目录
Ⅳ、void add(int pos,int data):在pos位置新增元素
Ⅴ、boolean checkPosIndex():判断查找的位置是否合法
Ⅵ 、boolean isFull():判断当前数组是不是满的
Ⅶ、boolean contain(int tofind):判断顺序表是否包含指定元素
Ⅸ、boolean checkPosInGet(int pos):判断指定位置是否合法
ⅠⅠ、set(int pos,int value):将pos位置元素跟新为value
ⅠⅡ、remove(int key):删除第一次出现的元素key
ⅠⅢ、boolean isEmpty():判断顺序表是否为空
Ⅳ、boolean addIndex(int Index,int data):指定位置插入,第一个有效元素的下标为0
Ⅴ、void checkIndexAdd(int index):检查index位置是否合法
Ⅵ、ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index):返回index-1的节点
Ⅶ、boolean contains(int key):判断链表是否包含key元素
Ⅷ、void remove(int key):删除第一次出现key的节点
Ⅸ、void removeAll(int key):删除所有key的节点
前言
本章节是在IntelliJ IDEA集成开发环境测试的结果,内容多适用于学习Java方向数据结构的学者
一、顺序表(ArrayList<>)
读前须知
本章中会用到两个自定义异常:
MyArrayListEmptyException:顺序表为空异常
MyArrayListIndexOutOfException:指定位置超出顺序表有效范围
?Ⅰ、数据域:存放方式
?顺序表的底层其实就是一个数组(泛型),另外还有一个记录数组有效长度的标记。
排除数组长度不够,和标记大小太小的因素就是以下基本结构。另外加了一些初始常量,表示数组的初始大小。这里就使用int来代替泛型的思想,我们只需要知道内部结构是怎么样子的就行了。
泛型通道————<泛型>
int[]? elem;
//顺序表的有效长度
int useSize?;
//表示数组初始化的默认容量
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10
Ⅱ、ArrayList():构造方法
?使用默认容量初始化数据域
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}Ⅲ、void add():添加元素,默认在最后添加
public void add(int data) {
//1、判断是否是满的,如果满的,那么进行扩容
if (isFull()) {
//扩容
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);
}
//2、不满进行插入
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}Ⅳ、void add(int pos,int data):在pos位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) throws MyArrayListIndexOutOfException{
//判断下标是否是合法的
if (!checkPosInAdd(pos)) {
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfException("添加方法的pos不合理!");
}
//判断是否是满的
if (isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);
}
//挪数据
for (int i = this.usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i];
}
//挪完了数据
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}Ⅴ、boolean checkPosIndex():判断查找的位置是否合法
private boolean checkPosInAdd(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return false;
}
return true;//合法
}Ⅵ 、boolean isFull():判断当前数组是不是满的
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
Ⅶ、boolean contain(int tofind):判断顺序表是否包含指定元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Ⅷ、int indexOf():查找指定元素的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
Ⅸ、boolean checkPosInGet(int pos):判断指定位置是否合法
private boolean checkPosInGet(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return false;
}
return true;//合法
}Ⅹ 、int get(int pos):获取指定位置的元素
public int get(int pos) throws MyArrayListIndexOutOfException,MyArrayListEmptyException{
if (!checkPosInGet(pos)) {
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfException("获取pos下标时,位置不合法");
}
//不用写判断空不空 没有问题的
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new MyArrayListEmptyException("获取元素的时候,顺序表为空!");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}ⅠⅠ、set(int pos,int value):将pos位置元素跟新为value
public void set(int pos, int value) throws MyArrayListIndexOutOfException,MyArrayListEmptyException{
if (!checkPosInGet(pos)) {
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfException("更新pos下标的元素,位置不合法");
}
//如果合法 ,那么其实不用判断顺序表为空的状态了
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new MyArrayListEmptyException("顺序表为空!");
}
//顺序表为满的情况也可以更新
this.elem[pos] = value;
}ⅠⅡ、remove(int key):删除第一次出现的元素key
public void remove(int key) throws MyArrayListEmptyException{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new MyArrayListEmptyException("顺序表为空,不能删除!");
}
int index = indexOf(key);
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("不存在你要删除的数据");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i + 1];
}
//删除完成
this.usedSize--;
// this.elem[usedSize] = null; 如果是引用类型 这里需要置为空
}ⅠⅢ、boolean isEmpty():判断顺序表是否为空
private boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}ⅠⅣ、int size():返回顺序表的长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}ⅠⅤ、void clear():清空顺序表
public void clear() {
/*
如果是引用数据类型 得一个一个置为空 这样做才是最合适的
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
this.elem[i] = null;
}
this.usedSize = 0;
*/
this.usedSize = 0;
}ⅠⅥ、void display():打印顺序表
public void display() {
//usedSize==0
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}?二、链表(LinkedList<>)
读前须知
本章使用了一个自定义类ListNode,用来表示节点。
与一个自定义异常MyListIndexOutOfException,表示指定位置index超出链表范围。异常不做介绍
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
//指定数据域的构造方法
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}Ⅰ、链表的概念
链表的类型其实有8种:比如带头单向循环链表,以下组合总共8种
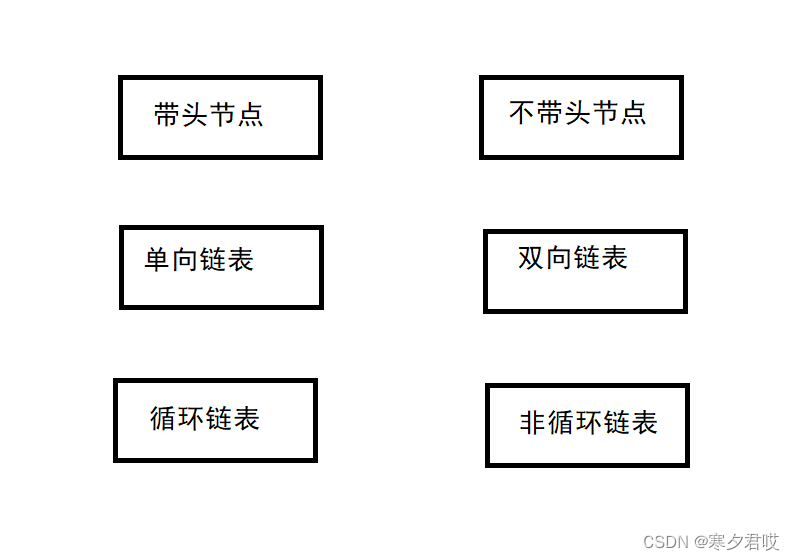
?
注:linkedList的底层是带头双向链表,双向链表就是加了一个前驱引用。
?虽然有这么多种类,但是原理都是相通的,这里我们主要介绍单向不带头非循环链表。
单向不带头非循环链表结构如下

?我们把一整个方框叫做一个节点,每个节点有具体的数据域与指向下一个节点的引用,且链表可以使用泛型来确定数据域的类型,下我们使用Int来代替泛型。
Ⅱ、void addFirst(int val):头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}Ⅲ、void addLast(int val):尾插法
public void addLast(int val){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//运行到这里时cur.next == null;
cur.next = node;
}
}Ⅳ、boolean addIndex(int Index,int data):指定位置插入,第一个有效元素的下标为0
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws MyListIndexOutOfException{
checkIndexAdd(index);
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = findIndexSubOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}Ⅴ、void checkIndexAdd(int index):检查index位置是否合法
private void checkIndexAdd(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new MyListIndexOutOfException("任意位置插入的时候,index不合法!");
}
}Ⅵ、ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index):返回index-1的节点
private ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index-1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
Ⅶ、boolean contains(int key):判断链表是否包含key元素
public boolean contains(int key) {
//head == null
ListNode cur = this.head;
//cur != null 说明 没有遍历完 链表
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}Ⅷ、void remove(int key):删除第一次出现key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("此时链表为空,不能进行删除!");
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
//判断 第一个节点是不是等于我要删除的节点
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
//进行删除了
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}Ⅸ、void removeAll(int key):删除所有key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
ListNode prev = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//单独处理了头节点
if(this.head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}Ⅹ、int size():返回数据元素个数
public int size(){
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}ⅠⅠ、void display():打印链表
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}ⅠⅡ、void clear():清空链表
public void clear(){
//this.head = null;//这种做法 比较粗暴!不建议使用
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode curNext = null;
while (cur != null) {
curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}