Easy
创建链表
给定数组,创建链表
- 创建头节点和头指针,然后移动头指针
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self,x=None):
self.val = x
self.next = None
def List2Node(array):
head = ListNode()#创建头结点
p = head #创建头指针
for i in range(0, len(array)):
if not head.val:
head.val = array[i]
else:
p.next = ListNode(array[i])
p = p.next
return head#返回头结点
if __name__ == "__main__":
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
link = List2Node(array)
删除
删除指定节点
请编写一个函数,用于 删除单链表中某个特定节点 。在设计函数时需要注意,你无法访问链表的头节点 head ,只能直接访问 要被删除的节点 。
题目数据保证需要删除的节点 不是末尾节点
- 注意:这道题只告诉我们要删除的节点,并不知道该节点的上一个节点是什么
- 思路:将下一节点的值赋给该节点,删除下一节点
lass Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, node):
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next
删除最靠前的指定值
如果有多个,仅删除最前面的指定值
```python
class Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, head, val):
if head.val == val:
return head.next
pre,p = head, head.next
while p and p.val!=val:
pre = p
p = pre.next
if p:
pre.next = p.next
return head
#### 删除所有指定值

注意:[7777]这样的
- 方法一:头结点处分情况考虑
```python
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
# 头结点可能等于val
if head == None:
return head
while head!= None and head.val == val:
head = head.next
if head==None:
return head
pre = head
while pre.next:
if pre.next.val == val:
pre.next = pre.next.next
else:
pre = pre.next
return head
- 方法二:增加哑变量dummy,下个指向head
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
dummy = ListNode(val-1)
dummy.next = head
pre = dummy
while pre.next:
if pre.next.val == val:
pre.next = pre.next.next
else:
pre = pre.next
return dummy.next
删除链表的中间节点(Medium)


- 思路:快慢指针,快指针移动两个,慢指针移动一个,快指针移完后满指针刚好移到中间。再加个pre用来删除
class Solution(object):
def deleteMiddle(self, head):
if head.next is None:
return None
# 链表从两个元素起
slow, fast, pre = head, head, None
# 保证fast.next不为空
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
pre = slow
slow = slow.next
pre.next = slow.next
return head
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List 删除链表的重复元素(链表已排序)
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
- 注意:小心链表[1,1,1],删除1个1后,pre的位置先不动,看看后面还有没有其他重复值,只有后面的数字不一样,才pre=p进行移动
class Solution(object):
def deleteDuplicates(self, head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head
pre,p = head,head.next
while p:
if pre.val == p.val:
pre.next = p.next
else:
pre = p
p = p.next
return head
删除已排序链表有重复的元素(Medium)
注意:只留下没有重复的数字,例如
输入:head = [1,1,1,2,3]
输出:[2,3]
- 思路:
- 设计哑变量dummy,dummy 下一个点只向head,这样计算我们可能会删掉head点,还是可以返回dummy.head
- 找出有重复值的区间,pre在这个区间前一个节点不动,cur.val==cur.nex.val找重复,期间cur不断往后,直到跳出重复区间,再让pre.next = cur.next
- 巧妙的是,可以用pre.next == cur判断pre和cur之间是否有重复节点,如果没有就移动pre
比如: 1 -> 2 -> 2 -> 2 -> 3,我们用一个 pre 指向 1;当 cur 指向第一个 2 的时候,发现 cur.val == cur.next.val ,所以出现了值重复的节点啊,所以 cur 一直后移到最后一个 2 的时候,发现 cur.val != cur.next.val ,此时 cur.next = 3 ,所以 pre.next = cur.next ,即让1 的 next 节点是 3,就把中间的所有 2 都删除了。
class Solution(object):
def deleteDuplicates(self, head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
pre, cur = dummy, head
while cur:
while cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val:
cur = cur.next
if pre.next == cur:
# pre和cur之间没有重复节点,pre后移
pre = pre.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点

- 方法一(自己):计算链表长度,找到被删除的点
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
if head==None:
return None
def length(head):
n = 0
while head:
n+=1
head = head.next
return n
length = length(head)
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
pre= dummy
# 遍历到前一个节点
for i in range(length-n):
pre = pre.next
pre.next = pre.next.next
return dummy.next
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(进阶:仅遍历一次)
即不能先算出长度,再找点
- 方法:设置两个节点p,q,间距为n
- 首先,p.next=head,q=head
- 接着,q向后移动n个,然后p,q一起向后移动
- 最后,q移动到None的时候,p刚好指向要删去节点的前一个
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
if head==None:
return None
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
p, q = dummy,head
for i in range(n):
q = q.next
while q:
p = p.next
q = q.next
p.next = p.next.next
return dummy.next
反转链表
从尾到头打印链表

class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self,x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def reversePrint(self, head):
queue = []
temp = head
while temp !=None:
queue.append(temp)
temp = temp.next
res= []
for i in range(len(queue)):
res.append(queue.pop().val)
return res
- 注意:pop()是弹出最后一个元素,pop(0)是弹出第一个元素
反转链表 I
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
- 方法一(自己):链表转数组,将数组反转,根据这个数组再生成链表
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
# 链表转数组
def get_list(head):
res = []
p = head
while p:
res.append(p.val)
p = p.next
return res
# 数组转链表
def list_to_node(res):
if len(res)==0:
return None
head = ListNode(res[0])
p = head
for i in range(1,len(res)):
p.next = ListNode(res[i])
p = p.next
return head
res = get_list(head)
res = list(reversed(res))
return list_to_node(res)
- 方法二:利用python的多元赋值
python的多元赋值:右边的值不会随着左边值改变而改变
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head):
p, rev = head, None
while p:
rev, rev.next, p = p, rev, p.next
return rev
- 方法三:调转指向
 cur.nex指向前一个节点,cur再依次往后遍历
cur.nex指向前一个节点,cur再依次往后遍历
public static ListNode reverseListIterative(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null; //前指针节点
ListNode curr = head; //当前指针节点
//每次循环,都将当前节点指向它前面的节点,然后当前节点和前节点后移
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next; //临时节点,暂存当前节点的下一节点,用于后移
curr.next = prev; //将当前节点指向它前面的节点
prev = curr; //前指针后移
curr = nextTemp; //当前指针后移
}
return prev;
}
92. Reverse Linked List II 反转链表 II(Medium)
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。

- 方法一(自己):链表转列表,操作列表,列表转链表
- 注意,列表部分反转
res[left-1:right] = reversed(res[left-1:right])
class Solution(object):
def reverseBetween(self, head, left, right):
# 将链表转为列表
def node2list(head):
res = []
while head:
res.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return res
# 列表生成链表
def list2node(res):
if len(res)==0:
return None
head = ListNode(res[0])
p = head
for i in range(1,len(res)):
p.next = ListNode(res[i])
p = p.next
return head
res = node2list(head)
#列表部分反转
res[left-1:right] = reversed(res[left-1:right])
return list2node(res)
- 方法二,链表指向反转,当前节点指向前一个,当前节点和前节点后移
举例
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
将234部分反转为432
我们需要找到2前面的节点1,也就是这里的begin,然后pre=none,q=2开始,反转链表,结束后。q在5这个节点,pre在4这个点,我们需要把2指向5,然后把1指向4,这时候begin.next其实就是这里的2,所以begin.next.next = q,begin.next = pre
class Solution(object):
def reverseBetween(self, head, left, right):
dummy = ListNode(-100)
dummy.next = head
begin = dummy
# 遍历到left前一个节点
for i in range(left-1):
begin = begin.next
cur = begin.next
pre = None
# 180度反转
for i in range(left,right+1):
next_ = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next_
# 两个边界处理,注意这两行位置不能换
begin.next.next = cur
begin.next = pre
return dummy.next
61. Rotate List 旋转链表(Medium)

- 方法:环形链表
把链表收尾相接变成环形,计算出链表长度n,k=1时,第n- 1个为head,第n-2个为尾巴,k时,n-(k % n)是新链表头节点的索引,n-(k % n)-1 为尾巴
找到尾巴处,新建dummy哑结点,哑结点指向新头结点,即尾巴下一个节点,再令尾巴指向none,返回dummy.next
注意:k可能大于n,这时仅需用k%n代替k即可
class Solution(object):
def rotateRight(self, head, k):
if head==None or head.next == None or k==0:
return head
n = 1
cur = head
# 移到最后一个节点处
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
n += 1
cur.next = head
# 尾巴:n-k%n-1,哑结点指向尾巴下一个,尾巴指向None
for i in range(n-k%n-1):
head = head.next
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head.next
head.next = None
return dummy.next
交换每个相邻链表
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode temp = dummy;
while(temp.next!=null&& temp.next.next!=null){
ListNode pre = temp.next;
ListNode p = temp.next.next;
temp.next = p;
pre.next = p.next;
p.next = pre;
temp = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- Swap迭代
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(newHead.next);
newHead.next = head;
return newHead;
}
}
Easy
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(判断两链表是否交于一点)
 假设链表 A 的头节点到相交点的距离是 a,链表 B 的头节点到相交点的距离是 b,相交点到链表终点的距离为 c。我们使用两个指针,分别指向两个链表的头节点,并以相同的速度前进,若到达链表结尾,则移动到另一条链表的头节点继续前进。按照这种前进方法,两个指针会在a + b + c 次前进后同时到达相交节点。注意:另一个头结点
假设链表 A 的头节点到相交点的距离是 a,链表 B 的头节点到相交点的距离是 b,相交点到链表终点的距离为 c。我们使用两个指针,分别指向两个链表的头节点,并以相同的速度前进,若到达链表结尾,则移动到另一条链表的头节点继续前进。按照这种前进方法,两个指针会在a + b + c 次前进后同时到达相交节点。注意:另一个头结点
比如说:A=[1,2,3,4,5] B=[6,7,4,5],相交节点是4。A到相交节点距离为a=3,B到相交节点距离为b=2,c=2。所以B先走完b+c步,然后B开始从A处走,得走a步到交点,而A走完a+c步后转到B走,再走b步到交点,他们刚好都走了a+b+c步
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
Medium
判断是否是回文链表
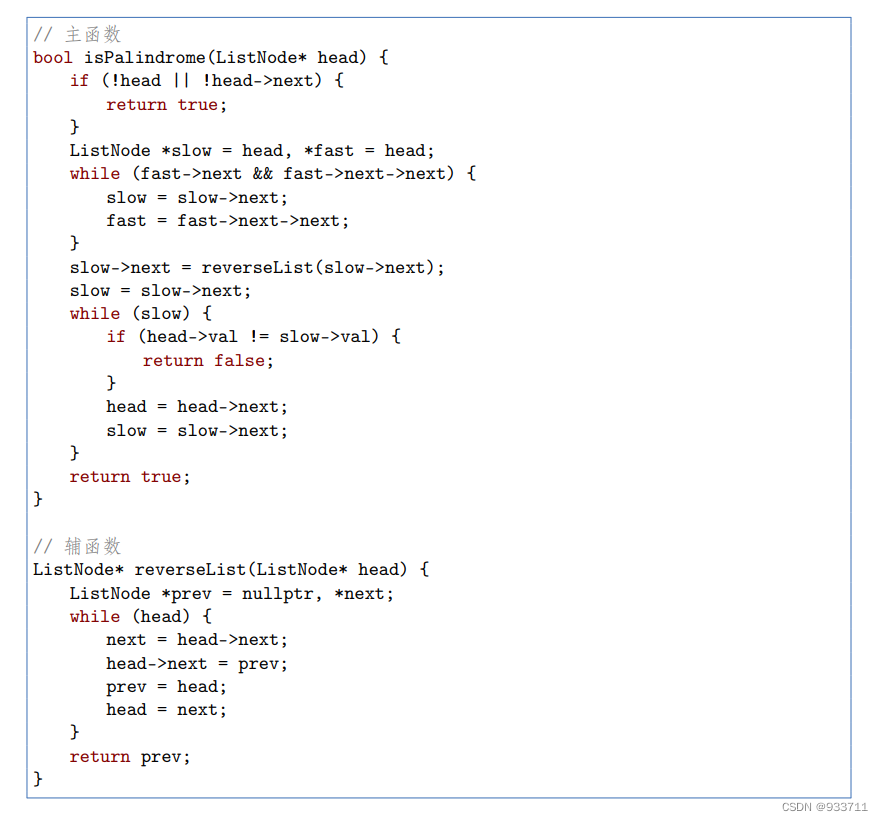
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。PS,回文数组:前后对称
- 方法一:将数组逆序,判断是否相同
-
可以直接
b=list(reversed(a)) -
也可以利用stack栈来实现逆序,利用栈先进后出的性质
-
也可以利用对称,考察前后两半
if len(tempNum)>0:
while i<len(tempNum)/2: #对称的特点
if tempNum[i]!=tempNum[len(tempNum)-1-i]:
print('不是回文')
break
i=i+1 #循环变量自增,差点忘记写
if i>=len(tempNum)/2:
print(tempNum, '是回文')
直接reversed
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, head):
def node2list(head):
res = []
while head:
res.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return res
res = node2list(head)
res_re = list(reversed(res))
return res == res_re
- 题解
先使用快慢指针找到链表中点,再把链表切成两半;然后把后半段翻转;最后比较两半是否相等。
两数相加

-
方法一:数组+字符串
数组转为字符串:str = ''.join(str(x) for x in A) -
方法二:链表对应相加
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
dummy = ListNode(-1)
cur = dummy
carry = 0
# carry为满进值
while l1 or l2:
# 链长较短就补0
x = l1.val if l1!=None else 0
y = l2.val if l2!=None else 0
sum_ = x+y+carry
carry = sum_/10
sum_ = sum_%10
cur.next = ListNode(sum_)
cur = cur.next
l1 = l1.next if l1!=None else None
l2 = l2.next if l2!=None else None
if carry == 1:
cur.next = ListNode(carry)
return dummy.next
两数相加 II

- 方法:栈
计算过程需要从个位数开始算,逆序相加,因此加入栈中,然后注意进位,和之前一样用carry = sum/10, sum =sum%10
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
s1, s2 = [], []
while l1:
s1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
s2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
carry = 0
ans = None
# 注意要加上carry!=0,最后可能需要进位
while s1 or s2 or carry!=0:
a = s1.pop() if s1 else 0
b = s2.pop() if s2 else 0
sum_ = a+b+carry
carry = sum_/10
sum_ = sum_%10
curnode = ListNode(sum_)
curnode.next = ans
ans = curnode
return ans
两两交换链表中的节点


class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
if head == None:
return None
dummy = ListNode(-100)
dummy.next = head
pre, p, next_ = dummy, head, head.next
while next_:
temp = next_.next
next_.next = p
p.next = temp
pre.next = next_
pre = p
p = p.next
next_ = temp.next if temp!= None else None
return dummy.next
- 方法二:递归(还是不会)

class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(next.next);
next.next = head;
return next;
}
}
分隔链表

- 方法:构造两个链表small和large
分别存储原链表中小于x和大于等于x的数,注意记得要把large的最后指向变为None,否则可能指向小于x的一个节点。最后让small的尾结点指向large的头结点。
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, head, x):
if head==None or head.next==None:
return head
small = ListNode(-1)
large = ListNode(-1)
smallHead = small
largeHead = large
# 构造两个链表
while head:
if head.val < x:
small.next = head
small = small.next
else:
large.next = head
large = large.next
head = head.next
large.next = None
small.next = largeHead.next
return smallHead.next
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists(合并两个增序链表)
给定两个增序的链表,试将其合并成一个增序的链表。
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
- 迭代
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prehead = ListNode(-1)
prev = prehead
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
prev.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
prev.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
prev = prev.next
# 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 if l1 is not None else l2
return prehead.next
java版本
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
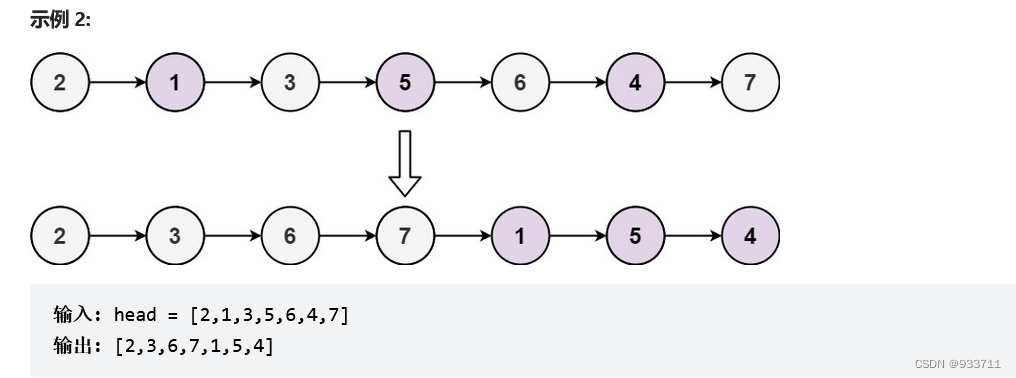
328. Odd Even Linked List(奇偶链表)
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将下标为奇数的放在一起,偶数的放在一起,顺序不变,默认第一个数为奇数。要求时间复杂度O(1),空间复杂度O(N)
- 初步思路
新生成一个链表和一个队列存储偶数的元素,然后奇数遍历结束,就把偶数加进去。
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = head, temp = dummy;
int count = 0;
Deque ll = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
while(p!=null){
count ++;
if(count%2==1){
temp.next = new ListNode(p.val);
temp = temp.next;
}else ll.add(p.val);
p = p.next;
}
while(!ll.isEmpty()){
Integer a = (Integer)ll.pollFirst();
temp.next = new ListNode(a.intValue());
temp = temp.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
但是这样做太复杂了,有没有更简单的呢?
分别建立两个链表,一个奇数链一个偶数链,然后连一起
举例说明:2-1-3-5-6-4-7
奇头odd 指向2,偶头even 指向1,然后odd 指向even后一个即3,odd移动到3,这时候偶even 再指向奇的后一个即5,偶移动到5,以此类推。最后odd在指向偶的第一个evenhead。
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode evenHead = head.next;
ListNode odd = head, even = evenHead;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd.next = even.next;
odd = odd.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}
148. Sort List(链表排序)
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
要求递增,时间复杂度O(n logn) ,空间复杂度O(1)
- 初步想法:链表转为优先队列,再变为链表
但是这个超出内存限制,因此我们不能新建一个优先队列
- 分治法,对每半段排序,然后合并在一起
注意:利用快慢指针找到链表中点后
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 1、递归结束条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 2、找到链表中间节点并断开链表 & 递归下探
ListNode midNode = middleNode(head);
ListNode rightHead = midNode.next;
midNode.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(rightHead);
// 3、当前层业务操作(合并有序链表)
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
找中点
// 找到链表中间节点(876. 链表的中间结点)
private ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
合并两个有序链表
// 合并两个有序链表(21. 合并两个有序链表)
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode sentry = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = sentry;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
curr.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
curr.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return sentry.next;
}