目录
单链表
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表
中的指针链接次序实现的 。
????????头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;//数据
struct SListNode* next;//下一个节点
}SLTNode;
void SListPrint(SLTNode** pphead);//打印链表
void SListDestroy(SLTNode** pphead);//释放链表
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//尾插
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);//头删
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);//尾删
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//查找指定的值,返回地址
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);//在 pos 后插入数据
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);//删除 pos 的后一个数据????????源文件
#include"SList.h"
void SListPrint(SLTNode** pphead)//打印链表
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void SListDestroy(SLTNode** pphead)//释放链表
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
SLTNode* del = cur;//保存当前节点
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x)//创建新节点
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(newnode);//判断是否开辟空间失败
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
return newnode;
}
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)//头插
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)//尾插
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
//当链表为空时,新节点即为头节点
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
//当链表不为空,找到最后一个节点
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;
}
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)//头删
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)
return;
SLTNode* del = *pphead;//保存头结点
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;//更改头节点为下一个节点
free(del);//删除头结点
del = NULL;
}
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)//尾删
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
if (cur == NULL)
return;
//当只有一个节点时,直接调用头删
if (cur->next == NULL)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
return;
}
//当有多个节点时,需找倒数第二个节点
while (cur->next->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
SLTNode* del = cur->next;
cur->next = NULL;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)//查找指定的值,返回地址
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)//在 pos 后插入数据
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
SLTNode* next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->next = next;
}
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)//删除 pos 的后一个数据
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == NULL)
return;
//当只有一个节点时,直接调用头删
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
return;
}
//当有多个节点时:
SLTNode* next = pos->next->next;
SLTNode* del = pos->next;
pos->next = next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}相关练习
(1)203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
思路:将头删和非头删分开进行。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
//头删
while (head)
{
if (head->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* del = head;
head = head->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
//非头删
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
//由于要保存上一个节点,所以按照当前节点的下一个节点来寻找 val
if (cur->next && cur->next->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* del = cur->next;
struct ListNode* next = cur->next->next;
cur->next = next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}(2)206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
思路:创将一个空的头结点,依次取出原节点进行头插
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
while (cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//保存下一个节点
//头插
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
//迭代
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}(3)876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
思路:利用快慢指针,快的一次走 2?步,慢的一次走 1?步,当快指针走完时,满指针正好到达中间节点。
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}(4)链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
思路:使用快慢指针,快指针先走 k?步,再让快慢依次向后,当快指针走到 NULL?时,慢指针指向倒数第 k?个节点。
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
if (pListHead == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
while (k && fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
k--;
}
if (k > 0)
return NULL;
while (fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}(5)21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
思路:创建一个新的带头单链表,将给出的两个链表依次向后比较,将较大值放入新链表。
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newhead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail = newhead;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
if (cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
tail->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
tail = tail->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
//将剩余部分进行连接
if (cur1)
{
tail->next = cur1;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
}
struct ListNode* returnValue = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = NULL;
return returnValue;
}思路:创建两个带头单链表,分别存放大于、小于 x?的值,将原链表中的值与 x?进行比较,放入对应链表,最后将两个链表进行连接。
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
ListNode* less, * lesstail, * great, * greattail;
less = lesstail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
great = greattail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode* cur = pHead;
//比较大小
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val < x)
{
lesstail->next = cur;
lesstail = lesstail->next;
}
else
{
greattail->next = cur;
greattail = greattail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//连接两个链表
lesstail->next = great->next;
greattail->next = NULL;
pHead = less->next;
free(less);
free(great);
less = great = NULL;
return pHead;
}
};(7)链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
思路:先找到链表的中间节点,再将中间节点进行逆序,最后和原链表的前半部进行比较。
ListNode* FindMid(ListNode* phead)//找到中间节点
{
ListNode* fast = phead;
ListNode* slow = phead;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* phead)//逆序
{
ListNode* newhead = NULL;
ListNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
class PalindromeList
{
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
ListNode* B = FindMid(A);//找到中间节点
B = reverseList(B);//将中间节点进行逆序
//比较
while (B)
{
if (A->val != B->val)
return false;
A = A->next;
B = B->next;
}
return true;
}
};(8)160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
思路:先计算两个两个链表长度,算出两个链表节点数量的差值,再让较长的链表向后,两个链表同时向后,找到相同节点。
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* ca = headA;
struct ListNode* cb = headB;
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
while (ca->next)
{
ca = ca->next;
a++;
}
while (cb->next)
{
cb = cb->next;
b++;
}
//若最后一个节点不同,说明不存在相交,直接返回
//若最后一个节点相同,说明一定相交,最后一步可直接判断相等
if (ca != cb)
return NULL;
int c = abs(a - b);
ca = headA;
cb = headB;
//让较长链表向后
if (a < b)
{
while (c--)
{
cb = cb->next;
}
}
else
{
while (c--)
{
ca = ca->next;
}
}
while (ca != cb)
{
ca = ca->next;
cb = cb->next;
}
return ca;
}(9)141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
思路:使用快慢指针,快指针一次走 2?步,若存在环路,双指针之间每走一次距离 - 1,最后一定相遇。
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
return true;
}
return false;
}(10)141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
方法一:相交法
思路:以相遇点为准将链表分开,找交点。
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* ca = headA;
struct ListNode* cb = headB;
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
while (ca->next)
{
ca = ca->next;
a++;
}
while (cb->next)
{
cb = cb->next;
b++;
}
//若最后一个节点不同,说明不存在相交,直接返回
//若最后一个节点相同,说明一定相交,最后一步可直接判断相等
if (ca != cb)
return NULL;
int c = abs(a - b);
ca = headA;
cb = headB;
//让较长链表向后
if (a < b)
{
while (c--)
{
cb = cb->next;
}
}
else
{
while (c--)
{
ca = ca->next;
}
}
while (ca != cb)
{
ca = ca->next;
cb = cb->next;
}
return ca;
}
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//找相遇点
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
break;
}
if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
//找相交点
struct ListNode* tmp = fast->next;
fast->next = NULL;//分成两个链表
struct ListNode* start = head;
struct ListNode* meet = tmp;
struct ListNode* intersect = getIntersectionNode(start, meet);
//恢复链表
fast->next = tmp;
return intersect;
}方法二:公式法
思路:找到相遇点,用两个指针分别从起始点与相遇点以相同速度同时向后,即可找到入环点。
证明:
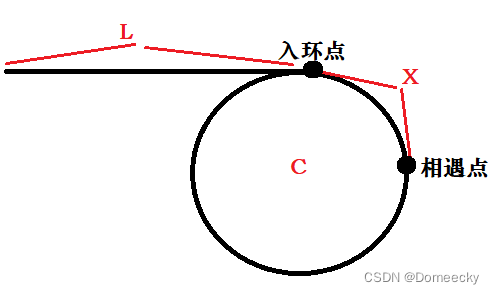
设起点到入环点距离为 L,入环点到相遇点距离为 X,圆的长度为 C。那么?slow?走的距离为 L + X,fast?走的距离为 L + X + N * C(N?为走的圆圈数)。
∵ fast?是?slow?的 2?倍,∴?2(L + X)= L + X + N * C
(L + X)= N * C
L = N * C - X
L = (N - 1)* C + C - X
由此得出:两个指针分别从起始点和相遇点开始走,最终会在入环点相遇。(起始点走 L?的距离可到达入环点,相遇点走「(N - 1)* C + C - X」的距离也可到达入环点)
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//找相遇点
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
break;
}
if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
//找入环点
struct ListNode* a = head;
struct ListNode* b = fast;
slow = head;
while (a != b)
{
a = a->next;
b = b->next;
}
return a;
}