一.前提引入
双向链表也叫双向表,是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null
,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。

按照面向对象的思想,我们需要设计一个类,来描述结点这个事物。由于结点是属于链表的,所以我们把结点类作为链表类的一个内部类来实现。
结点API设计

// 结点内部类
private class Node{
//存储数据
public T item;
//指向下一个节点
public Node next;
//指向上一个节点
public Node pre;
// 构造方法
public Node(T item,Node next,Node pre){
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
this.pre=pre;
}
}?双向链表API设计
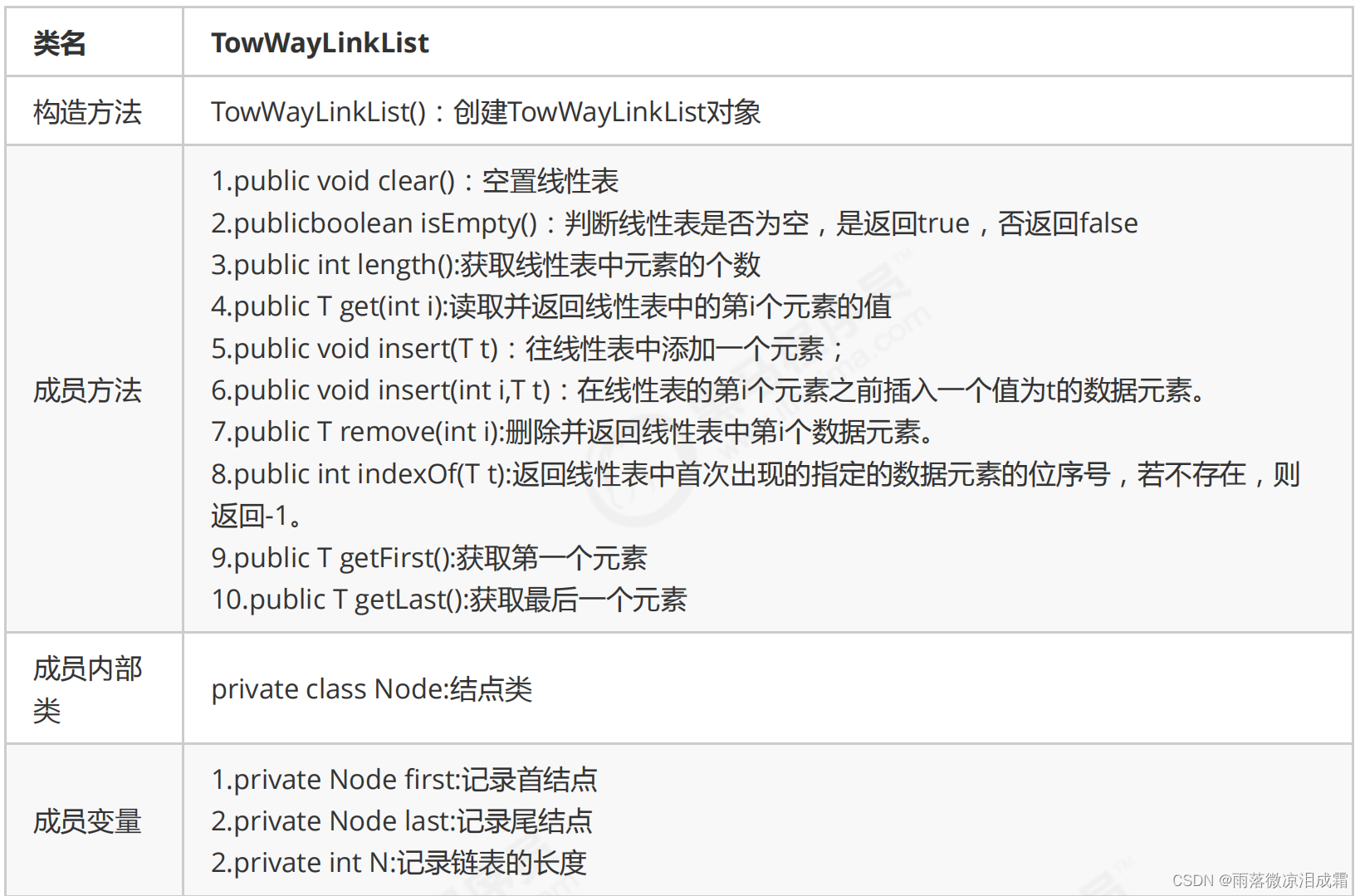
?1.简单API:
//链表结点说明:头节点——>第一个结点——>第二个结点——>第三个结点——>第四个结点——>第五个结点——>....——>尾节点;
//i的值: 0 1 2 3 4
public class TwoWayLinkList<T>{
//头结点
private Node head;
//尾结点
private Node last;
//记录链表的长度
private int N;
// 结点内部类
private class Node{
//存储数据
public T item;
//指向下一个节点
public Node next;
//指向上一个节点
public Node pre;
// 构造方法
public Node(T item,Node pre,Node next){
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
this.pre=pre;
}
}
//构造方法
public TwoWayLinkList(){
//初始化头结点
this.head=new Node(null,null,null);
//初始化尾结点,因为尾结点开始是没有数据的,所以让其==null
this.last=null;
//初始化长度
this.N=0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
//让头结点指向null
this.head.next=null;
//让尾结点指向null
this.last=null;
//让头结点的数据域指向null
this.head.item=null;
//让尾结点的数据域指向null
this.last.item=null;
//让头结点的前驱指向null
this.head.pre=null;
//让尾结点的后继指向null
this.last.next=null;
//让长度为0
this.N=0;
}
//获取链表长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
//获取第一个元素;
public T getFirst(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
//返回头结点的下一个结点的数据域,即第一个元素
return head.next.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素;
public T getLast(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}
//返回尾结点的数据域,即最后一个元素;
return last.item;
}2.较复杂API
?插入元素:
//插入元素t
public void insert(T t) {
//判断链表是否为空;
if (isEmpty()) {
//让头结点的下一个结点指向新结点,及其上一个结点为头结点,而他自己就变成了尾结点,所以他没有洗一个结点;
head.next = new Node(t, head, null);
//新结点变成尾结点
last = head.next;
}else{
//让尾结点的下一个结点指向新结点,而新结点的上一个结点为尾结点,而新结点变成了尾结点;
last.next=new Node(t,last,null);
//新结点变成尾结点
last=last.next;
}
//长度+1
N++;
}在指定位置i处插入元素t:
//在指定位置i处插入元素t
public void insert(int i, T t) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//链表结点说明:头节点——>第一个结点——>第二个结点——>第三个结点——>第四个结点——>第五个结点——>....——>尾节点;
//i的值: 0 1 2 3 4
//找到位置i的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//构建新结点,插入在pre后,curr前
Node newNode = new Node(t, pre, curr);
//让pre的下一个结点指向新结点
curr.pre = newNode;
//让curr的上一个结点指向新结点
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
获取指定位置i处的元素?
//获取指定位置i处的元素
public T get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//找到位置i的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
return curr.item;
}找到元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
Node n = head;
for (int i = 0; n.next != null; i++) {
n = n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}删除i结点,并返回该结点的值;
//删除i结点,并返回该结点的值;
public T remove(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//找到i位置的前一个结点;
Node pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//找到i结点的后一个结点;
Node next = curr.next;
//让i位置前一个结点指向i位置后一个结点;
pre.next=next;
//让i位置的后一个结点指向i位置的前一个结点;
next.pre = pre;
//长度-1
N--;
//返回i结点的值;
return curr.item;
}测试代码:
//测试代码
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建顺序表对象
TwoWayLinkList<String> list = new TwoWayLinkList<>();
//测试插入
list.insert("张三");
list.insert("李四");
list.insert("王五");
list.insert(2,"赵六");
//测试length方法
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println(list.length());
//测试get方法
System.out.println(list.get(2));
System.out.println("------------------------");
//测试remove方法
String remove = list.remove(1);
System.out.println(remove);
System.out.println(list.length());
System.out.println("------------------------");
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("第一个元素是:"+list.getFirst());
System.out.println("最后一个元素是:"+list.getLast());
System.out.println("------------------------");
}注:java中LinkedList集合的底层也是使用双向链表实现,并提供了增删改查等相关方法。
链表的时间复杂度分析:
get(int i):
每一次查询,都需要从链表的头部开始,依次向后查找,随着数据元素
N
的增多,比较的元素越多,时间复杂度为
O(n)
insert(int i,T t):
每一次插入,需要先找到
i
位置的前一个元素,然后完成插入操作,随着数据元素
N
的增多,查找的元素越多,时间复杂度为
O(n)
;
remove(int i):
每一次移除,需要先找到
i
位置的前一个元素,然后完成插入操作,随着数据元素
N
的增多,查找的元素越多,时间复杂度为
O(n)
相比较顺序表,链表插入和删除的时间复杂度虽然一样,但仍然有很大的优势,因为链表的物理地址是不连续的,它不需要预先指定存储空间大小,或者在存储过程中涉及到扩容等操作,,
同时它并没有涉及的元素的交换。
相比较顺序表,链表的查询操作性能会比较低。因此,如果我们的程序中查询操作比较多,建议使用顺序表,增删操作比较多,建议使用链表。
总结:
本文介绍了常见数据结构链表中双向链表的介绍,并用Java对其进行了简单的实现,同时对其进行了时间复杂度的分析和与线性表的比较。下篇文章将介绍单链表反转,快慢指针,循环链表,约瑟夫问题等链表的补充知识。