3 其他
平方取中、折叠法、随机数法、数学分析法
四、避免冲突-负载因子
负载因子=填入表中的元素个数 / 散列表的长度

?负载因子越大,冲突率越高。因为需要存储的关键字的个数不能改变,所以要降低负载因子,只能调整哈希表中的数组的大小。
五、解决冲突-闭散列
当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表没有装满。可以将key放到冲突位置的下一个空位置去。
5.1 线性探测
从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
要插入44,4这个位置已经被占用,从4这个位置往后找,知道找到一个空位置?
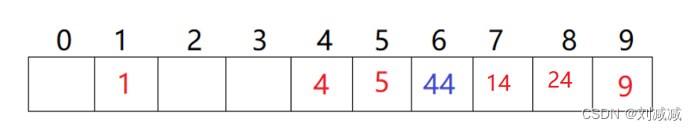 ?缺点:
?缺点:
- 采用这种方法处理哈希冲突,不能随便物理删除哈希表中的元素。因为会影响其他元素的查找。删掉4,44也就找不到了。删除采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
- 冲突的数据会堆积在一块。
5.2 二次探测
寻找空位置的方法:
i为第i次冲突。

??开散列最大的缺点就是空间利用率低。
六、解决冲突-开散列(哈希桶)
将相同地址的关键码归于同一个集合,每一个子集称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,将各链表的头节点存储在哈希表中。

JDK1.7以前是头插法,从1.8开始,是尾插法。?
七、手动实现HashMap
7.1?手动实现HashMap(key的类型是int)
实现原理:
底层:数组+单链表
哈希函数:hash(key) = key%数组长度
负载因子:0.75
class HashBuck{
static class Node{
public int key;
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int key,int val){
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize; // 已经存放的元素的个数
public HashBuck(){
this.array = new Node[4];
}
public int get(int key){
// 找位置
int index = key % array.length;
// 遍历当前index下标的链表
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur!= null){
if(cur.key == key){
return cur.val;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return -1; // 找不到的情况
}
// 采用尾插法
public void put(int key,int value){
// 先计算下标
int index = key % array.length;
Node node = new Node(key,value);
Node cur = array[index];
Node pre = null;
// 判断index下标是否有值
if(cur == null){
array[index] = node;
}else{
// 遍历当前index下标,判断是否有相同key
while (cur != null) {
// 遍历的时候判断,如果key这个位置已经有值,则需要进行覆盖
if(cur.key == key){
cur.val = value;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
pre.next = node;
}
this.usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75){
// 扩容的问题:重新哈希 每个下标的每个列表的每个节点
resize();
}
}
public double loadFactor(){
return this.usedSize *1.0 /array.length;
}
public void resize(){
Node[] newArray = new Node[array.length*2];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 得到i下标的节点
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur!= null){
// 将节点放入新数组的链表时,需要将next置null。为了保证可以遍历,所以需要将cur.next保存下来
Node curNext = cur.next;
// 计算在新数组的位置
int index = cur.key% newArray.length;
Node curNew = newArray[index];
// 如果该位置上没有元素,直接放
if(curNew == null){
newArray[index] = cur;
}else{
// 有的话,尾插法
while (curNew.next != null){
curNew = curNew.next;
}
curNew.next = cur;
}
// 因为节点放到新的链表,所以之前链表的顺序已经不成立,所以需要将cur.next=null
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
}
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashBuck hashBuck = new HashBuck();
hashBuck.put(0,11);
hashBuck.put(1,111);
hashBuck.put(2,12);
hashBuck.put(4,13);
System.out.println(hashBuck);
}
}7.2 手动实现HashMap(key的类型是引用类型)
在7.1中,采用的哈希函数是 hash(key) = key%数组长度。如果此时的key不是int,而是String,就不能计算元素的存储位置。将问题总结为:如果key不是int类型,需要将key转为数字,才能使用哈希函数计算位置。
解决方案:Object类的hashcode()方法,可以将传来的对象转为一个合法的数字。
新建一个Student类。假设key是student对象,为了能够将student对象转为数字,Student类需要重写hashcode()函数。在put元素时,涉及到对象的比较,所以需要重写equals方法。
class Student{
public String id;
public Student(String id){
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return super.equals(obj);
}
}与7.1中代码不同的是:
- 使用hashcode()将key转为数字
- 比较key、value是否相等,采用的是equals方法
public class HashBuck<K,V> {
static class Node<K,V>{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node<K,V> next;
public Node(K key,V value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public Node<K,V>[] array = new Node[4];
public int usedSize;
public void put(K key,V value){
// 使用hashcode()将key转为数字
int hashKey = key.hashCode();
int index = hashKey % array.length;
Node<K,V> node = new Node<>(key,value);
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
if(cur == null){
array[index] = node;
}else{
while (cur.next != null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
cur.value = value;
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
this.usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75){
resize();;
}
}
public double loadFactor(){
return this.usedSize *1.0 /array.length;
}
public void resize(){
Node<K,V>[] newArray = new Node[array.length*2];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 得到i下标的节点
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur!= null){
Node curNext = cur.next;
// 遍历
int index = (cur.key.hashCode())% newArray.length;
Node curNew = newArray[index];
if(curNew == null){
newArray[index] = cur;
}else{
while (curNew.next != null){
curNew = curNew.next;
}
curNew.next = cur;
}
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
}
}
public V get(K key){
int index = key.hashCode() % array.length;
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
while (cur != null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
return cur.value;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
7.3 hashcode和equals的作用
hashcode:将key转为数字,可以决定该元素存储在数组的哪个位置。
equals:比较元素的key是否相同。
- 当hashcode结果一样,equals结果一样吗?
? ? ? ? 不一定。hashcode相同,说明在数组中的存储位置相同,不能证明在哈希桶的位置是否相同。
- 当equals一样,hashcode结果一样吗?
? ? ? ? 一样。元素的key一样,肯定存储位置是相同的。所以hashcode一定是一样的。
八、HashMap源码解读
8.1 HashMap的默认容量是16
 8.2 HashMap的最大容量:1<<30
8.2 HashMap的最大容量:1<<30

8.3 HashMap的容量必须为2的倍数
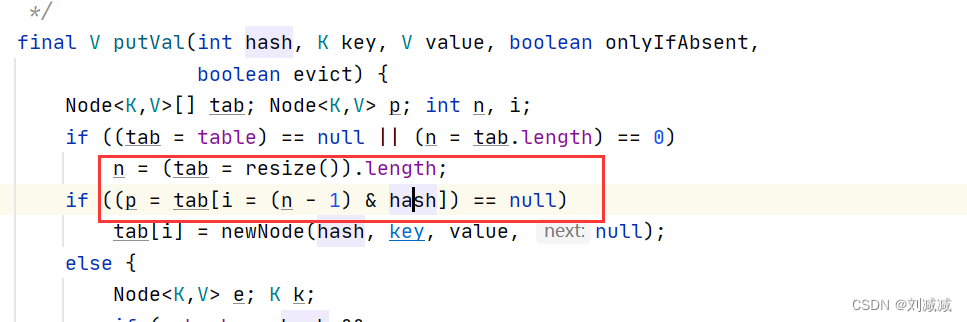
当容量是2的倍数时,key&(table.length-1) 和key%table.length的结果相同。?
8.4 HashMap的默认负载因子是0.75

8.5 HashMap有四种构造方法
// 方法1:传入初始大小和负载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 方法2:传入初始大小
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
// 方法3:不带任何参数
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
// 方法4:传入一个Map参数
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}最常用的是第三种方法。
?该方法的初始容量大小是0,第一次put的时候容量大小变成16
8.6 HashMap中的单链表变红黑树的条件
当前链表的长度超过8.并且当前桶的个数大于等于64的时候,才会将当前这个超过8的链表变成红黑树,否则只是2倍扩容。
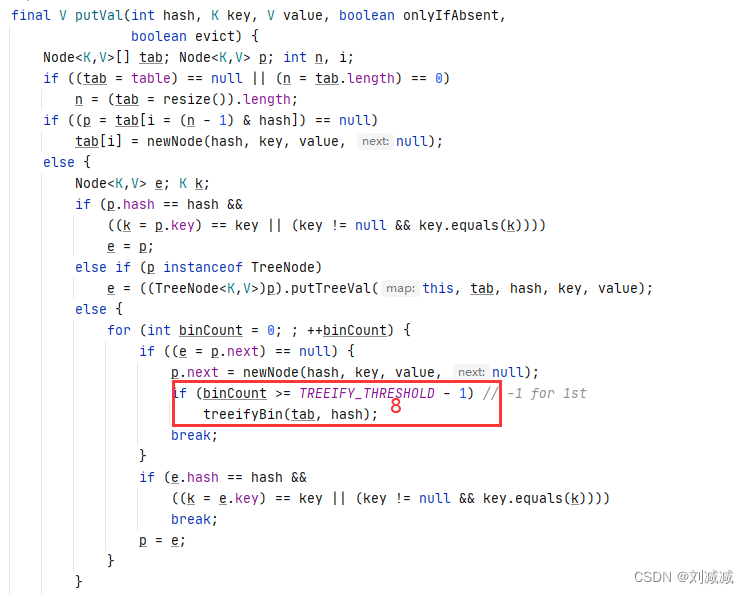
 ?
?
九、常见的考题
- 如果 new HashMap(19),那么 bucket 数组有多大?
? ? ? ? 32。数组大小必须是2的倍数
- HashMap?什么时候开辟 bucket 数组占用内存?
? ? ? ? 第一次put的时候
- HashMap 何时扩容?
? ? ? ?计算出的负载因子大于等于默认负载因子
- 当两个对象的 hashCode 相同时会发生什么?
? ? ? ?发生哈希冲突
- 如果两个键的 hashCode 相同,你如何获取值对象?
? ? ? ?遍历当前的链表,通过equals方法确定和查询key一样的key的value
- 你了解重新调整 HashMap 大小存在什么问题吗?
? ? ? ?要进行重新哈希