目录
Trie树?
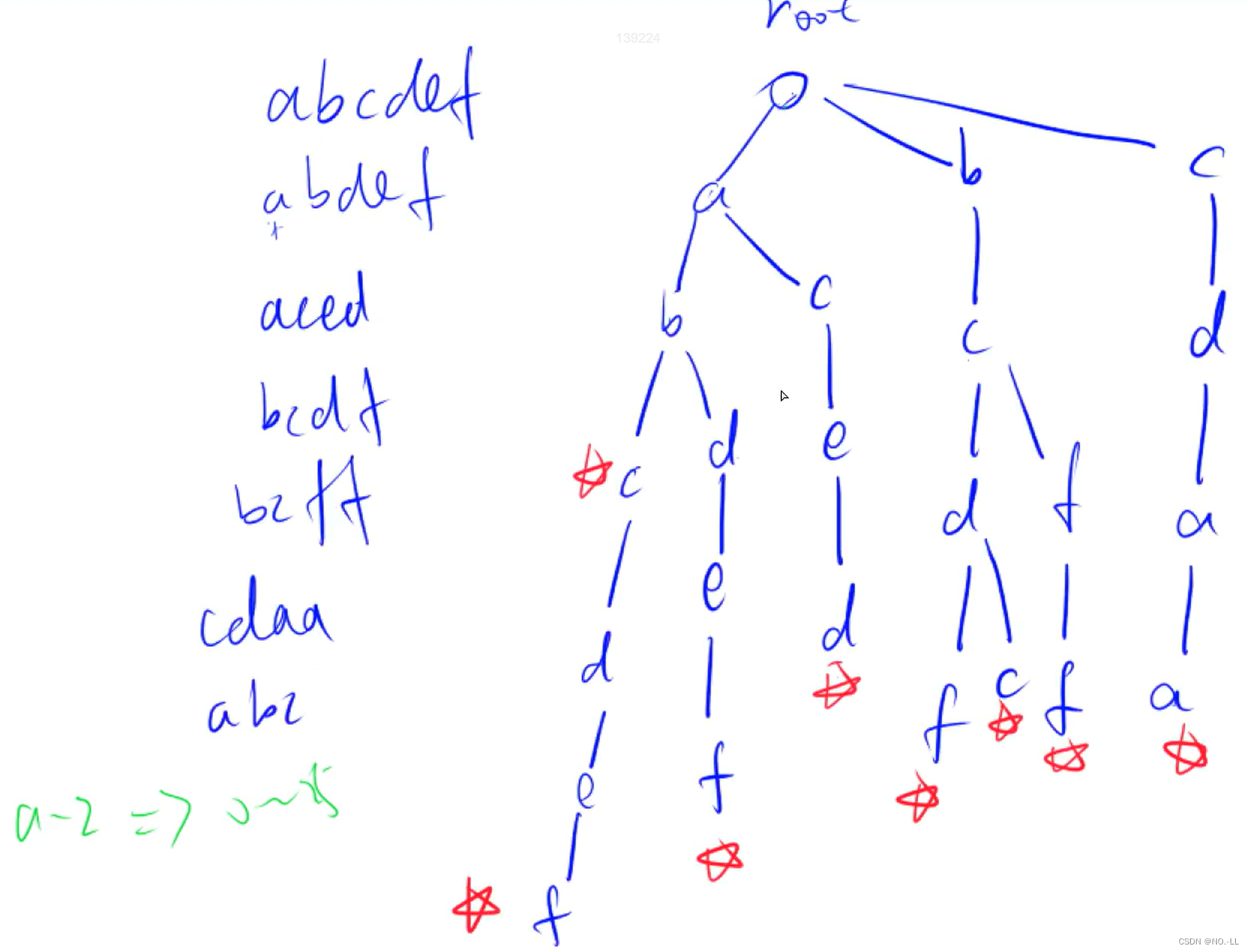
Trie字符串统计

思路:
设 idx索引用于构建树, 结点son[节点位置][节点分支指针],cnt[]记录单词个数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx; //因为只包含小写字母,所以每个节点最多有26个子节点
char str[N];
void insert(char *str)
{
int p = 0; //下标是0的点即是根节点,又是空节点,如son[0][0]为根节点的分支'a'
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ ) //字符串末尾有'\0'
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++ ; //记录这个单词
}
int query(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);
if (*op == 'I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}
最大异或对
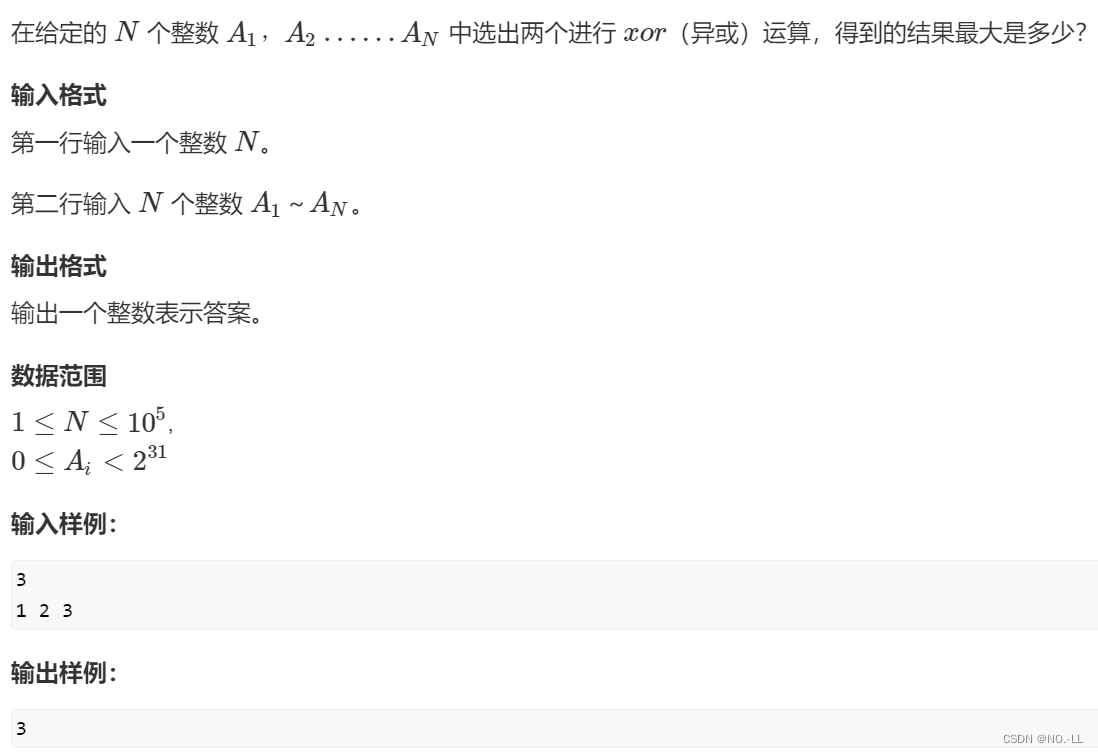
思路:
字典树不单单可以高效存储和查找字符串集合,还可以存储二进制数字:将每个数以二进制方式存入字典树,找的时候从最高位去找有无该位的异.?
?
?
取x的第i位二进制数作为结点
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int const N=100010,M=31*N; //M表示trie树的结点个数,即:31个二进制长度*总数
int n,idx;
int a[N];
int son[M][2]; //因为只需要存二进制1和0,所以2即可
void insert(int x)
{
int p=0;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--)
{
int u=x>>i&1; //取x的第i位二进制数是什么
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u]=++idx;
p=son[p][u];
}
}
int search(int x)
{
int p=0,res=0;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--) //遍历31个二进制位
{
int u=x>>i&1;
if(son[p][!u]) //为了取异或后最大值,如果有不同的就先走
{
p=son[p][!u];
res=res*2+1; //异或相异为1,res整体向前挪一位+1
}
else
{
p=son[p][u];
res=res*2+0; //相同为0
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
insert(a[i]);
}
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
res=max(res,search(a[i]));
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}并查集
合并集合

思路:
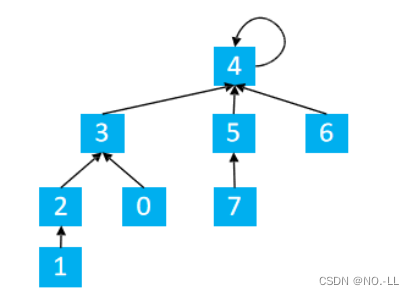
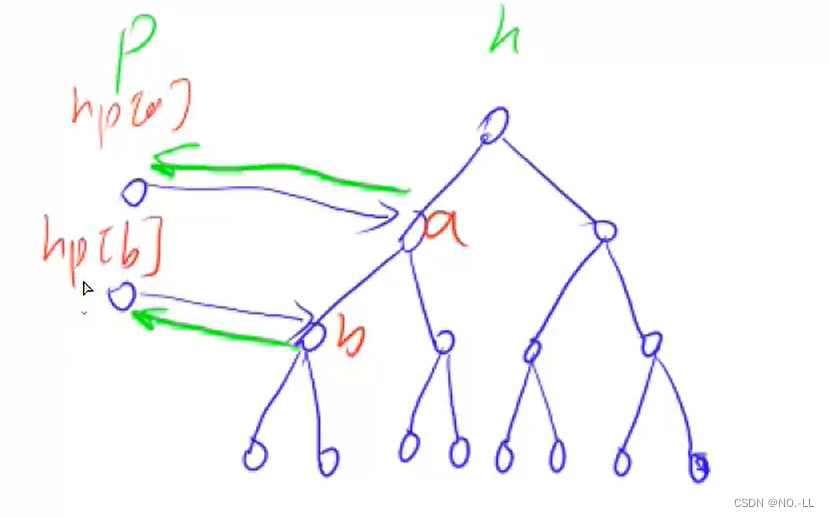
路径压缩具体操作:?
如图
find(1) p[1] = 2 ?p[1] = find(2)
find(2) p[2] = 3 ?p[2] = find(3)
find(3) p[3] = 4 ?p[3] = find(4)
find(4) p[4] = 4 ?将p[4]返回?于是一路回溯;4=p[4]=p[3]=p[2]=p[1];
?

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int p[100010];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
char op;
int a,b;
cin>>op>>a>>b;
if(op=='M') p[find(a)]=find(b); //将a的根插到b的根下,成为b分支
else
{
if(find(a)==find(b))
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
连通块中点的数量

算法 - 并查集详解:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int p[100010],cnt[100010];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
p[i]=i;
cnt[i]=1;
}
while(m--)
{
int a,b;
string s;
cin>>s;
if(s=="C")
{
cin>>a>>b;
a=find(a),b=find(b);
p[a]=b;
if(a!=b) cnt[b]+=cnt[a];
}
else if(s=="Q1")
{
cin>>a>>b;
a=find(a),b=find(b);
if(a==b) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
else
{
cin>>a;
cout<<cnt[find(a)]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}食物链

思路
?
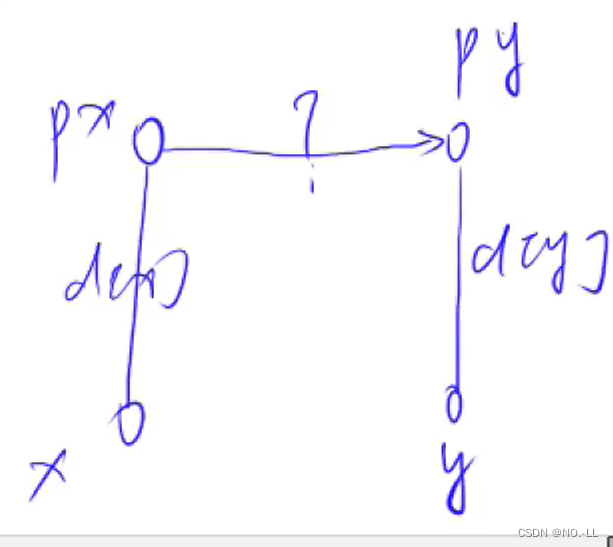
如果不是同一颗树,就把x树插到y树下,成为分支;由前面的合并操作,我们已经算出x到根px的距离d[x],y到根py的距离d[y];那么如何算px到py的距离呢?
我们设距离为 ?;
由于需要满足是同一种类,即最终的x到根距离%3==y到根距离%3
公式为(d[x]+?)%3==(d[y])%3;
简化得? ?=d[y]-d[x];
else if (px != py) //如果是不同的树 { p[px] = py; //把x树插到y树下,成为分支 d[px] = d[y] - d[x]; // }
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50010;
int n, m;
int p[N], d[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
{
int t = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]]; //d[p[x]]就指p[x]到上一个节点的距离,最终d[x]为该节点到宗结点距离
p[x] = t;
}
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i; //有n种动物
int res = 0;
while (m -- )
{
int t, x, y;
scanf("%d%d%d", &t, &x, &y);
if (x > n || y > n) res ++ ; //大于范围,直接假
else
{
int px = find(x), py = find(y); //找x和y的根节点
if (t == 1) //判断同类,顺手记录
{
if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3) res ++ ; //x和y在同一颗树上,
//两个值到根节点的距离%3不同,说明不是同一类
else if (px != py) //如果是不同的树
{
p[px] = py; //把x树插到y树下,成为分支
d[px] = d[y] - d[x]; //根px到根py的距离
}
}
else //判断是否x吃y
{
if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1) % 3) res ++ ;//x和y在同一颗树上,
//x值到根节点的距离没有比y距离多1,说明吃不掉
else if (px != py)
{
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] + 1 - d[x]; //同理
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
堆
?
堆排序

?思路:
1、向上调整算法:
void up(int u)
{
while(u/2&&h[u/2]>h[u])
{
swap(h[u/2],h[u]);
u/=2;
}
}
2、向下调整算法 :
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t)
{
swap(h[u], h[t]);
down(t);
}
}如何手写一个堆?完全二叉树 5个操作
- 插入一个数 ? ? ? ? heap[ ++ size] = x; up(size);
- 求集合中的最小值 ? heap[1]
- 删除最小值 ? ? ? ? heap[1] = heap[size]; size -- ;down(1);
- 删除任意一个元素 ? heap[k] = heap[size]; size -- ;up(k); down(k);
- 修改任意一个元素 ? heap[k] = x; up(k); down(k);
h[i] 表示第i个结点存储的值,i从1开始,2*i是左子节点,2*i + 1是右子节点
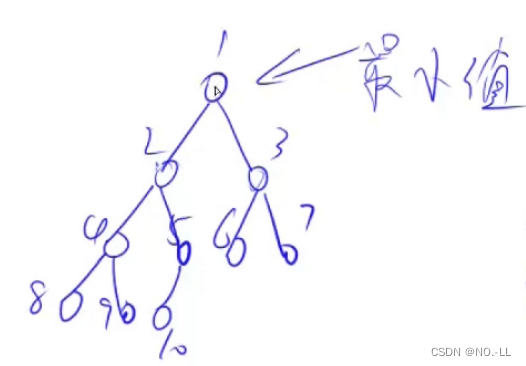
size 既表示堆里存储的元素个数,又表示最后一个结点的下标i为什么从n/2开始down?
????????因为n是最大值,n/2是n的父节点,因为n是最大,所以n/2是最大的有子节点的父节点,所以从n/2往前遍历,就可以把整个数组的父节点遍历一遍
?如图,我们找到最大父节点5,然后向上遍历4321都是父节点,而5就是n/2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int const N = 100010;
int h[N], siz; //堆有两个变量h[N],size; 怎么这里的size和文件里有冲突,只能改成siz了
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;//t存储三个结点中存在的最小的结点的下标,初始化为当前结点u
if (u * 2 <= siz && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2; // 左子节点存在并且小于当前结点,更新t的下标
if (u * 2 + 1 <= siz && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;//右子节点存在并且小于当前结点,更新t的下标
if (t != u)//如果t==u意味着不用变动,u就是三个结点中拥有最小值的结点下标,否则交换数值
{
swap(h[t], h[u]);
down(t); //交换数值后,t这个结点存储原本u的值,u存储存储t的值(三个数中的最小值)。u不用调整了,但t情况不明,可能需要调整。直到它比左右子节点都小
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &h[i]);
siz = n; //初始化size,表示堆里有n 个元素
for (int i = n / 2; i; i --) down(i); //把堆初始化成小根堆,从二叉树的倒数第二行开始,把数字大的下沉
while (m -- )
{
printf("%d ", h[1]);
h[1] = h[siz];
siz --;
down(1);
}
return 0;
}
模拟堆

思路:
操作与堆排序一样,但由于需要插入和删除第k个数,要用额外数组作为指针存储位置,以便快速找到k,于是交换位置的同时也要交换指针
因为需要插入和删除第k个数,所以需要用hp[]记录idx值,然后用ph[]记录hp[]对应的结点?
?
理解hp与ph数组,以及为什么需要它们
- 堆h[i]只能存放数据,不能存放是第几个数字,所以需要ph[k] = i来指明,第k个数字在h[]中对应的i是多少
- 在执行交换操作的时候,可以直接交换数字,swap(h[a],h[b])
- 但是对于ph[k_1] = a和ph[k_2] = b来说,a和b是它们存放的值,不 能通过值来找下标,也就是找不k_1,k_2是多少
- 于是引入hp[a] = k_2,hp[b] = k_2,则可以实现反向的操作
例如:?
h[a] = 10, h[b] = 20 swap: h[a] = 20,h [b] = 10
hp[a] = 1 ,hp[b] = 2 swap:hp[a] = 2 ,hp[b] = 1
ph[1] = a ,ph[2] = b swap:ph[1] = b ,ph[2] = a
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], ph[N], hp[N], cnt;
void heap_swap(int a, int b)
{
swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t)
{
heap_swap(u, t);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u)
{
while (u / 2 && h[u] < h[u / 2])
{
heap_swap(u, u / 2);
u >>= 1;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[5];
int k, x;
scanf("%s", op);
if (!strcmp(op, "I"))
{
scanf("%d", &x);
cnt ++ ;
m ++ ;
ph[m] = cnt, hp[cnt] = m;
h[cnt] = x;
up(cnt);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "PM")) printf("%d\n", h[1]);
else if (!strcmp(op, "DM"))
{
heap_swap(1, cnt);
cnt -- ;
down(1);
}
else if (!strcmp(op, "D"))
{
scanf("%d", &k);
k = ph[k];
heap_swap(k, cnt);
cnt -- ;
up(k);
down(k);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
up(k);
down(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
?哈希表
模拟散列表

拉链法:
//拉链法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100003;//取大于1e5的第一个质数
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;//开一个h槽,邻接表,h[]表示每个链表头节点,e[]表示x值,ne[]下一个节点下标
int n;
void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;//c++中如果是负数,那他取模也是负的,加N再%N就一定是一个正数
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k]; //相当于创建单链表
h[k] = idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for(int i = h[k];i != -1;i = ne[i]) //遍历链表
{
if(e[i] == x) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);//先将槽清空,用-1表示
while(n--)
{
string op;
int x;
cin >> op >> x;
if(op == "I")
{
insert(x);
}
else
{
if(find(x))
{
puts("Yes");
}
else
{
puts("No");
}
}
}
return 0;
}开放选址法
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+9; //开放寻址法一般开 数据范围的 2~3倍, 这样大概率就没有冲突了(我开了10倍)
//开成质数取模时减小冲突概率
const int null=0x3f3f3f3f; //比1e9大的数(在数据范围找不到的数)
int h[N],n;
int find(int x)
{
int t=(x%N+N)%N;
while(h[t]!=null&&h[t]!=x) //如果位置不空并且不是x(不是自己)
{
t++; //就找下一个位置
if(t==N) t=0; //找到最后一个时再从0开找
}
return t; //如果这个位置是空的, 则返回的是他应该存储的位置
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
memset(h,0x3f,sizeof h); //将每个值变为0x3f3f3f3f(以字节赋值 int4字节)
while(n--)
{
string op;
int x;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op=="I")
{
h[find(x)]=x;
}
else
{
if(h[find(x)]==null) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
return 0;
}
字符串哈希

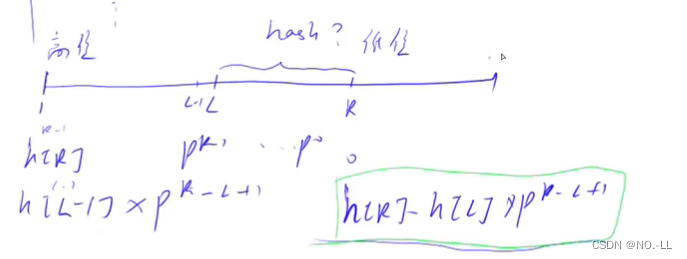
设 h[i]前i个字符的hash值;
?为什么是h[l-1]? 由题意得,在abcdef中2 4为bcde,那么就是h[4]-h[2-1];
为什么是P^(r-l+1)? ?ABCDE 与 ABC 的前三个字符值是一样,只差两位,乘上 P^2 把 ABC 变为 ABC00,再用 ABCDE - ABC00 得到 DE 的哈希值。而P^2==p[3]==p[r-l+1](p从0次幂开始)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N=1e5+10,P=131; //或者P=13331
ull h[N],p[N]; //非常刚好的免去了取模的操作
ull find(int l,int r)
{
return h[r]-h[l-1]*p[r-l+1]; //部分求和
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
string x;
cin>>x;
p[0]=1; //p^0==1
h[0]=0; //hash表从1开始有值,处理边界
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p[i+1]=p[i]*P;
h[i+1]=h[i]*P+x[i]; //前缀和
}
while(m--)
{
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
if(find(l1,r1)==find(l2,r2)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
?