目录
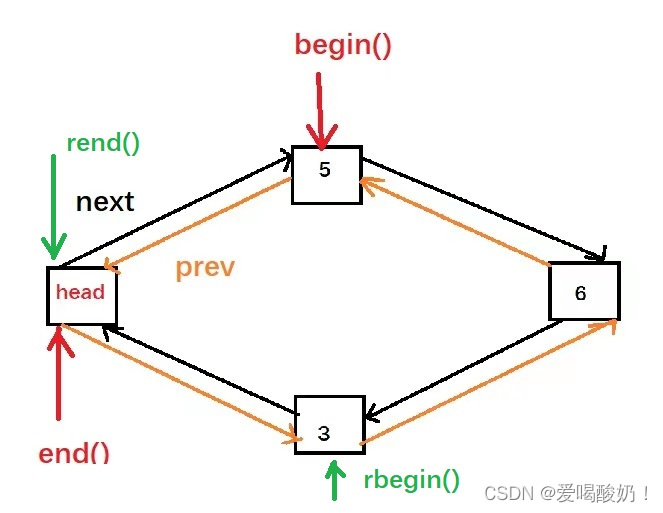
????????list是C++中带头结点的双向链表(也是模板),示意图如下。begin迭代器指向头结点正方向的第一个有效元素,end迭代器指向正方向最后一个有效元素的下一个位置,也就是头结点。 反向迭代器与之相反。
?
????????跟其他容器一样,list也是主要讲解六大模块:构造模块、迭代器模块、容量模块、元素访问模块、修改模块、特殊操作模块。
????????本文代码均在win10系统的vs2019中验证。
1.构造模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
|
list(size_type n, const value_type & val = value_type())
| 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list(const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| ?list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 区间构造 |
? (1)无参构造函数
? ? ? ? 注意:list也是模板,也需要在实例化时声明存储的元素的类型。使用时也需要加上list的头文件。
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1;
}? (2)n个相同元素的构造函数
#include "list"
void Test() {
//用10个5构造
list<int>L2(10,5);
}? (3)区间构造
#include "list"
void Test() {
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int>L3(arr,arr+sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]));
}? (4)C++11构造新形式
? ? ? ? C++11中提供的新方式,可以在构造时直接传入数组。
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L4{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
}? (5)拷贝构造函数
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L5(4, 9);
list<int>L6(L5);
}? (6)赋值运算符重载?
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int> L1{ 1,2,3 };
list<int> L2 = L1;
}2.迭代器模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| begin()? | 正向迭代器,返回指向正向第一个有效元素的迭代器 |
| end() | 正向迭代器,返回指向正向最后一个有效元素下一个元素的迭代器 |
| rbegin() | 反向迭代器,返回指向反向第一个有效元素的迭代器 |
| rend() | 反向迭代器,返回指向反向最后一个有效元素下一个元素的迭代器 |
示意图已经在开头给出。
? (1)正向迭代器
????????注意,list的迭代器不可以+1,因为这是链表,不是一段连续的空间。 但可以使用++,因为++已经被重载过了。
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
auto it = L1.begin();
while (it != L1.end()) {
cout << *it;
it++;
}
}? (2)反向迭代器
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L2{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
auto it = L2.rbegin();
while (it != L2.rend()) {
cout << *it;
it++;
}
}3.容量模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| empty() | 判断list是否是空,如果是,返回true |
| size() | 返回list中有效元素的个数 |
| resize(size_t num, const T& value = T()) | 将list的有效元素个数设置为num,如果num大于size(),多余的位置用value填充,没有给出value,就用T()填充。 |
? (1)判空函数
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << L1.empty();
}? (2)获取有效元素个数
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << L1.size();
}? (3)设置有效元素个数
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
//将元素增加到10个多余空间用4填充
L1.resize(10,4);
//将元素缩减到4个
L1.resize(4);
}4.元素访问模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| front() | 返回list中正方向第一个有效元素的引用 |
| back() | 返回list中正方向最后一个有效元素的引用 |
? (1)获取首元素
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
//获取首元素
cout << L1.front() << endl;
}? (2)获取尾元素
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
//获取尾部元素
cout << L1.back() << endl;
}5.修改模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| push_front(T& value) | 头插,在list第一个有效元素前插入一个value元素 |
| push_back(T& value) | 尾插,在list最后一个有效元素后插入一个value元素 |
| pop_front() | 头删,删除list中第一个有效元素 |
| pop_back() | 尾删,删除list中最后一个有效元素 |
insert(iterator position, const value_type & val) | 在迭代器position的位置插入一个val |
| insert(iterator position, size_type n, const value_type & val) | 在迭代器position的位置插入n个val |
| insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 在迭代器position的位置插入一段区间。 |
| void assign(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用区间中的元素取代原本空间中的所有元素 |
| void assign(size_type n, const value_type& val) | 用n个val元素取代原本空间中的所有元素 |
| void clear() | 清空list的有效元素 |
? (1)头插
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1 };
//头插
L1.push_front(2);
}? (2)尾插
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1 };
//尾插
L1.push_back(2);
}? (3)头删
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2};
//头删
L1.pop_front();
}? (4)尾删
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2};
//尾删
L1.pop_back();
}? (5)任意位置插入
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2};
//在某个迭代器的位置插入元素
L1.insert(L1.begin(), 3);
//在某个迭代器的位置插入3个4
L1.insert(L1.begin(), 3, 4);
//在某个迭代器的位置插入一个区间
int arr[] = { 9,7,5,8,6 };
L1.insert(L1.end(), arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
}? (6)任意位置删除?
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
//删除某个迭代器位置的元素
L1.erase(L1.begin());
//删除迭代器区间内的元素
L1.erase(L1.begin(), L1.end());
}? (7)assign函数
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1;
//给L1中放入10个5
L1.assign(10, 5);
//给L1中放入一个区间
//注意:每次使用时,会把原本的内容全部替换掉
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4 };
L1.assign(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
}
? (9)清空
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
L1.clear();
}6.特殊操作模块
| 函数说明 | 功能说明 |
| remove(T& value) | 删除list中的全部value元素 |
| sort() | 为list排序 |
| unique() | 为list去除重复元素,但去重前必须先排序 |
| reverse() | 逆置list中的元素 |
| remove_if(函数名) | 定义一个函数用来筛选需要删除的元素,函数名作为参数传递给remove_if函数,就可以自定义删除元素了。 |
? (1)删除特定元素
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7};
//删除所有1
L1.remove(1);
}? (2)排序
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7};
//排序
L1.sort();
}? (3)去重
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7};
//排序
L1.sort();
//去重 去重之前必须排序
L1.unique();
}? (4)逆置元素
#include "list"
void Test() {
list<int>L1{1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7};
//逆置
L1.reverse();
}? (5)指定条件的删除
? ? ? ? 需要自己给出一个函数来确定删除的元素需要满足的条件,然后把函数名作为参数传递给remove_if函数。
#include "list"
bool isEven(int data) {
return data % 2 == 0;
}
void Test() {
list<int>L1{1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7};
//删除2的倍数
L1.remove_if(isEven);
}7.迭代器失效?
????????跟vector一样,list也需要考虑迭代器失效的问题。但因为之前的文章已经讲过了,这里就简单给几个例子。
????????迭代器本质:指针
????????迭代器失效:指针指向的空间非法。即指针指向了被释放的空间。
? (1)迭代器失效原因? ? ? ?
????????导致list迭代器失效的操作:
? ? [1]删除操作
????????如:erase,pop_back,pop_front
????????如下代码:? ? ? ??
? ? ? ? it首先指向元素1。头删后,元素1被删除,元素1所处的空间被释放,也就是it指向的空间被释放,但it仍旧指向它。
? ? ? ? 在循环体中,试图对it进行解引用,但it此时已经是野指针,所以会报错。
#include "iostream"
#include "list"
using namespace std;
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7 };
//it此时指向元素1所在的空间
auto it = L1.begin();
//将元素1删除,释放元素1的空间,可是it仍旧指向那块空间
L1.pop_front();
while (it != L1.end()) {
//试图对已经释放的空间的地址进行解引用
cout << *it;
it++;
}
}
int main() {
Test();
}? ? [2]改变容量的操作
????????如:resize assign
????????it最初指向元素7的空间,但resize将有效元素个数缩减,只保留前三个元素,将其余元素空间释放。it指向了被释放的空间,成为野指针,试图解引用,就会报错。
#include "iostream"
#include "list"
using namespace std;
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7 };
//it首先指向元素7的空间
auto it = L1.end();
//改变list的有效元素个数,此时有效元素只有前三个
//其余元素被删除,空间被释放,但此时it仍旧指向元素7的空间
//也就是it指向被释放的空间
L1.resize(3);
//试图对被释放的空间地址进行解引用
cout << *it << endl;
}
int main() {
Test();
}? (2)迭代器失效解决办法
????????当进行了可能会导致之前使用的迭代器失效的操作后,如果还要使用迭代器,就在使用前对其进行重新赋值。
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7 };
auto it = L1.begin();
L1.pop_front();
//使用前重新赋值
it = L1.begin();
while (it != L1.end()) {
cout << *it;
it++;
}
}
void Test() {
list<int>L1{ 1,2,6,1,2,4,6,7 };
auto it = L1.end();
L1.resize(3);
//使用前重新赋值
it = L1.end();
cout << *it << endl;
}