题目链接:2413. 最小偶倍数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution { public: int smallestEvenMultiple(int n) { if (n % 2) return n * 2; return n; } };
题目链接:
2414. 最长的字母序连续子字符串的长度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
使用双指针算法每遍历到一个字母就判断它后面的字母是否符合条件class Solution { public: int longestContinuousSubstring(string s) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) { int j = i + 1; while (j < s.size() && s[j] == s[j - 1] + 1) j ++ ; res = max(res, j - i); i = j - 1; } return res; } };
题目链接:2414. 最长的字母序连续子字符串的长度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
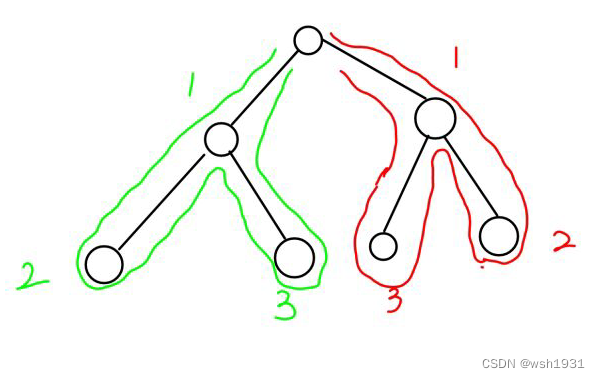
对于一个完全二叉树,可以使用深搜按照如图顺序遍历
例如:
第一次遍历的两个点分别为绿色的1和红色的1第二次遍历的两个点分别为绿色的2和红色的2
以此类推:
代码如下:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void dfs(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b, int d) { if (!a) return; if (d % 2) swap(a->val, b->val); dfs(a->left, b->right, d + 1); dfs(a->right, b->left, d + 1); } TreeNode* reverseOddLevels(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root->left, root->right, 1); return root; } };
题目链接:
2416. 字符串的前缀分数和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:这里可以用trie树来存储每个单词,求一个单词的前缀即把这个单词后面出现的单词全部加上,如图:
样例1的trie树如图,比如要求ab前缀出现的次数,即计算ab以及ab后面子树存在的单词的数目,我们可以用一个数组cnt[i]:表示以点i为根节点的后面子树的单词个数:
代码如下:
const int N = 1000010; int tr[N][26], cnt[N], idx; class Solution { public: void insert(string& word) { int p = 0; for (auto c: word) { int u = c - 'a'; if (!tr[p][u]) tr[p][u] = ++ idx; p = tr[p][u]; cnt[p] ++ ; } } int query(string& word) { int p = 0, res = 0; for (auto c: word) { int u = c - 'a'; p = tr[p][u]; res += cnt[p]; } return res; } vector<int> sumPrefixScores(vector<string>& words) { idx = 0; memset(tr, 0, sizeof tr); memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt); for (auto& word: words) insert(word); vector<int> res; for (auto& word: words) res.push_back(query(word)); return res; } };?