前言
unordered_set&unordered_map的底层是哈希,因此要想模拟实现还得先详细了解下哈希。
1.哈希概念
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较。
顺序查找时间复杂度为 O(N)。
平衡树中为树的高度,即
O
(
l
o
g
2
N
)
O(log_2 N)
O(log2?N),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素的比较次数。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。
如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素。
当向该结构中:
- 插入元素时:
根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放。 - 搜索元素时:
对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,
在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功。
该方式即为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表(Hash Table)(或者称散列表)
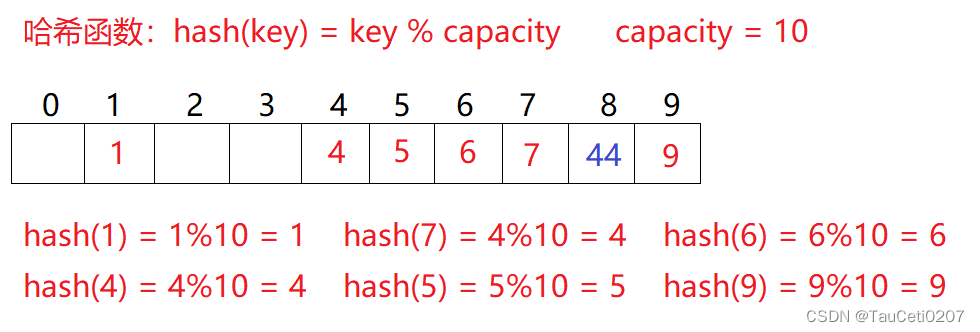
例如:数据集合{1,7,6,4,5,9};
哈希函数设置为:hash(key) = key % capacity; capacity 为存储元素底层空间总的大小。
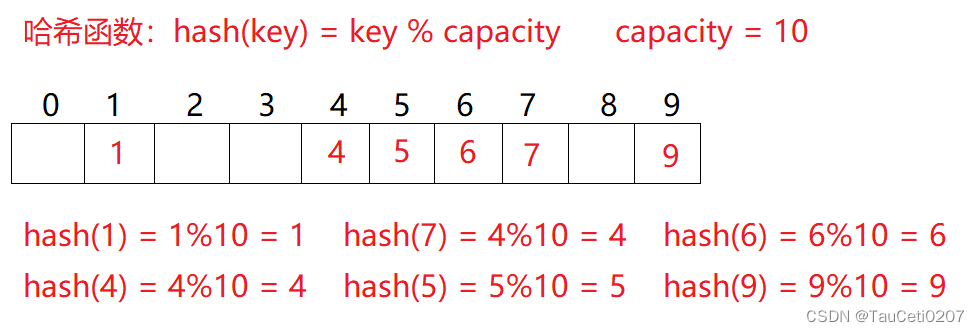
用该方法进行搜索不必进行多次关键码的比较,因此搜索的速度比较快。
简单来说,哈希/散列就是一种映射
存储关键字和存储位置建立关联关系
但是直接建立映射也会存在一些问题:
1、数据范围分布很广、数据不集中怎么办
2、key 的数据不是整数,是 stirng 类型,是自定义类型对象怎么办
2.哈希冲突
对于两个数据元素的关键字
k
i
k_i
ki?和
k
j
k_j
kj?(i != j),有
k
i
k_i
ki? !=
k
j
k_j
kj?,但有:Hash(
k
i
k_i
ki?) == Hash(
k
j
k_j
kj?),即:不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,
该现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞。
把具有不同关键码而具有相同哈希地址的数据元素称为“同义词”。
3.哈希函数
引起哈希冲突的一个原因可能是:哈希函数设计不够合理。
哈希函数设计原则:
- 哈希函数的定义域必须包括需要存储的全部关键码,而如果散列表允许有 m 个地址时,其值域必须在 0 到 m-1 之间。
- 哈希函数计算出来的地址能均匀分布在整个空间中。
- 哈希函数应该比较简单
常见哈希函数:
1、直接定址法 – (常用)
取关键字的某个线性函数为散列地址:Hash(Key)= A * Key + B
优点:简单、均匀
缺点:需要事先知道关键字的分布情况
使用场景:适合查找比较小且连续的情况
2、除留余数法 – (常用)
设散列表中允许的地址数为 m ,取一个不大于 m ,但最接近或者等于 m 的质数 p 作为除数,按照哈希函数:Hash(key) = key% p(p<=m),将关键码转换成哈希地址
通常 p 选择的是容器的大小
3、平方取中法 – (了解)
假设关键字为 1234 ,平方就是 1522756 ,抽取中间的 3 位 227 作为哈希地址;
再比如关键字为 4321 ,平方就是 18671041 ,抽取中间的 3 位 671 (或 710 )作为哈希地址。
平方取中法比较适合:不知道关键字的分布,而位数又不是很大的情况。
4、折叠法 – (了解)
折叠法是将关键字从左到右分割成位数相等的几部分(最后一部分位数可以短些),然后将这几部分叠加求和,并按散列表表长,取后几位作为散列地址。
折叠法适合事先不需要知道关键字的分布,适合关键字位数比较多的情况
5、随机数法 – (了解)
选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值为它的哈希地址,即 H(key) = random(key),其中 random 为随机数函数。
通常应用于关键字长度不等时采用此法
6、数学分析法–(了解)
设有 n 个 d 位数,每一位可能有 r 种不同的符号,这 r 种不同的符号在各位上出现的频率不一定相同,可能在某些位上分布比较均匀,每种符号出现的机会均等,在某些位上分布不均匀只有某几种符号经常出现。可根据散列表的大小,选择其中各种符号分布均匀的若干位作为散列地址。
例如:
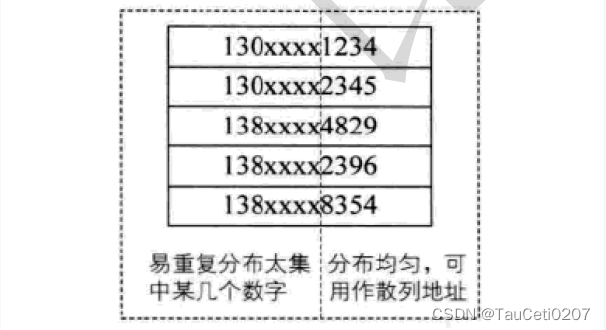
假设要存储某家公司员工登记表,如果用手机号作为关键字,那么极有可能前 7 位都是 相同的,那么我们可以选择后面的四位作为散列地址,如果这样的抽取工作还容易出现 冲突,还可以对抽取出来的数字进行反转(如 1234 改成 4321 )、右环位移
(如 1234 改成 4123 )、左环移位、前两数与后两数叠加(如 1234 改成 12+34=46 )等方法。
数字分析法通常适合处理关键字位数比较大的情况,如果事先知道关键字的分布且关键字的若干位分布较均匀的情况
注意:
哈希函数设计的越精妙,产生哈希冲突的可能性就越低,但是无法避免哈希冲突。
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法是:闭散列和开散列。
4.闭散列
闭散列也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把 key 存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。
可以通过线性探测或二次探测寻找下一个空位置。
线性探测
当要删除闭散列中某个元素时,不能直接物理删除,如果直接物理删除了(置空啥的),会影响查找,找不到真正的值。
比如:
如果删除了 10,再去查找 50,由于 10 在 50 前面,因此会在 10 的位置就停下来,就找不到 50 了。
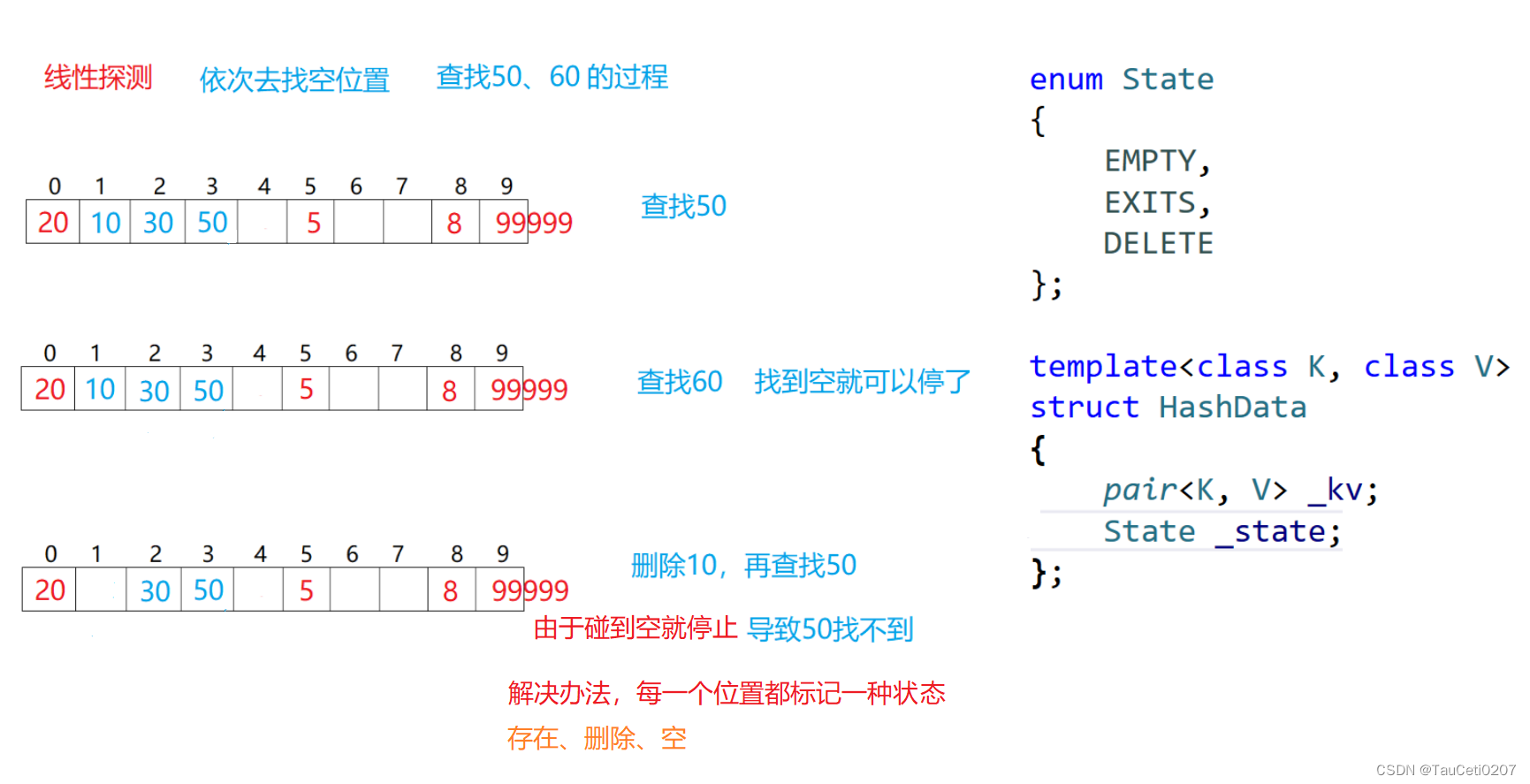
线性探测实现起来比较简单,但其缺点也比较明显。
线性探测缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的冲突连在一起,容易产生数据“堆积”,即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,产生堵塞,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低。
二次探测
线性探测找空位置的方式就是挨着往后逐个去找,而二次探测为了避免线性探测持续拥堵的问题,找下一个空位置的方法为:
H
i
H_i
Hi? = (
H
0
H_0
H0? +
i
2
i^2
i2 ) % m , 或者
H
i
H_i
Hi? = (
H
0
H_0
H0? -
i
2
i^2
i2 ) % m。其中:i = 1,2,3…
H
0
H_0
H0?是通过散列函数 Hash(x) 对元素的关键码 key 进行计算得到的位置,m 是表的大小。
研究表明:
当表的长度为质数且表装载因子 a 不超过 0.5 时,新的表项一定能够插入,而且任何一个位置都不会被探查两次。因此只要表中有一半的空位置,就不会存在表满的问题。在搜索时可以不考虑表装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的装载因子 a 不超过 0.5,如果超出必须考虑增容。
但是这样也就导致闭散列的空间利用率比较低。
insert
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
size_t starti = kv.first;
starti %= _tables.size(); // 这里得用size而不能capacity,因为如果模capacity,
// 结果starti可能超出size的范围,报错。
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXITS) // 等于删除时也得继续遍历
{
hasi = starti + i; // 线性探测,换成i*i就变成二次探测
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size(); // 一直++但不能超出size的界限
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv; // 出来时就表示找到空的位置 EMPTY或者DELETE
_tables[hashi]._state = EXITS;
}
但是如果表已经满了,就会一直循环的去找。
或者表接近满了,会找很久,效率极大降低。
因此提出负载因子的概念:

还要考虑到排除冗余数据。
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first) != nullptr) // 排除冗余值
return false;
// 负载因子>0.7就扩容
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
// 扩容以后 映射关系会发生变化。 比如原来10映射到0,扩容到20个空间后,10应该映射到10
// 因此扩容之后需要重新映射
// 利用现代写法 复用insert然后再swap
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
// 遍历旧表插入newHT
for (auto& e : _tables)
if (e._state == EXITS)
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
newHT._tables.swap(_tables);
}
size_t starti = kv.first;
starti %= _tables.size(); // 这里得用size而不能capacity,因为如果模capacity,
// 结果starti可能超出size的范围,报错。
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXITS) // 等于删除时也得继续遍历
{
hashi = starti + i; // 线性探测,换成i*i就变成二次探测
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size(); // 一直++但不能超出size的界限
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv; // 出来时就表示找到空的位置 EMPTY或者DELETE
_tables[hashi]._state = EXITS;
_n++;
return true;
}
Find&Erase
Find 的时候要考虑空表,查找元素已经被 delete
Erase 之后注意要修改 _n
Data* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) // 空表返回空
return nullptr;
size_t starti = key;
starti %= _tables.size();
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
// 已经delete的值不能去找
if (_tables[hashi]._state != DELETE && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
return &_tables[hashi]; // 找到后返回的是Data*
hashi = starti + i;
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Data* ret = Find(key);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
void TestHT1()
{
int a[] = { 20, 5, 8, 99999, 10, 30, 50 };
//HashTable<int, int, DefaultHash<int>> ht;
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
测试扩容
//ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
//ht.Insert(make_pair(5, 5));
//ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
if (ht.Find(50))
{
cout << "找到了50" << endl;
}
if (ht.Find(10))
{
cout << "找到了10" << endl;
}
ht.Erase(10);
ht.Erase(10);
if (ht.Find(50))
{
cout << "找到了50" << endl;
}
if (ht.Find(10))
{
cout << "找到了10" << endl;
}
//找到了50
//找到了10
//找到了50
}
key 是 sting、自定义对象
如果 key 是 string 时,无法直接强转成整形,也就无法映射了。
借助仿函数完成操作,取 string 第一个字符强转成 size_t 。
但是直接将 string 对象第一个字符强转成无符号整型来映射。
很容易碰到重复的,产生哈希冲突。
比如 “abcd” “aabd” “苹果 1” “苹果 2”
优化一下,将每一个字符都加起来再转换成 size_t
struct StringHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
//return key[0]; // 容易冲突
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash += ch;
return hash;
}
};
但是这样还是有问题的,每个字符加起来的 ascii 码也是有可能相同的,虽然说冲突不可避免,但这种冲突还是尽可能减少比较好。
比如 “abba” “baba” 、“abcd” “aadd” 都会冲突
为此,专门有人研究了 字符串哈希算法
其中,C 语言之父给出的解决方式是:
struct StringHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
//return key[0]; // 容易冲突
/*size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash += ch;
return hash;*/ // 还是会有冲突
// BKDR 的字符串哈希算法
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
return hash;
}
};

这样大体上是解决 key 是字符串的问题,如果是自定义的 Student、Date 等类型,同样去自己写有个 StudentHash、DateHash,利用好唯一标识符,比如学号、身份证号或者拼接多个标识符,比如专业+班级+姓名等等。
// 对应类型配一个仿函数,仿函数对象实现把key对象转换成映射的整数
HashTable<Date, int, DateHash> countHT;
HashTable<Student, int, StudentHash> countHT;
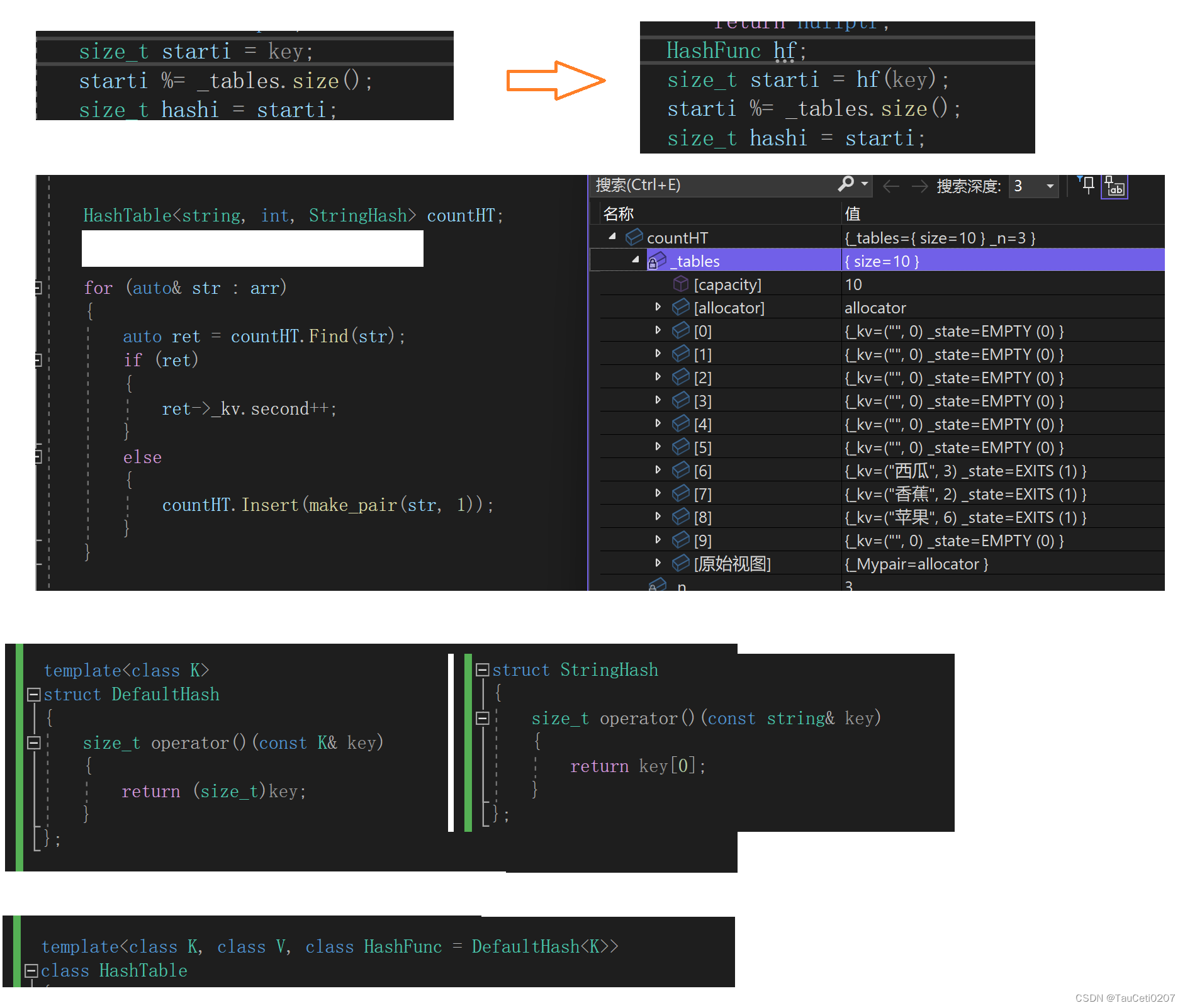
如果不想每次调用还得显性去传相应的 Hash 函数呢?
利用模板特化!针对 string,调用 string 版本的 DefaultHash 。
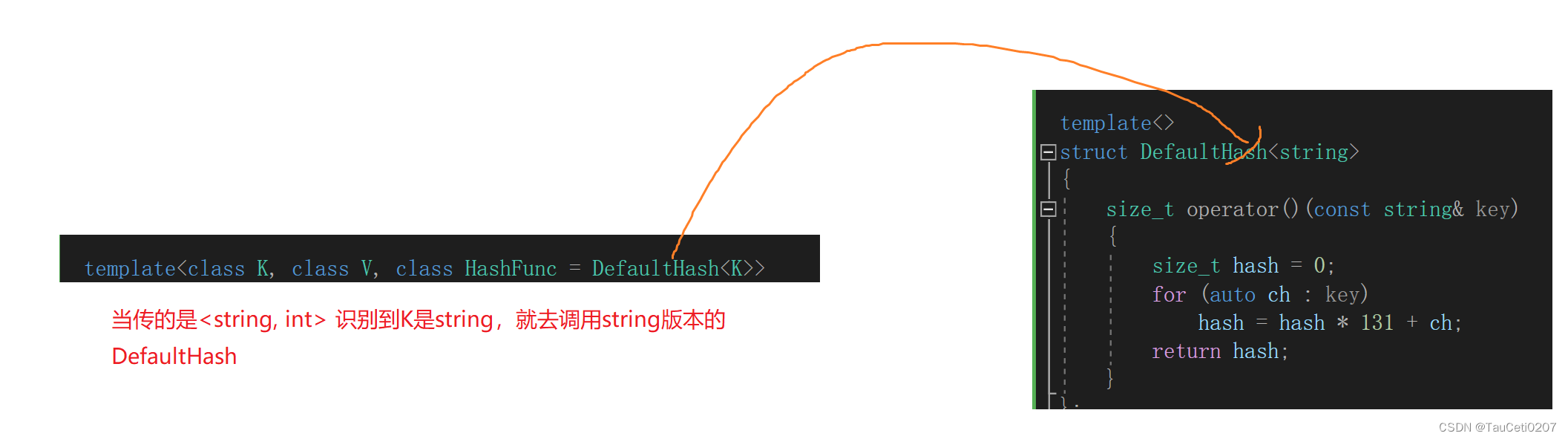
template<class K>
struct DefaultHash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefaultHash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
return hash;
}
};
void TestHT2()
{
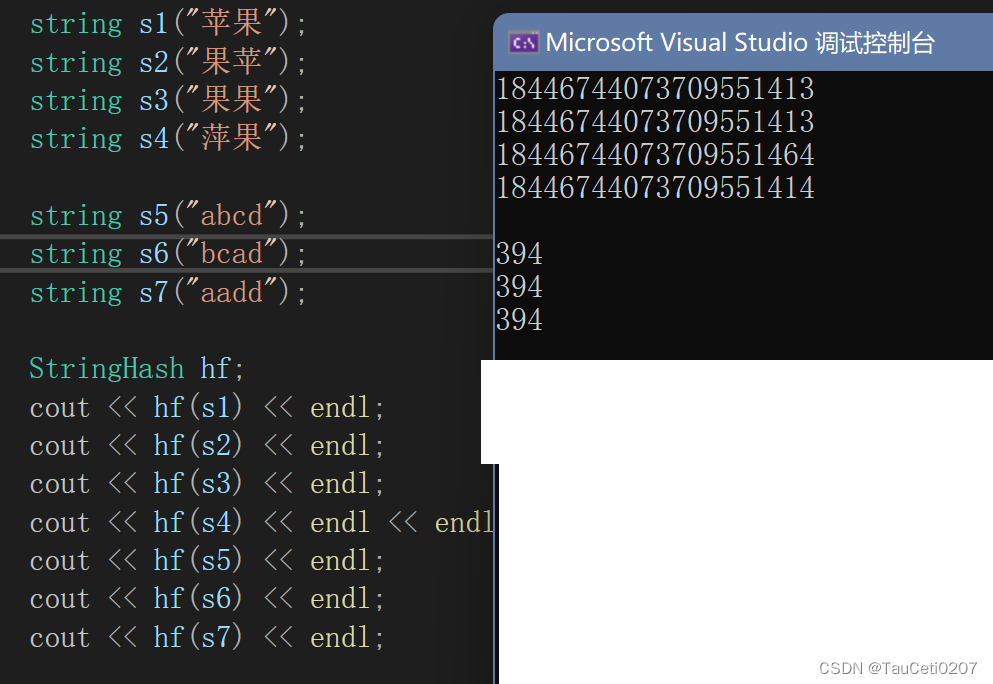
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
string s1("苹果");
string s2("果苹");
string s3("果果");
string s4("萍果");
string s5("abcd");
string s6("bcad");
string s7("aadd");
StringHash hf;
cout << hf(s1) << endl;
cout << hf(s2) << endl;
cout << hf(s3) << endl;
cout << hf(s4) << endl << endl;
cout << hf(s5) << endl;
cout << hf(s6) << endl;
cout << hf(s7) << endl;
//HashTable<string, int, StringHash> countHT;
HashTable<string, int> countHT; // 缺省
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ret = countHT.Find(str);
if (ret)
{
ret->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
// 对应类型配一个仿函数,仿函数对象实现把key对象转换成映射的整数
//HashTable<Date, int, DateHash> countHT;
//HashTable<Student, int, StudentHash> countHT;
//HashTable<string, int> copy(countHT);
}

注意,我们不需要去写 HashTable 的构造、析构、拷贝构造,会自动调用自定义对象的默认成员函数完成相应操作。
源代码
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include<iostream>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
namespace closeHash // 闭散列
{
enum State
{
EMPTY,
EXITS,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class K>
struct DefaultHash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefaultHash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
return hash;
}
};
struct StringHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
//return key[0]; // 容易冲突
/*size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash += ch;
return hash;*/ // 还是会有冲突
// BKDR 的字符串哈希算法
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = DefaultHash<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashData<K, V> Data;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first) != nullptr) // 排除冗余值
return false;
// 负载因子>0.7就扩容
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
// 扩容以后 映射关系会发生变化。 比如原来10映射到0,扩容到20个空间后,10应该映射到10
// 因此扩容之后需要重新映射
// 利用现代写法 复用insert然后再swap
HashTable<K, V, HashFunc> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
// 遍历旧表插入newHT
for (auto& e : _tables)
if (e._state == EXITS)
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
newHT._tables.swap(_tables);
}
HashFunc hf;
size_t starti = hf(kv.first);
starti %= _tables.size(); // 这里得用size而不能capacity,因为如果模capacity,
// 结果starti可能超出size的范围,报错。
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXITS) // 等于删除时也得继续遍历
{
hashi = starti + i; // 线性探测,换成i*i就变成二次探测
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size(); // 一直++但不能超出size的界限
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv; // 出来时就表示找到空的位置 EMPTY或者DELETE
_tables[hashi]._state = EXITS;
_n++;
return true;
}
Data* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) // 空表返回空
return nullptr;
HashFunc hf;
size_t starti = hf(key);
starti %= _tables.size();
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
// 已经delete的值不能去找
if (_tables[hashi]._state != DELETE && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
return &_tables[hashi]; // 找到后返回的是Data*
hashi = starti + i;
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Data* ret = Find(key);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
private:
// 注意,hashTable不需要我们自己写构造、析构、拷贝构造,它会去调用vector自己的完成相应操作
vector<Data> _tables;
size_t _n = 0; // 存储的有效关键字个数 给了缺省参数就不需要再写个默认构造了
};
void TestHT1()
{
int a[] = { 20, 5, 8, 99999, 10, 30, 50 };
//HashTable<int, int, DefaultHash<int>> ht;
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
测试扩容
//ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
//ht.Insert(make_pair(5, 5));
//ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
if (ht.Find(50))
{
cout << "找到了50" << endl;
}
if (ht.Find(10))
{
cout << "找到了10" << endl;
}
ht.Erase(10);
ht.Erase(10);
if (ht.Find(50))
{
cout << "找到了50" << endl;
}
if (ht.Find(10))
{
cout << "找到了10" << endl;
}
//找到了50
//找到了10
//找到了50
}
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
string s1("苹果");
string s2("果苹");
string s3("果果");
string s4("萍果");
string s5("abcd");
string s6("bcad");
string s7("aadd");
StringHash hf;
cout << hf(s1) << endl;
cout << hf(s2) << endl;
cout << hf(s3) << endl;
cout << hf(s4) << endl << endl;
cout << hf(s5) << endl;
cout << hf(s6) << endl;
cout << hf(s7) << endl;
//HashTable<string, int, StringHash> countHT;
HashTable<string, int> countHT; // 缺省
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ret = countHT.Find(str);
if (ret)
{
ret->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
// 对应类型配一个仿函数,仿函数对象实现把key对象转换成映射的整数
//HashTable<Date, int, DateHash> countHT;
//HashTable<Student, int, StudentHash> countHT;
HashTable<string, int> copy(countHT); // 完成的是深拷贝,借助vector的深拷贝完成
}
}
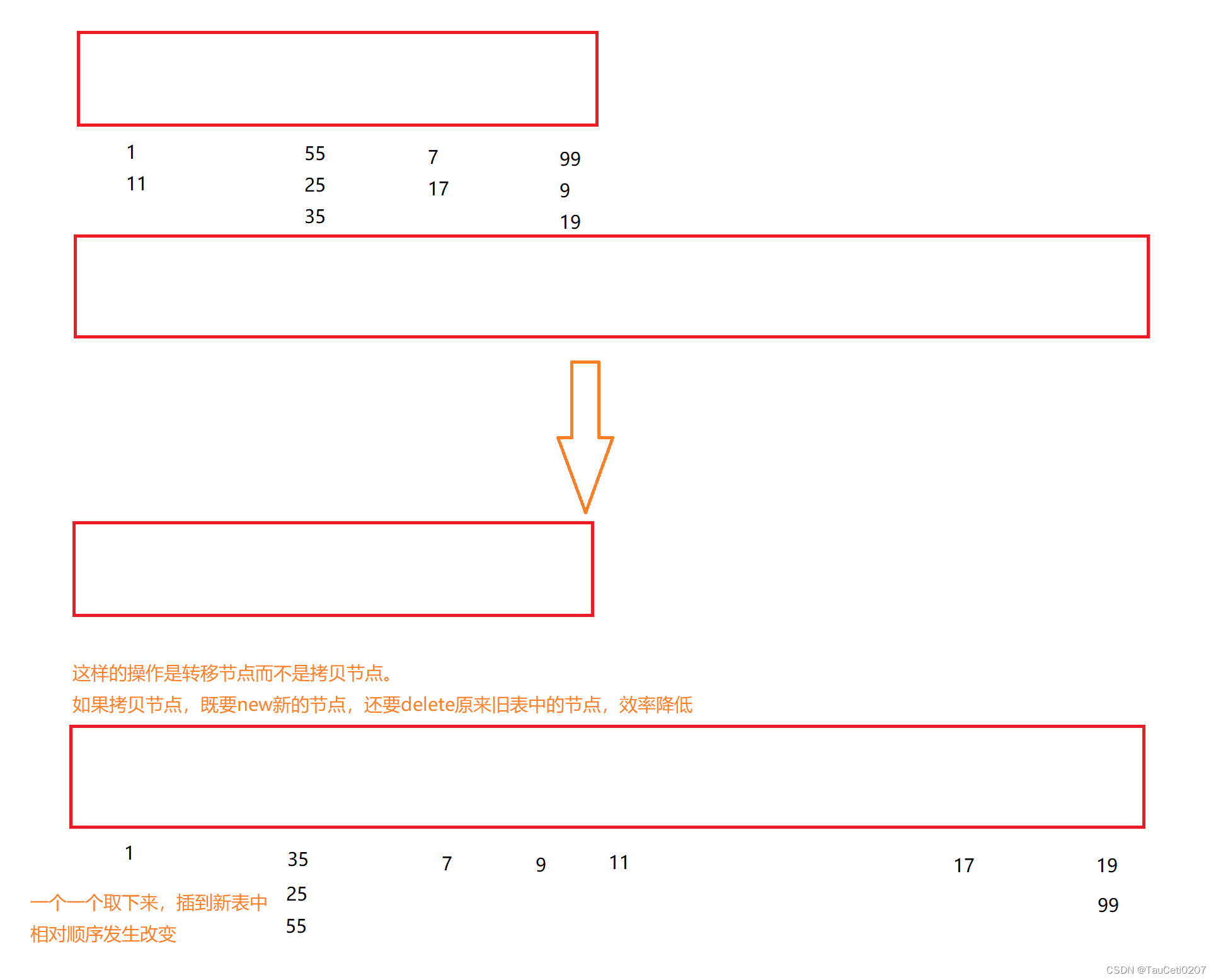
5.开散列
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
其实就是哈希桶。
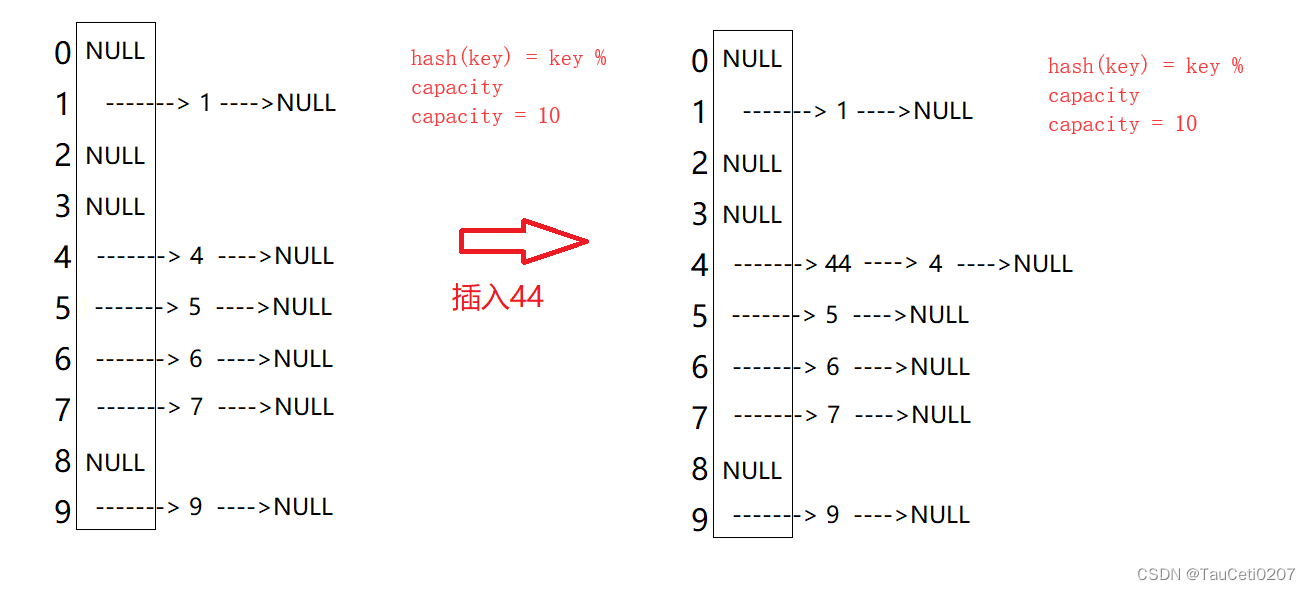
开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素。
insert
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first)) // Eliminate redundant
return false;
// load factor == 1,expand capacity.
// that is,one node per bucket on average
/*if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize, nullptr);
// traverse old table,insert into new table
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
newHT.Insert(cur->_kv);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
// contemporary writing method
newHT._tables.swap(_tables); // swap the vector
}*/
// above implement of expand capacity is copy nodes,
// New nodes are created and old nodes are deleted --> decrease efficiency
if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur) // head-insert
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newSize;
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next; // update cur
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
newTables.swap(_tables);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first;
hashi %= _tables.size();
// head-insert to the bucket counterpart
Node* newNode = new Node(kv);
newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newNode;
++_n; // increase size
return true;
}
erase
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return false;
size_t hashi = key;
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
// prev cur cur->next
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
如果不让用 prev 如何 delete 呢?
这是单链表,可以用替换法删除。
也就是下一个节点的值赋给 cur,然后删除 cur。
拷贝构造
由于 vector 中的数据是 Node*,内置类型,因此析构的时候需要手动释放,拷贝构造的时候也需要手动完成一个节点一个节点完成深拷贝。
HashTable(const HashTable<K, V, HashFunc>& ht)
{
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->_kv);
tmp->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = tmp;
_n++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
源代码
namespace HashBucket
{
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K>
struct DefaultHash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefaultHash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = DefaultHash<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
// vector free itself,but the node in the vector need free mannually
// these nodes are pointer , built-in type
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
// delete every bucket
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
HashTable()
:_tables(0, nullptr)
, _n(0)
{}
HashTable(const HashTable<K, V, HashFunc>& ht)
{
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->_kv);
tmp->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = tmp;
_n++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
HashTable<K, V, HashFunc> operator=(HashTable<K, V, HashFunc> ht)
{
if (this != &ht)
{
swap(_tables, ht._tables);
swap(_n, ht._n);
}
return *this;
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first)) // Eliminate redundant
return false;
// load factor == 1,expand capacity.
// that is,one node per bucket on average
/*if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize, nullptr);
// traverse old table,insert into new table
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
newHT.Insert(cur->_kv);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
// contemporary writing method
newHT._tables.swap(_tables); // swap the vector
}*/
// above implement of expand capacity is copy nodes,
// New nodes are created and old nodes are deleted --> decrease efficiency
HashFunc hf;
if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur) // head-insert
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newSize;
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next; // update cur
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
newTables.swap(_tables);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first);
hashi %= _tables.size();
// head-insert to the bucket counterpart
Node* newNode = new Node(kv);
newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newNode;
++_n; // increase size
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
// size_t hashi = HashFunc()(key); // anonymous object
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return false;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
// prev cur cur->next
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
void TestHashBucket1()
{
int a[] = { 20, 5, 8, 99999, 10, 30, 50 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
if (ht.Find(10))
{
cout << "找到了10" << endl;
}
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
// test expand capacity
ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
ht.Insert(make_pair(5, 5));
ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
ht.Insert(make_pair(25, 15));
ht.Insert(make_pair(35, 15));
ht.Insert(make_pair(45, 15));
}
void TestHashBucket2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable<string, int, StringHash> countHT;
HashTable<string, int> countHT; // 缺省
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ret = countHT.Find(str);
if (ret)
{
ret->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
// 对应类型配一个仿函数,仿函数对象实现把key对象转换成映射的整数
//HashTable<Date, int, DateHash> countHT;
//HashTable<Student, int, StudentHash> countHT;
// 需要手动实现深拷贝
HashTable<string, int> copy(countHT);
HashTable<string, int> copy2;
copy2.Insert(make_pair("abcd", 1234));
copy2.Insert(make_pair("acd", 1234));
copy2.Insert(make_pair("cd", 1234));
copy2 = copy; // 赋值重载必须得是已经有的对象才能叫赋值重载
}
}
尾声
🌹🌹🌹
写文不易,如果有帮助烦请点个赞~ 👍👍👍
Thanks?(・ω・)ノ🌹🌹🌹
😘😘😘
👀👀由于笔者水平有限,在今后的博文中难免会出现错误之处,本人非常希望您如果发现错误,恳请留言批评斧正,希望和大家一起学习,一起进步ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ,期待您的留言评论。
附GitHub仓库链接