代码随想录算法训练营第四天|链表专题二
今日题目总汇:
- leetcode 24 两两交换链表中的节点
- leetcode 19 删除链表中倒数第N个节点
- leetcode 160 链表相交
- leetcode 142 环形链表II
对于链表操作来说,我觉得如果是涉及头节点可能需要改变,或者是需要删除头节点或者在头节点前添加节点的操作,我建议都使用虚拟头节点,这样可以使得在操作链表的时候能够统一进行操作,没有必要进行单独处理。
例如,我们在删除节点的时候,一般是要知道该节点的前一个节点才能进行删除操作,如果需要删除头节点呢,头节点没有前驱节点,那么就要对头节点进行单独处理了。而我们添加一个虚拟头节点后,可以把头节点的操作看成普通节点的操作,不需要进行单独处理。
leetcode 24 两两交换链表中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0024.%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%A4%E4%BA%A4%E6%8D%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1YT411g7br/
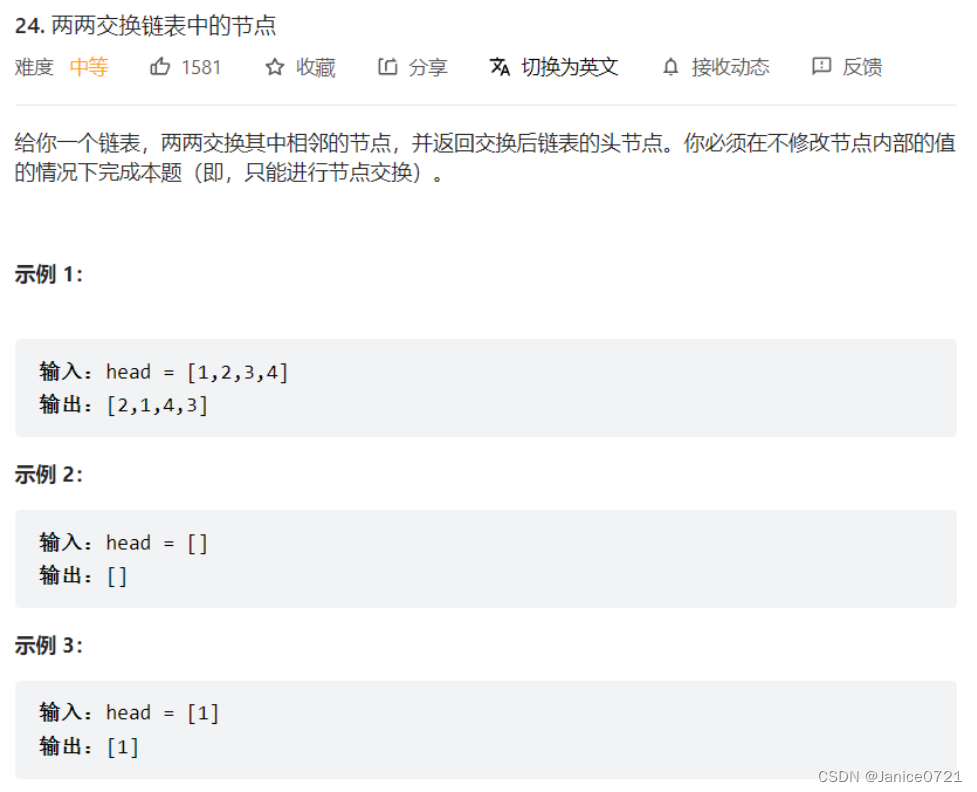
题目详情:
思路
? 因为本题是两两交换节点,那么两个节点完成交换后,还需将整个链表给串起来,那么就要知道两个节点的前驱节点和后继节点,才能完成一组交换。
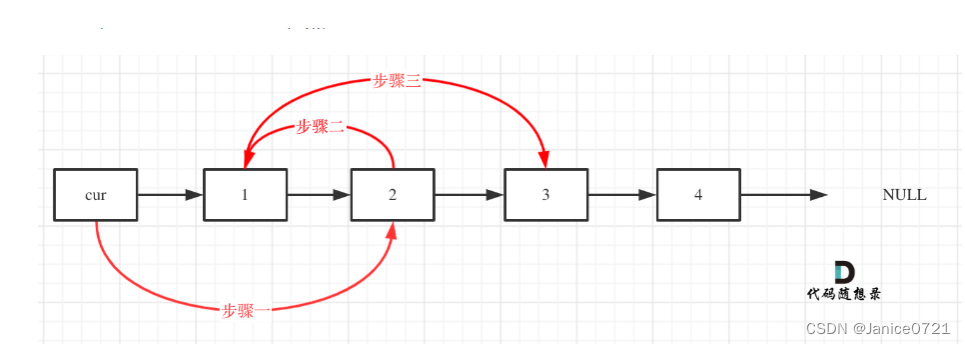
比如交换1,2这个两个节点,那么我们需要知道1节点的前驱节点,和2节点的后继节点,这样的话交换1,2这两个链表只需要改变next指针的指向,也就是让2节点指向1节点,让1节点指向后继节点,让前驱节点指向2节点。
这一系列操作完成后就是下面这个效果:
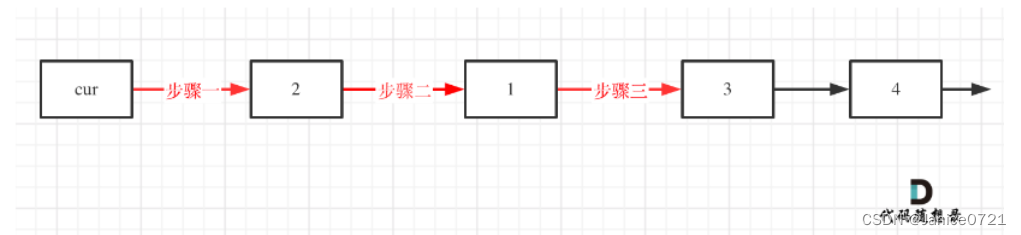
在这里我们还是需要借助虚拟头节点,如果交换的是前面两个节点,也就是头节点的话,头节点无前驱节点,就要进行单独操作。
结束条件:
? 因为我是使用一个temp保存了后继节点,那么结束循环的条件应该是,当链表遍历结束或者还剩最后一个节点时退出,也就是当tempnull || temp.nextnull 时退出。
方法一:使用虚拟头节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
//如果链表为空,或者链表长度为1时,直接返回head,不需要交换
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
//使用虚拟头节点
ListNode dummyHead=new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next=head;
//pre节点为两个交换节点的第一个节点
ListNode pre =head;
//tail节点为两个交换节点的第二个节点
ListNode tail=head.next;
//temp节点保存后继节点
ListNode temp=tail.next;
//node节点保存前驱节点
ListNode node=dummyHead;
while(true){
//保存后继节点
temp=tail.next;
//交换两个节点
tail.next=pre;
//连接后继节点
pre.next=temp;
//连接前驱节点
node.next=tail;
//结束判断
if(temp!=null&&temp.next!=null){
//为true则说明,后面还有至少两个节点可以交换
//更新前驱节点
node=pre;
//更新两两交换节点的第一个节点
pre=temp;
//更新两两交换节点的第二个节点
tail=temp.next;
}else{
//为flase则说明后面就剩一个节点或者没有节点了,退出循环
break;
}
}
//返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,也就是新的头节点
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
方法二:不使用虚拟头节点
操作与上面操作一样,不同的地方就是需要单独处理头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre =head;
ListNode tail=head.next;
ListNode temp=tail.next;
ListNode node =pre;
//单独处理头节点
tail.next=pre;
pre.next=temp;
head=tail;
while(temp!=null && temp.next!=null){
node=pre;
pre=temp;
tail=temp.next;
temp=tail.next;
tail.next=pre;
pre.next=temp;
node.next=tail;
}
return head;
}
}
leetcode 19 删除链表中倒数第N个节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0019.%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E5%80%92%E6%95%B0%E7%AC%ACN%E4%B8%AA%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1U7Gf/
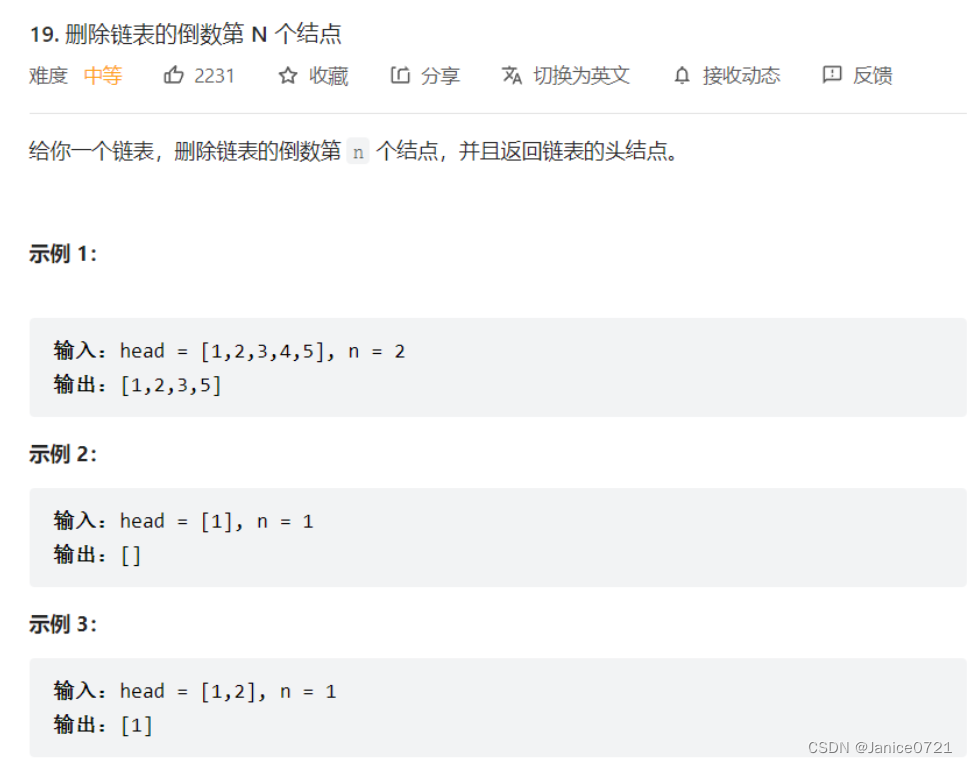
题目详情:
? 
思路
首先最简单的思路就是,通过遍历链表得到其长度,然后用长度减去n,然后遍历到该位置就是需要删除节点的前驱节点。然后进行删除操作。
方法一:(两次遍历)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int len=getLength(head);
if(len==1|| head==null){
return null;
}
head=deleteListNode(head,len,n);
return head;
}
public ListNode deleteListNode(ListNode head, int len, int n){
ListNode tail =head;
//首先需要固定头节点,若删除的是头节点那么直接返回head.next,
//不然就固定head,移动tail
if(len-n==0){
return head.next;
}
for(int i=len-n;i>1;i--){
tail=tail.next;
}
tail.next=tail.next.next;
return head;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
int size=0;
while(head!=null){
size++;
head=head.next;
}
return size;
}
}
那么我们如何通过一次遍历就能删除对应的节点呢?
? 答案就是通过快慢指针,这里我们还是借助虚拟头节点,可以先让快指针走n步,然后快慢指针一起走,这样当快指针走到最后时,慢指针就在需要删除节点的前驱节点上。结束条件就是当fast走到链表末尾了,也就是当fast.next==null时结束。
方法二:(快慢指针)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int len=getLength(head);
if(len==1|| head==null){
return null;
}
head=deleteListNode(head,len,n);
return head;
}
public ListNode deleteListNode(ListNode head, int len, int n){
ListNode tail =head;
//首先需要固定头节点,若删除的是头节点那么直接返回head.next,
//不然就固定head,移动tail
if(len-n==0){
return head.next;
}
for(int i=len-n;i>1;i--){
tail=tail.next;
}
tail.next=tail.next.next;
return head;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
int size=0;
while(head!=null){
size++;
head=head.next;
}
return size;
}
}
leetcode 160 链表相交
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%9802.07.%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9B%B8%E4%BA%A4.html
题目详情:

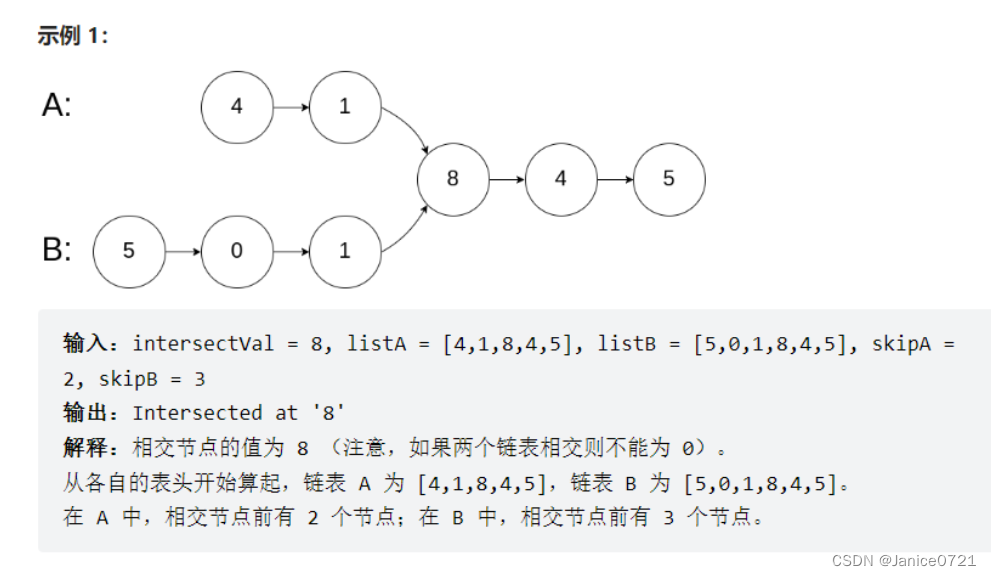
思路
? 我们可以使用hashmap用来遍历两个链表的节点,如果出现了相交的话那么就会出现相等节点,containsKey则会返回true,则代表相交。繁反之不相交。时间复杂度为O(n),但空间复杂度也是O(n)。
? 我们换一种想法,如果两个链表相交,则后半部分一定相等,从相交的节点开始,两个链表的节点都相同,那么我们是不是可以让两个链表都从较短链表的位置开始遍历,也就是让两个链表后边对齐,这样可以完全遍历较短链表,也就是可以找到是否相交。
看图演示:
?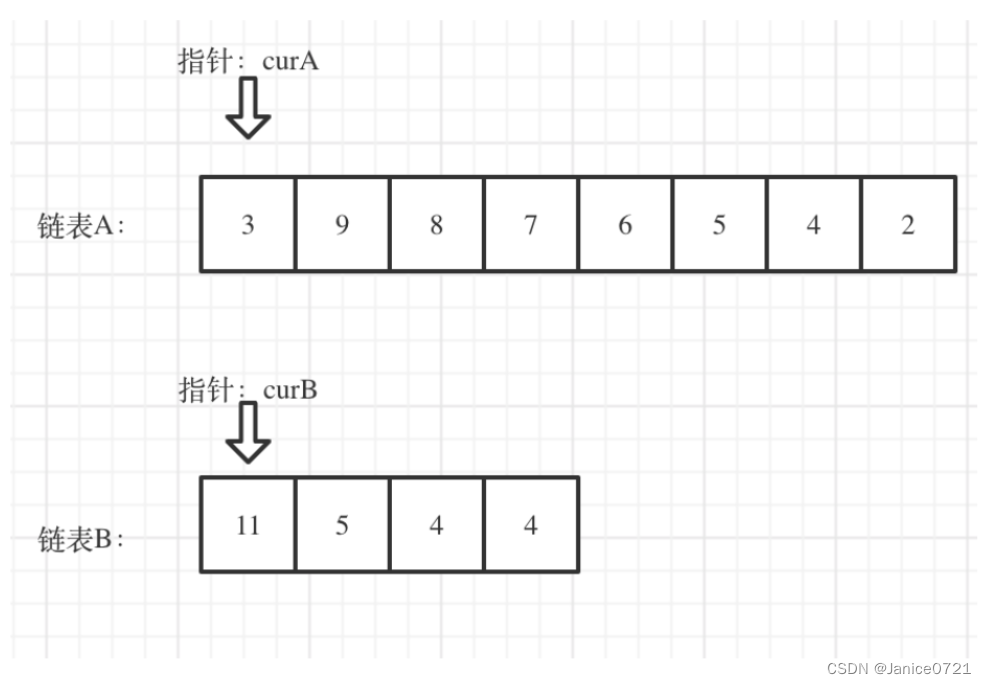
我们求出两个链表的长度,并求出两个链表长度的差值,然后让curA移动到,和curB 末尾对齐的位置,如图:
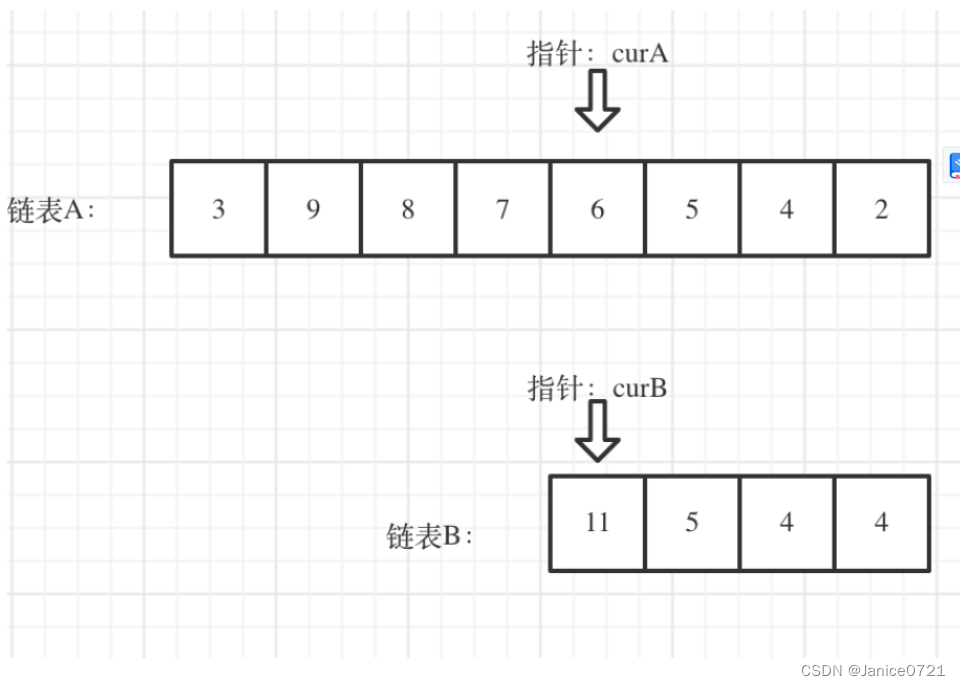
此时我们就可以比较curA和curB是否相同,如果不相同,同时向后移动curA和curB,如果遇到curA == curB,则找到交点。
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//如果两个链表相交,那么一定是后半部分,所以我们可以让两链表后半部分对其,
//较长链表先走一部分,走到正好能与较短链表后半部分对其的位置
//那么我们可以从较短链表开始遍历,如果相交那么节点就一定相等
if(headA==null || headB==null){
return null;
}
//先计算两个链表长度
int countA=0;
ListNode curA=headA;
while(curA!=null){
curA=curA.next;
countA++;
}
int countB=0;
ListNode curB=headB;
while(curB!=null){
curB=curB.next;
countB++;
}
//我们始终让curA指向较长链表,curB指向较短链表
//因为这样可以避免重复操作,若A长得让A先走,B长得让B先走
if(countA<countB){
curA=headB;
curB=headA;
}else{
curA=headA;
curB=headB;
}
///curA先走到后部分与curB对齐的位置,也就是先走(|countA-countB|)
int len=Math.abs(countA-countB);
while(len>0){
curA=curA.next;
len--;
}
while(curA!=null && curB!=null){
if(curA==curB) return curA;
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
leetcode 142 环形链表II
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
文章链接:https://programmercarl.com/0142.%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8II.html
视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1if4y1d7ob/
题目详情:

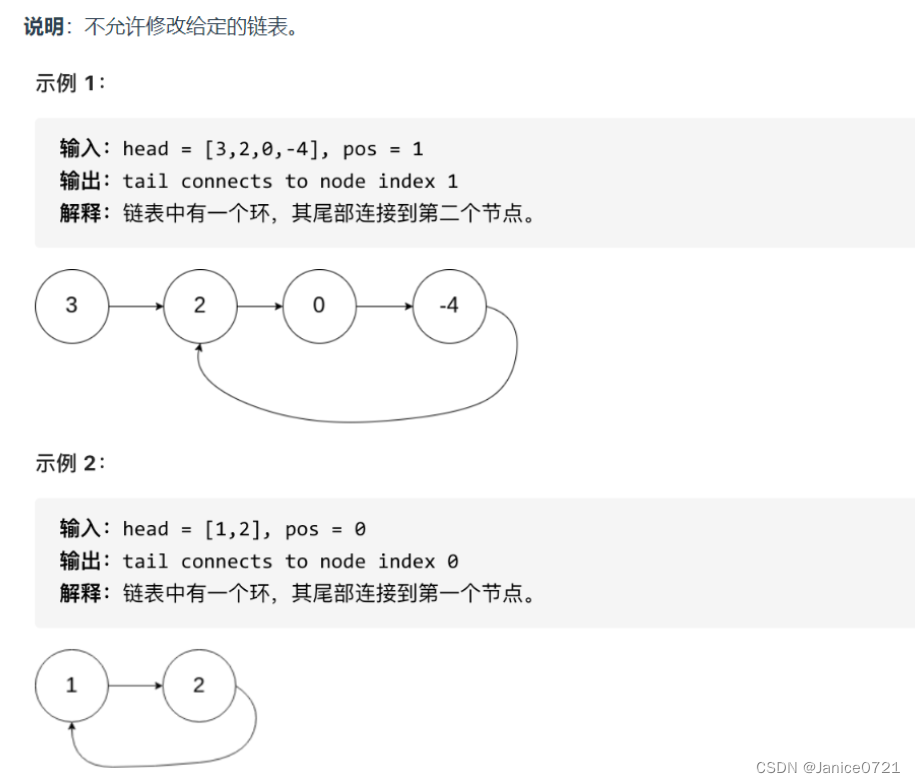
思路
题目的进阶要求是使用O(1)空间,那么我先讲述一下如何使用O(n)空间来解决本题,之后再讲述使用O(1)空间来解决。
方法一:HashMap O(n)空间
我们知道HashMap的特点是按键值对存储key-value,并且key不重复,也就是说在hashmap中相同的key只能存在一个,那么问题就好解决了,我们是不是可以把ListNode作为HashMap的key,当出现首次重复时,是不是就是入环的节点,如果遍历完链表还没出现重复,那么说明链表是无环的。关键就是遍历链表,map中不存在对应的key,则就将其存储起来,map中已经存在key了,那么就将这个key也就是ListNode返回。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
HashMap<ListNode,Integer> hash=new HashMap<>();
while(head!=null){
if(hash.containsKey(head)){
return head;
}else{
hash.put(head,1);
head=head.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
方法二:双指针法(多走一个环)O(1)空间
大致流程就是:快慢指针从头节点开始走,快指针每次比慢指针多走一个,如果有环的话,那么一定快慢指针一定会相遇,如果说在某时刻快指针为null了,或者快指针的next节点为null了,那么就说明链表是没有环的。
如果有环的话,首先确定了相遇节点,那么我从相遇节点开始转一圈,求一下这个环的长度,当知道环的长度就好办了,我让快慢指针重新从头节点开始,这次我让快指针先走一个环的长度,然后快慢指针同时走,每次都移动一个节点,这样的话会发现一个事情,快指针始终比慢指针多一个环的长度,那么当慢指针走到入环口的时候,快指针应该在哪?既然是多一个环的长度的话,是不是也应该在入环口,两者就会相遇了,这也是为什么快指针要多走一个环的长度,这样就保证了在入环口时相遇。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast =head;
ListNode slow=head;
//判断是否有环,找相遇点
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow) break;
}
//无环情况
if(fast==null || fast.next==null) return null;
//有环情况,相遇点为fast
//计算环的大小
int len=1;
ListNode temp=fast.next;
while(temp!=fast){
len++;
temp=temp.next;
}
//知道环大小后,让slow和fast重新从头节点开始走,fast先走len个,也就是一个环的大小
//因为fast永远比slow多走一个环,那么当slow走到入环口时,是不是fast刚好多走一个环
//即fast也走到了入环口,也就是说,当fast和slow相遇时,就是入环口的位置
//fast先走一个环的长度
slow=fast=head;
while(len>0){
fast=fast.next;
len--;
}
//现在fast多走了一个环,那么现在fast和slow一起走,当相遇时就是入环口
while(slow!=fast){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
//最后fast和slow都在入环口,返回一个即可
return fast;
}
}
}
//知道环大小后,让slow和fast重新从头节点开始走,fast先走len个,也就是一个环的大小
//因为fast永远比slow多走一个环,那么当slow走到入环口时,是不是fast刚好多走一个环
//即fast也走到了入环口,也就是说,当fast和slow相遇时,就是入环口的位置
//fast先走一个环的长度
slow=fast=head;
while(len>0){
fast=fast.next;
len--;
}
//现在fast多走了一个环,那么现在fast和slow一起走,当相遇时就是入环口
while(slow!=fast){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
//最后fast和slow都在入环口,返回一个即可
return fast;
}
}