二叉树
(一)二叉树简介
1.线性结构与非线性结构
线性结构:数组、链表、栈、队列
非线性结构:二叉树
2.为什么学习二叉树
前面学习的链表,如果我们需要检索出一个数据,有可能只需要检索一次,就可以找到数据,也有可能检索到最后一个节点才找到数据。这就是链表特性,寻找一条长度为N个节点的链表,搜索次数为1~N-1(头节点无效),二叉树的出现就是为了减少检索时的次数
3.什么是二叉树?
二义树是一种特殊的储存结构,是一种非线性的储存结构。所谓一棵树,都是有一个根节点,这个根节点也是可以用来存储数据的,二叉树结构就是把小于根节点的数据储存到根节点的左边,把大于根节点的数据储存到根节点的右边,这样就实现了检索数据时,例如,根节点是20,根左边是18,根右边是23,当我们需要守我一个数据为23时,就不需要去根节点的左边寻找只需要去根节点的右边寻找即可,所谓:义树搜索,就是不需要比较每一个节点,都可以快速找到日标,其效率要比链表高。
4.二叉树基本概念
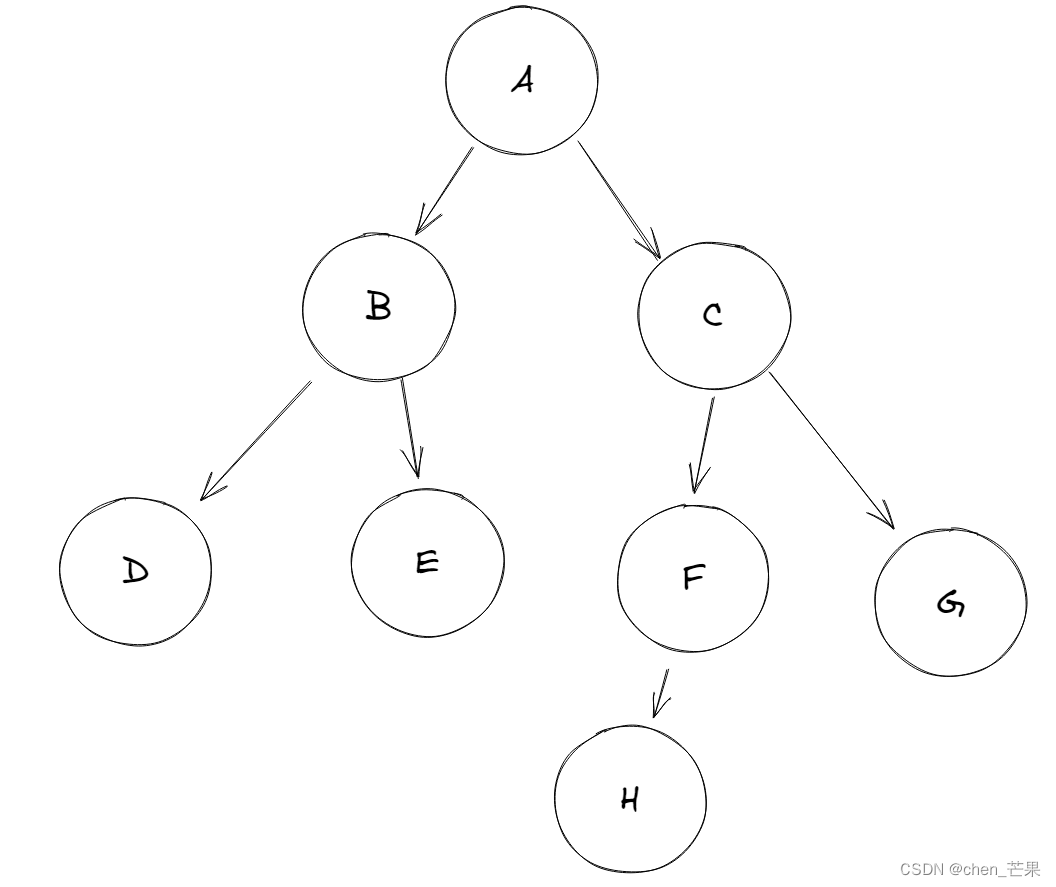
- 双亲和孩子:A是B/C的双亲,B/C是A的孩子
- 兄弟:拥有共同双亲的两个节点称为兄弟,B和C为兄弟 DE为兄弟
- 度:形容一个孩子的个数 A的度是2,C的度是2 ,F的度是1
- 层:A的层是1,B/C的层是2,DEFG的层是3
5.二叉树种类
- 只有一个根节点的二叉
根是一棵树的基本,哪怕只有一个根节点,也可以形成二叉树 - 普通二叉树
树上面任意的一个节点的度都是小于等于2的 - 满二叉树
树上的任意一个节点的度都等于2。假设有一棵树,有N层,其树总结点个数达到2的N次方-1,每层度都为2,那么这棵树称为满二叉树 - 非二叉树
只要树上有任意一个节点,其度大于2,那么这颗树就是非二叉树
6.左节点和右节点
一棵没有任何存储规则的二叉树是没有任何意义的,像上述所说的规则一样,把小于根节点的数据存储在左边,把大于根节点的数据放在右边,如果整棵树都遵循以上原则,就是有存储规律的树,那么左边的节点称为左节点,右边的节点称为右节点。
(二)二叉树模型
每一个节点都需要存储数据,所以都有数据域
每一个节点都需要有指向左节点的指针、每一个节点都需要有指向右节点的指针
//节点设计
struct node{
int data;//数据域
struct node* lchild;//指向左孩子指针
struct node* rchild;//指向右孩子指针
};
3.二叉树增删改查
初始化根节点
struct node* init_new_node(struct node*root,int num)
{
//1.为新节点申请空间
root = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(root ==NULL)
{
printf("malloc new fail!\n");
}
//2.为新节点赋值
root->data = num;
root->lchild = NULL;
root->rchild = NULL;
return root;
}
插入数据
struct node* insert_node(struct node*new,struct node*root)
{
//1.先判断树是否为空
if(root==NULL)
{
return new;//如果这棵树没有根,那么这个新节点就作为根
}
//2.如果树不为空,则寻找正常位置插入数据
if(new->data < root->data)//如果新节点比根节点小
{
root->lchild = insert_node(new,root->lchild);//那么让新节点与我的左孩子节点比较
}
else if(new->data > root->data)
{
root->rchild=insert_node(new,root->rchild);
}
else{
printf("%d node already exists!\n",new->data);
}
return root;
}
在二叉树中搜索节点
struct node* find_node(struct node* root,int num)
{
//1.如果这棵树没有根,那么这个新节点就作为根
if(root==NULL)
{
return NULL;//返回空
}
if(num < root->data)//如果数字小于root,则去root的左节点
{
return find_node(root->lchild,num);
}a
else if(num > root->data)//如果数字大于root,则去root的右节点
{
return find_node(root->rchild,num);
}
else{
return root;
}
}
二叉树删除节点🔥
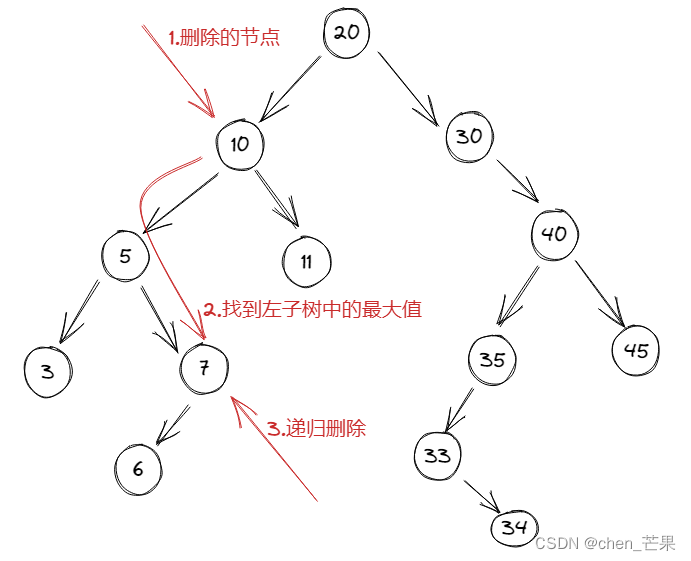
1. 如果需要删除的节点有左子树(不管有没有右子树),其方法是把左子树中最大值节点替换该节点
第一步:通过递归寻找需要删除的节点
第二步:找到这个删除节点的左子树的最大值
第三步:将这个最大值替换掉需要删除的节点
第四步:通过调用删除函数,递归删除最大值(不能直接删,需要递归删除,因为这个节点肯定没右子树,如果有右子树,这个节点肯定不是最大,但是可能存在左子树)。
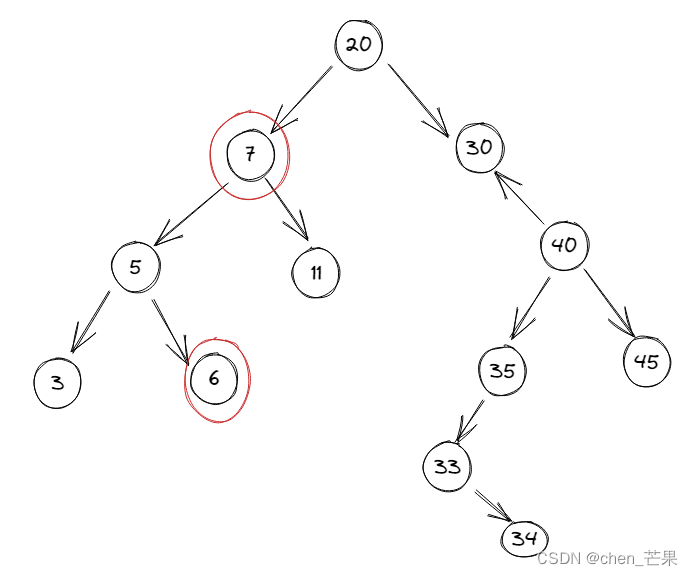
例如要删除10节点时,找到10节点后,寻找10节点左子树的最大值,将找到 的最大值7替换10,然后递归删除最大值7,同理6替换7的位置
删除前二叉树:
删除后二叉树:
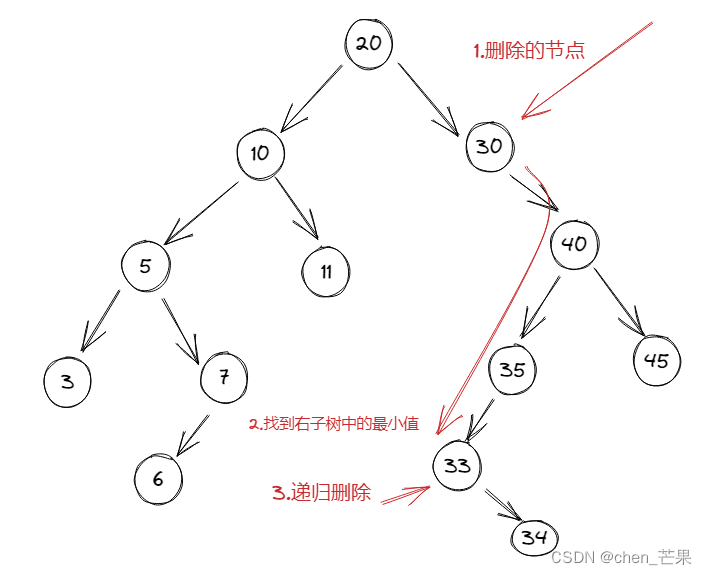
2. 如果需要删除的节点有右子树,,其方法是把右子树中最小值节点替换该节点
第一步:通过递归寻找需要删除的节点
第二步:找到这个删除节点的右子树的最小值
第三步:将这个最小值替换掉需要删除的节点
第四步:通过调用删除函数,递归删除最小值(不能直接删,需要递归删除,因为这个节点肯定没左子树,如果有左子树,这个节点肯定不是最小,但是可能存在右子树)。
例如要删除30节点时,找到30节点后,寻找30节点右子树的最小值,将找到 的最大值33替换30,然后递归删除最大值33,同理34替换33的位置
删除前二叉树:
删除后二叉树:
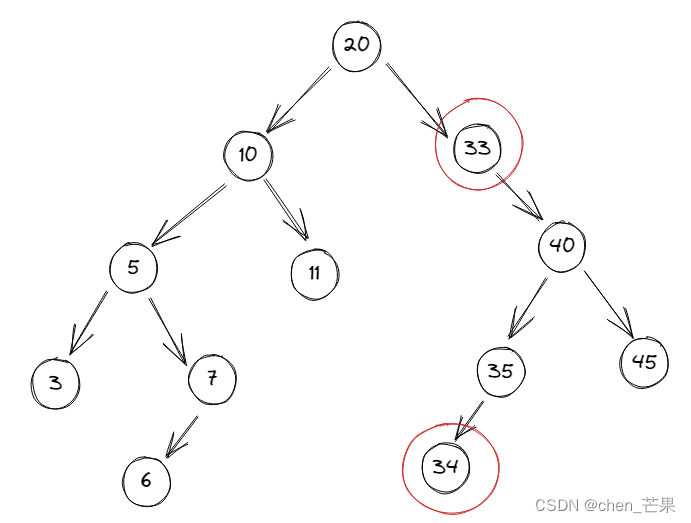
3. 如果需要删除的节点是一个度为0的节点,直接删除即可
第一步:通过递归寻找需要删除的节点
第二步:直接调用free()删除该节点的空间
struct node* delete_node(struct node* root,int num)
{
//1.如果找到底都没有
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//2.寻找需要删除的节点
if(num < root->data)
{
root->lchild = delete_node(root->lchild,num);
}
else if(num > root->data)
{
root->rchild = delete_node(root->rchild,num);
}
else {
//3.判断需要删除的节点有没有左子树
struct node* tmp=NULL;
if(root->lchild!=NULL)//不为空则有左子树
{
//4.寻找左子树中的最大值
for(tmp=root->lchild;tmp->rchild!=NULL;tmp = tmp->rchild);//循环找到最大值,结束循环tmp是最大值节点
//5.将这个最大值替换root
root->data = tmp->data;
//6.递归删除tmp
root->lchild = delete_node(root->lchild,tmp->data);
}else if(root->rchild!=NULL)
{
//4.寻找右子树中的最小值
for(tmp=root->rchild;tmp->lchild!=NULL;tmp = tmp->lchild);//循环找到最小值,结束循环tmp是最小值节点
//5.将这个最小值替换root
root->data = tmp->data;
//6.递归删除tmp
root->rchild = delete_node(root->rchild,tmp->data);
}else
{
free(root);
return NULL;
}
}
return root;
}
遍历二叉树
先序遍历
顺序:根->左->右
void show_node_first(struct node*root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
show_node_first(root->lchild);//左
show_node_first(root->rchild);//右
}
中序遍历
顺序:左->根->右
void show_node_middle(struct node * root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
show_node_middle(root->lchild);//左
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
show_node_middle(root->rchild);//右
}
后序遍历
顺序:左->右->根
void show_node_last(struct node *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
show_node_last(root->lchild);//左
show_node_last(root->rchild);//右
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
}
按层遍历
顺序:按每一层值遍历
设计步骤如下:
1.初始化一条空队
2.根节点入队
3.出队:如果出队失败,则结束程序;如果出队成功,则打印节点
4.打印刚刚出队的节点
5.判断刚刚出队的节点有没有左孩子,如果有则将左孩子入队
6.判断刚刚出队的节点有没有右孩子 ,如果有则右孩子入队
7.重复第三步
//设计一条队列的节点结构体
struct q_node{
int data;
struct q_node *next;
};
//设计队列的管理结构体
struct queue{
struct q_node *head;
struct q_node *tail;
int size;
};
struct queue* init_queue(void)
{
//为队列管理结构体申请空间
struct queue* q = malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
//为管理结构体赋值
q->head =NULL;
q->tail= NULL;
q->size=0;
return q;
}
int in_queue(struct queue*q,int num)
{
//1.为新节点申请空间
struct q_node* new=malloc(sizeof(struct q_node));
if(new==NULL)
{
printf("malloc q_node error!\n");
}
//2.赋值
new->data = num;
new->next=NULL;
if(q->size ==0)
{
q->head=new;
q->tail=new;
}else{
q->tail->next = new;
q->tail = new;
}
q->size++;
return 0;
}
//出队
int out_queue(struct queue*q,int *a)
{
if(q->size ==0)
{
return -1;
}
struct q_node *tmp = q->head;
if(q->size ==1){
q->head =NULL;
q->tail=NULL;
}
else{
q->head = q->head->next;
}
*a = tmp->data;
free(tmp);
q->size--;
return 0;
}
//按层遍历
int show_node_level(struct node*root)
{
if(root ==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//初始化一条空队
struct queue* q = NULL;
q=init_queue();
//将根节点入队
in_queue(q,root->data);
//3.出队,
int a;
struct node*tmp=NULL;
while(1)
{
//3.1 如果出队失败,则结束程序;
if(out_queue(q,&a) == -1){
break;
}
//3.2 如果出队成功,则打印节点
printf("%d\n",a);
//4.在二叉树中找到刚刚出队的那个节点
tmp = find_node(root,a);
//5.判断刚刚出队的节点有没有左孩子,如果有则将左孩子入队
if(tmp->lchild !=NULL)
{
in_queue(q,tmp->lchild->data);
}
if(tmp->rchild !=NULL){//判断刚刚出队的节点有没有右孩子 ,如果有则右孩子入队
in_queue(q,tmp->rchild->data);
}
}
free(q);
return 0;
}
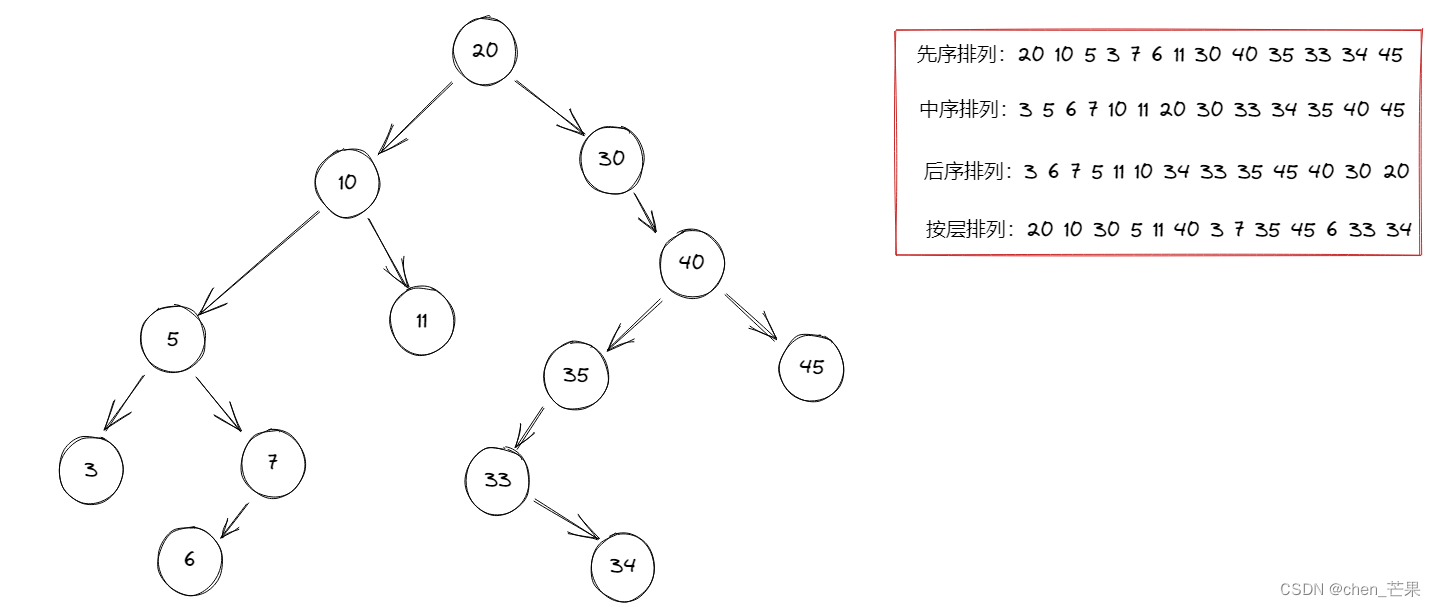
(三)完整main函数
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct node{
int data;
struct node * lchild;
struct node * rchild;
};
//设计一条队列的节点结构体
struct q_node{
int data;
struct q_node *next;
};
//设计队列的管理结构体
struct queue{
struct q_node *head;
struct q_node *tail;
int size;
};
struct node* init_new_node(struct node*root,int num)
{
//1.为新节点申请空间
root = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(root ==NULL)
{
printf("malloc new fail!\n");
}
//2.为新节点赋值
root->data = num;
root->lchild = NULL;
root->rchild = NULL;
return root;
}
struct node* insert_node(struct node*new,struct node*root)
{
//1.先判断树是否为空
if(root==NULL)
{
return new;//如果这棵树没有根,那么这个新节点就作为根
}
//2.如果树不为空,则寻找正常位置插入数据
if(new->data < root->data)//如果新节点比根节点小
{
root->lchild = insert_node(new,root->lchild);//那么让新节点与我的左孩子节点比较
}
else if(new->data > root->data)
{
root->rchild=insert_node(new,root->rchild);
}
else{
printf("%d node already exists!\n",new->data);
}
return root;
}
struct node* find_node(struct node* root,int num)
{
//1.如果这棵树没有根,那么这个新节点就作为根
if(root==NULL)
{
return NULL;//返回空
}
if(num < root->data)//如果数字小于root,则去root的左节点
{
return find_node(root->lchild,num);
}
else if(num > root->data)//如果数字大于root,则去root的右节点
{
return find_node(root->rchild,num);
}
else{
return root;
}
}
struct node* delete_node(struct node* root,int num)
{
//1.如果找到底都没有
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//2.寻找需要删除的节点
if(num < root->data)
{
root->lchild = delete_node(root->lchild,num);
}
else if(num > root->data)
{
root->rchild = delete_node(root->rchild,num);
}
else {
//3.判断需要删除的节点有没有左子树8
struct node* tmp=NULL;
if(root->lchild!=NULL)//不为空则有左子树
{
//4.寻找左子树中的最大值
for(tmp=root->lchild;tmp->rchild!=NULL;tmp = tmp->rchild);//循环找到最大值,结束循环tmp是最大值节点
//5.将这个最大值替换root
root->data = tmp->data;
//6.递归删除tmp
root->lchild = delete_node(root->lchild,tmp->data);
}else if(root->rchild!=NULL)
{
//4.寻找右子树中的最小值
for(tmp=root->rchild;tmp->lchild!=NULL;tmp = tmp->lchild);//循环找到最小值,结束循环tmp是最小值节点
//5.将这个最大值替换root
root->data = tmp->data;
//6.递归删除tmp
root->rchild = delete_node(root->rchild,tmp->data);
}else
{
free(root);
return NULL;
}
}
return root;
}
void show_node_first(struct node*root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
show_node_first(root->lchild);//左
show_node_first(root->rchild);//右
}
void show_node_middle(struct node * root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
show_node_middle(root->lchild);//左
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
show_node_middle(root->rchild);//右
}
void show_node_last(struct node *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
show_node_last(root->lchild);//左
show_node_last(root->rchild);//右
printf("%d\n",root->data); //根节点
}
struct queue* init_queue(void)
{
//为队列管理结构体申请空间
struct queue* q = malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
//为管理结构体赋值
q->head =NULL;
q->tail= NULL;
q->size=0;
return q;
}
int in_queue(struct queue*q,int num)
{
//1.为新节点申请空间
struct q_node* new=malloc(sizeof(struct q_node));
if(new==NULL)
{
printf("malloc q_node error!\n");
}
//2.赋值
new->data = num;
new->next=NULL;
if(q->size ==0)
{
q->head=new;
q->tail=new;
}else{
q->tail->next = new;
q->tail = new;
}
q->size++;
return 0;
}
//出队
int out_queue(struct queue*q,int *a)
{
if(q->size ==0)
{
return -1;
}
struct q_node *tmp = q->head;
if(q->size ==1){
q->head =NULL;
q->tail=NULL;
}
else{
q->head = q->head->next;
}
*a = tmp->data;
free(tmp);
q->size--;
return 0;
}
//按层遍历
int show_node_level(struct node*root)
{
if(root ==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//初始化一条空队
struct queue* q = NULL;
q=init_queue();
//将根节点入队
in_queue(q,root->data);
//3.出队,
int a;
struct node*tmp=NULL;
while(1)
{
//3.1 如果出队失败,则结束程序;
if(out_queue(q,&a) == -1){
break;
}
//3.2 如果出队成功,则打印节点
printf("%d\n",a);
//4.在二叉树中找到刚刚出队的那个节点
tmp = find_node(root,a);
//5.判断刚刚出队的节点有没有左孩子,如果有则将左孩子入队
if(tmp->lchild !=NULL)
{
in_queue(q,tmp->lchild->data);
}
if(tmp->rchild !=NULL){//判断刚刚出队的节点有没有右孩子 ,如果有则右孩子入队
in_queue(q,tmp->rchild->data);
}
}
free(q);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//1.初始化根节点
struct node*root =NULL;
root = init_new_node(root,20);
//2.插入节点到二叉树中
struct node*new1=NULL;
new1 = init_new_node(new1,10);
insert_node(new1,root);
struct node*new2=NULL;
new2 = init_new_node(new2,30);
insert_node(new2,root);
struct node*new3=NULL;
new3 = init_new_node(new3,5);
insert_node(new3,root);
struct node*new4=NULL;
new4 = init_new_node(new4,11);
insert_node(new4,root);
struct node*new5=NULL;
new5 = init_new_node(new5,40);
insert_node(new5,root);
struct node*new6=NULL;
new6 = init_new_node(new6,3);
insert_node(new6,root);
struct node*new7=NULL;
new7 = init_new_node(new7,7);
insert_node(new7,root);
struct node*new8=NULL;
new8 = init_new_node(new8,35);
insert_node(new8,root);
struct node*new9=NULL;
new9 = init_new_node(new9,45);
insert_node(new9,root);
struct node*new10=NULL;
new10 = init_new_node(new10,6);
insert_node(new10,root);
struct node*new11=NULL;
new11 = init_new_node(new11,33);
insert_node(new11,root);
struct node*new12=NULL;
new12 = init_new_node(new12,34);
insert_node(new12,root);
//3.在二叉树中搜索节点
struct node* tmp = find_node(root,33);
if(tmp!=NULL)
{
printf("二叉树寻找的目标:%d\n",tmp->data);
}
else
{
printf("二叉树中没有这个节点\n");
}
printf("==============\n");
//4.删除二叉树节点
/*
printf("delete before root->lchild->data:%d\n",root->lchild->data);
/delete_node(root,10);
printf("delete after root->lchild->data:%d\n",root->lchild->data);
printf("delete beforeroot->rchild->data:%d\n",root->rchild->data);
delete_node(root,30);
printf("delete after root->rchild->data:%d\n",root->rchild->data);
printf("==============\n");
*/
//5.先序遍历:根->左->右
show_node_first(root);
printf("==============\n");
//6.中序遍历
show_node_middle(root);
printf("==============\n");
//7.后序遍历
show_node_last(root);
printf("==============\n");
//8.按层遍历
show_node_level(root);
printf("==============\n");
return 0;
}